Spring Security Ldap 登录认证流程的源码梳理
一、通过请求Controller开始登录认证
通过authenticationManager调用authenticate()方法开始登录认证,因为authenticationManager是通过@Bean注入,因为SecurityLdapConfig是继承的WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter类,所以authenticationManager的类型就是在WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter类的内部类AuthenticationManagerDelegator,所以在调用authenticate()方法时候是在调用AuthenticationManagerDelegator类的authenticate()方法。
代码如下:
package com.framework.ldap.controller;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.security.authentication.AuthenticationManager;
import org.springframework.security.authentication.UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken;
import org.springframework.security.core.Authentication;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
/**
* @Author: LongGE
* @Date: 2023-03-27
* @Description:
*/
@Slf4j
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/AuthLdapController")
public class AuthLdapController {
//在SecurityLdapConfig中通过@Bean注入
@Autowired
private AuthenticationManager authenticationManager;
@PostMapping(value = "/login")
public String login(String username, String password) {
log.info("start spring security login to!");
//登录认证流程
Authentication authentication = authenticationManager
.authenticate(new UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(username, password));
log.info("登录返回信息:{}", authentication);
return "login to success!";
}
}二、分析AuthenticationManagerDelegator类
它本身是WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter类的内部类,由WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter初始化生成的。
代码如下:
/**
* 在项目启动时候通过@Bean构建的 AuthenticationManagerDelegator类,
* 所以在登录我们注入的AuthenticationManager就是它
*/
static final class AuthenticationManagerDelegator implements AuthenticationManager {
//它在是通过构造函数传入的参数构建
private AuthenticationManagerBuilder delegateBuilder;
//项目启动后第一请求的时候他是空值
private AuthenticationManager delegate;
private final Object delegateMonitor = new Object();
private Set beanNames;
//构造函数
AuthenticationManagerDelegator(AuthenticationManagerBuilder delegateBuilder, ApplicationContext context) {
Assert.notNull(delegateBuilder, "delegateBuilder cannot be null");
Field parentAuthMgrField = ReflectionUtils.findField(AuthenticationManagerBuilder.class,
"parentAuthenticationManager");
ReflectionUtils.makeAccessible(parentAuthMgrField);
this.beanNames = getAuthenticationManagerBeanNames(context);
validateBeanCycle(ReflectionUtils.getField(parentAuthMgrField, delegateBuilder), this.beanNames);
this.delegateBuilder = delegateBuilder;
}
/**
* 登录认证
* 首次请求登录时候 delegate 是空值,我们需要去赋值一个在初始化已经创建好的ProviderManager,这个ProviderManager的providers集合中只有一个AuthenticationProvider,就是AnonymousAuthenticationProvider
* 参数Authentication authentication看似和我们在Controller时候传入的UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken不同,实际上UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken是实现了Authentication
* Authentication是接口,AbstractAuthenticationToken是实现Authentication接口的抽象类,UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken是继承了AbstractAuthenticationToken抽象类的,所以可以使用Authentication泛指
*/
@Override
public Authentication authenticate(Authentication authentication) throws AuthenticationException {
//项目启动后首次请求时候 delegate 为空值,但是第二次请求时候就不在为空
if (this.delegate != null) {
return this.delegate.authenticate(authentication);
}
//因为首次请求 delegate 为空值,所以我们需要对 delegate 进行赋值操作,这里通过 synchronized 关键字来做线程锁,保证线程安全
synchronized (this.delegateMonitor) {
if (this.delegate == null) {
//通过项目启动已经配置好的 AuthenticationManagerBuilder 去获取AuthenticationManager
this.delegate = this.delegateBuilder.getObject();
