Netty服务端启动的整体流程-基于源码4.1.96Final分析
Netty采用的是主从Reactor多线程的模型,参考Scalable IO in Java,但netty的subReactor为一个组
一、从FileServer服务器示例入手
public final class FileServer {
static final boolean SSL = System.getProperty("ssl") != null;
// Use the same default port with the telnet example so that we can use the telnet client example to access it.
static final int PORT = Integer.parseInt(System.getProperty("port", SSL? "8992" : "8023"));
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// Configure SSL.
final SslContext sslCtx = ServerUtil.buildSslContext();
// Configure the server.主从Reactor线程组
EventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(1);
EventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
ServerBootstrap b = new ServerBootstrap();
b.group(bossGroup, workerGroup)
//配置主Reactor中的channel类型
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)
// 设置主Reactor中channel的option选项,设置底层JDK NIO Socket的一些选项
.option(ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG, 100)
//设置主Reactor中Channel->pipline->handler
.handler(new LoggingHandler(LogLevel.INFO))
//设置 SocketChannel 对应的 Handler;
.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer() {
@Override
public void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
ChannelPipeline p = ch.pipeline();
if (sslCtx != null) {
p.addLast(sslCtx.newHandler(ch.alloc()));
}
p.addLast(
new StringEncoder(CharsetUtil.UTF_8),
new LineBasedFrameDecoder(8192),
new StringDecoder(CharsetUtil.UTF_8),
new ChunkedWriteHandler(),
new FileServerHandler());
}
});
// Start the server.
ChannelFuture f = b.bind(PORT).sync();
// Wait until the server socket is closed.
f.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} finally {
// Shut down all event loops to terminate all threads.
bossGroup.shutdownGracefully();
workerGroup.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
}
1.1 netty的主从模式
首先大致了解netty的主从模式中:bossGroup 中的MainReactor管理的Channel类型为NioServerSocketChannel,用来监听端口,接收客户端连接,为客户端创建初始化NioSocketChannel,然后采用round-robin轮询的方式从workerGroup中选择一个SubReactor与该客户端NioSocketChannel进行绑定。一个SubReactor线程负责处理多个NioSocketChannel上的IO事件
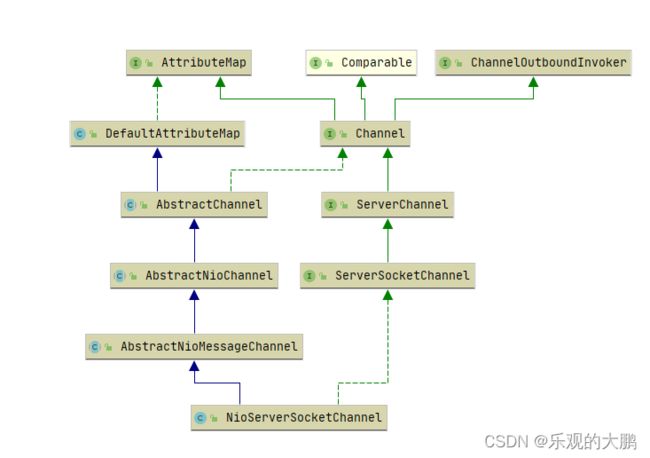
1.2 NioServerSocketChannel
包含了JDK原生的ServerSocketChannel属性
1.2.1 channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)
在执行channel的时候,返回的是channelFactory属性,如下:
return channelFactory(new ReflectiveChannelFactory(
ObjectUtil.checkNotNull(channelClass, "channelClass")
// ReflectiveChannelFactory通过泛型,反射,工厂的方式灵活创建不同类型的channel
public class ReflectiveChannelFactory implements ChannelFactory {
private final Constructor constructor;
public ReflectiveChannelFactory(Class clazz) {
ObjectUtil.checkNotNull(clazz, "clazz");
try {
this.constructor = clazz.getConstructor();
} catch (NoSuchMethodException e) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Class " + StringUtil.simpleClassName(clazz) +
" does not have a public non-arg constructor", e);
}
}
@Override
public T newChannel() {
try {
return constructor.newInstance();
} catch (Throwable t) {
throw new ChannelException("Unable to create Channel from class " + constructor.getDeclaringClass(), t);
}
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return StringUtil.simpleClassName(ReflectiveChannelFactory.class) +
'(' + StringUtil.simpleClassName(constructor.getDeclaringClass()) + ".class)";
}
}
1.3 ChannelInitializer的作用
Pipeline添加ChannelHandler:1、显式添加的方式是由用户在main线程中通过ServerBootstrap#handler的方式添加。2、如果需要添加多个ChannelHandler,则可以通过ChannelInitializer向pipeline中进行添加。
1.3.1 childHandler(new ChannelInitializer() {}使用的原因:
NioSocketChannel是在服务端accept连接后,在服务端NioServerSocketChannel中被创建出来的。但是此时我们正处于配置ServerBootStrap阶段,服务端还没有启动,更没有客户端连接上来,此时客户端NioSocketChannel还没有被创建出来,所以也就没办法向客户端NioSocketChannel的pipeline中添加ChannelHandler。 以及客户端NioSocketChannel中Pipeline里可以添加任意多个ChannelHandler,但是Netty框架无法预知用户到底需要添加多少个ChannelHandler,所以Netty框架提供了回调函数ChannelInitializer#initChannel,使用户可以自定义ChannelHandler的添加行为。
