Spring boot 读取properties文件内容
文章目录
- 1.读取properties内容
-
- 1.1 读取properties中的字符串
- 1.2 读取properties中的list和map
- 2. properties内容到静态类
-
- 2.1 Java
- 2.2 Kotlin
- 3.把值赋值给静态变量
-
- 3.1 Java
-
- 3.1.1 使用@ConfigurationProperties注解
- 3.1.2 使用@Value注解
- 3.2 Kotlin
-
- 3.2.1 使用@ConfigurationProperties注解
- 3.2.2 使用@Value注解
使用kotlin的spring boot项目,读取properties中的内容,包括读取字符串,列表和map等。
1.读取properties内容
1.1 读取properties中的字符串
从配置文件中读取book的名字与数量
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration
@Configuration
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "test.book")
class BookProperties {
lateinit var name: String
var count by Delegates.notNull<Int>()
}
然后在properties中配置如下内容:
test.book.name=Kotlin
test.book.count=20
这样,当程序启动之后,就可以获取到配置的name值Kotlin和count值20
1.2 读取properties中的list和map
从配置文件中读取list,其中包含author的名字,读取map形式的customer,表示每个人买了多少本书。
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration
@Configuration
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "test.book")
class BookProperties {
lateinit var authors: List<String>
lateinit var customers: Map<String, Int>
}
在properties中配置的内容如下
test.book.authors=AAA,BBB,CCC
test.book.customers[tom]=23
test.book.customers[jerry]=20
这样在使用BookProperties这个bean的时候,就可以读取到list和map中的值。
2. properties内容到静态类
有这样的需求,把properties的内容映射到一个静态类上,这个类只会被加载一次。(这样的意义我没搞明白,先挖坑)
2.1 Java
在Java中,我们可以这样写
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.Getter;
import lombok.RequiredArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Setter;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
@Data
@RequiredArgsConstructor
@Configuration
public class YYProperties {
private final BookProperties bookProperties;
@Getter
@Setter
@Configuration
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "test.book")
public static class BookProperties {
private String name;
private int count;
private List<String> authors;
private Map<String, Integer> customers;
}
}
properties文件的配置如下:
test.book.name=JAVA
test.book.count=40
test.book.authors=AAA,BBB,CCC
test.book.customers[tom]=12
test.book.customers[jerry]=28
这样我们在使用yYProperties这个bean的时候,就可以读取这个成员变量bookProperties的值,如
import lombok.RequiredArgsConstructor;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service
@RequiredArgsConstructor
public class YYService {
private final YYProperties yyProperties;
public void hello() {
System.out.println(yyProperties.getBookProperties().getAuthors());
System.out.println(yyProperties.getBookProperties().getName());
System.out.println(yyProperties.getBookProperties().getCount());
System.out.println(yyProperties.getBookProperties().getCustomers());
}
}
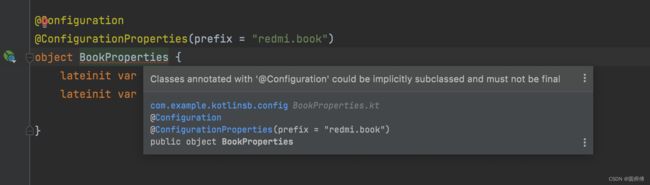
2.2 Kotlin
那再kotlin中,是否可以这样写呢?
我们都知道,kotlin中是没有静态修饰符static的,有的只是object。而object类经过编译成class文件,会被添加上final,而final修饰的类是无法添加@Configuration注解的。
3.把值赋值给静态变量
有的时候,我就是想把properties配置的值赋值给静态变量,应该怎么做呢?