//在将项目启动配置好的 AuthenticationManagerBuilder 赋值为空
this.delegateBuilder = null;
}
}
//首次请求时候去调用AuthenticationManager 的 认证接口。
return this.delegate.authenticate(authentication);
}
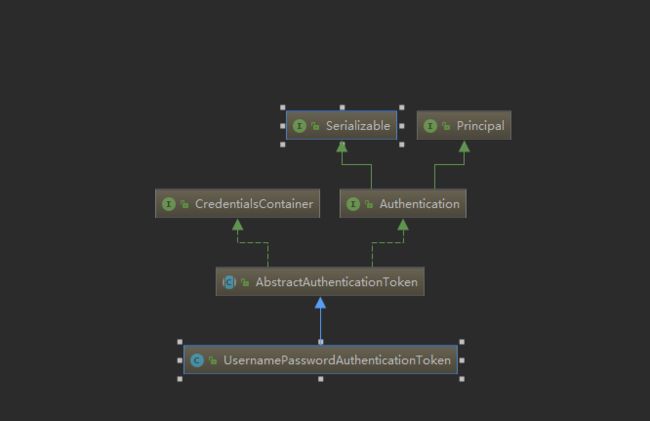
} 登录认证我们在Controller传入的UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken类,但是在AuthenticationManagerDelegator类的authenticate()方法时候参数却是Authentication类型,所以要解释一下二者之间的关系。
关系如图:
三、解析ProviderManager类
ProviderManager类主要判断AuthenticationProvider集合中是否由满足要求的AuthenticationProvider,如果存在那么调用authenticate()方法进行认证。
ProviderManager类主要代码如下:
package org.springframework.security.authentication;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.List;
import org.apache.commons.logging.Log;
import org.apache.commons.logging.LogFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean;
import org.springframework.context.MessageSource;
import org.springframework.context.MessageSourceAware;
import org.springframework.context.support.MessageSourceAccessor;
import org.springframework.core.log.LogMessage;
import org.springframework.security.core.Authentication;
import org.springframework.security.core.AuthenticationException;
import org.springframework.security.core.CredentialsContainer;
import org.springframework.security.core.SpringSecurityMessageSource;
import org.springframework.util.Assert;
import org.springframework.util.CollectionUtils;
/**
* 通过循环遍历AuthenticationProvider集合,找到符合要求的AuthenticationProvider进行认证流程
* 它是一个中央的调度器,主要是管理不同的AuthenticationProvider认证器
*/
public class ProviderManager implements AuthenticationManager, MessageSourceAware, InitializingBean {
private static final Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(ProviderManager.class);
private AuthenticationEventPublisher eventPublisher = new NullEventPublisher();
// 登录认证器集合
private List providers = Collections.emptyList();
protected MessageSourceAccessor messages = SpringSecurityMessageSource.getAccessor();
// 这里还是一个ProviderManager 在加载过程中我们的AuthenticationManagerDelegator会生成一个自定义的抽闲AuthenticationProvider
private AuthenticationManager parent;
private boolean eraseCredentialsAfterAuthentication = true;
@Override
public Authentication authenticate(Authentication authentication) throws AuthenticationException {
//获取Authentication的实现类的Class格式,后面用于判断具体由哪个AuthenticationProvider去执行认证流程
Class toTest = authentication.getClass();
AuthenticationException lastException = null;
AuthenticationException parentException = null;
Authentication result = null;
Authentication parentResult = null;
//获取AuthenticationProvider的数量
int currentPosition = 0;
int size = this.providers.size();
for (AuthenticationProvider provider : getProviders()) {
//判断入参的Authentication类型是否是AuthenticationProvider内的Authentication同类或者子类型
//如果是同类型或者子类返回true,不是返回false
if (!provider.supports(toTest)) {
continue;
}
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace(LogMessage.format("Authenticating request with %s (%d/%d)",
provider.getClass().getSimpleName(), ++currentPosition, size));
}
try {
//当ProviderManager中的providers集合中的AuthenticationProvider由满足条件
result = provider.authenticate(authentication);
if (result != null) {
copyDetails(authentication, result);
break;
}
}
catch (AccountStatusException | InternalAuthenticationServiceException ex) {
prepareException(ex, authentication);
throw ex;
}
catch (AuthenticationException ex) {
lastException = ex;
}
}
//当AuthenticationProvider集合中都没有满足要求的,并且parent不是空值时候那么久要通过parent去进行认证
if (result == null && this.parent != null) {
try {
//通过parent去调用authenticate()方法进行校验
parentResult = this.parent.authenticate(authentication);
//返回结果赋值给 result
result = parentResult;
}
catch (ProviderNotFoundException ex) {
