Spring Boot 整合 Redis,使用 RedisTemplate 客户端
文章目录
- 一、SpringBoot 整合 Redis
-
- 1.1 整合 Redis 步骤
-
- 1.1.1 添加依赖
- 1.1.2 yml 配置文件
- 1.1.3 Config 配置文件
- 1.1.4 使用示例
- 1.2 RedisTemplate 概述
-
- 1.2.1 RedisTemplate 简介
- 1.2.2 RedisTemplate 功能
- 二、RedisTemplate API
-
- 2.1 RedisTemplate 公共 API
- 2.2 String 类型 API
-
- 2.1.1 添加缓存
- 2.1.2 删除缓存
- 2.1.3 修改缓存
- 2.1.4 其他操作
- 2.3 Hash 类型 API
-
- 2.3.1 添加缓存
- 2.3.2 删除缓存
- 2.3.3 获取缓存
- 2.3.4 其他操作
- 2.4 List 类型 API
-
- 2.4.1 添加缓存
- 2.4.2 删除缓存
- 2.4.3 获取缓存
- 2.5 Set 类型 API
-
- 2.5.1 添加缓存
- 2.5.2 删除缓存
- 2.5.3 获取缓存
- 2.5.4 其他操作
- 2.6 ZSet 类型 API
-
- 2.6.1 添加缓存
- 2.6.2 删除缓存
- 2.6.3 获取缓存
- 三、RedisUtil 工具类封装
一、SpringBoot 整合 Redis
1.1 整合 Redis 步骤
1.1.1 添加依赖
redis 的依赖:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId>
</dependency>
1.1.2 yml 配置文件
server:
port: 8070
spring:
# redis
redis:
host: localhost
port: 6379
password:
database: 0
1.1.3 Config 配置文件
@Configuration
public class RedisConfig {
@Bean
public RedisTemplate<String, Object> redisTemplate(RedisConnectionFactory factory) {
RedisTemplate<String, Object> redisTemplate = new RedisTemplate<>();
redisTemplate.setConnectionFactory(factory);
redisTemplate.setKeySerializer(new StringRedisSerializer());
//使用Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer来序列化和反序列化redis的value值
redisTemplate.setValueSerializer(new Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer<>(Object.class));
redisTemplate.afterPropertiesSet();
return redisTemplate;
}
}
1.1.4 使用示例
注入 RedisTemplate,即可操作 Redis,简单示例如下:
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest
public class RedisUtilTest {
@Autowired
private RedisTemplate<String, Object> redisTemplate;
@Test
public void test() {
ValueOperations<String, Object> operations = redisTemplate.opsForValue();
operations.set("key1","value1");
operations.set("key1","value1");
operations.set("key1","value1");
Object object = operations.get("key1");
System.out.println(object);
}
1.2 RedisTemplate 概述
1.2.1 RedisTemplate 简介
RedisTemplate 是 Spring Data Redis 项目的一部分,旨在简化在Java应用程序中使用 Redis 的过程。它提供了一组简单的方法,可以在 Redis 数据库中存储和获取各种类型的数据,包括字符串、散列、列表、集合、有序集合等。
此外,RedisTemplate 还提供了许多其他功能,如事务支持、发布/订阅、消息队列等。
以下是 RedisTemplate 的一些主要特点:
- 简化 Redis 访问:通过提供简单的方法和模板,RedisTemplate 简化了对 Redis 数据库的访问。它抽象了 Redis 底层的一些细节,使得开发者可以专注于业务逻辑。
- 类型安全:RedisTemplate 支持类型安全的操作,这意味着编译器可以检查操作的类型是否正确,从而减少了运行时错误。
- 事务支持:RedisTemplate 提供了事务支持,确保在执行多个操作时,要么所有操作都成功,要么回滚。
- 发布/订阅和消息队列:RedisTemplate 提供了发布/订阅和消息队列的功能,使得应用程序可以异步接收和处理消息。
- 集成测试:RedisTemplate 提供了一些用于集成测试的工具和方法,使得开发者可以方便地对 Redis 数据库进行单元测试和集成测试。
RedisTemplate 部分源码:
public class RedisTemplate<K, V> extends RedisAccessor implements RedisOperations<K, V>, BeanClassLoaderAware {
private boolean enableTransactionSupport = false;
private boolean exposeConnection = false;
private boolean initialized = false;
private boolean enableDefaultSerializer = true;
private @Nullable RedisSerializer<?> defaultSerializer;
private @Nullable ClassLoader classLoader;
// 序列化属性
@SuppressWarnings("rawtypes") private @Nullable RedisSerializer keySerializer = null;
@SuppressWarnings("rawtypes") private @Nullable RedisSerializer valueSerializer = null;
@SuppressWarnings("rawtypes") private @Nullable RedisSerializer hashKeySerializer = null;
@SuppressWarnings("rawtypes") private @Nullable RedisSerializer hashValueSerializer = null;
private RedisSerializer<String> stringSerializer = RedisSerializer.string();
private @Nullable ScriptExecutor<K> scriptExecutor;
// 相关操作属性
private final ValueOperations<K, V> valueOps = new DefaultValueOperations<>(this);
private final ListOperations<K, V> listOps = new DefaultListOperations<>(this);
private final SetOperations<K, V> setOps = new DefaultSetOperations<>(this);
private final StreamOperations<K, ?, ?> streamOps = new DefaultStreamOperations<>(this, new ObjectHashMapper());
private final ZSetOperations<K, V> zSetOps = new DefaultZSetOperations<>(this);
private final GeoOperations<K, V> geoOps = new DefaultGeoOperations<>(this);
private final HyperLogLogOperations<K, V> hllOps = new DefaultHyperLogLogOperations<>(this);
private final ClusterOperations<K, V> clusterOps = new DefaultClusterOperations<>(this);
// 构造函数
public RedisTemplate() {}
}
1.2.2 RedisTemplate 功能
RedisTemplate 支持 Redis 的五种基本数据类型,并对其进行了封装,RedisTemplate 对应的封装如下:
String 类型:
ValueOperations<String, Object> valueOperations = redisTemplate.opsForValue();
Hash 类型:
HashOperations<String, Object, Object> hashOperations = redisTemplate.opsForHash();
List 类型:
ListOperations<String, Object> listOperations = redisTemplate.opsForList();
Set 类型:
SetOperations<String, Object> setOperations = redisTemplate.opsForSet();
ZSet 类型:
ZSetOperations<String, Object> zSetOperations = redisTemplate.opsForZSet();
另外,RedisTemplate 还提供了以下封装,用于 Redis 的额外操作:
redisTemplate.opsForCluster():用于操作 Redis Cluster。Redis Cluster 是一种分布式 Redis 解决方案,它允许将多个 Redis 节点组织成一个集群,并提供数据分片和故障转移等功能。
ClusterOperations<String, Object> clusterOperations = redisTemplate.opsForCluster();
redisTemplate.opsForGeo():Geo数据类型允许存储地理位置相关的数据,并执行基于地理位置的查询和计算。
GeoOperations<String, Object> geoOperations = redisTemplate.opsForGeo();
redisTemplate.opsForHyperLogLog():HyperLogLog数据类型是一种用于估算集合中元素数量的数据结构。它通过使用一种特殊的算法,可以在非常小的内存消耗下估算出集合中元素的数量。
HyperLogLogOperations<String, Object> hyperLogLogOperations = redisTemplate.opsForHyperLogLog();
redisTemplate.opsForStream():Stream数据类型是一种持久化的消息队列,它可以保存长期的消息数据,并且支持消费者组和消息的消费确认等功能。
StreamOperations<String, Object, Object> streamOperations = redisTemplate.opsForStream();
二、RedisTemplate API
2.1 RedisTemplate 公共 API
Boolean delete(K key):根据缓存的键 key 删除整个缓存。
- 参数:
- key:缓存的键。
- 返回值:返回 Boolean 类型,删除成功为 true,删除失败为 false。
示例:
String key = "key1";
Boolean result = redisTemplate.delete(key);
Long delete(Collection::根据缓存的键集合 keys 批量删除整个缓存。
- 参数:
- keys:缓存的键集合。
- 返回值:返回删除成功的数量,Long 类型。
示例:
List<String> keys = Arrays.asList("key1", "key2", "key3");
Long result = redisTemplate.delete(keys);
Boolean hasKey(K key):根据缓存的键 key 判断缓存是否存在。
- 参数:
- key:缓存的键。
- 返回值:返回 Boolean 类型,存在为 true,不存在为 false。
示例:
String key = "key1";
Boolean result = redisTemplate.hasKey(key);
Set:根据匹配规则,匹配出满足条件的所有缓存键
- 参数:
- pattern:匹配规则。
- 返回值:返回 Set 类型,满足匹配规则的缓存键集合。
示例:
String pattern = "key*";
Set<String> result = redisTemplate.keys(pattern);
System.out.println(result);
输出结果:
[key1, key2, key3]
void rename(K oldKey, K newKey):重命名缓存键 oldKey 为 newKey。
- 参数:
- oldKey:原缓存键名称。
- newKey:新缓存键名称。
示例:
String oldKey= "key1";
String newKey= "key-new";
redisTemplate.rename(oldKey, newKey);
2.2 String 类型 API
2.1.1 添加缓存
void set(K key, V value):添加缓存。
- 参数:
- key:键
- value:值
示例:
ValueOperations<String, Object> valueOperations = redisTemplate.opsForValue();
valueOperations.set("string-key-1","string-value-1");
valueOperations.set("string-key-2","string-value-2");
valueOperations.set("string-key-3","string-value-3");
System.out.println("string-key-1: "valueOperations.get("string-key-1"));
System.out.println("string-key-2: "valueOperations.get("string-key-2"));
System.out.println("string-key-3: "valueOperations.get("string-key-3"));
输出结果:
string-key-1: string-value-1
string-key-2: string-value-2
string-key-3: string-value-3
void set(K key, V value, long timeout, TimeUnit unit):添加缓存,并设定过期时间。
- 参数:
- key:键
- value:值
- timeout:过期时间
- unit:时间单位
示例:
ValueOperations<String, Object> valueOperations = redisTemplate.opsForValue();
valueOperations.set("string-key-1", "string-value-1", 2000, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
valueOperations.set("string-key-2", "string-value-2", 10, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
valueOperations.set("string-key-3", "string-value-3", 7, TimeUnit.DAYS);
default void set(K key, V value, Duration timeout):添加缓存,并设定过期时间。
- 参数:
- key:键
- value:值
- timeout:超时时间,自带有单位,部分方法如下:
Duration.ofDays(long days)Duration.ofHours(long hours)Duration.ofMinutes(long minutes)Duration.ofSeconds(long seconds)Duration.ofSeconds(long seconds, long nanoAdjustment)Duration.ofMillis(long millis)Duration.ofNanos(long nanos)Duration.of(long amount, TemporalUnit unit)
示例:
ValueOperations<String, Object> valueOperations = redisTemplate.opsForValue();
valueOperations.set("string-key-1", "string-value-1", Duration.ofMillis(2000));
valueOperations.set("string-key-2", "string-value-2", Duration.ofSeconds(5));
valueOperations.set("string-key-3", "string-value-3", Duration.ofDays(7));
Boolean setIfAbsent(K key, V value):添加缓存,key 不存在则添加,否则添加失败。
- 参数:
- key:键
- value:值
- 返回值:返回 Boolean 类型,key 不存在时添加成功返回true,key 存在时添加失败返回false。
示例:
ValueOperations<String, Object> valueOperations = redisTemplate.opsForValue();
Boolean result1 = valueOperations.setIfAbsent("string-key-1", "string-value-1");
Boolean result2 = valueOperations.setIfAbsent("string-key-4", "string-value-4");
System.out.println(result1);
System.out.println(result2);
输出结果:
false
true
Boolean setIfAbsent(K key, V value, long timeout, TimeUnit unit):添加缓存并设定过期时间,key 不存在则添加,否则添加失败。
- 参数:
- key:键
- value:值
- timeout:过期时间
- unit:时间单位
- 返回值:返回 Boolean 类型,key 不存在时添加成功返回true,key 存在时添加失败返回false。
示例:
ValueOperations<String, Object> valueOperations = redisTemplate.opsForValue();
Boolean result1 = valueOperations.setIfAbsent("string-key-1", "string-value-1", 2000, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
Boolean result2 = valueOperations.setIfAbsent("string-key-4", "string-value-4", 2000, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
default Boolean setIfAbsent(K key, V value, Duration timeout):添加缓存并设定过期时间,key 不存在则添加,否则添加失败。
- 参数:
- key:键
- value:值
- timeout:超时时间,自带有单位
- 返回值:返回 Boolean 类型,key 不存在时添加成功返回true,key 存在时添加失败返回false。
示例:
ValueOperations<String, Object> valueOperations = redisTemplate.opsForValue();
Boolean result1 = valueOperations.setIfAbsent("string-key-1", "string-value-1", Duration.ofMillis(2000));
Boolean result2 = valueOperations.setIfAbsent("string-key-4", "string-value-4", Duration.ofMillis(2000));
void multiSet(Map map):批量添加缓存,有重复的key直接覆盖原来的缓存内容
- 参数:
- map:要添加的缓存内容键值对集合
示例:
Map<String,Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("string-key-1", "string-value-1");
map.put("string-key-2", "string-value-2");
map.put("string-key-3", "string-value-3");
ValueOperations<String, Object> valueOperations = redisTemplate.opsForValue();
valueOperations.multiSet(map);
Boolean multiSetIfAbsent(Map map):批量添加缓存,当 key 不存在的时候才添加,只要有一个 key 已存在则添加失败。
- 参数:
- map:要添加的缓存内容键值对集合
- 返回值:返回 Boolean 类型,添加成功返回 true,失败则为 false
示例:
Map<String,Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("string-key-1", "string-value-1");
map.put("string-key-2", "string-value-2");
map.put("string-key-3", "string-value-3");
ValueOperations<String, Object> valueOperations = redisTemplate.opsForValue();
Boolean result = valueOperations.multiSetIfAbsent(map);
V getAndSet(K key, V value):给指定 key 的缓存设置新值,并返回原来的旧值。如果 key 不存在,则直接添加这个缓存,但返回值为 null
- 参数:
- key:指定缓存键
- value:新值
- 返回值:返回原来的旧值。
示例:
ValueOperations<String, Object> valueOperations = redisTemplate.opsForValue();
valueOperations.set("s-key", "s-value");
System.out.println("s-key : " + valueOperations.get("s-key"));
Object result = valueOperations.getAndSet("s-key", "s-value-new");
System.out.println("result = " + result);
System.out.println("s-key : " + valueOperations.get("s-key"));
// 一个不存在的key
Object result1 = valueOperations.getAndSet("s-key1", "s-value-new1");
System.out.println("result1 = " + result1);
System.out.println("s-key1 : " + valueOperations.get("s-key1"));
