第十一章内容与总结
目录
一.包装类
1.Integer类
【例11.1】Integer类的常用方法
【例11.2】查看Integer类的常量值
2.Double类
【例11.3】Double类的常用方法
3.Boolean类
【例11.4】Boolean类的常用方法
4.Character类
【例11.5】Character类的常用方法
5.Number类
二.数字处理
1.数字格式化
【例11.6】DecimalFormat类的常用方法
2.Math类
(1)三角函数方法
【例11.7】在Java代码中进行三角函数运算
(2)指数函数方法
【例11.8】在Java代码中进行指数函数运算
(3)取整函数方法
【例11.9】各场景下取整函数的运算结果
(4)取最大值、最小值、绝对值函数方法
【例11.10】取最大值、最小值、绝对值的方法
3.Random类
【例11.11】获取不同取值范围、不同类型的随机数
4.BigInteger类
【例11.12】使用BigInteger类进行数学运算
5.BigDecimal类
【例11.13】使用BigDecimal类进行数学运算
总结:
三.System类
1.控制台输出字符
(1)不会自动换行的print()方法
(2)可以自动换行的println()方法
2.计时
【例11.14】查看执行一万次字符串拼接所消耗的时间
四.Scanner类
【例11.15】猜数字游戏
五.日期时间类
1.Date类
【例11.16】获取当前的日期和时间
2.日期时间格式化
【例11.17】以中文的形式打印当前的日期和时间
总结:
3.Calendar类
【例11.18】今天离中华人民共和国成立100周年差多少天
对Calendar类的使用的总结:
六.Runtime类
1.执行本地命令
【例11.19】让Java程序执行Windows系统的help命令
2.查看内存
【例11.20】监控虚拟机内存使用情况
public class IntergerDaemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
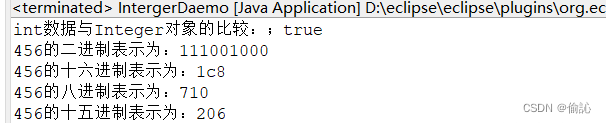
int num = Integer.parseInt("456"); //将字符串转换为int类型
Integer iNum = Integer.valueOf("456"); //创建一个intefer对象
System.out.println("int数据与Integer对象的比较:;"+iNum.equals(num));
String str2 = Integer.toBinaryString(num); //获取数字的二进制表示
String str3 = Integer.toHexString(num); //获取数字的十六进制表示
String str4 = Integer.toOctalString(num); //获取数字的八进制表示
String str5 = Integer.toString(num,15); //获取数字的十五进制
System.out.println("456的二进制表示为:"+str2);
System.out.println("456的十六进制表示为:"+str3);
System.out.println("456的八进制表示为:"+str4);
System.out.println("456的十五进制表示为:"+str5);
}
}
//例题11.1
11.1.2 Double类
public class DoubleDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
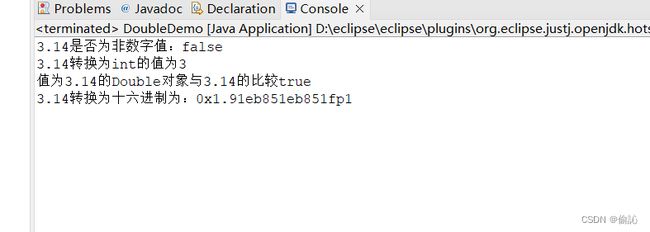
Double dNum =Double.valueOf("3.14");
//判断是否为非数字值
System.out.println("3.14是否为非数字值:"+Double.isNaN(dNum.doubleValue()));
System.out.println("3.14转换为int的值为"+dNum.intValue());//转换为int类型
//判断大小
System.out.println("值为3.14的Double对象与3.14的比较"+dNum.equals(3.14));
//转换为十六进制
System.out.println("3.14转换为十六进制为:"+Double.toHexString(dNum));
