模板Plus【完整版】
文章目录
- 1.非类型模板参数的引入
- 2.标准库和普通数组
- 3.模板的特化
-
- 3.1介绍
- 3.2代码讲解
- 3.3画图讲解
- 4.类、函数模板特化初识
- 5.全特化与偏特化
- 6.模板不能分离编译
-
- 1.typename的使用
- 2.预处理相关知识
- 3.为什么不能分离编译?
- 4.怎么解决?
- 5.代码详解
-
- 1.vector.h
- 2.vector.cpp
- 3.test.cpp
- 7.模板优缺点
1.非类型模板参数的引入
//非类型模板参数 -- 常量
template<class T, size_t N = 10>
class array
{
private:
T _a[N];
};
int main()
{
array<int> a1;
array<int, 100> a2;
array<double, 1000> a3;
return 0;
}
1. 浮点数、类对象、字符串不允许作为非类型模板参数
2. 非类型的模板参数必须在编译期就能确认结果
2.标准库和普通数组
int main()
{
array<int, 10> a1;
int a2[10] = { 0 };
//a1[10]; 越界检查--operator()函数调用
//a2[15] = 0; 写会检查(部分会检查)读不检查
return 0;
}
3.模板的特化
3.1介绍
在原模板类的基础上,针对特殊类型进行特殊化的实现方式。分为函数模板特化与类模板特化。
3.2代码讲解
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include
#include 3.3画图讲解
4.类、函数模板特化初识
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include
#include ,class Compare = less >
//class priority_queue;
Date类型
std::priority_queue<Date, vector<Date>, apex::less<Date>> dq1;
dq1.push(Date(2023, 8, 10));
dq1.push(Date(2023, 8, 11));
dq1.push(Date(2023, 8, 12));
dq1.push(Date(2023, 8, 13));
while (!dq1.empty())
{
const Date& top = dq1.top();
cout << top._year << "-" << top._month << "-" << top._day << endl;
dq1.pop();
}
cout << endl;
Date*类型
std::priority_queue<Date*, vector<Date*>, apex::less<Date*>> dq2;
dq2.push(new Date(2023, 8, 10));
dq2.push(new Date(2023, 8, 11));
dq2.push(new Date(2023, 8, 12));
dq2.push(new Date(2023, 8, 13));
while (!dq2.empty())
{
Date* top = dq2.top();
cout << top->_year << "-" << top->_month << "-" << top->_day << endl;
dq2.pop();
}
return 0;
}
5.全特化与偏特化
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include
#include " << endl;
}
private:
T1 _d1;
T2 _d2;
};
// 全特化:将模板参数列表中所有参数确定化
//template" << endl;
}
private:
int _d1;
char _d2;
};
//偏特化
//template" << endl;
}
private:
T1 _d1;
int _d2;
};
//template" << endl;
}
private:
T1 _d1;
T2 _d2;
};
//template" << endl;
}
};
//template" << endl;
}
};
int main()
{
Data<int, int> d0;
Data<double, int> d1;
Data<int, char> d2;
Data<double, double> d3;
Data<double*, double*> d4;
Data<int*, char*> d5;
Data<int*, char> d6;
Data<int&, char&> d7;
Data<int&, double&> d8;
Data<int&, double*> d9;
return 0;
}
6.模板不能分离编译
1.typename的使用
当出现这种情况:vector < T >::iterator
即一个在另一个类里typedef的内嵌类型或内部类从属于一个模板时 需要在前面加typename 目的是告诉编译器 这个整体是一个类型而非变量 否则编译器无法识别而报错
template<class T>
void func(const vector<T>& v)
{
typename vector<T>::iterator it = v.begin();
}
int main()
{
vector<int> v;
func(v);
return 0;
}
2.预处理相关知识
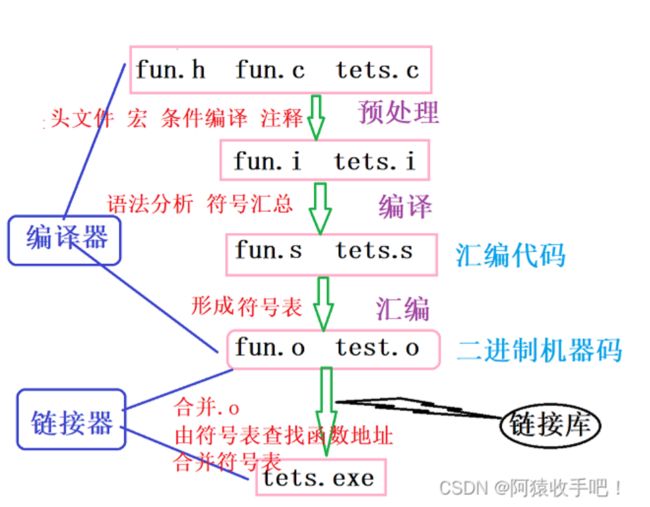
3.为什么不能分离编译?
4.怎么解决?
5.代码详解
1.vector.h
#pragma once
#include 2.vector.cpp
#include"vector.h"
namespace apex
{
template<class T>
void vector<T>::reserve(size_t n)
{
if (n > capacity())
{
size_t sz = size();
T* tmp = new T[n];
if (_start != nullptr)
{
for (size_t i = 0; i < sz; ++i)
{
tmp[i] = _start[i];
}
delete[] _start;
}
_start = tmp;
_finish = _start + sz;
_end_of_storage = _start + n;
}
}
template<class T>
typename vector<T>::iterator vector<T>::insert(typename vector<T>::iterator pos, const T& x)
{
assert(pos >= _start && pos <= _finish);
if (_finish == _end_of_storage)
{
size_t len = pos - _start;
reserve(capacity() == 0 ? 4 : capacity() * 2);
pos = _start + len;
}
iterator end = _finish - 1;
while (end >= pos)
{
*(end + 1) = *end;
--end;
}
*pos = x;
++_finish;
return pos;
}
}
3.test.cpp
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include
#include 7.模板优缺点
优点:
- 增强复用性–减少代码量–介绍资源–使得开发迭代更快–是STL泛型编程的基础
- 增强灵活性
缺点: - 若实例化过多–代码膨胀问题–编译时间变长
- 编译器给出的编译错误信息杂乱–不易修正