输出结果:
s-key : s-value
result = s-value
s-key : s-value-new
result = null
s-key1 : s-value-new1
2.1.2 删除缓存
V get(Object key):根据键 key 获取缓存值,key 不存在则返回 null
- 参数:
- key:缓存键
- 返回值:返回对应的值,key 不存在则返回 null
示例:
ValueOperations<String, Object> valueOperations = redisTemplate.opsForValue();
valueOperations.set("s-key", "s-value-new");
Object result = valueOperations.get("s-key");
System.out.println("result = " + result);
Object result1 = valueOperations.get("s-key-s");
System.out.println("result1 = " + result1);
输出结果:
result = s-value-new
result1 = null
String get(K key, long start, long end):根据键 key 获取缓存值,并根据指定的开始和结束位置截取结果
- 参数:
- key:缓存键
- start:开始位置
- end:结束位置
- 返回值:返回结果,key 不存在则返回 null
示例:
ValueOperations<String, Object> valueOperations = redisTemplate.opsForValue();
valueOperations.set("s-key", "s-value-new");
Object result1 = valueOperations.get("s-key");
Object result2 = valueOperations.get("s-key", 0, -1);
Object result3 = valueOperations.get("s-key", 2, 4);
System.out.println("result1 = " + result1);
System.out.println("result2 = " + result2);
System.out.println("result3 = " + result3);
输出结果:
result1 = s-value-new
result2 = "s-value-new"
result3 = -va
List:根据键集合 keys 批量获取缓存,键不存在的对应元素返回 null
- 参数:
- keys:缓存键集合
- 返回值:缓存值集合
示例:
ValueOperations<String, Object> valueOperations = redisTemplate.opsForValue();
valueOperations.set("s-key1", "s-value-new1");
valueOperations.set("s-key2", "s-value-new2");
valueOperations.set("s-key3", "s-value-new3");
List<Object> result = valueOperations.multiGet(Arrays.asList("s-key1", "s-key2", "s-key3", "s-key4"));
System.out.println("result = " + result);
输出结果:
result = [s-value-new1, s-value-new2, s-value-new3, null]
2.1.3 修改缓存
void set(K key, V value, long offset):缓存内容替换,用值 value 替换缓存键 key 对应的缓存,指定替换的开始位置 offset。
- 参数:
- key:缓存键
- value:替换值
- offset:偏移位置,即开始位置
示例:
ValueOperations<String, Object> valueOperations = redisTemplate.opsForValue();
valueOperations.set("s-key", "aaabbbcccddd");
Object oldResult = valueOperations.get("s-key");
valueOperations.set("s-key","6666",3);
Object newResult = valueOperations.get("s-key");
System.out.println("oldResult = " + oldResult);
System.out.println("newResult = " + newResult);
输出结果:
oldResult = aaabbbcccddd
newResult = aaa6666ccddd
Integer append(K key, String value):在缓存键 key 对应的缓存内容后面追加值 value,并返回追加值后的缓存值长度。如果 key 不存在,则直接添加这个缓存,返回这个缓存的长度
- 参数:
- key:缓存键
- value:追加值
- 返回值:Integer 类型,返回操作成功后的值的长度
示例:
ValueOperations<String, Object> valueOperations = redisTemplate.opsForValue();
valueOperations.set("s-key", "111222");
Integer result = valueOperations.append("s-key", "aaaa");
System.out.println("result = " + result);
System.out.println("s-key = " + valueOperations.get("s-key-s"));
Integer result1 = valueOperations.append("s-key-s", "aaaa");
System.out.println("result1 = " + result1);
System.out.println("s-key-s = " + valueOperations.get("s-key-s"));
输出结果:
result = 10
s-key = 111222aaaa
result1 = 4
s-key-s = aaaa
2.1.4 其他操作
Boolean setBit(K key, long offset, boolean value):设置缓存键 key 对应缓存的指定位置的 bit 值,用于设置 Redis 中位图(bitmaps)的指定偏移量的值。位图是由位(0或1)组成的数据结构,可以用于表示某个事件的状态或者进行位运算。
- 参数:
- key:缓存键
- offset:要设置的位置。
- value:要设置的值,0 或 1
- 返回值:返回操作结果
示例:
ValueOperations<String, Object> valueOperations = redisTemplate.opsForValue();
Boolean result = valueOperations.setBit("bit-key", 2, true);
Boolean getBit(K key, long offset):获取指定位置的 bit 值
- 参数:
- key:缓存键
- offset:要设置的位置。
- 返回值:返回结果
示例:
ValueOperations<String, Object> valueOperations = redisTemplate.opsForValue();
Boolean result = valueOperations.getBit("bit-key", 2);
Long increment(K key):将缓存键 key 对应的缓存的值增加1,缓存的内容必须为 Integer 类型,否则会出现错误 ERR value is not an integer or out of range。
- 参数:
- key:缓存键
- 返回值:返回增加后的结果
示例:
ValueOperations<String, Integer> valueOperations = redisTemplate.opsForValue();
valueOperations.set("s-key", 1);
Long result = valueOperations.increment("s-key");
System.out.println("result = " + result);
System.out.println("s-key = " + valueOperations.get("s-key"));
Long increment(K key, long delta):将缓存键 key 对应的缓存的值增加 delta,缓存的内容必须为 Integer 类型,否则会出现错误 ERR value is not an integer or out of range。
- 参数:
- key:缓存键
- delta:增加的值,long 类型
- 返回值:返回增加后的结果
示例:
ValueOperations<String, Integer> valueOperations = redisTemplate.opsForValue();
valueOperations.set("s-key", 1);
Long result = valueOperations.increment("s-key", 2);
System.out.println("result = " + result);
System.out.println("s-key = " + valueOperations.get("s-key"));
Double increment(K key, double delta):将缓存键 key 对应的缓存的值增加 delta,缓存的内容必须为 Integer 类型,否则会出现错误 ERR value is not an integer or out of range。
- 参数:
- key:缓存键
- delta:增加的值,double 类型
- 返回值:返回增加后的结果
示例:
ValueOperations<String, Integer> valueOperations = redisTemplate.opsForValue();
valueOperations.set("s-key", 1);
Doubleresult = valueOperations.increment("s-key", 3.5);
System.out.println("result = " + result);
System.out.println("s-key = " + valueOperations.get("s-key"));
Long decrement(K key):将缓存键 key 对应的缓存的值减少1,缓存的内容必须为 Integer 类型,否则会出现错误 ERR value is not an integer or out of range。
- 参数:
- key:缓存键
- 返回值:返回减少后的结果
示例:
ValueOperations<String, Integer> valueOperations = redisTemplate.opsForValue();
valueOperations.set("s-key", 1);
Long result = valueOperations.decrement("s-key");
System.out.println("result = " + result);
System.out.println("s-key = " + valueOperations.get("s-key"));
Long decrement(K key, long delta):将缓存键 key 对应的缓存的值减少 delta,缓存的内容必须为 Integer 类型,否则会出现错误 ERR value is not an integer or out of range。
- 参数:
- key:缓存键
- delta:减少的值,long 类型
- 返回值:返回减少后的结果
示例:
ValueOperations<String, Integer> valueOperations = redisTemplate.opsForValue();
valueOperations.set("s-key", 1);
Long result = valueOperations.decrement("s-key", 2);
System.out.println("result = " + result);
System.out.println("s-key = " + valueOperations.get("s-key"));
Long size(K key):统计缓存键 key 对应缓存的值的大小。
- 参数:
- key:缓存键
- 返回值:返回统计结果
示例:
ValueOperations<String, Object> valueOperations = redisTemplate.opsForValue();
System.out.println(valueOperations.size("s-key"));
System.out.println(valueOperations.size("s-key1"));
System.out.println(valueOperations.size("s-key2"));
2.3 Hash 类型 API
2.3.1 添加缓存
void put(H key, HK hashKey, HV value):添加一个 hash 缓存,key 相同,后者会覆盖前者。
- 参数:
- key:缓存键
- hashKey:缓存 map 的 key
- value:缓存 map 的值
示例:
HashOperations<String, String, String> operations = redisTemplate.opsForHash();
operations.put("H-KEY", "KEY1", "VALUE1");
operations.put("H-KEY", "KEY1", "VALUE11");
operations.put("H-KEY", "KEY2", "VALUE2");
operations.put("H-KEY", "KEY3", "VALUE3");
void putAll(H key, Map m):批量添加 hash 缓存。
- 参数:
- key:缓存键
- m:缓存内容,map 形式
示例:
HashOperations<String, String, String> operations = redisTemplate.opsForHash();
Map<String, String> map = new HashMap<String, String>() {{
put("key-a", "value-a");
put("key-b", "value-b");
put("key-c", "value-c");
}};
operations.putAll("H-KEY1", map);
Boolean putIfAbsent(H key, HK hashKey, HV value):添加一个 hash 缓存,缓存的 hashkey 不存在则添加成功,否则添加失败,如果 key 不存在则直接作为新的 hash 缓存添加。
- 参数:
- key:
- 返回值:返回操作结果,成功返回 true,失败为 false
示例:
HashOperations<String, String, String> operations = redisTemplate.opsForHash();
Boolean result1 = operations.putIfAbsent("H-KEY", "KEY3", "VALUE33");
System.out.println(result1);
Boolean result2 = operations.putIfAbsent("H-KEY", "KEY4", "VALUE4");
System.out.println(result2);
Boolean result3 = operations.putIfAbsent("H-KEY-NEW", "KEY-NEW", "VALUE-NEW");
System.out.println(result3);
输出结果:
false
true
true
2.3.2 删除缓存
Long delete(H key, Object... hashKeys):根据缓存键 key 和缓存 map 的 hashKeys 批量删除缓存。
- 参数:
- key:缓存键
- hashKeys:缓存 map 的 hashKey
- 返回值:返回删除结果数量
示例:
HashOperations<String, String, String> operations = redisTemplate.opsForHash();
Long delete1 = operations.delete("H-KEY","KEY1");
System.out.println("delete1 = " + delete1);
Long delete2 = operations.delete("H-KEY","KEY1","KEY2","KEY3");
System.out.println("delete1 = " + delete2);
输出结果:
delete1 = 1
delete2 = 2
2.3.3 获取缓存
HV get(H key, Object hashKey):根据缓存 key 和 hashKey 获取一个缓存值。
- 参数:
- key:缓存键
- hashKey:缓存 map 的键
- 返回值:返回获取的缓存值
示例:
HashOperations<String, String, String> operations = redisTemplate.opsForHash();
String result = operations.get("H-KEY", "KEY1");
System.out.println("result = " + result);
String result1 = operations.get("H-KEY", "KEY99");
System.out.println("result = " + result1);
输出结果:
result = VALUE11
result = null
List:
- 参数:根据缓存 key 和 hashKey 批量获取缓存值。
- key:缓存键
- hashKeys:缓存 map 的键集合
- 返回值:返回缓存值集合
示例:
HashOperations<String, String, String> operations = redisTemplate.opsForHash();
List<String> result = operations.multiGet("H-KEY", Arrays.asList("KEY1", "KEY2", "KEY3"));
System.out.println("result = " + result);
List<String> result1 = operations.multiGet("H-KEY", Arrays.asList("KEY1", "KEY99", "KEY98"));
System.out.println("result = " + result1);
输出结果:
result = [VALUE11, VALUE2, VALUE3]
result = [VALUE11, null, null]
Set:获取缓存 key 对应缓存 map 的所有 hashKey
- 参数:
- key:缓存键
- 返回值:缓存 map 对应的所有 hashKey 集合
示例:
HashOperations<String, String, String> operations = redisTemplate.opsForHash();
Set<String> keys = operations.keys("H-KEY");
System.out.println("keys = " + keys);
输出结果:
keys = [KEY1, KEY2, KEY3, KEY4]
List:获取缓存 key 对应缓存 map 的所有 value
- 参数:
- key:缓存键
- 返回值:缓存 map 对应的所有 value 集合
示例:
HashOperations<String, String, String> operations = redisTemplate.opsForHash();
List<String> values = operations.values("H-KEY");
System.out.println("values = " + values);
输出结果:
values = [VALUE11, VALUE2, VALUE3, VALUE4]
Map:获取缓存 key 对应缓存 map,以键值对方式返回。
- 参数:
- key:缓存键
- 返回值:缓存 map 集合
示例:
HashOperations<String, String, String> operations = redisTemplate.opsForHash();
Map<String, String> map = operations.entries("H-KEY");
System.out.println("map = " + map);
输出结果:
map = {KEY1=VALUE11, KEY2=VALUE2, KEY3=VALUE3, KEY4=VALUE4}
2.3.4 其他操作
Boolean hasKey(H key, Object hashKey):缓存键 key 下的 hashKey 键是否存在。
- 参数:
- key:缓存键
- 返回值:返回结果,存在为 true,不存在为 false
示例:
HashOperations<String, String, String> operations = redisTemplate.opsForHash();
Boolean result1 = operations.hasKey("H-KEY", "KEY1");
System.out.println("result1 = " + result1);
Boolean result2 = operations.hasKey("H-KEY1", "key-a");
System.out.println("result2 = " + result2);
输出结果:
result1 = false
result2 = true
Long lengthOfValue(H key, HK hashKey):缓存键 key 下 hashKey 键对应的值的长度。低版本 redis 会出现错误 ERR unknown command 'HSTRLEN'。
- 参数:
- key:缓存键
- hashKey:缓存 map 的 hashKey
- 返回值:返回统计结果值
示例:
HashOperations<String, String, String> operations = redisTemplate.opsForHash();
Long result1 = operations.lengthOfValue("H-KEY", "KEY1");
System.out.println("result1 = " + result1);
Long result2 = operations.lengthOfValue("H-KEY1", "key-a");
System.out.println("result2 = " + result2);
输出结果:
result1 = 1
result2 = 3
Long size(H key):获取缓存键 key 下的缓存内容的数量。
- 参数:
- key:缓存键
- 返回值:返回统计结果值
示例:
HashOperations<String, String, String> operations = redisTemplate.opsForHash();
System.out.println(operations.size("H-KEY1"));
System.out.println(operations.size("long-key"));
输出结果:
3
1
Cursor:匹配获取缓存键 key 下的缓存内容。
- 参数:
- key:缓存键
- options:匹配规则
- 返回值:返回匹配结果值
示例:
HashOperations<String, String, String> operations = redisTemplate.opsForHash();
Map<String,String> map = new HashMap<String, String>(){{
put("key-a-a","value-a-a");
put("key-a-b","value-a-b");
put("key-a-c","value-a-c");
put("key-b-a","value-a-a");
put("key-b-b","value-b-b");
put("key-b-c","value-b-c");
}};
operations.putAll("scan-key",map);
ScanOptions build = ScanOptions.scanOptions().match("key-a*").build();