这种需求会是什么时候有呢?比方说,我配置了一个密钥,需要在一个util类里使用,这个util类没有注册成bean,其中也没有注入配置的类容,就想要静态变量值。
3.1 Java
3.1.1 使用@ConfigurationProperties注解
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
@Configuration
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "test.book")
public class YYProperties {
public static String name;
public static int count;
public static List<String> authors;
public static Map<String, String> customers;
public void setName(String name) {
YYProperties.name = name;
}
public void setCount(int count) {
YYProperties.count = count;
}
public void setAuthors(List<String> authors) {
YYProperties.authors = authors;
}
public void setCustomers(Map<String, String> customers) {
YYProperties.customers = customers;
}
}
在properties中这样配置
test.book.name=JAVA
test.book.count=40
test.book.authors=AAA,BBB,CCC
test.book.customers[tom]=12
test.book.customers[jerry]=28
这样就可以使用这写值了
System.out.println(YYProperties.name);
System.out.println(YYProperties.authors);
System.out.println(YYProperties.customers);
System.out.println(YYProperties.count);
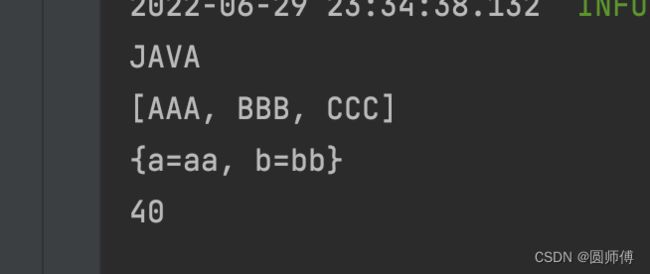
打印结果如下:
JAVA
[AAA, BBB, CCC]
{tom=12, jerry=28}
40
3.1.2 使用@Value注解
当然了,如果不使用@configurationProperties注解,直接使用@Value注解,应该怎么做呢?
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
@Configuration
//@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "test.book")
public class YYProperties {
public static String name;
public static int count;
public static List<String> authors;
public static Map<String, String> customers;
@Value("${test.book.name}")
public void setName(String name) {
YYProperties.name = name;
}
@Value("${test.book.count}")
public void setCount(int count) {
YYProperties.count = count;
}
@Value("${test.book.authors}")
public void setAuthors(List<String> authors) {
YYProperties.authors = authors;
}
@Value("#{${test.book.customers}}")
public void setCustomers(Map<String, String> customers) {
YYProperties.customers = customers;
}
}
其中要注意的是map的配置,这个@value的注解是在方法上的,同时,用的是
#{${test.book.customers}}
而且配置文件properties也不一样
test.book.name=JAVA
test.book.count=40
test.book.authors=AAA,BBB,CCC
test.book.customers={'a': 'aa', 'b':'bb'}
3.2 Kotlin
3.2.1 使用@ConfigurationProperties注解
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration
@Configuration
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "redmi.book")
class BookProperties {
fun setName(name: String) {
BookProperties.name = name
}
fun setAuthors(authors: List<String>) {
BookProperties.authors = authors
}
fun setCustomers(customers: Map<String, String>) {
BookProperties.customers = customers
}
companion object {
var name: String = ""
var authors: List<String> = ArrayList()
var customers: Map<String, String> = HashMap()
}
}
properties中这样配置即可
redmi.book.customers[aa]=AA
redmi.book.customers[bb]=BB
redmi.book.name=lisi
redmi.book.authors=aaa,bbb,ccc
这样在别的类里面就可以直接调用静态变量了
println(BookProperties.authors)
println(BookProperties.customers)
输出结果为
[aaa, bbb, ccc]
{aa=AA, bb=BB}
3.2.2 使用@Value注解
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration
@Configuration
class BookProperties {
@Value("\${redmi.book.name}")
fun setName(name: String) {
BookProperties.name = name
}
@Value("\${redmi.book.authors}")
fun setAuthors(authors: List<String>) {
BookProperties.authors = authors
}
@Value("#{\${redmi.book.customers}}")
fun setCustomers(customers: Map<String, String>) {
BookProperties.customers = customers
}
companion object {
var name: String = ""
var authors: List<String> = ArrayList()
var customers: Map<String, String> = HashMap()
}
}
properties配置如下
redmi.book.customers={'a': 'aa', 'b': 'bb'}
redmi.book.name=lisi
redmi.book.authors=aaa,bbb,ccc
这样也可以获取到对应的值。