}
catch (AuthenticationException ex) {
parentException = ex;
lastException = ex;
}
}
//判断认证返回结果,如果返回结果不为空,
if (result != null) {
if (this.eraseCredentialsAfterAuthentication && (result instanceof CredentialsContainer)) {
((CredentialsContainer) result).eraseCredentials();
}
if (parentResult == null) {
this.eventPublisher.publishAuthenticationSuccess(result);
}
//返回认证结果,Authentication
return result;
}
//认证错误并且没有抛出异常时候,那么这里抛出一个新的异常。
if (lastException == null) {
lastException = new ProviderNotFoundException(this.messages.getMessage("ProviderManager.providerNotFound",
new Object[] { toTest.getName() }, "No AuthenticationProvider found for {0}"));
}
if (parentException == null) {
prepareException(lastException, authentication);
}
throw lastException;
}
} 四、分析AbstractLdapAuthenticationProvider类
因为我们使用的Security的Ldap登录认证,所以我们这里主要分析一下AbstractLdapAuthenticationProvider类:(主要分析我们登录认证相关联的部分代码)
部分源代码如下:
package org.springframework.security.ldap.authentication;
import java.util.Collection;
import org.apache.commons.logging.Log;
import org.apache.commons.logging.LogFactory;
import org.springframework.context.MessageSource;
import org.springframework.context.MessageSourceAware;
import org.springframework.context.support.MessageSourceAccessor;
import org.springframework.ldap.core.DirContextOperations;
import org.springframework.security.authentication.AuthenticationProvider;
import org.springframework.security.authentication.BadCredentialsException;
import org.springframework.security.authentication.UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken;
import org.springframework.security.core.Authentication;
import org.springframework.security.core.AuthenticationException;
import org.springframework.security.core.GrantedAuthority;
import org.springframework.security.core.SpringSecurityMessageSource;
import org.springframework.security.core.authority.mapping.GrantedAuthoritiesMapper;
import org.springframework.security.core.authority.mapping.NullAuthoritiesMapper;
import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UserDetails;
import org.springframework.security.ldap.userdetails.LdapUserDetailsMapper;
import org.springframework.security.ldap.userdetails.UserDetailsContextMapper;
import org.springframework.util.Assert;
import org.springframework.util.StringUtils;
/**
* AbstractLdapAuthenticationProvider 是由Security给我们提供的一个关于Ldap的登录认证器
* 认证器主要是用于用户登录认证
*/
public abstract class AbstractLdapAuthenticationProvider implements AuthenticationProvider, MessageSourceAware {
protected final Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(getClass());
protected MessageSourceAccessor messages = SpringSecurityMessageSource.getAccessor();
private boolean useAuthenticationRequestCredentials = true;
private GrantedAuthoritiesMapper authoritiesMapper = new NullAuthoritiesMapper();
protected UserDetailsContextMapper userDetailsContextMapper = new LdapUserDetailsMapper();
@Override
public Authentication authenticate(Authentication authentication) throws AuthenticationException {
Assert.isInstanceOf(UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken.class, authentication,
() -> this.messages.getMessage("LdapAuthenticationProvider.onlySupports",
"Only UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken is supported"));
//强制转换将我们在Controller中登录认证的传入参数转回来
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken userToken = (UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken) authentication;
//获取登录用户账号
String username = userToken.getName();
//获取登录的密码
String password = (String) authentication.getCredentials();
//校验是否为空,或者空字符串