Cursor<Map.Entry<String, String>> scan = operations.scan("scan-key", build);
while (scan.hasNext()){
Map.Entry<String, String> next = scan.next();
System.out.println(next.getKey() + " : " + next.getValue());
}
try {
scan.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
输出结果:
key-a-a : value-a-a
key-a-c : value-a-c
key-a-b : value-a-b
Long increment(H key, HK hashKey, long delta):使缓存键 key 下的 hashKey 键对应的值以 long 类型增加 delta,如果指定的哈希表或字段不存在,那么将会创建一个新的哈希表和字段,并指定值为 delta。
- 参数:
- key:缓存键
- hashKey:缓存 map 的 hashKey
- delta:要增加的值
- 返回值:返回增加后的结果值
示例:
HashOperations<String, String, String> operations = redisTemplate.opsForHash();
operations.put("long-key","key1","1");
System.out.println(operations.get("long-key", "key1"));
Long result = operations.increment("long-key","key1",2);
System.out.println("result = " + result);
System.out.println(operations.get("long-key", "key1"));
输出结果:
1
result = 3
3
Double increment(H key, HK hashKey, double delta):使缓存键 key 下的 hashKey 键对应的值以 double 类型增加 delta,如果指定的哈希表或字段不存在,那么将会创建一个新的哈希表和字段,并指定值为 delta。
- 参数:
- key:缓存键
- hashKey:缓存 map 的 hashKey
- delta:要增加的值
- 返回值:返回增加后的结果值
示例:
HashOperations<String, String, String> operations = redisTemplate.opsForHash();
operations.put("long-key","key1","1");
System.out.println(operations.get("long-key", "key1"));
Double result = operations.increment("long-key", "key1", 2.0);
System.out.println("result = " + result);
System.out.println(operations.get("long-key", "key1"));
输出结果:
1
result = 3.5
3.5
2.4 List 类型 API
2.4.1 添加缓存
Long leftPush(K key, V value):向缓存键 key 对应缓存队列的头部添加缓存。
- 参数
- key:缓存键
- value:缓存值
- 返回值:返回每次添加成功之后,缓存队列的数量
示例:
ListOperations<String, String> operations = redisTemplate.opsForList();
Long result1 = operations.leftPush("l-key", "l-value");
Long result2 = operations.leftPush("l-key", "l-value1");
Long result3 = operations.leftPush("l-key", "l-value2");
System.out.println("result1 = " + result1);
System.out.println("result2 = " + result2);
System.out.println("result3 = " + result3);
输出结果:
result1 = 1
result2 = 2
result3 = 3
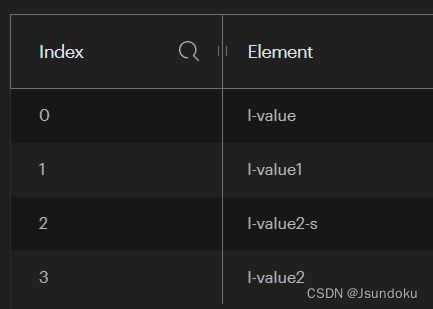
Long leftPush(K key, V pivot, V value):在缓存键 key 对应缓存队列中,将值 value 添加到指定值 pivot 的前面。
- 参数
- key:缓存键
- pivot:指定值
- value:缓存值
- 返回值:返回每次添加成功之后,缓存队列的数量
示例:
ListOperations<String, String> operations = redisTemplate.opsForList();
Long result1 = operations.leftPush("l-key", "l-value");
Long result2 = operations.leftPush("l-key", "l-value1");
Long result3 = operations.leftPush("l-key", "l-value2");
Long result = operations.leftPush("l-key", "l-value", "l-value-s");
System.out.println("result = " + result);
输出结果:
result3 = 4
Long leftPushAll(K key, V... values):批量向缓存键 key 对应缓存队列的头部添加缓存。
- 参数
- key:缓存键
- value:缓存值列表
- 返回值:返回每次添加成功之后,缓存队列的数量
示例:
ListOperations<String, String> operations = redisTemplate.opsForList();
Long result1 = operations.leftPushAll("l-key1", "l-value1", "l-value2", "l-value3");
System.out.println("result = " + result);
输出结果:
result = 3
Long leftPushAll(K key, Collection:批量向缓存键 key 对应缓存队列的头部添加缓存。
- 参数
- key:缓存键
- value:缓存值集合
- 返回值:返回每次添加成功之后,缓存队列的数量
示例:
ListOperations<String, String> operations = redisTemplate.opsForList();
Long result2 = operations.leftPushAll("l-key2", Arrays.asList("l-value1", "l-value2", "l-value3"));
System.out.println("result = " + result);
输出结果:
result = 3
Long leftPushIfPresent(K key, V value):向缓存键 key 对应缓存队列的头部添加缓存,只有缓存列表存在才成功,否则添加失败。
- 参数
- key:缓存键
- value:缓存值
- 返回值:返回执行结果,成功为 true,否则为 false
示例:
ListOperations<String, String> operations = redisTemplate.opsForList();
Long result1 = operations.leftPushIfPresent("l-key1", "l-value1");
System.out.println("result1 = " + result1);
Long result2 = operations.leftPushIfPresent("l-key1", "l-value-s");
System.out.println("result2 = " + result2);
Long result3 = operations.leftPushIfPresent("l-key-s", "l-value1");
System.out.println("result3 = " + result3);
输出结果:
result1 = 4
result2 = 5
result3 = 0
Long rightPush(K key, V value):向缓存键 key 对应缓存队列的尾部添加缓存。
- 参数
- key:缓存键
- value:缓存值
- 返回值:返回每次添加成功之后,缓存队列的数量
示例:
ListOperations<String, String> operations = redisTemplate.opsForList();
Long result1 = operations.rightPush("l-key", "l-value");
Long result2 = operations.rightPush("l-key", "l-value1");
Long result3 = operations.rightPush("l-key", "l-value2");
System.out.println("result1 = " + result1);
System.out.println("result2 = " + result2);
System.out.println("result3 = " + result3);
输出结果:
result1 = 1
result2 = 2
result3 = 3
Long rightPush(K key, V pivot, V value):在缓存键 key 对应缓存队列中,将值 value 添加到指定值 pivot 的后面。
- 参数
- key:缓存键
- pivot:
- value:缓存值
- 返回值:返回每次添加成功之后,缓存队列的数量
示例:
ListOperations<String, String> operations = redisTemplate.opsForList();
Long result1 = operations.rightPush("l-key", "l-value");
Long result2 = operations.rightPush("l-key", "l-value1");
Long result3 = operations.rightPush("l-key", "l-value2");
Long result = operations.rightPush("l-key", "l-value1", "l-value2-s");
System.out.println("result = " + result);
输出结果:
result = 4
Long rightPushAll(K key, V... values):批量向缓存键 key 对应缓存队列的尾部添加缓存。
- 参数
- key:缓存键
- value:缓存值列表
- 返回值:返回每次添加成功之后,缓存队列的数量
示例:
ListOperations<String, String> operations = redisTemplate.opsForList();
Long result1 = operations.rightPushAll("l-key1", "l-value1", "l-value2", "l-value3");
System.out.println("result = " + result);
输出结果:
result = 3
Long rightPushAll(K key, Collection:批量向缓存键 key 对应缓存队列的尾部添加缓存。
- 参数
- key:缓存键
- value:缓存值集合
- 返回值:返回每次添加成功之后,缓存队列的数量
示例:
ListOperations<String, String> operations = redisTemplate.opsForList();
Long result2 = operations.rightPushAll("l-key2", Arrays.asList("l-value1", "l-value2", "l-value3"));
System.out.println("result = " + result);
输出结果:
result = 3
Long rightPushIfPresent(K key, V value):向缓存键 key 对应缓存队列的尾部添加缓存,只有缓存列表存在才成功,否则添加失败
- 参数
- key:缓存键
- value:缓存值
- 返回值:返回每次添加成功之后,缓存队列的数量
示例:
ListOperations<String, String> operations = redisTemplate.opsForList();
Long result1 = operations.rightPushIfPresent("l-key1", "l-value1");
System.out.println("result1 = " + result1);
Long result2 = operations.rightPushIfPresent("l-key1", "l-value-s");
System.out.println("result2 = " + result2);
Long result3 = operations.rightPushIfPresent("l-key-s", "l-value1");
System.out.println("result3 = " + result3);
输出结果:
result1 = 4
result2 = 5
result3 = 0
void set(K key, long index, V value):缓存键 key 对应缓存队列中,替换索引 index 对应的值为 value。
- 参数
- key:缓存键
- index:索引位置
- value:缓存值
示例:
ListOperations<String, String> operations = redisTemplate.opsForList();
operations.set("l-key",2,"new-value");
2.4.2 删除缓存
Long remove(K key, long count, Object value):键 key 的缓存中,移除值 value 出现的前 count 个
- 参数
- key:缓存键
- count:数量
- value:缓存值
- 返回值:
示例:
ListOperations<String, String> operations = redisTemplate.opsForList();
operations.rightPushAll("l-key", "aaa", "bbb", "ccc", "aaa", "ddd", "aaa", "eee", "aaa");
Long result = operations.remove("l-key", 2, "aaa");
System.out.println("result = " + result);
输出结果:
result = 2
V leftPop(K key):从键 key 的缓存中,从头部移除第一个元素。
- 参数
- key:缓存键
- 返回值:
示例:
ListOperations<String, String> operations = redisTemplate.opsForList();
operations.rightPushAll("l-key", "aaa", "bbb", "ccc", "aaa", "ddd", "aaa", "eee", "aaa");
String result = operations.leftPop("l-key");
System.out.println("result = " + result);
输出结果:
result = aaa
V leftPop(K key, long timeout, TimeUnit unit):键 key 的缓存中,从头部移除第一个元素。阻塞连接,直到元素可用或者时间超时。
- 参数
- key:缓存键
- timeout:过期时间
- unit:时间单位
- 返回值:
示例:
ListOperations<String, String> operations = redisTemplate.opsForList();
operations.rightPushAll("l-key", "aaa", "bbb", "ccc", "aaa", "ddd", "aaa", "eee", "aaa");
String result = operations.leftPop("l-key",2000, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
System.out.println("result = " + result);
输出结果:
result = aaa
V leftPop(K key, Duration timeout):键 key 的缓存中,从头部移除第一个元素。阻塞连接,直到元素可用或者时间超时。
- 参数
- key:缓存键
- timeout:过期时间,自带单位
- 返回值:
示例:
ListOperations<String, String> operations = redisTemplate.opsForList();
operations.rightPushAll("l-key", "aaa", "bbb", "ccc", "aaa", "ddd", "aaa", "eee", "aaa");
String result = operations.leftPop("l-key", Duration.ofMillis(2000));
System.out.println("result = " + result);
输出结果:
result = aaa
V rightPop(K key):从键 key 的缓存中,从尾部移除第一个元素。
- 参数
- key:缓存键
- 返回值:
示例:
ListOperations<String, String> operations = redisTemplate.opsForList();
operations.rightPushAll("l-key", "aaa", "bbb", "ccc", "aaa", "ddd", "aaa", "eee", "aaa");
String result = operations.rightPop("l-key");
System.out.println("result = " + result);
输出结果:
result = aaa
V rightPop(K key, long timeout, TimeUnit unit):键 key 的缓存中,从尾部移除第一个元素。阻塞连接,直到元素可用或者时间超时。
- 参数
- key:缓存键
- timeout:过期时间
- unit:时间单位
- 返回值:
示例:
ListOperations<String, String> operations = redisTemplate.opsForList();
operations.rightPushAll("l-key", "aaa", "bbb", "ccc", "aaa", "ddd", "aaa", "eee", "aaa");
String result = operations.rightPop("l-key", 2000, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
System.out.println("result = " + result);
输出结果:
result = aaa
V rightPop(K key, Duration timeout):键 key 的缓存中,从尾部移除第一个元素。阻塞连接,直到元素可用或者时间超时。
- 参数
- key:缓存键
- timeout:过期时间,自带单位
- 返回值:
示例:
ListOperations<String, String> operations = redisTemplate.opsForList();
operations.rightPushAll("l-key", "aaa", "bbb", "ccc", "aaa", "ddd", "aaa", "eee", "aaa");
String result = operations.rightPop("l-key", Duration.ofMillis(2000));
System.out.println("result = " + result);
输出结果:
result = aaa
V rightPopAndLeftPush(K sourceKey, K destinationKey):从键 sourceKey 的缓存尾部移除一个元素,并将此元素添加到键 destinationKey 的缓存头部。
- 参数
- sourceKey:源缓存键
- destinationKey:目标缓存键
- 返回值:
示例:
ListOperations<String, String> operations = redisTemplate.opsForList();
operations.rightPushAll("l-key", "aaa", "bbb", "ccc", "aaa", "ddd", "aaa", "eee", "aaa");
String result = operations.rightPopAndLeftPush("l-key", "target-key");
System.out.println("result = " + result);
输出结果:
result = aaa
V rightPopAndLeftPush(K sourceKey, K destinationKey, long timeout, TimeUnit unit):从键 sourceKey 的缓存尾部移除一个元素,并将此元素添加到键 destinationKey 的缓存头部。阻塞连接,直到元素可用或者时间超时。
- 参数
- sourceKey:源缓存键
- destinationKey:目标缓存键
- timeout:过期时间
- unit:时间单位
- 返回值:
示例:
ListOperations<String, String> operations = redisTemplate.opsForList();
operations.rightPushAll("l-key", "aaa", "bbb", "ccc", "aaa", "ddd", "aaa", "eee", "aaa");
String result = operations.rightPopAndLeftPush("l-key", "target-key", 2000, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
System.out.println("result = " + result);
输出结果:
result = aaa
V rightPopAndLeftPush(K sourceKey, K destinationKey, Duration timeout):从键 sourceKey 的缓存尾部移除一个元素,并将此元素添加到键 destinationKey 的缓存头部。阻塞连接,直到元素可用或者时间超时。
- 参数
- sourceKey:源缓存键
- destinationKey:目标缓存键
- timeout:过期时间,自带单位
- 返回值:
示例:
ListOperations<String, String> operations = redisTemplate.opsForList();
operations.rightPushAll("l-key", "aaa", "bbb", "ccc", "aaa", "ddd", "aaa", "eee", "aaa");
String result = operations.rightPopAndLeftPush("l-key", "target-key", Duration.ofMillis(2000));
System.out.println("result = " + result);
输出结果:
result = aaa
2.4.3 获取缓存
List:获取键 key 的缓存,指定开始索引和结束索引。
- 参数
- key:缓存键
- start:开始位置
- end:结束位置
- 返回值:返回取出的结果列表
示例:
ListOperations<String, String> operations = redisTemplate.opsForList();
List<String> result1 = operations.range("l-key", 0, -1);
System.out.println("result1 = " + result1);
List<String> result2 = operations.range("l-key", 0, 3);
System.out.println("result2 = " + result2);
List<String> result3 = operations.range("l-key", 2, 5);