二、服务端启动全过程
public ChannelFuture bind(int inetPort) {
return bind(new InetSocketAddress(inetPort));
}
public ChannelFuture bind(SocketAddress localAddress) {
//校验Netty核心组件是否配置齐全
validate();
//服务端开始启动,绑定端口地址,接收客户端连接
return doBind(ObjectUtil.checkNotNull(localAddress, "localAddress"));
}
private ChannelFuture doBind(final SocketAddress localAddress) {
//异步创建,初始化,注册ServerSocketChannel到main reactor上
final ChannelFuture regFuture = initAndRegister();
final Channel channel = regFuture.channel();
if (regFuture.cause() != null) {
return regFuture;
}
if (regFuture.isDone()) {
........serverSocketChannel向Main Reactor注册成功后开始绑定端口....,
} else {
//如果此时注册操作没有完成,则向regFuture添加operationComplete回调函数,注册成功后回调。
regFuture.addListener(new ChannelFutureListener() {
@Override
public void operationComplete(ChannelFuture future) throws Exception {
........serverSocketChannel向Main Reactor注册成功后开始绑定端口....,
});
return promise;
}
}2.1 初始化并注册channel
final ChannelFuture initAndRegister() {
Channel channel = null;
try {
// io.netty.channel.ReflectiveChannelFactory.newChannel
channel = channelFactory.newChannel();
// 初始化channel
init(channel);
} catch (Throwable t) {
if (channel != null) {
// channel can be null if newChannel crashed (eg SocketException("too many open files"))
channel.unsafe().closeForcibly();
// as the Channel is not registered yet we need to force the usage of the GlobalEventExecutor
return new DefaultChannelPromise(channel, GlobalEventExecutor.INSTANCE).setFailure(t);
}
// as the Channel is not registered yet we need to force the usage of the GlobalEventExecutor
return new DefaultChannelPromise(new FailedChannel(), GlobalEventExecutor.INSTANCE).setFailure(t);
}
ChannelFuture regFuture = config().group().register(channel);
if (regFuture.cause() != null) {
if (channel.isRegistered()) {
channel.close();
} else {
channel.unsafe().closeForcibly();
}
}
// If we are here and the promise is not failed, it's one of the following cases:
// 1) If we attempted registration from the event loop, the registration has been completed at this point.
// i.e. It's safe to attempt bind() or connect() now because the channel has been registered.
// 2) If we attempted registration from the other thread, the registration request has been successfully
// added to the event loop's task queue for later execution.
// i.e. It's safe to attempt bind() or connect() now:
// because bind() or connect() will be executed *after* the scheduled registration task is executed
// because register(), bind(), and connect() are all bound to the same thread.
return regFuture;
}2.1.1 channelFactory.newChannel();
根据1.2.1 可以知道,实际就是调用return constructor.newInstance();也就是实例化NioServerSocketChannel
public class NioServerSocketChannel extends AbstractNioMessageChannel
implements io.netty.channel.socket.ServerSocketChannel {
//SelectorProvider(用于创建Selector和Selectable Channels)
private static final SelectorProvider DEFAULT_SELECTOR_PROVIDER = SelectorProvider.provider();
/**
* Create a new instance
*/
public NioServerSocketChannel() {
this(DEFAULT_SELECTOR_PROVIDER);
}
/**
* Create a new instance using the given {@link SelectorProvider}.
*/
public NioServerSocketChannel(SelectorProvider provider) {
this(provider, null);
}
/**
* Create a new instance using the given {@link SelectorProvider} and protocol family (supported only since JDK 15).
*/
public NioServerSocketChannel(SelectorProvider provider, InternetProtocolFamily family) {
this(newChannel(provider, family));
}
/**
* Create a new instance using the given {@link ServerSocketChannel}.