}
}
//例题11.3、
11.1.3 Boolean类
public class BooleanDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Boolean b1 =Boolean.valueOf("true"); //创建Boolean对象
Boolean b2 =Boolean.valueOf("ok");
System.out.println("b1:"+b1.booleanValue());
System.out.println("b2:"+b2.booleanValue());
}
}

11.1.4 Character类
public class UpperOrLower {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Character mychar1=Character.valueOf('A');
Character mychar2=Character.valueOf('a');
if(Character.isUpperCase(mychar1)) {
System.out.println(mychar1+"是大写字母");
//转换为小写字母输出
System.out.println("转换为小写字母的结果:"+Character.toLowerCase(mychar1));
}
if(Character.isLowerCase(mychar2)) {
System.out.println(mychar1+"是小写字母");
//转换为大写字母输出
System.out.println("转换为小写字母的结果:"+Character.toUpperCase(mychar2));
}
}
}//例题11.5
11.1.5 Number类
表11.6
方法 功能描述
byteValue()
int Value()
int Value()
int Value()
int Value()
int Value()
11.1.5 Number类
返回数值
import java.text.DecimalFormat;
public class DecimalFormatSimpleDemo {
//使用实例化对象时设置格式
static public void SimgleFormat(String pattern,double value) {
DecimalFormat myFormat =new DecimalFormat(pattern);
String output =myFormat.format(value);
System.out.println(value+""+pattern+""+output);
}
//使用applyPattern()方法对数字进行格式化
static public void UseApplyPatternMethodFormat(String pattern,double value) {
DecimalFormat myFormat =new DecimalFormat();
myFormat.applyPattern(pattern);
System.out.println(value+""+pattern+""+myFormat.format(value));
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
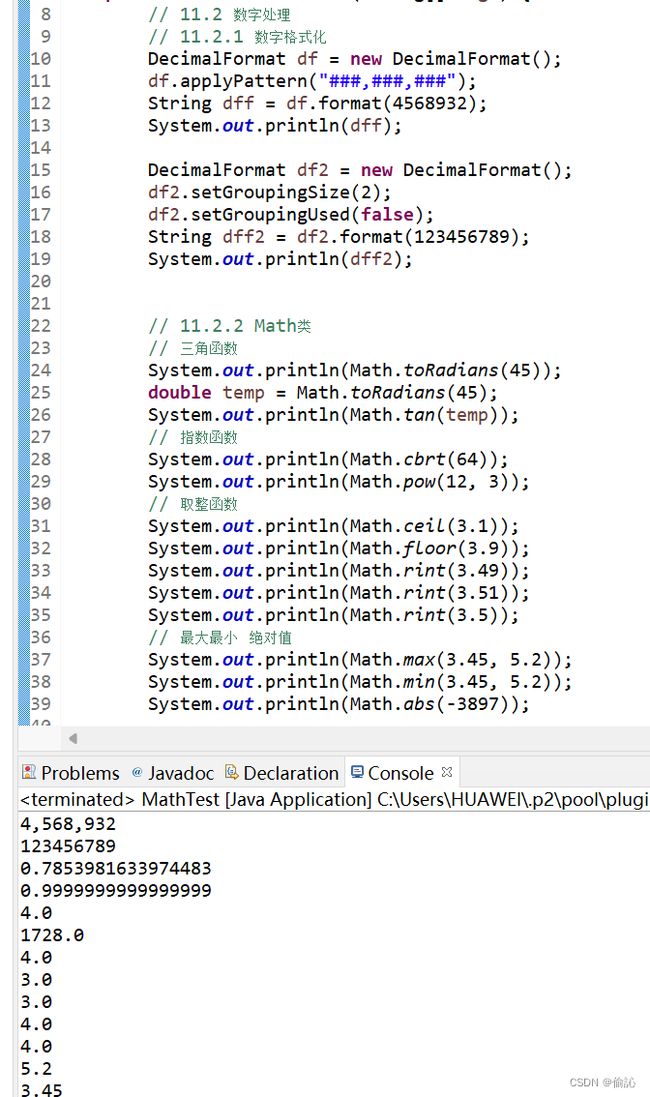
SimgleFormat("###,###,###",123456.789);
SimgleFormat("00000000.###",123456.789);
//按照格式化模板格式化数字,不存在的位以0显示
SimgleFormat("000000.000",123.78);
//调用静态 UseApplyPatternMethodFormat()方法
UseApplyPatternMethodFormat("#.###%", 00.789);
UseApplyPatternMethodFormat("###.##", 123456.789);
UseApplyPatternMethodFormat("0.00\u2030", 0.789);
}
}
//例题11.6
11.2:数字处理
11.2.1数字化格式