if (!StringUtils.hasLength(username)) {
throw new BadCredentialsException(
this.messages.getMessage("LdapAuthenticationProvider.emptyUsername", "Empty Username"));
}
//校验是否为空,或者空字符串
if (!StringUtils.hasLength(password)) {
throw new BadCredentialsException(
this.messages.getMessage("AbstractLdapAuthenticationProvider.emptyPassword", "Empty Password"));
}
Assert.notNull(password, "Null password was supplied in authentication token");
//登录认证,核心操作由LdapAuthenticationProvider去重写完成
DirContextOperations userData = doAuthentication(userToken);
//获取用户的权限信息并且封装成UserDetails
UserDetails user = this.userDetailsContextMapper.mapUserFromContext(userData, authentication.getName(),
loadUserAuthorities(userData, authentication.getName(), (String) authentication.getCredentials()));
//将Authentication和UserDetails封装成返回结果,返回给登录成功
return createSuccessfulAuthentication(userToken, user);
}
/**
* 这里提供一个抽象方法,由LdapAuthenticationProvider类去重写doAuthentication()方法来完成登录认证。
*/
protected abstract DirContextOperations doAuthentication(UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken auth);
/**
* 这里提供一个抽象方法,由LdapAuthenticationProvider类去重写loadUserAuthorities(),来获取用户的权限信息
*/
protected abstract Collection loadUserAuthorities(DirContextOperations userData,
String username, String password);
/**
* 在登录认证成功后,构建一个 Authentication 作为登录成功的返回值
*/
protected Authentication createSuccessfulAuthentication(UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken authentication,
UserDetails user) {
Object password = this.useAuthenticationRequestCredentials ? authentication.getCredentials()
: user.getPassword();
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken result = UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken.authenticated(user, password,
this.authoritiesMapper.mapAuthorities(user.getAuthorities()));
result.setDetails(authentication.getDetails());
this.logger.debug("Authenticated user");
return result;
}
/**
* 这里可以呼应到上面的ProviderManager,在ProviderManager中我们循环AuthenticationProvider集合时候就是通过每一个AuthenticationProvider的supports()方法
* 来判断我们登录认证在Controller时候传入的Authentication是否能够和AuthenticationProvider中的对应,如果类型相同那么就可以判断去使用当前的Provider去完成登录认证。
*/
@Override
public boolean supports(Class authentication) {
return UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken.class.isAssignableFrom(authentication);
}
}五、分析LdapAuthenticationProvider类
LdapAuthenticationProvider主要就是一个承上启下功能,主要做一下两部分内容:
1.主要通过LdapAuthenticator接口的authenticate()方法去完成认证功能,这个接口会被Security自己的AbstractLdapAuthenticator抽象类实现,同样AbstractLdapAuthenticator也被BindAuthenticator类继承,这样子类BindAuthenticator去实现authenticate()方法。
2.为AbstractLdapAuthenticationProvider 类的loadUserAuthorities()方法,提供向下的一个实现功能,这里会通过LdapAuthoritiesPopulator接口的getGrantedAuthorities()方法来获取用户的权限信息,这样我们就能通过实现LdapAuthoritiesPopulator接口来完成用户的权限封装。
LdapAuthenticationProvider类的部分源码如下:
package org.springframework.security.ldap.authentication;
import java.util.Collection;
import org.springframework.ldap.NamingException;
import org.springframework.ldap.core.DirContextOperations;
import org.springframework.security.authentication.BadCredentialsException;
import org.springframework.security.authentication.InternalAuthenticationServiceException;
import org.springframework.security.authentication.LockedException;
import org.springframework.security.authentication.UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken;
import org.springframework.security.core.GrantedAuthority;
import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UsernameNotFoundException;
import org.springframework.security.ldap.ppolicy.PasswordPolicyException;