*/
public NioServerSocketChannel(ServerSocketChannel channel) {
super(null, channel, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
config = new NioServerSocketChannelConfig(this, javaChannel().socket());
}
}2.1.1.1 SelectorProvider选择器和可选择通道的服务提供者类
public static SelectorProvider provider() {
synchronized (lock) {
if (provider != null)
return provider;
return AccessController.doPrivileged(
new PrivilegedAction() {
public SelectorProvider run() {
if (loadProviderFromProperty())
return provider;
if (loadProviderAsService())
return provider;
provider = sun.nio.ch.DefaultSelectorProvider.create();
return provider;
}
});
}
}
// 支持根据系统属性名进行实例化。
private static boolean loadProviderFromProperty() {
String cn = System.getProperty("java.nio.channels.spi.SelectorProvider");
if (cn == null)
return false;
try {
Class c = Class.forName(cn, true,
ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader());
provider = (SelectorProvider)c.newInstance();
return true;
} catch (ClassNotFoundException x) {
throw new ServiceConfigurationError(null, x);
} catch (IllegalAccessException x) {
throw new ServiceConfigurationError(null, x);
} catch (InstantiationException x) {
throw new ServiceConfigurationError(null, x);
} catch (SecurityException x) {
throw new ServiceConfigurationError(null, x);
}
}
// 根据spi进行实例化,即META-INF/services/下的定义名为java.nio.channels.spi.SelectorProvider的SPI文件,文件中第一个定义的SelectorProvider实现类全限定名就会被加载。
private static boolean loadProviderAsService() {
ServiceLoader sl =
ServiceLoader.load(SelectorProvider.class,
ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader());
Iterator i = sl.iterator();
for (;;) {
try {
if (!i.hasNext())
return false;
provider = i.next();
return true;
} catch (ServiceConfigurationError sce) {
if (sce.getCause() instanceof SecurityException) {
// Ignore the security exception, try the next provider
continue;
}
throw sce;
}
}
}
//因为是windows
public class DefaultSelectorProvider {
private DefaultSelectorProvider() {
}
public static SelectorProvider create() {
return new WindowsSelectorProvider();
}
}
nio中的channel注册selector
2.1.1.2 newChannel(provider, family)
private static ServerSocketChannel newChannel(SelectorProvider provider, InternetProtocolFamily family) {
try {
// family为空时 SelectorProviderUtil.newChannel 返回null
ServerSocketChannel channel =
SelectorProviderUtil.newChannel(OPEN_SERVER_SOCKET_CHANNEL_WITH_FAMILY, provider, family);
// 创建 JDK 底层的 ServerSocketChannel
return channel == null ? provider.openServerSocketChannel() : channel;
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new ChannelException("Failed to open a socket.", e);
}
}因为初始化的时候family为null,所以调用的是JDK底层的openServerSocketChannel
2.1.1.3 NioServerSocketChannel构造
//设置的是SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT事件
super(null, channel, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
// 创建Channel的配置类NioServerSocketChannelConfig,在配置类中封装了对Channel底层的一些配置行为,以及JDK中的ServerSocket。以及创建NioServerSocketChannel接收数据用的Buffer分配器AdaptiveRecvByteBufAllocator
config = new NioServerSocketChannelConfig(this, javaChannel().socket());
protected AbstractNioChannel(Channel parent, SelectableChannel ch, int readInterestOp) {
super(parent);
this.ch = ch;
this.readInterestOp = readInterestOp;
try {
// 设置 Channel 为非阻塞模式。
ch.configureBlocking(false);
} catch (IOException e) {
try {
ch.close();
} catch (IOException e2) {
logger.warn(
"Failed to close a partially initialized socket.", e2);
}
throw new ChannelException("Failed to enter non-blocking mode.", e);
}
}
protected AbstractChannel(Channel parent) {
this.parent = parent;
id = newId(); // 全局唯一id
unsafe = newUnsafe(); // unsafe 操作底层读写
pipeline = newChannelPipeline(); // pipeline 负责业务处理器编排
}
protected DefaultChannelPipeline newChannelPipeline() {
return new DefaultChannelPipeline(this);
}
protected DefaultChannelPipeline(Channel channel) {
this.channel = ObjectUtil.checkNotNull(channel, "channel");
succeededFuture = new SucceededChannelFuture(channel, null);
voidPromise = new VoidChannelPromise(channel, true);
tail = new TailContext(this);
head = new HeadContext(this);
head.next = tail;
tail.prev = head;
}此时channel的pipeline只有head和tail两个节点;
2.1.2 init(channel);初始化
@Override
void init(Channel channel) {
setChannelOptions(channel, newOptionsArray(), logger);
setAttributes(channel, newAttributesArray());
ChannelPipeline p = channel.pipeline();
final EventLoopGroup currentChildGroup = childGroup;
final ChannelHandler currentChildHandler = childHandler;