System.out.println("result3 = " + result3);
输出结果:
result1 = [ccc, aaa, ddd, aaa, eee, aaa, aaa, bbb, ccc, aaa, ddd, aaa, eee, aaa]
result2 = [ccc, aaa, ddd, aaa]
result3 = [ddd, aaa, eee, aaa]
void trim(K key, long start, long end):截取键 key 对应的缓存,指定开始索引和结束索引。
- 参数
- key:缓存键
- start:开始位置
- end:结束位置
示例:
ListOperations<String, String> operations = redisTemplate.opsForList();
operations.trim("l-key", 0, -1);
System.out.println("result1 = " + operations.range("l-key",0,-1));
operations.trim("l-key", 0, 7);
System.out.println("result2 = " + operations.range("l-key",0,-1));
operations.trim("l-key", 2, 5);
System.out.println("result3 = " + operations.range("l-key",0,-1));
输出结果:
result1 = [ccc, aaa, ddd, aaa, eee, aaa, aaa, bbb, ccc, aaa, ddd, aaa, eee, aaa]
result2 = [ccc, aaa, ddd, aaa, eee, aaa, aaa, bbb]
result3 = [ddd, aaa, eee, aaa]
Long size(K key):统计键key对应缓存的元素个数。
- 参数
- key:缓存键
- 返回值:返回统计结果
示例:
ListOperations<String, String> operations = redisTemplate.opsForList();
System.out.println("result2 = " + operations.range("l-key",0,-1));
Long size = operations.size("l-key");
System.out.println("size = " + size);
输出结果:
result2 = [ddd, aaa, eee, aaa]
size = 4
V index(K key, long index):从键 key 对应的缓存中取出索引为 index 的元素。
- 参数
- key:缓存键
- index:
- 返回值:返回获取结果
示例:
ListOperations<String, String> operations = redisTemplate.opsForList();
System.out.println(operations.range("l-key", 0, -1));
String result1 = operations.index("l-key", 0);
System.out.println("result1 = " + result1);
String result2 = operations.index("l-key", 2);
System.out.println("result2 = " + result2);
String result3 = operations.index("l-key", 4);
System.out.println("result3 = " + result3);
输出结果:
[ddd, aaa, eee, aaa]
result1 = ddd
result2 = eee
result3 = null
2.5 Set 类型 API
2.5.1 添加缓存
Long add(K key, V... values):添加缓存。
- 参数:
- key:缓存键
- values:缓存值列表
- 返回值:返回添加成功的个数
示例:
SetOperations<String, String> operations = redisTemplate.opsForSet();
Long result = operations.add("s-key", "aaa", "bbb", "ccc", "ddd");
System.out.println("result = " + result);
输出结果:
result = 4
2.5.2 删除缓存
Long remove(K key, Object... values):移除缓存中的元素。
- 参数:
- key:缓存键
- values:缓存元素列表
- 返回值:返回删除成功的个数
示例:
SetOperations<String, String> operations = redisTemplate.opsForSet();
Long result = operations.remove("s-key", "aaa", "vvv");
System.out.println("result = " + result);
输出结果:
result = 1
V pop(K key):从键 key 的缓存中随机移除一个元素,并返回元素的值,key 不存在则返回 null。
- 参数:
- key:缓存键
- 返回值:返回移除元素的值
示例:
SetOperations<String, String> operations = redisTemplate.opsForSet();
String result = operations.pop("s-key");
System.out.println("result = " + result);
输出结果:
result = ddd
List:从键 key 的缓存中随机移除 count 个元素,并返回这些元素的值,redis 版本过低会报错 ERR wrong number of arguments for 'spop' command。
- 参数:
- key:缓存键
- count:元素个数
- 返回值:返回移除成功的元素列表
示例:
SetOperations<String, String> operations = redisTemplate.opsForSet();
operations.add("s-key","aaa");
List<String> result = operations.pop("s-key", 3);
System.out.println("result = " + result);
输出结果:
result = [aaa]
2.5.3 获取缓存
Set:获取缓存键 key 下的所有缓存元素。
- 参数:
- key:缓存键
- 返回值:返回元素集合
示例:
SetOperations<String, String> operations = redisTemplate.opsForSet();
operations.add("s-key","aaa","bbb","ccc","ddd");
Set<String> result = operations.members("s-key");
System.out.println("result = " + result);
输出结果:
result = [bbb, aaa, ccc, ddd]
V randomMember(K key):从缓存键 key 的缓存中随机返回一个元素。
- 参数:
- key:缓存键
- 返回值:返回元素
示例:
SetOperations<String, String> operations = redisTemplate.opsForSet();
operations.add("s-key","aaa","bbb","ccc","ddd");
String result1 = operations.randomMember("s-key");
System.out.println("result1 = " + result1);
String result2 = operations.randomMember("s-key");
System.out.println("result2 = " + result2);
输出结果:
result1 = ccc
result2 = ddd
List:从缓存键 key 的缓存中随机返回 count 个元素,返回元素可重复。
- 参数:
- key:缓存键
- count:元素个数
- 返回值:返回元素集合
示例:
SetOperations<String, String> operations = redisTemplate.opsForSet();
operations.add("s-key","aaa","bbb","ccc","ddd");
List<String> result = operations.randomMembers("s-key",10);
System.out.println("result = " + result);
输出结果:
result = [ddd, ddd, ddd, ccc, ccc, ccc, ccc, bbb, bbb, ddd]
Set:从缓存键 key 的缓存中随机返回 count 个元素,返回元素不可重复。
- 参数:
- key:缓存键
- count:元素个数
- 返回值:返回元素集合
示例:
SetOperations<String, String> operations = redisTemplate.opsForSet();
operations.add("s-key","aaa","bbb","ccc","ddd");
Set<String> result = operations.distinctRandomMembers("s-key",10);
System.out.println("result = " + result);
输出结果:
result = [bbb, ddd, ccc, aaa]
Set:比较并返回指定键和其他键对应的缓存中不同的元素,返回的元素为指定缓存键 key 中不同的元素。
- 参数:
- key:缓存键
- otherKey:其他缓存键
- 返回值:返回结果集
示例:
SetOperations<String, String> operations = redisTemplate.opsForSet();
operations.add("s-key-1", "aaa", "bbb", "ccc", "ddd");
operations.add("s-key-2", "aaa", "bbb", "eee", "fff");
operations.add("s-key-3", "aaa", "bbb", "ggg", "hhh");
Set<String> result1 = operations.difference("s-key-1", "s-key-2");
System.out.println("result1 = " + result1);
Set<String> result2 = operations.difference("s-key-1", "s-key-3");
System.out.println("result2 = " + result2);
Set<String> result3 = operations.difference("s-key-2", "s-key-3");
System.out.println("result3 = " + result3);
Set<String> result4 = operations.difference("s-key-3", "s-key-2");
System.out.println("result4 = " + result4);
输出结果:
result1 = [ccc, ddd]
result2 = [ccc, ddd]
result3 = [eee, fff]
result4 = [ggg, hhh]
Set:比较并返回指定键和其他键对应的缓存中不同的元素,返回的元素为指定缓存键中不同的元素。
- 参数:
- key:缓存键
- otherKeys:其他缓存键集合
- 返回值:返回结果集
示例:
SetOperations<String, String> operations = redisTemplate.opsForSet();
operations.add("s-key-1", "aaa", "bbb", "ccc", "ddd");
operations.add("s-key-2", "aaa", "bbb", "eee", "fff");
operations.add("s-key-3", "aaa", "bbb", "ggg", "hhh");
Set<String> result1 = operations.difference("s-key-1", Arrays.asList("s-key-2","s-key-3"));
System.out.println("result1 = " + result1);
Set<String> result2 = operations.difference("s-key-2", Arrays.asList("s-key-1","s-key-3"));
System.out.println("result2 = " + result2);
Set<String> result3 = operations.difference("s-key-3", Arrays.asList("s-key-1","s-key-2"));
System.out.println("result3 = " + result3);
Set<String> result4 = operations.difference("s-key-3", Arrays.asList("s-key-2","s-key-1"));
System.out.println("result4 = " + result4);
输出结果:
result1 = [ccc, ddd]
result2 = [eee, fff]
result3 = [ggg, hhh]
result4 = [ggg, hhh]
Set:比较缓存键集合中各个键对应的缓存中不同的元素,返回的元素为缓存键集合中第一个键对应的缓存中不同的元素。
- 参数:
- keys:缓存键集合
- 返回值:返回结果集
示例:
SetOperations<String, String> operations = redisTemplate.opsForSet();
operations.add("s-key-1", "aaa", "bbb", "ccc", "ddd");
operations.add("s-key-2", "aaa", "bbb", "eee", "fff");
operations.add("s-key-3", "aaa", "bbb", "ggg", "hhh");
Set<String> result1 = operations.difference(Arrays.asList("s-key-1","s-key-2","s-key-3"));
System.out.println("result1 = " + result1);
Set<String> result2 = operations.difference(Arrays.asList("s-key-2","s-key-1","s-key-3"));
System.out.println("result2 = " + result2);
Set<String> result3 = operations.difference(Arrays.asList("s-key-3","s-key-1","s-key-2"));
System.out.println("result3 = " + result3);
Set<String> result4 = operations.difference(Arrays.asList("s-key-3","s-key-2","s-key-1"));
System.out.println("result4 = " + result4);
输出结果:
result1 = [ccc, ddd]
result2 = [eee, fff]
result3 = [ggg, hhh]
result4 = [ggg, hhh]
Long differenceAndStore(K key, K otherKey, K destKey):比较指定键和其他键对应的缓存中不同的元素,并将不同的元素另外缓存,缓存的元素为指定缓存键中不同的元素。
- 参数:
- key:缓存键
- otherKey:其他缓存键
- destKey:目标缓存键
- 返回值:返回结果集数量
示例:
SetOperations<String, String> operations = redisTemplate.opsForSet();
operations.add("s-key-1", "aaa", "bbb", "ccc", "ddd");
operations.add("s-key-2", "aaa", "bbb", "eee", "fff");
operations.add("s-key-3", "aaa", "bbb", "ggg", "hhh");
Long result = operations.differenceAndStore("s-key-1", "s-key-2", "new-key");
System.out.println("result = " + result);
Set<String> members = operations.members("new-key");
System.out.println("new-key = " + members);
输出结果:
result = 2
new-key = [ccc, ddd]
Long differenceAndStore(K key, Collection:比较指定键和其他键对应的缓存中不同的元素,并将不同的元素另外缓存,缓存的元素为指定缓存键中不同的元素。
- 参数:
- key:缓存键
- otherKeys:其他缓存键集合
- destKey:目标缓存键
- 返回值:返回结果集数量
示例:
SetOperations<String, String> operations = redisTemplate.opsForSet();
operations.add("s-key-1", "aaa", "bbb", "ccc", "ddd");
operations.add("s-key-2", "aaa", "bbb", "eee", "fff");
operations.add("s-key-3", "aaa", "bbb", "ggg", "hhh");
Long result = operations.differenceAndStore("s-key-1", Arrays.asList("s-key-2","s-key-3"), "new-key");
System.out.println("result = " + result);
Set<String> members = operations.members("new-key");
System.out.println("new-key = " + members);
输出结果:
result = 2
new-key = [ccc, ddd]
Long differenceAndStore(Collection:比较缓存键集合中各个键对应的缓存中不同的元素,并将不同的元素另外缓存,缓存的元素为缓存键集合中第一个键对应的缓存中不同的元素。
- 参数:
- keys:缓存键集合
- destKey:目标缓存键
- 返回值:返回结果集数量
示例:
SetOperations<String, String> operations = redisTemplate.opsForSet();
operations.add("s-key-1", "aaa", "bbb", "ccc", "ddd");
operations.add("s-key-2", "aaa", "bbb", "eee", "fff");
operations.add("s-key-3", "aaa", "bbb", "ggg", "hhh");
Long result = operations.differenceAndStore( Arrays.asList("s-key-1","s-key-2","s-key-3"), "new-key");
System.out.println("result = " + result);
Set<String> members = operations.members("new-key");
System.out.println("new-key = " + members);
输出结果:
result = 2
new-key = [ccc, ddd]
Set:取交集,比较并返回指定键和其他键对应的缓存中相同的元素,返回的元素为指定缓存键 key 中相同的元素。
- 参数:
- key:缓存键
- otherKey:其他缓存键
- 返回值:返回结果集
示例:
SetOperations<String, String> operations = redisTemplate.opsForSet();
operations.add("s-key-1", "aaa", "bbb", "ccc", "ddd");
operations.add("s-key-2", "aaa", "bbb", "eee", "fff");
operations.add("s-key-3", "aaa", "bbb", "ggg", "hhh");
Set<String> result= operations.intersect("s-key-1", "s-key-2");
System.out.println("result = " + result);
输出结果:
result = [aaa, bbb]
Set:取交集,比较并返回指定键和其他键对应的缓存中相同的元素,返回的元素为指定缓存键中相同的元素。
- 参数:
- key:缓存键
- otherKeys:其他缓存键集合
- 返回值:返回结果集
示例:
SetOperations<String, String> operations = redisTemplate.opsForSet();
operations.add("s-key-1", "aaa", "bbb", "ccc", "ddd");
operations.add("s-key-2", "aaa", "bbb", "eee", "fff");
operations.add("s-key-3", "aaa", "bbb", "ggg", "hhh");
Set<String> result= operations.intersect("s-key-1", Arrays.asList("s-key-2", "s-key-3"));
System.out.println("result = " + result);
输出结果:
result = [aaa, bbb]
Set:取交集,比较缓存键集合中各个键对应的缓存中相同的元素,返回的元素为缓存键集合中第一个键对应的缓存中相同的元素。
- 参数:
- keys:缓存键集合
- 返回值:返回结果集
示例:
SetOperations<String, String> operations = redisTemplate.opsForSet();
operations.add("s-key-1", "aaa", "bbb", "ccc", "ddd");
operations.add("s-key-2", "aaa", "bbb", "eee", "fff");
operations.add("s-key-3", "aaa", "bbb", "ggg", "hhh");
Set<String> result= operations.intersect(Arrays.asList("s-key-1", "s-key-2", "s-key-3"));
System.out.println("result = " + result);
输出结果:
result = [aaa, bbb]
Long intersectAndStore(K key, K otherKey, K destKey):取交集,比较指定键和其他键对应的缓存中相同的元素,并将相同的元素另外缓存,缓存的元素为指定缓存键中相同的元素。
- 参数:
- key:缓存键
- otherKey:其他缓存键
- destKey:目标缓存键
- 返回值:返回结果集数量
示例:
SetOperations<String, String> operations = redisTemplate.opsForSet();
operations.add("s-key-1", "aaa", "bbb", "ccc", "ddd");
operations.add("s-key-2", "aaa", "bbb", "eee", "fff");
operations.add("s-key-3", "aaa", "bbb", "ggg", "hhh");
Long result = operations.intersectAndStore("s-key-1", "s-key-2", "new-key");
System.out.println("result = " + result);
Set<String> members = operations.members("new-key");
System.out.println("new-key = " + members);