import org.springframework.security.ldap.userdetails.DefaultLdapAuthoritiesPopulator;
import org.springframework.security.ldap.userdetails.LdapAuthoritiesPopulator;
import org.springframework.util.Assert;
public class LdapAuthenticationProvider extends AbstractLdapAuthenticationProvider {
// LdapAuthenticator 是一个接口类,会被AbstractLdapAuthenticator抽象类实现,但是authenticate()方法会由AbstractLdapAuthenticator类的子类实现
private LdapAuthenticator authenticator;
// LdapAuthoritiesPopulator 接口,这个接口我们可以选择自己实现,这样可以完成用户的权限的查询
private LdapAuthoritiesPopulator authoritiesPopulator;
private boolean hideUserNotFoundExceptions = true;
private LdapAuthenticator getAuthenticator() {
return this.authenticator;
}
protected LdapAuthoritiesPopulator getAuthoritiesPopulator() {
return this.authoritiesPopulator;
}
/**
* 登录认证,通过 LdapAuthenticator 接口的实现BindAuthenticator类,由它的authenticate()来实现用户的登录认证。
*/
@Override
protected DirContextOperations doAuthentication(UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken authentication) {
try {
//获取BindAuthenticator类,调用它的authenticate()方法进行登录认证
return getAuthenticator().authenticate(authentication);
}
catch (PasswordPolicyException ex) {
throw new LockedException(
this.messages.getMessage(ex.getStatus().getErrorCode(), ex.getStatus().getDefaultMessage()));
}
catch (UsernameNotFoundException ex) {
if (this.hideUserNotFoundExceptions) {
throw new BadCredentialsException(
this.messages.getMessage("LdapAuthenticationProvider.badCredentials", "Bad credentials"));
}
throw ex;
}
catch (NamingException ex) {
throw new InternalAuthenticationServiceException(ex.getMessage(), ex);
}
}
/**
* 这里是为AbstractLdapAuthenticationProvider类调用用户权限查询进行实现
* 这里通过获取一个LdapAuthoritiesPopulator接口的实现类的getGrantedAuthorities()查询用户的角色权限集合
*/
@Override
protected Collection loadUserAuthorities(DirContextOperations userData, String username,
String password) {
return getAuthoritiesPopulator().getGrantedAuthorities(userData, username);
}
}六、分析AbstractLdapAuthenticator类
AbstractLdapAuthenticator类主要是封装Ldap的连接数据以及在SecurityLdapConfig注入的查询用户的条件信息。
源代码如下:
package org.springframework.security.ldap.authentication;
import java.text.MessageFormat;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.List;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean;
import org.springframework.context.MessageSource;
import org.springframework.context.MessageSourceAware;
import org.springframework.context.support.MessageSourceAccessor;
import org.springframework.ldap.core.ContextSource;
import org.springframework.security.core.SpringSecurityMessageSource;
import org.springframework.security.ldap.search.LdapUserSearch;
import org.springframework.util.Assert;
/**
* AbstractLdapAuthenticator 类虽然实现了LdapAuthenticator接口但是并未实现接口的authenticate()方法去做登录认证,此方法由 AbstractLdapAuthenticator 子类去实现。
*/
public abstract class AbstractLdapAuthenticator implements LdapAuthenticator, InitializingBean, MessageSourceAware {
//Ldap的连接实例
private final ContextSource contextSource;
/**
* 当通过DN不能搜索到用户时候可以通过userSearch去搜索用户
*/
private LdapUserSearch userSearch;
protected MessageSourceAccessor messages = SpringSecurityMessageSource.getAccessor();
/**
* 目录列表信息
*/
private String[] userAttributes = null;
/**
* 通过userDnPatterns 查询用户时候设置对应的userDN路径值,默认格式一般为uid={0}, ou=people
*/
private MessageFormat[] userDnFormat = null;
/**
* 初始化时候给Ldap的连接实例赋值
*/
public AbstractLdapAuthenticator(ContextSource contextSource) {
Assert.notNull(contextSource, "contextSource must not be null.");
this.contextSource = contextSource;
}
//获取Ldap连接实例
protected ContextSource getContextSource() {
return this.contextSource;
}
//获取所有的目录列表
public String[] getUserAttributes() {