final Entry, Object>[] currentChildOptions = newOptionsArray(childOptions);
final Entry, Object>[] currentChildAttrs = newAttributesArray(childAttrs);
// ChannelInitializer 实现的 initChannel() 方法用于添加 ServerSocketChannel 对应的 Handler
p.addLast(new ChannelInitializer() {
@Override
public void initChannel(final Channel ch) {
final ChannelPipeline pipeline = ch.pipeline();
// 将handler(new LoggingHandler(LogLevel.INFO)) 中的handler加入pipeLine
ChannelHandler handler = config.handler();
if (handler != null) {
pipeline.addLast(handler);
}
// 然后 Netty 通过异步 task 的方式又向 Pipeline 一个处理器 ServerBootstrapAcceptor,这是一个连接接入器,专门用于接收新的连接,然后把事件分发给 EventLoop 执行
ch.eventLoop().execute(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
pipeline.addLast(new ServerBootstrapAcceptor(
ch, currentChildGroup, currentChildHandler, currentChildOptions, currentChildAttrs));
}
});
}
});
} -
ServerBootstrapAcceptor:也就是对应MainReactor中的acceptor,本质上也是一种ChannelHandler,主要负责在客户端连接建立好后,初始化客户端NioSocketChannel,在从Reactor线程组中选取一个SubReactor,将客户端NioSocketChannel注册到SubReactor中的selector上。
-
初始化NioServerSocketChannel中pipeline的时机是:当NioServerSocketChannel注册到Main Reactor之后,绑定端口地址之前,同时为了保证
线程安全地初始化pipeline,初始化的动作netty统一交给了Reactor线程进行 -
ServerBootstrapAcceptor 的注册过程为什么又需要封装成异步 task 呢?因为本文案例是
handler(new LoggingHandler(LogLevel.INFO))但是考虑到过程中可能为new ChannelInitializer
() ,那么在后续Main Reactor处理register0任务invokeHandlerAddedIfNeeded方法时会调用具体的ChannelInitializer的initChannel方法进行实例会进行添加到最后一个处理节点,如果这里不是异步task那么就会导致该Acceptor为pipeline的一个中间Handler,因此为了保证ServerBootstrapAcceptor是最后一个处理节点,所以本文就封装了一个异步任务。 等到新连接接入时,就可以调用 pipeline.fireChannelRead();从head节点依次往下进行传播,直到传播到ServerBootstrapAcceptor
2.2 注册channel到mainReactor中
2.2.1 轮询选取MainReactor
ChannelFuture regFuture = config().group().register(channel);
从ServerBootstrap获取主Reactor线程组NioEventLoopGroup,将NioServerSocketChannel注册到NioEventLoopGroup中。
@Override
public ChannelFuture register(Channel channel) {
return next().register(channel);
}
@Override
public EventExecutor next() {
return chooser.next();
}
//获取绑定策略
@Override
public EventExecutorChooser newChooser(EventExecutor[] executors) {
// 判断2的次幂
if (isPowerOfTwo(executors.length)) {
return new PowerOfTwoEventExecutorChooser(executors);
} else {
return new GenericEventExecutorChooser(executors);
}
}
//采用轮询round-robin的方式选择Reactor
@Override
public EventExecutor next() {
return executors[(int) Math.abs(idx.getAndIncrement() % executors.length)];
}
private static boolean isPowerOfTwo(int val) {
return (val & -val) == val;
}
正数的补码,反码,原码都是一样的。
负数的补码为反码加1,负数的反码为除符号位原码按位取反。2.2.2 register
@Override
public ChannelFuture register(Channel channel) {
return register(new DefaultChannelPromise(channel, this));
}
@Override
public ChannelFuture register(final ChannelPromise promise) {
ObjectUtil.checkNotNull(promise, "promise");
promise.channel().unsafe().register(this, promise);
return promise;
}
@Override
public final void register(EventLoop eventLoop, final ChannelPromise promise) {
ObjectUtil.checkNotNull(eventLoop, "eventLoop");
if (isRegistered()) {
promise.setFailure(new IllegalStateException("registered to an event loop already"));
return;
}
if (!isCompatible(eventLoop)) {
promise.setFailure(
new IllegalStateException("incompatible event loop type: " + eventLoop.getClass().getName()));
return;
}
//在channel上设置绑定的Reactor
AbstractChannel.this.eventLoop = eventLoop;
/**
* 执行channel注册的操作必须是Reactor线程来完成
*
* 1: 如果当前执行线程是Reactor线程,则直接执行register0进行注册
* 2:如果当前执行线程是外部线程,则需要将register0注册操作 封装程异步Task 由Reactor线程执行
* */
if (eventLoop.inEventLoop()) {
register0(promise);
} else {//外部线程调用
try {
eventLoop.execute(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
register0(promise);
}
});
} catch (Throwable t) {
logger.warn(
"Force-closing a channel whose registration task was not accepted by an event loop: {}",
AbstractChannel.this, t);
closeForcibly();
closeFuture.setClosed();
safeSetFailure(promise, t);
}
}
}当前执行线程并不是Reactor线程,而是用户程序的启动线程Main线程,所以提交异步task并进行了启动Reactor线程
//Reactor线程的启动是在向Reactor提交第一个异步任务的时候启动的。
private void execute(Runnable task, boolean immediate) {
boolean inEventLoop = inEventLoop();
addTask(task);
if (!inEventLoop) {
startThread();
if (isShutdown()) {
boolean reject = false;
try {
if (removeTask(task)) {
reject = true;
}
} catch (UnsupportedOperationException e) {
// The task queue does not support removal so the best thing we can do is to just move on and
// hope we will be able to pick-up the task before its completely terminated.