输出结果:
result = 2
new-key = [bbb, aaa]
Long intersectAndStore(K key, Collection:取交集,比较指定键和其他键对应的缓存中相同的元素,并将相同的元素另外缓存,缓存的元素为指定缓存键中相同的元素。
- 参数:
- key:缓存键
- otherKeys:其他缓存键集合
- destKey:目标缓存键
- 返回值:返回结果集数量
示例:
SetOperations<String, String> operations = redisTemplate.opsForSet();
operations.add("s-key-1", "aaa", "bbb", "ccc", "ddd");
operations.add("s-key-2", "aaa", "bbb", "eee", "fff");
operations.add("s-key-3", "aaa", "bbb", "ggg", "hhh");
Long result = operations.intersectAndStore("s-key-1", Arrays.asList("s-key-2", "s-key-3"), "new-key");
System.out.println("result = " + result);
Set<String> members = operations.members("new-key");
System.out.println("new-key = " + members);
输出结果:
result = 2
new-key = [bbb, aaa]
Long intersectAndStore(Collection:取交集,比较缓存键集合中各个键对应的缓存中相同的元素,并将相同的元素另外缓存,缓存的元素为缓存键集合中第一个键对应的缓存中相同的元素。
- 参数:
- keys:缓存键集合
- destKey:目标缓存键
- 返回值:返回结果集数量
示例:
SetOperations<String, String> operations = redisTemplate.opsForSet();
operations.add("s-key-1", "aaa", "bbb", "ccc", "ddd");
operations.add("s-key-2", "aaa", "bbb", "eee", "fff");
operations.add("s-key-3", "aaa", "bbb", "ggg", "hhh");
Long result = operations.intersectAndStore( Arrays.asList("s-key-1", "s-key-2", "s-key-3"), "new-key");
System.out.println("result = " + result);
Set<String> members = operations.members("new-key");
System.out.println("new-key = " + members);
输出结果:
result = 2
new-key = [bbb, aaa]
Set:取并集,比较并返回指定键和其他键对应的缓存中所有的元素,会去重
- 参数:
- key:缓存键
- otherKey:其他缓存键
- 返回值:返回结果集
示例:
SetOperations<String, String> operations = redisTemplate.opsForSet();
operations.add("s-key-1", "aaa", "bbb", "ccc", "ddd");
operations.add("s-key-2", "aaa", "bbb", "eee", "fff");
operations.add("s-key-3", "aaa", "bbb", "ggg", "hhh");
Set<String> result= operations.union("s-key-1", "s-key-2");
System.out.println("result = " + result);
输出结果:
result = [hhh, eee, aaa, bbb, fff, ccc, ddd, ggg]
Set:取并集,比较并返回指定键和其他键对应的缓存中所有的元素,会去重。
- 参数:
- key:缓存键
- otherKeys:其他缓存键集合
- 返回值:返回结果集
示例:
SetOperations<String, String> operations = redisTemplate.opsForSet();
operations.add("s-key-1", "aaa", "bbb", "ccc", "ddd");
operations.add("s-key-2", "aaa", "bbb", "eee", "fff");
operations.add("s-key-3", "aaa", "bbb", "ggg", "hhh");
Set<String> result= operations.union("s-key-1", Arrays.asList("s-key-2", "s-key-3"));
System.out.println("result = " + result);
输出结果:
result = [hhh, eee, aaa, bbb, fff, ccc, ddd, ggg]
Set:取并集,比较缓存键集合中各个键对应的缓存中所有的元素,会去重。
- 参数:
- keys:缓存键集合
- 返回值:返回结果集
示例:
SetOperations<String, String> operations = redisTemplate.opsForSet();
operations.add("s-key-1", "aaa", "bbb", "ccc", "ddd");
operations.add("s-key-2", "aaa", "bbb", "eee", "fff");
operations.add("s-key-3", "aaa", "bbb", "ggg", "hhh");
Set<String> result= operations.union(Arrays.asList("s-key-1", "s-key-2", "s-key-3"));
System.out.println("result = " + result);
输出结果:
result = [hhh, eee, aaa, bbb, fff, ccc, ddd, ggg]
Long unionAndStore(K key, K otherKey, K destKey):取并集,比较指定键和其他键对应的缓存中所有的元素,会去重,并将合并的元素另外缓存。
- 参数:
- key:缓存键
- otherKey:其他缓存键
- destKey:目标缓存键
- 返回值:返回结果集数量
示例:
SetOperations<String, String> operations = redisTemplate.opsForSet();
operations.add("s-key-1", "aaa", "bbb", "ccc", "ddd");
operations.add("s-key-2", "aaa", "bbb", "eee", "fff");
operations.add("s-key-3", "aaa", "bbb", "ggg", "hhh");
Long result = operations.unionAndStore("s-key-1", "s-key-2", "new-key");
System.out.println("result = " + result);
Set<String> members = operations.members("new-key");
System.out.println("members = " + members);
输出结果:
result = 6
members = [eee, aaa, bbb, fff, ccc, ddd]
Long unionAndStore(K key, Collection:取并集,比较指定键和其他键对应的缓存中所有的元素,会去重,并将合并的元素另外缓存。
- 参数:
- key:缓存键
- otherKeys:其他缓存键集合
- destKey:目标缓存键
- 返回值:返回结果集数量
示例:
SetOperations<String, String> operations = redisTemplate.opsForSet();
operations.add("s-key-1", "aaa", "bbb", "ccc", "ddd");
operations.add("s-key-2", "aaa", "bbb", "eee", "fff");
operations.add("s-key-3", "aaa", "bbb", "ggg", "hhh");
Long result = operations.unionAndStore("s-key-1", Arrays.asList("s-key-2", "s-key-3"), "new-key");
System.out.println("result = " + result);
Set<String> members = operations.members("new-key");
System.out.println("members = " + members);
输出结果:
result = 8
members = [hhh, eee, aaa, bbb, fff, ccc, ddd, ggg]
Long unionAndStore(Collection:取并集,比较缓存键集合中各个键对应的缓存中所有的元素,会去重,并将合并的元素另外缓存。
- 参数:
- keys:缓存键集合
- destKey:目标缓存键
- 返回值:返回结果集数量
示例:
SetOperations<String, String> operations = redisTemplate.opsForSet();
operations.add("s-key-1", "aaa", "bbb", "ccc", "ddd");
operations.add("s-key-2", "aaa", "bbb", "eee", "fff");
operations.add("s-key-3", "aaa", "bbb", "ggg", "hhh");
Long result = operations.unionAndStore(Arrays.asList("s-key-1", "s-key-2", "s-key-3"), "new-key");
System.out.println("result = " + result);
Set<String> members = operations.members("new-key");
System.out.println("members = " + members);
输出结果:
result = 8
members = [hhh, eee, aaa, bbb, fff, ccc, ddd, ggg]
Cursor:从键 key 的缓存中匹配查找元素
- 参数:
- key:缓存键
- options:匹配规则
- 返回值:返回匹配到的元素
示例:
SetOperations<String, String> operations = redisTemplate.opsForSet();
operations.add("s-key", "aaa", "aab", "aac", "bba", "bbb", "bbc", "cca", "ccb", "ccc");
Cursor<String> cursor1 = operations.scan("s-key", ScanOptions.NONE);
while (cursor1.hasNext()) {
System.out.print(cursor1.next() + ",");
}
System.out.println("");
Cursor<String> cursor2 = operations.scan("s-key", ScanOptions.scanOptions().match("aa*").build());
while (cursor2.hasNext()) {
System.out.print(cursor2.next() + ",");
}
try {
cursor1.close();
cursor2.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
输出结果:
aaa,bbb,aab,cca,ccc,bbc,aac,ddd,bba,ccb,
aaa,aab,aac,
2.5.4 其他操作
Boolean move(K key, V value, K destKey):从键 key 的缓存中取出元素 value 并添加到目标缓存键 destKey 的缓存中。
- 参数:
- key:缓存键
- 返回值:返回操作结果,成功为 true,失败为 false
示例:
SetOperations<String, String> operations = redisTemplate.opsForSet();
operations.add("s-key", "aaa", "bbb", "ccc", "ddd");
System.out.println(operations.members("s-key"));
Boolean result1 = operations.move("s-key", "ccc", "target-key");
System.out.println("result1 = " + result1);
Boolean result2 = operations.move("s-key", "zzz", "target-key");
System.out.println("result2 = " + result2);
System.out.println("s-key = " + operations.members("s-key"));
System.out.println("target-key = " + operations.members("target-key"));
输出结果:
[aaa, bbb, ccc, ddd]
result1 = true
result2 = false
s-key = [aaa, bbb, ddd]
target-key = [ccc]
Long size(K key):统计键 key 的缓存元素个数。
- 参数:
- key:缓存键
- 返回值:返回统计个数
示例:
SetOperations<String, String> operations = redisTemplate.opsForSet();
operations.add("s-key", "aaa", "bbb", "ccc", "ddd");
Long result = operations.size("s-key");
System.out.println("result = " + result);
输出结果:
result = 4
Boolean isMember(K key, Object o):判断指定元素在键 key 的缓存是否存在。
- 参数:
- key:缓存键
- o:指定缓存元素
- 返回值:返回判断结果,存在为 true,不存在为 false
示例:
SetOperations<String, String> operations = redisTemplate.opsForSet();
operations.add("s-key", "aaa", "bbb", "ccc", "ddd");
Boolean result1 = operations.isMember("s-key","aaa");
System.out.println("result1 = " + result1);
Boolean result2 = operations.isMember("s-key","zzz");
System.out.println("result2 = " + result2);
输出结果:
result1 = true
result2 = false
2.6 ZSet 类型 API
2.6.1 添加缓存
Boolean add(K key, V value, double score):添加缓存,如果 value 已经存在,会更新分数 score,但是返回结果为 false。
- 参数:
- key:缓存键
- value:缓存值,
- score:缓存值对应的分数
- 返回值:返回添加结果,成功为 true,失败为 false
示例:
ZSetOperations<String, String> operations = redisTemplate.opsForZSet();
Boolean result1 = operations.add("zs-key", "aaa", 40);
System.out.println("result1 = " + result1);
Boolean result2 = operations.add("zs-key", "bbb", 23);
System.out.println("result2 = " + result2);
Boolean result3 = operations.add("zs-key", "ccc", 56);
System.out.println("result3 = " + result3);
Boolean result4 = operations.add("zs-key", "aaa", 66);
System.out.println("result4 = " + result4 );
输出结果:
result1 = true
result2 = true
result3 = true
result4 = false
Long add(K key, Set:添加缓存,如果 value 已经存在,会更新分数 score,但是返回结果总数量不会加1。
- 参数:
- key:缓存键
- tuples:缓存内容
- 返回值:返回添加成功数量
示例:
ZSetOperations<String, String> operations = redisTemplate.opsForZSet();
Set<ZSetOperations.TypedTuple<String>> tuples = new HashSet<>();
tuples.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("aaa", 45.5));
tuples.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("bbb", 23.0));
tuples.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("ccc", 12.9));
tuples.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("aaa",77.7));
Long result = operations.add("zs-key", tuples);
System.out.println("result = " + result);
输出结果:
result = 3
2.6.2 删除缓存
Long remove(K key, Object... values):删除缓存。
- 参数:
- key:缓存键
- 返回值:返回删除成功数量
示例:
ZSetOperations<String, String> operations = redisTemplate.opsForZSet();
Set<ZSetOperations.TypedTuple<String>> tuples = new HashSet<>();
tuples.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("aaa", 45.5));
tuples.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("bbb", 23.0));
tuples.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("ccc", 12.9));
tuples.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("ddd", 42.2));
tuples.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("aaa", 77.7));
operations.add("zs-key", tuples);
Long result = operations.remove("zs-key", "aaa", "bbb", "zzz");
System.out.println("result = " + result);
输出结果:
result = 2
Long removeRange(K key, long start, long end):根据索引排序后,删除指定索引范围内的缓存,指定开始索引和结束索引。
- 参数:
- key:缓存键
- start:开始索引
- end:结束索引
- 返回值:返回删除成功数量
示例:
ZSetOperations<String, String> operations = redisTemplate.opsForZSet();
Set<ZSetOperations.TypedTuple<String>> tuples = new HashSet<>();
tuples.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("aaa", 45.5));
tuples.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("bbb", 23.0));
tuples.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("ccc", 12.9));
tuples.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("ddd", 42.2));
tuples.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("eee", 77.7));
tuples.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("fff", 45.7));
operations.add("zs-key", tuples);
Long result = operations.removeRange("zs-key", 2, 4);
System.out.println("result = " + result);
输出结果:
result = 3
Long removeRangeByScore(K key, double min, double max):根据分数排序后,删除指定范围内的缓存,指定最小分数和最大分数,包含指定分数值。
- 参数:
- key:缓存键
- min:最小分数
- max:最大分数
- 返回值:
示例:
ZSetOperations<String, String> operations = redisTemplate.opsForZSet();
Set<ZSetOperations.TypedTuple<String>> tuples = new HashSet<>();
tuples.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("aaa", 45.5));
tuples.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("bbb", 23.0));
tuples.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("ccc", 12.9));
tuples.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("ddd", 42.2));
tuples.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("eee", 77.7));
tuples.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("fff", 45.7));
operations.add("zs-key", tuples);
Long result = operations.removeRangeByScore("zs-key", 30,60);
System.out.println("result = " + result);
输出结果:
result = 3
2.6.3 获取缓存
Set:获取缓存元素,指定开始索引和结束索引
- 参数:
- key:缓存键
- start:开始索引
- end:结束索引
- 返回值:
示例:
ZSetOperations<String, String> operations = redisTemplate.opsForZSet();
Set<ZSetOperations.TypedTuple<String>> tuples = new HashSet<>();