return this.userAttributes;
}
/**
* 把用户名username拼接到用户ND列表中去替换到原来{0},原来的Nd=uid{0},ou=people,现在讲{0}替换成username,替换结果为 uid=username,ou=people
*/
protected List getUserDns(String username) {
if (this.userDnFormat == null) {
return Collections.emptyList();
}
List userDns = new ArrayList<>(this.userDnFormat.length);
String[] args = new String[] { LdapEncoder.nameEncode(username) };
synchronized (this.userDnFormat) {
for (MessageFormat formatter : this.userDnFormat) {
userDns.add(formatter.format(args));
}
}
return userDns;
}
/**
* 获取检索用户的条件
*/
protected LdapUserSearch getUserSearch() {
return this.userSearch;
}
/**
* 设置将从目录检索的用户属性。
*/
public void setUserAttributes(String[] userAttributes) {
Assert.notNull(userAttributes, "The userAttributes property cannot be set to null");
this.userAttributes = userAttributes;
}
/**
* 设置用于为用户提供DN的模式。模式应该是相对于根DN的名称。模式参数{0}将包含用户名。例如“cn={0},ou=people”。
*/
public void setUserDnPatterns(String[] dnPattern) {
Assert.notNull(dnPattern, "The array of DN patterns cannot be set to null");
// this.userDnPattern = dnPattern;
this.userDnFormat = new MessageFormat[dnPattern.length];
for (int i = 0; i < dnPattern.length; i++) {
this.userDnFormat[i] = new MessageFormat(dnPattern[i]);
}
}
/**
* 赋值根据userSearch搜用户的条件赋值
*/
public void setUserSearch(LdapUserSearch userSearch) {
Assert.notNull(userSearch, "The userSearch cannot be set to null");
this.userSearch = userSearch;
}
} 七、分析BindAuthenticator类
BindAuthentication类主要做如下功能:
1.通过父类AbstractLdapAuthenticator 获取用户的ND列表路径,如果不存在就通过父类在获取userSearch用户列表查询路径。
2.通过父类AbstractLdapAuthenticator 获取Ldap的连接contextSource。
3.实现了LdapAuthenticator接口的authenticate()方法,完成用户登录认证。
总结:无论是通过DN模式还是通过UserSearch的模式完成登录认证实际上使用的是统一中认证方式,只是在我们配置SecurityLdap的认证器时候可以选择不同方式。
源码分析如下:
package org.springframework.security.ldap.authentication;
import javax.naming.directory.Attributes;
import javax.naming.directory.DirContext;
import org.apache.commons.logging.Log;
import org.apache.commons.logging.LogFactory;
import org.springframework.core.log.LogMessage;
import org.springframework.ldap.NamingException;
import org.springframework.ldap.core.DirContextAdapter;
import org.springframework.ldap.core.DirContextOperations;
import org.springframework.ldap.core.DistinguishedName;
import org.springframework.ldap.core.support.BaseLdapPathContextSource;
import org.springframework.ldap.support.LdapUtils;
import org.springframework.security.authentication.BadCredentialsException;
import org.springframework.security.authentication.UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken;
import org.springframework.security.core.Authentication;
import org.springframework.security.ldap.ppolicy.PasswordPolicyControl;
import org.springframework.security.ldap.ppolicy.PasswordPolicyControlExtractor;
import org.springframework.util.Assert;
import org.springframework.util.StringUtils;
/**
* 作为用户绑定的身份验证器
*/
public class BindAuthenticator extends AbstractLdapAuthenticator {
private static final Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(BindAuthenticator.class);
/**
* 用BaseLdapPathContextSource初始化Ldap连接实例
*/
public BindAuthenticator(BaseLdapPathContextSource contextSource) {
super(contextSource);
}
/**
* 登录认证逻辑
* 1.先通过父类的getUserDns(username)获取用户ND模式,如果有返回值那么就采用DN模式登录认证
* 2.当DN模式不生效获取返回结果为空时候采用 userSearch的方式查询用户登录认证
* 总结两种模式实际是一样的登录认证,一种是直接配置ND路径,一种是路径和Username分离进行配置
*/
@Override
public DirContextOperations authenticate(Authentication authentication) {
DirContextOperations user = null;
Assert.isInstanceOf(UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken.class, authentication,
"Can only process UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken objects");