11.2.2Math类
1三角函数
public class TrigonometricFunction {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("90度的正弦值为:"+Math.sin(Math.PI/2));
System.out.println("0度的余弦值:"+Math.cos(0));
System.out.println("90度的正弦值为:"+Math.tan(Math.PI/3));
//取2的平方根与2商的反正弦
System.out.println("取2的平方根与2商的反正弦"+Math.asin(Math.sqrt(2)/2));
//取2的平方根与2商的反余弦
System.out.println("取2的平方根与2商的反余弦"+Math.asin(Math.sqrt(2)/2));
System.out.println("1的反正切值"+Math.atan(1));
System.out.println("120度的弧度制"+Math.toRadians(120.0));
System.out.println("Π/2的角度值"+Math.toDegrees(Math.PI/2));
}
}
//例题11.7
2.指数函数
public class ExceponentFunction {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("e的平方值"+Math.exp(2));
System.out.println("以e为底的2的对数值"+Math.log(2));
System.out.println("以10为底2的对数值"+Math.log10(2));
System.out.println("4的平方根值"+Math.sqrt(4));
System.out.println("8的立方根值"+Math.cbrt(8));
System.out.println("2的2次方值"+Math.pow(2, 2));
}
}
//例题11.8
3.取整函数
public class IntFunction {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("使用ceil()方法取整"+Math.ceil(5.2));
System.out.println("使用floor()方法取整"+Math.floor(2.5));
System.out.println("使用rint()方法取整"+Math.rint(2.7));
System.out.println("使用rint()方法取整"+Math.rint(2.5));
//将参数加上0.5后返回最接近的整数
System.out.println("使用round()方法取整"+Math.round(3.4f));
//将参数加上0.5后返回最接近的整数,并且将结果强制转换为长整型
System.out.println("使用round()方法取整"+Math.round(2.5));
}
}
//例题11.9
4.取最大值、最小值、绝对值
11.2.3 Random类
import java.util.Random;
public class RandomDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Random r = new Random();
//随机产生一个整数
System.out.println("随机产生一个整数"+r.nextInt());
//随机产生一个大于等于0且小于10的整数
System.out.println("随机产生一个大于等于0且小于10的整数"+r.nextInt(10));
//随机产生一个布尔型的值
System.out.println("随机产生一个布尔型的值"+r.nextBoolean());
//随机产生一个双精度浮点型的值
System.out.println("随机产生一个双精度浮点型的值"+r.nextDouble());
//随机产生一个单精度浮点型的值
System.out.println("随机产生一个单精度浮点型的值"+r.nextFloat());
//随机产生一个概率密度为高斯分布的双精度浮点型的值
System.out.println("随机产生一个概率密度为高斯分布的双精度浮点型的值"+r.nextGaussian());