tuples.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("aaa", 45.5));
tuples.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("bbb", 23.0));
tuples.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("ccc", 12.9));
tuples.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("ddd", 42.2));
tuples.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("eee", 77.7));
tuples.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("fff", 45.7));
operations.add("zs-key", tuples);
Set<String> result1 = operations.range("zs-key", 0, -1);
System.out.println("result1 = " + result1);
Set<String> result2 = operations.range("zs-key", 0, 4);
System.out.println("result2 = " + result2);
Set<String> result3 = operations.range("zs-key", 2, 5);
System.out.println("result3 = " + result3);
输出结果:
result1 = [ccc, bbb, ddd, aaa, fff, eee]
result2 = [ccc, bbb, ddd, aaa, fff]
result3 = [ddd, aaa, fff, eee]
Set:先根据分数排序,然后从缓存取出指定索引范围内的缓存元素及元素对应的分数,指定开始索引和结束索引。
- 参数:
- key:缓存键
- start:开始索引
- end:结束索引
- 返回值:返回结果集合
示例:
ZSetOperations<String, String> operations = redisTemplate.opsForZSet();
Set<ZSetOperations.TypedTuple<String>> tuples = new HashSet<>();
tuples.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("aaa", 45.5));
tuples.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("bbb", 23.0));
tuples.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("ccc", 12.9));
tuples.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("ddd", 42.2));
tuples.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("eee", 77.7));
tuples.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("fff", 45.7));
operations.add("zs-key", tuples);
Set<ZSetOperations.TypedTuple<String>> result1 = operations.rangeWithScores("zs-key", 0, -1);
for (ZSetOperations.TypedTuple<String> next : result1) {
System.out.println(next.getValue() + " - " + next.getScore());
}
System.out.println("----------------");
Set<ZSetOperations.TypedTuple<String>> result2 = operations.rangeWithScores("zs-key", 2, 4);
for (ZSetOperations.TypedTuple<String> next : result2) {
System.out.println(next.getValue() + " - " + next.getScore());
}
输出结果:
ccc - 12.9
bbb - 23.0
ddd - 42.2
aaa - 45.5
fff - 45.7
eee - 77.7
----------------
ddd - 42.2
aaa - 45.5
fff - 45.7
Set:先根据分数排序,然后从缓存取出指定分数范围内的缓存元素。
- 参数:
- key:缓存键
- min:最小分数
- max:最大分数
- 返回值:返回结果集合
示例:
ZSetOperations<String, String> operations = redisTemplate.opsForZSet();
Set<ZSetOperations.TypedTuple<String>> tuples = new HashSet<>();
tuples.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("aaa", 45.5));
tuples.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("bbb", 23.0));
tuples.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("ccc", 12.9));
tuples.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("ddd", 42.2));
tuples.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("eee", 77.7));
tuples.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("fff", 45.7));
operations.add("zs-key", tuples);
Set<String> result1 = operations.rangeByScore("zs-key", 0, 100);
System.out.println("result1 = " + result1);
Set<String> result2 = operations.rangeByScore("zs-key", 45.5, 100);
System.out.println("result2 = " + result2);
Set<String> result3 = operations.rangeByScore("zs-key", 0, 45.5);
System.out.println("result3 = " + result3);
输出结果:
result1 = [ccc, bbb, ddd, aaa, fff, eee]
result2 = [aaa, fff, eee]
result3 = [ccc, bbb, ddd, aaa]
Set:
- 参数:
- key:缓存键
- min:最小分数
- max:最大分数
- offset:偏移量
- count:数量
- 返回值:返回结果集合
示例:
ZSetOperations<String, String> operations = redisTemplate.opsForZSet();
Set<ZSetOperations.TypedTuple<String>> tuples = new HashSet<>();
tuples.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("aaa", 45.5));
tuples.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("bbb", 23.0));
tuples.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("ccc", 12.9));
tuples.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("ddd", 42.2));
tuples.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("eee", 77.7));
tuples.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("fff", 45.7));
operations.add("zs-key", tuples);
Set<String> result1 = operations.rangeByScore("zs-key", 0, 100, 1, 1);
System.out.println("result1 = " + result1);
Set<String> result2 = operations.rangeByScore("zs-key", 45.5, 100, 1, 1);
System.out.println("result2 = " + result2);
Set<String> result3 = operations.rangeByScore("zs-key", 0, 45.5, 1, 1);
System.out.println("result3 = " + result3);
输出结果:
result1 = [bbb]
result2 = [fff]
result3 = [bbb]
Set:先根据分数排序,然后从缓存取出指定分数范围内的缓存元素及元素对应的分数。
- 参数:
- key:缓存键
- min:最小分数
- max:最大分数
- 返回值:返回结果集合
示例:
ZSetOperations<String, String> operations = redisTemplate.opsForZSet();
Set<ZSetOperations.TypedTuple<String>> tuples = new HashSet<>();
tuples.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("aaa", 45.5));
tuples.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("bbb", 23.0));
tuples.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("ccc", 12.9));
tuples.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("ddd", 42.2));
tuples.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("eee", 77.7));
tuples.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("fff", 45.7));
operations.add("zs-key", tuples);
Set<ZSetOperations.TypedTuple<String>> result1 = operations.rangeByScoreWithScores("zs-key", 0, 100);
for (ZSetOperations.TypedTuple<String> next : result1) {
System.out.println(next.getValue() + " - " + next.getScore());
}
System.out.println("----------------");
Set<ZSetOperations.TypedTuple<String>> result2 = operations.rangeByScoreWithScores("zs-key", 20, 50);
for (ZSetOperations.TypedTuple<String> next : result2) {
System.out.println(next.getValue() + " - " + next.getScore());
}
输出结果:
ccc - 12.9
bbb - 23.0
ddd - 42.2
aaa - 45.5
fff - 45.7
eee - 77.7
----------------
bbb - 23.0
ddd - 42.2
aaa - 45.5
fff - 45.7
Set:先根据分数排序,然后从缓存取出指定分数范围内的缓存元素及元素对应的分数,指定偏移量和返回个数。
- 参数:
- key:缓存键
- min:最小分数
- max:最大分数
- 返回值:返回结果集合
示例:
ZSetOperations<String, String> operations = redisTemplate.opsForZSet();
Set<ZSetOperations.TypedTuple<String>> tuples = new HashSet<>();
tuples.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("aaa", 45.5));
tuples.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("bbb", 23.0));
tuples.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("ccc", 12.9));
tuples.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("ddd", 42.2));
tuples.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("eee", 77.7));
tuples.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("fff", 45.7));
operations.add("zs-key", tuples);
Set<ZSetOperations.TypedTuple<String>> result1 = operations.rangeByScoreWithScores("zs-key", 0, 100,1,3);
for (ZSetOperations.TypedTuple<String> next : result1) {
System.out.println(next.getValue() + " - " + next.getScore());
}
System.out.println("----------------");
Set<ZSetOperations.TypedTuple<String>> result2 = operations.rangeByScoreWithScores("zs-key", 20, 50,1,2);
for (ZSetOperations.TypedTuple<String> next : result2) {
System.out.println(next.getValue() + " - " + next.getScore());
}
输出结果:
bbb - 23.0
ddd - 42.2
aaa - 45.5
----------------
ddd - 42.2
aaa - 45.5
Set:获取缓存元素,指定开始索引和结束索引,根据索引倒序排序。
- 参数:
- key:缓存键
- start:开始索引
- end:结束索引
- 返回值:返回结果集合
示例:
ZSetOperations<String, String> operations = redisTemplate.opsForZSet();
Set<ZSetOperations.TypedTuple<String>> tuples = new HashSet<>();
tuples.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("aaa", 45.5));
tuples.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("bbb", 23.0));
tuples.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("ccc", 12.9));
tuples.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("ddd", 42.2));
tuples.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("eee", 77.7));
tuples.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("fff", 45.7));
operations.add("zs-key", tuples);
Set<String> result1 = operations.reverseRange("zs-key", 0, -1);
System.out.println("result1 = " + result1);
Set<String> result2 = operations.reverseRange("zs-key", 0, 3);
System.out.println("result2 = " + result2);
Set<String> result3 = operations.reverseRange("zs-key", 2, 5);
System.out.println("result3 = " + result3);
输出结果:
result1 = [eee, fff, aaa, ddd, bbb, ccc]
result2 = [eee, fff, aaa, ddd]
result3 = [aaa, ddd, bbb, ccc]
Set:先根据分数倒序排序,然后从缓存取出指定索引范围内的缓存元素及元素对应的分数,指定开始索引和结束索引。
- 参数:
- key:缓存键
- start:开始索引
- end:结束索引
- 返回值:返回结果集合
示例:
ZSetOperations<String, String> operations = redisTemplate.opsForZSet();
Set<ZSetOperations.TypedTuple<String>> tuples = new HashSet<>();
tuples.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("aaa", 45.5));
tuples.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("bbb", 23.0));
tuples.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("ccc", 12.9));
tuples.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("ddd", 42.2));
tuples.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("eee", 77.7));
tuples.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("fff", 45.7));
operations.add("zs-key", tuples);
Set<ZSetOperations.TypedTuple<String>> result1 = operations.reverseRangeWithScores("zs-key", 0, -1);
for (ZSetOperations.TypedTuple<String> next : result1) {
System.out.println(next.getValue() + " - " + next.getScore());
}
System.out.println("----------------");
Set<ZSetOperations.TypedTuple<String>> result2 = operations.reverseRangeWithScores("zs-key", 2, 5);
for (ZSetOperations.TypedTuple<String> next : result2) {
System.out.println(next.getValue() + " - " + next.getScore());
}
输出结果:
eee - 77.7
fff - 45.7
aaa - 45.5
ddd - 42.2
bbb - 23.0
ccc - 12.9
----------------
aaa - 45.5
ddd - 42.2
bbb - 23.0
ccc - 12.9
Set:先根据分数倒序排序,然后从缓存取出指定分数范围内的缓存元素。
- 参数:
- key:缓存键
- min:最小分数
- max:最大分数
- 返回值:返回结果集合
示例:
ZSetOperations<String, String> operations = redisTemplate.opsForZSet();
Set<ZSetOperations.TypedTuple<String>> tuples = new HashSet<>();
tuples.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("aaa", 45.5));
tuples.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("bbb", 23.0));
tuples.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("ccc", 12.9));
tuples.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("ddd", 42.2));
tuples.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("eee", 77.7));
tuples.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("fff", 45.7));
operations.add("zs-key", tuples);
Set<String> result1 = operations.reverseRangeByScore("zs-key", 0, 100);
System.out.println("result1 = " + result1);
Set<String> result2 = operations.reverseRangeByScore("zs-key", 20, 50);
System.out.println("result2 = " + result2);
输出结果:
result1 = [eee, fff, aaa, ddd, bbb, ccc]
result2 = [fff, aaa, ddd, bbb]
Set:先根据分数倒序排序,然后从缓存取出指定分数范围内的缓存元素,指定偏移量和返回个数。
- 参数:
- key:缓存键
- min:最小分数
- max:最大分数
- 返回值:返回结果集合
示例:
ZSetOperations<String, String> operations = redisTemplate.opsForZSet();
Set<ZSetOperations.TypedTuple<String>> tuples = new HashSet<>();
tuples.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("aaa", 45.5));
tuples.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("bbb", 23.0));
tuples.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("ccc", 12.9));
tuples.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("ddd", 42.2));
tuples.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("eee", 77.7));