String username = authentication.getName();
String password = (String) authentication.getCredentials();
if (!StringUtils.hasLength(password)) {
logger.debug(LogMessage.format("Failed to authenticate since no credentials provided"));
throw new BadCredentialsException(
this.messages.getMessage("BindAuthenticator.emptyPassword", "Empty Password"));
}
// 如果配置了DN模式,通过DN模式进行用户登录认证
for (String dn : getUserDns(username)) {
//通过DN模式登录认证
user = bindWithDn(dn, username, password);
if (user != null) {
break;
}
}
//当DN模式不生效或者查询不到用户时候才会采用userSearch方法登录认证
if (user == null) {
logger.debug(LogMessage.of(() -> "Failed to bind with any user DNs " + getUserDns(username)));
}
//当DN模式查询不生效,并且配置了userSearche的模式进行登录认证
if (user == null && getUserSearch() != null) {
logger.trace("Searching for user using " + getUserSearch());
//通过父类获取UserSearch拼接获取用户查询条件,实际等同DN模式下的路径
DirContextOperations userFromSearch = getUserSearch().searchForUser(username);
//同理还是使用DN模式完成用户登录认证
user = bindWithDn(userFromSearch.getDn().toString(), username, password, userFromSearch.getAttributes());
if (user == null) {
logger.debug("Failed to find user using " + getUserSearch());
}
}
if (user == null) {
throw new BadCredentialsException(
this.messages.getMessage("BindAuthenticator.badCredentials", "Bad credentials"));
}
return user;
}
/**
* DN模式登录认证
*/
private DirContextOperations bindWithDn(String userDnStr, String username, String password) {
return bindWithDn(userDnStr, username, password, null);
}
/**
* 通过DN模式完成用户登录认证
*/
private DirContextOperations bindWithDn(String userDnStr, String username, String password, Attributes attrs) {
//获取Ldap连接,这里是项目初始化的Ldap连接,主要获取他的Base路径
BaseLdapPathContextSource ctxSource = (BaseLdapPathContextSource) getContextSource();
//通过用户DN模式信息创建连接器
DistinguishedName userDn = new DistinguishedName(userDnStr);
//通过连接器创建连接器
DistinguishedName fullDn = new DistinguishedName(userDn);
//将Ldap连接的base路径添加到连接其中
fullDn.prepend(ctxSource.getBaseLdapPath());
logger.trace(LogMessage.format("Attempting to bind as %s", fullDn));
DirContext ctx = null;
try {
//通过连接器和用户名进行登录认证,成功返回当前用户的Ldap连接
ctx = getContextSource().getContext(fullDn.toString(), password);
// 检查密码策略控制
PasswordPolicyControl ppolicy = PasswordPolicyControlExtractor.extractControl(ctx);
if (attrs == null || attrs.size() == 0) {
//获取用户信息列表
attrs = ctx.getAttributes(userDn, getUserAttributes());
}
//封装用户信息,返回登录认证结果
DirContextAdapter result = new DirContextAdapter(attrs, userDn, ctxSource.getBaseLdapPath());
if (ppolicy != null) {
result.setAttributeValue(ppolicy.getID(), ppolicy);
}
logger.debug(LogMessage.format("Bound %s", fullDn));
//返回结果
return result;
}
catch (NamingException ex) {
// This will be thrown if an invalid user name is used and the method may
// be called multiple times to try different names, so we trap the exception
// unless a subclass wishes to implement more specialized behaviour.
if ((ex instanceof org.springframework.ldap.AuthenticationException)
|| (ex instanceof org.springframework.ldap.OperationNotSupportedException)) {
handleBindException(userDnStr, username, ex);
}
else {
throw ex;
}
}
catch (javax.naming.NamingException ex) {
throw LdapUtils.convertLdapException(ex);
}
finally {
LdapUtils.closeContext(ctx);
}
return null;
}
/**
* Allows subclasses to inspect the exception thrown by an attempt to bind with a
* particular DN. The default implementation just reports the failure to the debug
* logger.
*/
protected void handleBindException(String userDn, String username, Throwable cause) {
logger.trace(LogMessage.format("Failed to bind as %s", userDn), cause);
}
}