// In worst case we will log on termination.
}
if (reject) {
reject();
}
}
}
if (!addTaskWakesUp && immediate) {
wakeup(inEventLoop);
}
}
private void startThread() {
if (state == ST_NOT_STARTED) {
if (STATE_UPDATER.compareAndSet(this, ST_NOT_STARTED, ST_STARTED)) {
boolean success = false;
try {
doStartThread();
success = true;
} finally {
if (!success) {
STATE_UPDATER.compareAndSet(this, ST_STARTED, ST_NOT_STARTED);
}
}
}
}
}2.2.3 register0()-MainReactor异步任务执行
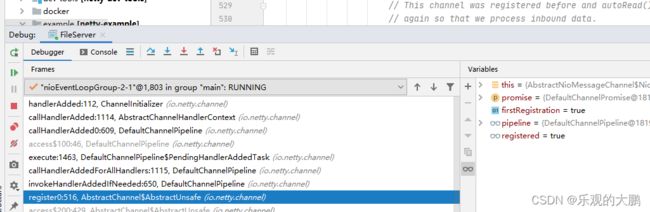
//一开始Reactor中的任务队列中只有一个任务register0,Reactor线程启动后,会从任务队列中取出任务执行。
private void register0(ChannelPromise promise) {
try {
// check if the channel is still open as it could be closed in the mean time when the register
// call was outside of the eventLoop
if (!promise.setUncancellable() || !ensureOpen(promise)) {
return;
}
boolean firstRegistration = neverRegistered;
// 调用 JDK 底层的 register() 进行注册
doRegister();
neverRegistered = false;
registered = true;
// Ensure we call handlerAdded(...) before we actually notify the promise. This is needed as the
// user may already fire events through the pipeline in the ChannelFutureListener.
//回调pipeline中添加的ChannelInitializer的handlerAdded方法,在这里初始化channelPipeline
pipeline.invokeHandlerAddedIfNeeded(); // 触发 handlerAdded 事件
safeSetSuccess(promise);
// channelRegistered 事件是由 fireChannelRegistered() 方法触发,沿着 Pipeline 的 Head 节点传播到 Tail 节点
pipeline.fireChannelRegistered();
// Only fire a channelActive if the channel has never been registered. This prevents firing
// multiple channel actives if the channel is deregistered and re-registered.
//对于服务端ServerSocketChannel来说 只有绑定端口地址成功后 channel的状态才是active的。
//此时绑定操作作为异步任务在Reactor的任务队列中,绑定操作还没开始,所以这里的isActive()是false
if (isActive()) {
if (firstRegistration) {
pipeline.fireChannelActive();
} else if (config().isAutoRead()) {
// This channel was registered before and autoRead() is set. This means we need to begin read
// again so that we process inbound data.
//
// See https://github.com/netty/netty/issues/4805
beginRead();
}
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
// Close the channel directly to avoid FD leak.
closeForcibly();
closeFuture.setClosed();
safeSetFailure(promise, t);
}
}2.2.3.1 doRegister
@Override
protected void doRegister() throws Exception {
boolean selected = false;
for (;;) {
try {
selectionKey = javaChannel().register(eventLoop().unwrappedSelector(), 0, this);
return;
} catch (CancelledKeyException e) {
if (!selected) {
// Force the Selector to select now as the "canceled" SelectionKey may still be
// cached and not removed because no Select.select(..) operation was called yet.
eventLoop().selectNow();
selected = true;
} else {
// We forced a select operation on the selector before but the SelectionKey is still cached
// for whatever reason. JDK bug ?