tuples.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("fff", 45.7));
operations.add("zs-key", tuples);
Set<String> result1 = operations.reverseRangeByScore("zs-key", 0, 100, 1, 3);
System.out.println("result1 = " + result1);
Set<String> result2 = operations.reverseRangeByScore("zs-key", 20, 50, 1, 2);
System.out.println("result2 = " + result2);
输出结果:
result1 = [fff, aaa, ddd]
result2 = [aaa, ddd]
Set:先根据分数倒序排序,然后从缓存取出指定分数范围内的缓存元素及元素对应的分数。
- 参数:
- key:缓存键
- min:最小分数
- max:最大分数
- 返回值:返回结果集合
示例:
ZSetOperations<String, String> operations = redisTemplate.opsForZSet();
Set<ZSetOperations.TypedTuple<String>> tuples = new HashSet<>();
tuples.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("aaa", 45.5));
tuples.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("bbb", 23.0));
tuples.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("ccc", 12.9));
tuples.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("ddd", 42.2));
tuples.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("eee", 77.7));
tuples.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("fff", 45.7));
operations.add("zs-key", tuples);
Set<ZSetOperations.TypedTuple<String>> result1 = operations.reverseRangeByScoreWithScores("zs-key", 0, 100);
for (ZSetOperations.TypedTuple<String> next : result1) {
System.out.println(next.getValue() + " - " + next.getScore());
}
System.out.println("----------------");
Set<ZSetOperations.TypedTuple<String>> result2 = operations.reverseRangeByScoreWithScores("zs-key", 20, 50);
for (ZSetOperations.TypedTuple<String> next : result2) {
System.out.println(next.getValue() + " - " + next.getScore());
}
输出结果:
eee - 77.7
fff - 45.7
aaa - 45.5
ddd - 42.2
bbb - 23.0
ccc - 12.9
----------------
fff - 45.7
aaa - 45.5
ddd - 42.2
bbb - 23.0
Set:先根据分数倒序排序,然后从缓存取出指定分数范围内的缓存元素及元素对应的分数,指定偏移量和返回个数。
- 参数:
- key:缓存键
- min:最小分数
- max:最大分数
- 返回值:返回结果集合
示例:
ZSetOperations<String, String> operations = redisTemplate.opsForZSet();
Set<ZSetOperations.TypedTuple<String>> tuples = new HashSet<>();
tuples.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("aaa", 45.5));
tuples.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("bbb", 23.0));
tuples.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("ccc", 12.9));
tuples.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("ddd", 42.2));
tuples.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("eee", 77.7));
tuples.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("fff", 45.7));
operations.add("zs-key", tuples);
Set<ZSetOperations.TypedTuple<String>> result1 = operations.reverseRangeByScoreWithScores("zs-key", 0, 100, 1, 3);
for (ZSetOperations.TypedTuple<String> next : result1) {
System.out.println(next.getValue() + " - " + next.getScore());
}
System.out.println("----------------");
Set<ZSetOperations.TypedTuple<String>> result2 = operations.reverseRangeByScoreWithScores("zs-key", 20, 50, 1, 2);
for (ZSetOperations.TypedTuple<String> next : result2) {
System.out.println(next.getValue() + " - " + next.getScore());
}
输出结果:
fff - 45.7
aaa - 45.5
ddd - 42.2
----------------
aaa - 45.5
ddd - 42.2
Set:从缓存中取出在范围range内的元素,并按照缓存元素value的字典顺序排序。这个排序只有在有相同分数的情况下才能使用,如果有不同的分数则返回值不确定。
- 参数:
- key:缓存键
- range:范围,内容为缓存元素value的值
- 返回值:返回结果集合
示例:
ZSetOperations<String, String> operations = redisTemplate.opsForZSet();
Set<ZSetOperations.TypedTuple<String>> tuples = new HashSet<>();
tuples.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("aaa", 11.0));
tuples.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("bbb", 11.0));
tuples.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("ccc", 11.0));
tuples.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("ddd", 11.0));
tuples.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("eee", 11.0));
tuples.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("fff", 11.0));
operations.add("zs-key", tuples);
Set<String> result1 = operations.rangeByLex("zs-key", RedisZSetCommands.Range.range().lt("ccc"));
System.out.println("result1 = " + result1);
Set<String> result2 = operations.rangeByLex("zs-key", RedisZSetCommands.Range.range().gt("ccc"));
System.out.println("result2 = " + result2);
输出结果:
result1 = [aaa, bbb]
result2 = [ddd, eee, fff]
Set:从缓存中取出在范围range内的元素,并按照缓存元素value的字典顺序排序,限制返回元素个数。这个排序只有在有相同分数的情况下才能使用,如果有不同的分数则返回值不确定。
- 参数:
- key:缓存键
- range:范围,内容为缓存元素value的值
- limit:限制返回元素个数
- 返回值:返回结果集合
示例:
ZSetOperations<String, String> operations = redisTemplate.opsForZSet();
Set<ZSetOperations.TypedTuple<String>> tuples = new HashSet<>();
tuples.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("aaa", 11.0));
tuples.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("bbb", 11.0));
tuples.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("ccc", 11.0));
tuples.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("ddd", 11.0));
tuples.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("eee", 11.0));
tuples.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("fff", 11.0));
operations.add("zs-key", tuples);
Set<String> result1 = operations.rangeByLex("zs-key", RedisZSetCommands.Range.range().lt("ddd"), RedisZSetCommands.Limit.limit().offset(1).count(2));
System.out.println("result1 = " + result1);
Set<String> result2 = operations.rangeByLex("zs-key", RedisZSetCommands.Range.range().gt("ccc"), RedisZSetCommands.Limit.limit().offset(1).count(2));
System.out.println("result2 = " + result2);
输出结果:
result1 = [bbb, ccc]
result2 = [eee, fff]
Long rank(K key, Object o):根据分数排序,获取指定元素在缓存中的位置索引。
- 参数:
- key:缓存键
- value:指定分数
- 返回值:返回索引值
示例:
ZSetOperations<String, String> operations = redisTemplate.opsForZSet();
Set<ZSetOperations.TypedTuple<String>> tuples = new HashSet<>();
tuples.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("aaa", 11.1));
tuples.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("bbb", 41.20));
tuples.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("ccc", 71.3));
tuples.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("ddd", 21.4));
tuples.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("eee", 61.5));
tuples.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("fff", 11.6));
operations.add("zs-key", tuples);
Long result1 = operations.rank("zs-key", "ccc");
System.out.println("result1 = " + result1);
Long result2 = operations.rank("zs-key", "aaa");
System.out.println("result2 = " + result2);
输出结果:
result1 = 5
result2 = 0
Long reverseRank(K key, Object o):根据分数倒序排序,获取指定元素在缓存中的位置索引。
- 参数:
- key:缓存键
- value:指定分数
- 返回值:返回索引值
示例:
ZSetOperations<String, String> operations = redisTemplate.opsForZSet();
Set<ZSetOperations.TypedTuple<String>> tuples = new HashSet<>();
tuples.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("aaa", 11.1));
tuples.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("bbb", 41.20));
tuples.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("ccc", 71.3));
tuples.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("ddd", 21.4));
tuples.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("eee", 61.5));
tuples.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("fff", 11.6));
operations.add("zs-key", tuples);
Long result1 = operations.reverseRank("zs-key", "ccc");
System.out.println("result1 = " + result1);
Long result2 = operations.reverseRank("zs-key", "aaa");
System.out.println("result2 = " + result2);
输出结果:
result1 = 0
result2 = 5
Double score(K key, Object o):获取缓存中某个元素的分数。
- 参数:
- key:缓存键
- value:指定分数
- 返回值:返回元素的分数
示例:
ZSetOperations<String, String> operations = redisTemplate.opsForZSet();
Set<ZSetOperations.TypedTuple<String>> tuples = new HashSet<>();
tuples.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("aaa", 11.1));
tuples.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("bbb", 41.20));
tuples.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("ccc", 71.3));
tuples.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("ddd", 21.4));
tuples.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("eee", 61.5));
tuples.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("fff", 11.6));
operations.add("zs-key", tuples);
Double result1 = operations.score("zs-key", "ccc");
System.out.println("result1 = " + result1);
Double result2 = operations.score("zs-key", "aaa");
System.out.println("result2 = " + result2);
输出结果:
result1 = 71.3
result2 = 11.1
Double incrementScore(K key, V value, double delta):将缓存中某个值的分组增加 delta,返回增加后的分数结果。
- 参数:
- key:缓存键
- value:指定分数
- delta:增加值
- 返回值:
示例:
ZSetOperations<String, String> operations = redisTemplate.opsForZSet();
Set<ZSetOperations.TypedTuple<String>> tuples = new HashSet<>();
tuples.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("aaa", 11.1));
tuples.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("bbb", 41.20));
tuples.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("ccc", 71.3));
tuples.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("ddd", 21.4));
tuples.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("eee", 61.5));
tuples.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("fff", 11.6));
operations.add("zs-key", tuples);
System.out.println("ccc = " + operations.score("zs-key", "ccc"));
Double result1 = operations.incrementScore("zs-key", "ccc", 22);
System.out.println("result1 = " + result1);
System.out.println("ccc = " + operations.score("zs-key", "ccc"));
输出结果:
ccc = 71.3
result1 = 93.3
ccc = 93.3
Long size(K key):获取缓存中元素的个数。
- 参数:
- key:缓存键
- 返回值:返回统计结果
示例:
ZSetOperations<String, String> operations = redisTemplate.opsForZSet();
Set<ZSetOperations.TypedTuple<String>> tuples = new HashSet<>();
tuples.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("aaa", 11.1));
tuples.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("bbb", 41.20));
tuples.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("ccc", 71.3));
tuples.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("ddd", 21.4));
tuples.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("eee", 61.5));
tuples.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("fff", 11.6));
operations.add("zs-key", tuples);
Long result1 = operations.size("zs-key");
System.out.println("result1 = " + result1);
输出结果:
result1 = 6
Long zCard(K key):获取缓存中元素的个数。
- 参数:
- key:缓存键
- 返回值:返回统计结果
示例:
ZSetOperations<String, String> operations = redisTemplate.opsForZSet();
Set<ZSetOperations.TypedTuple<String>> tuples = new HashSet<>();
tuples.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("aaa", 11.1));
tuples.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("bbb", 41.20));
tuples.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("ccc", 71.3));
tuples.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("ddd", 21.4));
tuples.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("eee", 61.5));
tuples.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("fff", 11.6));
operations.add("zs-key", tuples);
Long result1 = operations.zCard("zs-key");
System.out.println("result1 = " + result1);
输出结果:
result1 = 6
Long count(K key, double min, double max):获取指定分数范围缓存中元素的个数,指定最低分数和最高分数。
- 参数:
- key:缓存键
- 返回值:返回统计结果
示例:
ZSetOperations<String, String> operations = redisTemplate.opsForZSet();
Set<ZSetOperations.TypedTuple<String>> tuples = new HashSet<>();
tuples.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("aaa", 11.1));
tuples.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("bbb", 41.20));