}
}
//例题11.11
11.2.4 BigInteger类
import java.math.BigInteger;
public class BigIntegerDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
BigInteger b1 =new BigInteger("987654321987654321");
BigInteger b2 =new BigInteger("123456789123456789");
System.out.println("加法操作:"+b1.add(b2));
System.out.println("减法操作:"+b1.subtract(b2));
System.out.println("乘法操作:"+b1.multiply(b2));
System.out.println("除法操作:"+b1.divide(b2));
System.out.println("取商:"+b1.divideAndRemainder(b2)[0]);
System.out.println("取余数:"+b1.divideAndRemainder(b2)[1]);
System.out.println("做2次方操作:"+b1.pow(2));
System.out.println("取相反数操作:"+b1.negate());
}
}
//例题11.12
11.2.4 BigDecimal类
import java.math.BigDecimal;
import java.math.RoundingMode;
public class BigDecimalDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
//11.2.4 BigDecimal
BigDecimal b1=new BigDecimal("0.728382834535");
BigDecimal b2=new BigDecimal("0.00045353");
System.out.println("两个数字相加结果:"+b1.add(b2));
System.out.println("两个数字相减结果:"+b1.subtract(b2));
System.out.println("两个数字相乘结果:"+b1.multiply(b2));
//除法运算,商小数点后保留9位,并将结果进行四舍五入操作
System.out.println("两个数字相除,保留小数点后9位:"+b1.divide(b2,9,RoundingMode.HALF_UP));
}
}
//例题11.13
四.Scanner类
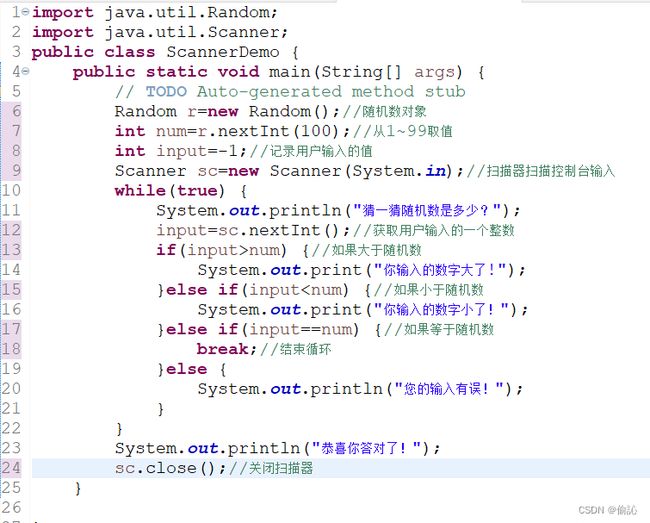
控制台输出内容用到了System.out就表示向控制台输出,System.in就表示从控制台输入,让Scanner扫描System.in就可以获取用户输入的值了。
使用Scanner类首先要引入该类,语法:
import java.util.Scanner;//引入Scanner类
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
【例11.15】猜数字游戏
代码:
结果:
五.日期时间类
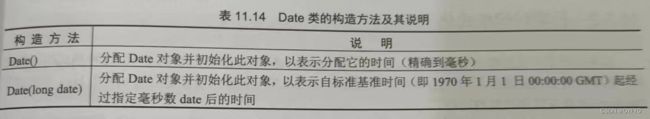
1.Date类
Date类用于表示日期时间,使用该类表示时间需要使用其构造方法创建对象。
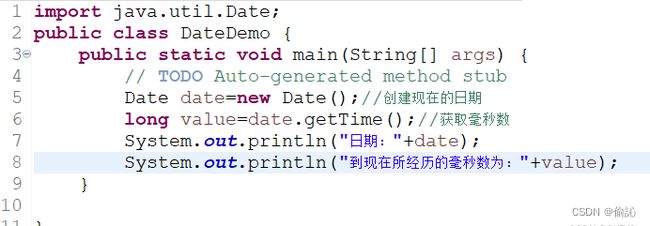
例如,使用Date类的第二种构造方法创建一个Date类的对象,代码:
long timeMillis=System.currentTimeMillis();//当前系统时间所经历的毫秒数
Date date=new Date(timeMillis);
结果:
2.日期时间格式化
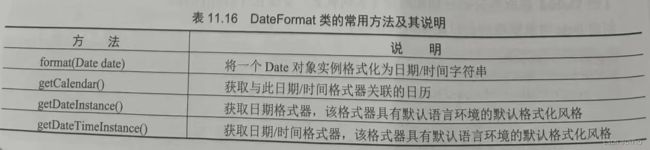
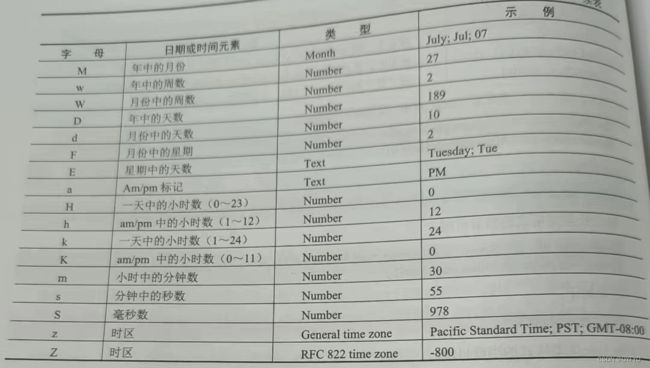
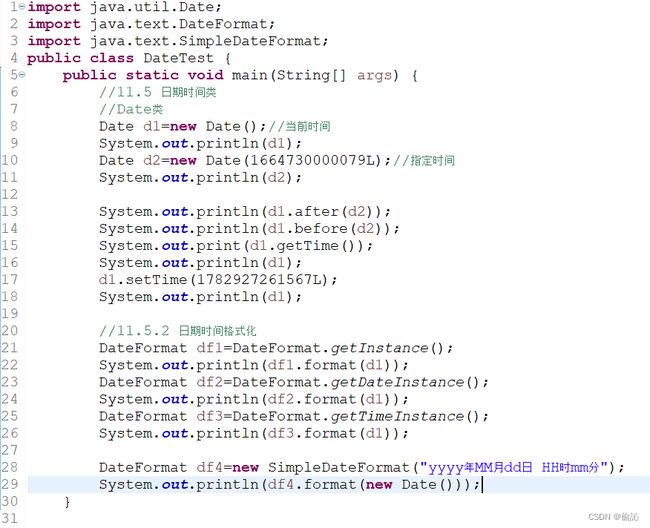
DateFormat类是日期时间格式化子类的抽象类,可以按照指定的格式对日期或时间进行格式化。