throw e;
}
}
}
}
public final SelectionKey register(Selector sel, int ops,
Object att)
throws ClosedChannelException
{
synchronized (regLock) {
if (!isOpen())
throw new ClosedChannelException();
if ((ops & ~validOps()) != 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
if (blocking)
throw new IllegalBlockingModeException();
SelectionKey k = findKey(sel);
if (k != null) {
k.interestOps(ops);
k.attach(att);
}
if (k == null) {
// New registration
synchronized (keyLock) {
if (!isOpen())
throw new ClosedChannelException();
k = ((AbstractSelector)sel).register(this, ops, att);
addKey(k);
}
}
return k;
}
}
javaChannel().register() 负责调用 JDK 底层,将 Channel 注册到 Selector 上,register() 的第三个入参传入的是 Netty 自己实现的 Channel 对象,调用 register() 方法会将它绑定在 JDK 底层 Channel 的attachment上。这样在每次 Selector 对象进行事件循环时,Netty 都可以从返回的 JDK 底层 Channel 中获得自己的 Channel 对象。
2.2.3.2 handlerAdded
初始化ChannelPipeline的时机是当Channel向对应的Reactor注册成功后,在handlerAdded事件回调中利用ChannelInitializer进行初始化。
io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer#handlerAdded
@Override
public void handlerAdded(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
// 必须是注册以后
if (ctx.channel().isRegistered()) {
// This should always be true with our current DefaultChannelPipeline implementation.
// The good thing about calling initChannel(...) in handlerAdded(...) is that there will be no ordering
// surprises if a ChannelInitializer will add another ChannelInitializer. This is as all handlers
// will be added in the expected order.
if (initChannel(ctx)) {
// We are done with init the Channel, removing the initializer now.
removeState(ctx);
}
}
}
//ChannelInitializer实例是被所有的Channel共享的,用于初始化ChannelPipeline
//通过Set集合保存已经初始化的ChannelPipeline,避免重复初始化同一ChannelPipeline
private final Set initMap = Collections.newSetFromMap(
new ConcurrentHashMap());
private boolean initChannel(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
if (initMap.add(ctx)) { // Guard against re-entrance.
try {
initChannel((C) ctx.channel());
} catch (Throwable cause) {
exceptionCaught(ctx, cause);
} finally {
ChannelPipeline pipeline = ctx.pipeline();
if (pipeline.context(this) != null) {
//初始化完毕后,从pipeline中移除自身
pipeline.remove(this);
}
}
return true;
}
return false;
}
//匿名类实现,这里指定具体的初始化逻辑
protected abstract void initChannel(C ch) throws Exception;
private void removeState(final ChannelHandlerContext ctx) {
//从initMap防重Set集合中删除ChannelInitializer
if (ctx.isRemoved()) {
initMap.remove(ctx);
} else {
ctx.executor().execute(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
initMap.remove(ctx);
}
});
}
} 执行完成后pipeline如下:
执行完整个 register0() 的注册流程之后,EventLoop 线程会将 ServerBootstrapAcceptor 添加到 Pipeline 当中(提交的任务执行)
ch.eventLoop().execute(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
pipeline.addLast(new ServerBootstrapAcceptor(
ch, currentChildGroup, currentChildHandler, currentChildOptions, currentChildAttrs));
}
}也就是统一在EventLoop 线程中初始化pipeLine,保证线程安全
2.2.4 Reactor线程触发注册成功safeSetSuccess(promise);
Reactor设置注册成功后,启动线程监听到完成任务,那么就进行接下来的绑定端口操作
// 若执行完毕进行端口绑定
if (regFuture.isDone()) {
// At this point we know that the registration was complete and successful.
ChannelPromise promise = channel.newPromise();
doBind0(regFuture, channel, localAddress, promise);
return promise;
} else {
// Registration future is almost always fulfilled already, but just in case it's not.
final PendingRegistrationPromise promise = new PendingRegistrationPromise(channel);
regFuture.addListener(new ChannelFutureListener() {
@Override
public void operationComplete(ChannelFuture future) throws Exception {
Throwable cause = future.cause();
if (cause != null) {
// Registration on the EventLoop failed so fail the ChannelPromise directly to not cause an
// IllegalStateException once we try to access the EventLoop of the Channel.
promise.setFailure(cause);
} else {
// Registration was successful, so set the correct executor to use.
// See https://github.com/netty/netty/issues/2586
promise.registered();
doBind0(regFuture, channel, localAddress, promise);
}
}
});
return promise;
}2.3 端口绑定
private static void doBind0(
final ChannelFuture regFuture, final Channel channel,
final SocketAddress localAddress, final ChannelPromise promise) {
// This method is invoked before channelRegistered() is triggered. Give user handlers a chance to set up
// the pipeline in its channelRegistered() implementation.
channel.eventLoop().execute(new Runnable() {
@Override
sss
if (regFuture.isSuccess()) {
channel.bind(localAddress, promise).addListener(ChannelFutureListener.CLOSE_ON_FAILURE);
} else {
promise.setFailure(regFuture.cause());
}
}
});
}提交到异步任务到Reactor,绑定逻辑需要注册逻辑处理完之后运行,如上面的ServerBootstrapAcceptor异步任务执行完
@Override
public ChannelFuture bind(SocketAddress localAddress, ChannelPromise promise) {
return pipeline.bind(localAddress, promise);
}
@Override
public final ChannelFuture bind(SocketAddress localAddress, ChannelPromise promise) {
return tail.bind(localAddress, promise);
}
@Override
public ChannelFuture bind(final SocketAddress localAddress, final ChannelPromise promise) {
ObjectUtil.checkNotNull(localAddress, "localAddress");
if (isNotValidPromise(promise, false)) {
// cancelled
return promise;
}
final AbstractChannelHandlerContext next = findContextOutbound(MASK_BIND);
EventExecutor executor = next.executor();
if (executor.inEventLoop()) {
next.invokeBind(localAddress, promise);
} else {
safeExecute(executor, new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
next.invokeBind(localAddress, promise);
}
}, promise, null, false);
}
return promise;
}
private void invokeBind(SocketAddress localAddress, ChannelPromise promise) {
if (invokeHandler()) {
try {
// DON'T CHANGE
// Duplex handlers implements both out/in interfaces causing a scalability issue
// see https://bugs.openjdk.org/browse/JDK-8180450
final ChannelHandler handler = handler();
final DefaultChannelPipeline.HeadContext headContext = pipeline.head;
if (handler == headContext) {
headContext.bind(this, localAddress, promise);
} else if (handler instanceof ChannelDuplexHandler) {
((ChannelDuplexHandler) handler).bind(this, localAddress, promise);
} else {
((ChannelOutboundHandler) handler).bind(this, localAddress, promise);
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
notifyOutboundHandlerException(t, promise);
}
} else {
bind(localAddress, promise);
}
}调用pipeline.bind(localAddress, promise)在pipeline中传播bind事件,触发回调pipeline中所有ChannelHandler的bind方法。
事件在pipeline中的传播具有方向性:
-
inbound事件从HeadContext开始逐个向后传播直到TailContext。 -
outbound事件则是反向传播,从TailContext开始反向向前传播直到HeadContext。 -
private AbstractChannelHandlerContext findContextOutbound(int mask) { AbstractChannelHandlerContext ctx = this; EventExecutor currentExecutor = executor(); do { ctx = ctx.prev; // 跳过了 private static class ServerBootstrapAcceptor extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter } while (skipContext(ctx, currentExecutor, mask, MASK_ONLY_OUTBOUND)); return ctx; } private static boolean skipContext( AbstractChannelHandlerContext ctx, EventExecutor currentExecutor, int mask, int onlyMask) { // Ensure we correctly handle MASK_EXCEPTION_CAUGHT which is not included in the MASK_EXCEPTION_CAUGHT return (ctx.executionMask & (onlyMask | mask)) == 0 || // We can only skip if the EventExecutor is the same as otherwise we need to ensure we offload // everything to preserve ordering. // // See https://github.com/netty/netty/issues/10067 (ctx.executor() == currentExecutor && (ctx.executionMask & mask) == 0); }
通过上面代码可以知道bind事件在Netty中被定义为outbound事件,所以它在pipeline中是反向传播。先从TailContext开始反向传播直到HeadContext。
因此bind的核心逻辑也正是实现在HeadContext中。
headContext.bind(this, localAddress, promise);
底层实际就是
@Override
public void bind(
ChannelHandlerContext ctx, SocketAddress localAddress, ChannelPromise promise) {
unsafe.bind(localAddress, promise);
}
@Override
public final void bind(final SocketAddress localAddress, final ChannelPromise promise) {
assertEventLoop();
if (!promise.setUncancellable() || !ensureOpen(promise)) {
return;
}
// See: https://github.com/netty/netty/issues/576
if (Boolean.TRUE.equals(config().getOption(ChannelOption.SO_BROADCAST)) &&
localAddress instanceof InetSocketAddress &&
!((InetSocketAddress) localAddress).getAddress().isAnyLocalAddress() &&
!PlatformDependent.isWindows() && !PlatformDependent.maybeSuperUser()) {
// Warn a user about the fact that a non-root user can't receive a
// broadcast packet on *nix if the socket is bound on non-wildcard address.