DateFormat类提供了很多类方法,以获得基于默认或给定语言环境和多种格式化风格的默认日期时间Formatter,格式化风格主要包括SHORT、MEDIUM、LONG和FULL4种:
(1)SHORT:完全为数字,如12.13.52或3:30pm。
(2)MEDIUM:较长,如Jan 12,1952。
(3)LONG:更长,如January 12,1952或3:30:32pm。
(4)FULL:完全指定,如Tuesday、April 12、1952 AD或3:30:42pm PST。
使用DateFormat类还可以自定义日期时间的格式。要格式化一个当前语言环境下的日期,首先需要创建DateFormat类的一个对象,由于它是抽象类,因此可以使用其静态方法getDateInstance()进行创建,语法:
DateFormat df=DateFormat.getDateInstance();
使用getDateInstance()方法获取的是所在国家或地区的标准日期格式。
DateFormat类还提供了一些其他静态方法。
由于DateFormat类是一个抽象类,不能用new创建实例对象。因此,除了使用getXXXInstance()方法创建其对象,还可以使用其子类,如SimpleDateFormat类,该类是一个以与语言环境相关的方式来格式化和分析日期的具体类,它允许进行格式化(日期→文本)、分析(文本→日期)和规范化。
【例11.17】以中文的形式打印当前的日期和时间
代码:
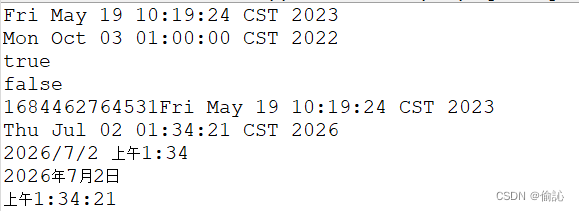
结果:
DateFormat类提供的Date parse(String source)方法可以将字符串转为其字面日期对应的Date对象,整个过程相当于日期格式化的逆操作。
例如,将“2021-02-19”这个字符串转成Date对象,代码:
DateFormat sdf=new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd");
Date date=sdf.parse("2021-02-19");
总结:
代码:
结果:
3.Calendar类
Calendar提供了一个类方法getInstance(),以获得其类型的一个通用的对象。Calendar类的getInstance()方法返回一个Calendar对象,其日历字段已由当前日期和时间格式化,使用方法:
Calendar rightNow=Calendar.getInstance();
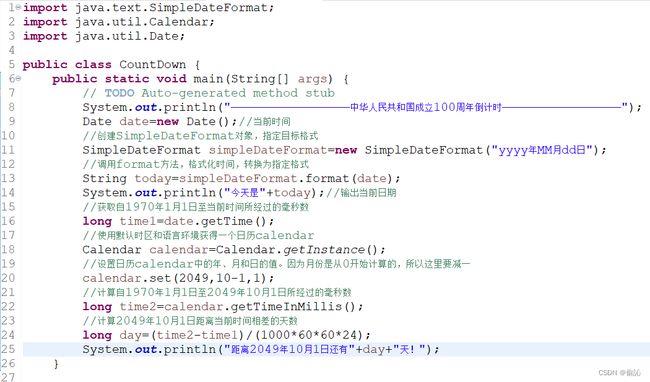
【例11.18】今天离中华人民共和国成立100周年差多少天
代码:
结果:
对Calendar类的使用的总结:
(1)c.set(Calendar.DAY_OF_MONTH,0)获取的是上个月的最后一天,所以调用前需要将月份往后加一个月。
(2)Calendar.MONTH的第一个月是使用0记录的,所以在获得月份数字后要加1。年和日是从1开始记录的不需要加1。
(3)Calendar.DAY_OF_WEEK的第一天是周日,周一是第二天,周六是最后一天。
六.Runtime类
Runtime类不能使用new关键字创建实例,只能通过Runtime.getRunntime()方法获取实例。
1.执行本地命令
本地命令指的是操作系统的命令。
Runtime类提供exec()方法让Java代码可以执行系统命令,exec()方法有很多重载形式,如:
Process exec(String command)
Process exec(String[] cmdarray)
command:要执行的系统命令,字符串类型。
cmdarray:要执行的命令和相应的命令参数,字符串数组类型。
使用第一种重载方式的代码:
Runtime.getRuntime().exec("javac hello.java");
使用第二种重载方式的代码:
String command[]={"javac","hello.java");
Runtime.getRuntime().exec(command);

【例11.19】让Java程序执行Windows系统的help命令
代码:
结果:
2.查看内存
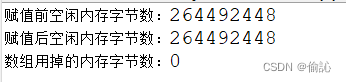
Runtime类可以通过freeMemory()方法查看当前Java虚拟机可用内存的剩余量。
【例11.20】监控虚拟机内存使用情况
代码:
结果:、
注意: freeMemory()方法得到的剩余内存量是近似值。