logger.warn(
"A non-root user can't receive a broadcast packet if the socket " +
"is not bound to a wildcard address; binding to a non-wildcard " +
"address (" + localAddress + ") anyway as requested.");
}
boolean wasActive = isActive();
try {
doBind(localAddress);
} catch (Throwable t) {
safeSetFailure(promise, t);
closeIfClosed();
return;
}
if (!wasActive && isActive()) {
invokeLater(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
pipeline.fireChannelActive();
}
});
}
safeSetSuccess(promise);
}
@SuppressJava6Requirement(reason = "Usage guarded by java version check")
@Override
protected void doBind(SocketAddress localAddress) throws Exception {
if (PlatformDependent.javaVersion() >= 7) {
javaChannel().bind(localAddress, config.getBacklog());
} else {
javaChannel().socket().bind(localAddress, config.getBacklog());
}
}Netty 会根据 JDK 版本的不同,分别调用 JDK 底层不同的 bind() 方法。我使用的是 JDK8,所以会调用 JDK 原生 Channel 的 bind() 方法。执行完 doBind() 之后,服务端 JDK 原生的 Channel 真正已经完成端口绑定了。
2.3.1 判断是否为激活
@Override
public boolean isActive() {
// As java.nio.ServerSocketChannel.isBound() will continue to return true even after the channel was closed
// we will also need to check if it is open.
return isOpen() && javaChannel().socket().isBound();
}2.3.2 channelActive事件
完成端口绑定之后,Channel 处于活跃 Active 状态,然后会调用 pipeline.fireChannelActive() 方法触发 channelActive 事件。
channelActive事件在Netty中定义为inbound事件,所以它在pipeline中的传播为正向传播,从HeadContext一直到TailContext为止。
在channelActive事件回调中需要触发向Selector指定需要监听的IO事件~~OP_ACCEPT事件。
@Override
public final ChannelPipeline fireChannelActive() {
AbstractChannelHandlerContext.invokeChannelActive(head);
return this;
}
private void invokeChannelActive() {
if (invokeHandler()) {
try {
// DON'T CHANGE
// Duplex handlers implements both out/in interfaces causing a scalability issue
// see https://bugs.openjdk.org/browse/JDK-8180450
final ChannelHandler handler = handler();
final DefaultChannelPipeline.HeadContext headContext = pipeline.head;
if (handler == headContext) {
headContext.channelActive(this);
} else if (handler instanceof ChannelDuplexHandler) {
((ChannelDuplexHandler) handler).channelActive(this);
} else {
((ChannelInboundHandler) handler).channelActive(this);
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
invokeExceptionCaught(t);
}
} else {
fireChannelActive();
}
}
@Override
public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) {
//pipeline中继续向后传播channelActive事件
ctx.fireChannelActive();
//如果是autoRead 则自动触发read事件传播
//在read回调函数中 触发OP_ACCEPT注册
readIfIsAutoRead();
}
private void readIfIsAutoRead() {
if (channel.config().isAutoRead()) {
channel.read();
}
}
@Override
public Channel read() {
pipeline.read();
return this;
}
@Override
public final ChannelPipeline read() {
tail.read();
return this;
}
@Override
public void read(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) {
unsafe.beginRead();
}
@Override
public final void beginRead() {
assertEventLoop();
try {
doBeginRead();
} catch (final Exception e) {
invokeLater(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
pipeline.fireExceptionCaught(e);
}
});
close(voidPromise());
}
}
@Override
protected void doBeginRead() throws Exception {
// Channel.read() or ChannelHandlerContext.read() was called
final SelectionKey selectionKey = this.selectionKey;
if (!selectionKey.isValid()) {
return;
}
readPending = true;
final int interestOps = selectionKey.interestOps();
if ((interestOps & readInterestOp) == 0) {
selectionKey.interestOps(interestOps | readInterestOp);
}
}
在执行完 channelActive 事件传播之后,会调用 readIfIsAutoRead() 方法触发 Channel 的 read 事件,而它最终调用到 AbstractNioChannel 中的 doBeginRead() 方法,其中 readInterestOp 参数就是在前面初始化 Channel 所传入的 SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT 事件,所以 OP_ACCEPT 事件会被注册到 Channel 的事件集合中。
2.4 服务启动总结
- 创建服务端 Channel:本质是创建 JDK 底层原生的 Channel,并初始化几个重要的属性,包括 id、unsafe、pipeline 等。
- 初始化服务端 Channel:设置 Socket 参数以及用户自定义属性,并添加两个特殊的处理器 ChannelInitializer 和 ServerBootstrapAcceptor。
- 注册服务端 Channel:调用 JDK 底层将 Channel 注册到 Selector 上。
- 端口绑定:调用 JDK 底层进行端口绑定,并触发 channelActive 事件,把 OP_ACCEPT 事件注册到 Channel 的事件集合中。