tuples.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("ccc", 71.3));
tuples.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("ddd", 21.4));
tuples.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("eee", 61.5));
tuples.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("fff", 11.6));
operations.add("zs-key", tuples);
Long result1 = operations.count("zs-key",0,100);
System.out.println("result1 = " + result1);
Long result2 = operations.count("zs-key",20,50);
System.out.println("result2 = " + result2);
输出结果:
result1 = 6
result2 = 2
Long intersectAndStore(K key, K otherKey, K destKey):两个集合取交集,并将交集结果保存到指定缓存键中,交集结果中,相同的值分数会直接累加。
- 参数:
- key:缓存键
- otherKey:其他缓存键
- destKey:目标缓存键
- 返回值:返回结果集数量
示例:
ZSetOperations<String, String> operations = redisTemplate.opsForZSet();
Set<ZSetOperations.TypedTuple<String>> tuples1 = new HashSet<>();
tuples1.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("aaa", 11.1));
tuples1.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("bbb", 41.20));
tuples1.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("ccc", 71.3));
tuples1.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("ddd", 21.4));
operations.add("zs-key-1", tuples1);
Set<ZSetOperations.TypedTuple<String>> tuples2 = new HashSet<>();
tuples2.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("aaa", 11.1));
tuples2.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("bbb", 41.20));
tuples2.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("eee", 61.5));
tuples2.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("fff", 11.6));
operations.add("zs-key-2", tuples2);
Long result = operations.intersectAndStore("zs-key-1", "zs-key-2", "zs-key-new");
System.out.println("result = " + result);
Set<ZSetOperations.TypedTuple<String>> tuples = operations.rangeWithScores("zs-key-new", 0, -1);
for (ZSetOperations.TypedTuple<String> next : tuples) {
System.out.println(next.getValue() + " - " + next.getScore());
}
输出结果:
result = 2
aaa - 22.2
bbb - 82.4
Long intersectAndStore(K key, Collection:多个集合取交集,并将交集结果保存到指定缓存键中,交集结果中,相同的值分数会直接累加。
- 参数:
- key:缓存键
- otherKeys:其他缓存键集合
- destKey:目标缓存键
- 返回值:返回结果集数量
示例:
ZSetOperations<String, String> operations = redisTemplate.opsForZSet();
Set<ZSetOperations.TypedTuple<String>> tuples1 = new HashSet<>();
tuples1.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("aaa", 11.1));
tuples1.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("bbb", 41.20));
tuples1.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("ccc", 71.3));
tuples1.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("ddd", 21.4));
operations.add("zs-key-1", tuples1);
Set<ZSetOperations.TypedTuple<String>> tuples2 = new HashSet<>();
tuples2.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("aaa", 11.1));
tuples2.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("bbb", 21.20));
tuples2.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("eee", 61.5));
tuples2.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("fff", 11.6));
operations.add("zs-key-2", tuples2);
Set<ZSetOperations.TypedTuple<String>> tuples3 = new HashSet<>();
tuples3.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("aaa", 11.1));
tuples3.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("ccc", 41.20));
tuples3.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("ddd", 61.5));
tuples3.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("fff", 11.6));
operations.add("zs-key-3", tuples3);
Long result = operations.intersectAndStore("zs-key-1", Arrays.asList("zs-key-2","zs-key-3"), "zs-key-new");
System.out.println("result = " + result);
Set<ZSetOperations.TypedTuple<String>> tuples = operations.rangeWithScores("zs-key-new", 0, -1);
for (ZSetOperations.TypedTuple<String> next : tuples) {
System.out.println(next.getValue() + " - " + next.getScore());
}
输出结果:
result = 1
aaa - 33.3
Long intersectAndStore(K key, Collection:多个集合取交集,并将交集结果保存到指定缓存键中,使用指定聚合函数获取交集元素,交集结果中,相同的值分数会直接累加。
- 参数:
- key:缓存键
- otherKeys:其他缓存键集合
- destKey:目标缓存键
- aggregate:聚合函数
- MAX:结果集中相同的值的分数取最大值
- MIN:结果集中相同的值的分数取最小值
- SUM:结果集中相同的值的分数相加
- 返回值:返回结果集数量
示例:
ZSetOperations<String, String> operations = redisTemplate.opsForZSet();
Set<ZSetOperations.TypedTuple<String>> tuples1 = new HashSet<>();
tuples1.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("aaa", 11.1));
tuples1.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("bbb", 41.20));
tuples1.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("ccc", 71.3));
tuples1.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("ddd", 21.4));
operations.add("zs-key-1", tuples1);
Set<ZSetOperations.TypedTuple<String>> tuples2 = new HashSet<>();
tuples2.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("aaa", 11.1));
tuples2.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("bbb", 21.20));
tuples2.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("ddd", 61.5));
tuples2.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("fff", 11.6));
operations.add("zs-key-2", tuples2);
Set<ZSetOperations.TypedTuple<String>> tuples3 = new HashSet<>();
tuples3.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("aaa", 11.1));
tuples3.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("ccc", 41.20));
tuples3.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("ddd", 61.5));
tuples3.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("fff", 11.6));
operations.add("zs-key-3", tuples3);
Long result1 = operations.intersectAndStore("zs-key-1", Arrays.asList("zs-key-2","zs-key-3"), "zs-key-new",RedisZSetCommands.Aggregate.MIN);
System.out.println("result1 = " + result1);
Set<ZSetOperations.TypedTuple<String>> tupleSet1 = operations.rangeWithScores("zs-key-new", 0, -1);
for (ZSetOperations.TypedTuple<String> next : tupleSet1) {
System.out.println(next.getValue() + " - " + next.getScore());
}
Long result2 = operations.intersectAndStore("zs-key-1", Arrays.asList("zs-key-2","zs-key-3"), "zs-key-new",RedisZSetCommands.Aggregate.MAX);
System.out.println("result2 = " + result2 );
Set<ZSetOperations.TypedTuple<String>> tupleSet2 = operations.rangeWithScores("zs-key-new", 0, -1);
for (ZSetOperations.TypedTuple<String> next : tupleSet2) {
System.out.println(next.getValue() + " - " + next.getScore());
}
输出结果:
result1 = 2
aaa - 11.1
ddd - 21.4
result2 = 2
aaa - 31.1
ddd - 61.5
Long intersectAndStore(K key, Collection:多个集合取交集,并将交集结果保存到指定缓存键中,使用指定聚合函数和权重来计算和获取交集元素,权重值会和元素的分数相乘,交集结果中,相同的值分数会直接累加。
- 参数:
- key:缓存键
- otherKeys:其他缓存键集合
- destKey:目标缓存键
- aggregate:聚合函数
- weights:权重
- 返回值:返回结果集数量
示例:
ZSetOperations<String, String> operations = redisTemplate.opsForZSet();
Set<ZSetOperations.TypedTuple<String>> tuples1 = new HashSet<>();
tuples1.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("aaa", 11.1));
tuples1.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("bbb", 41.20));
tuples1.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("ccc", 71.3));
tuples1.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("ddd", 21.4));
operations.add("zs-key-1", tuples1);
Set<ZSetOperations.TypedTuple<String>> tuples2 = new HashSet<>();
tuples2.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("aaa", 31.1));
tuples2.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("bbb", 21.20));
tuples2.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("ddd", 61.5));
tuples2.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("fff", 11.6));
operations.add("zs-key-2", tuples2);
Set<ZSetOperations.TypedTuple<String>> tuples3 = new HashSet<>();
tuples3.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("aaa", 21.1));
tuples3.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("ccc", 41.20));
tuples3.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("ddd", 41.5));
tuples3.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("fff", 61.6));
operations.add("zs-key-3", tuples3);
Long result1 = operations.intersectAndStore("zs-key-1", Arrays.asList("zs-key-2", "zs-key-3"), "zs-key-new",
RedisZSetCommands.Aggregate.MIN, RedisZSetCommands.Weights.of(2, 3, 5));
System.out.println("result1 = " + result1);
Set<ZSetOperations.TypedTuple<String>> tupleSet1 = operations.rangeWithScores("zs-key-new", 0, -1);
for (ZSetOperations.TypedTuple<String> next : tupleSet1) {
System.out.println(next.getValue() + " - " + next.getScore());
}
Long result2 = operations.intersectAndStore("zs-key-1", Arrays.asList("zs-key-2", "zs-key-3"), "zs-key-new",
RedisZSetCommands.Aggregate.MAX, RedisZSetCommands.Weights.of(2, 3, 5));
System.out.println("result2 = " + result2);
Set<ZSetOperations.TypedTuple<String>> tupleSet2 = operations.rangeWithScores("zs-key-new", 0, -1);
for (ZSetOperations.TypedTuple<String> next : tupleSet2) {
System.out.println(next.getValue() + " - " + next.getScore());
}
输出结果:
result1 = 2
aaa - 22.2
ddd - 42.8
result2 = 2
aaa - 105.5
ddd - 207.5
Long unionAndStore(K key, K otherKey, K destKey):两个集合取并集,并将并集结果保存到指定缓存键中。
- 参数:
- key:缓存键
- otherKey:其他缓存键
- destKey:目标缓存键
- 返回值:返回结果集数量
示例:
ZSetOperations<String, String> operations = redisTemplate.opsForZSet();
Set<ZSetOperations.TypedTuple<String>> tuples1 = new HashSet<>();
tuples1.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("aaa", 11.1));
tuples1.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("bbb", 41.20));
tuples1.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("ccc", 71.3));
tuples1.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("ddd", 21.4));
operations.add("zs-key-1", tuples1);
Set<ZSetOperations.TypedTuple<String>> tuples2 = new HashSet<>();
tuples2.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("aaa", 11.1));
tuples2.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("bbb", 21.20));
tuples2.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("eee", 61.5));
tuples2.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("fff", 11.6));
operations.add("zs-key-2", tuples2);
Long result = operations.unionAndStore("zs-key-1", "zs-key-2", "zs-key-new");
System.out.println("result = " + result);
Set<ZSetOperations.TypedTuple<String>> tuples = operations.rangeWithScores("zs-key-new", 0, -1);
for (ZSetOperations.TypedTuple<String> next : tuples) {
System.out.println(next.getValue() + " - " + next.getScore());
}
输出结果:
result = 6
fff - 11.6
ddd - 21.4
aaa - 22.2
eee - 61.5
bbb - 62.400000000000006
ccc - 71.3
Long unionAndStore(K key, Collection:多个集合取并集,并将并集结果保存到指定缓存键中。
- 参数:
- key:缓存键
- otherKeys:其他缓存键集合
- destKey:目标缓存键
- 返回值:返回结果集数量
示例:
ZSetOperations<String, String> operations = redisTemplate.opsForZSet();
Set<ZSetOperations.TypedTuple<String>> tuples1 = new HashSet<>();
tuples1.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("aaa", 11.1));
tuples1.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("bbb", 41.20));
tuples1.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("ccc", 71.3));
tuples1.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("ddd", 21.4));
operations.add("zs-key-1", tuples1);
Set<ZSetOperations.TypedTuple<String>> tuples2 = new HashSet<>();
tuples2.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("aaa", 11.1));
tuples2.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("bbb", 21.20));
tuples2.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("eee", 61.5));
tuples2.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("fff", 11.6));
operations.add("zs-key-2", tuples2);
Set<ZSetOperations.TypedTuple<String>> tuples3 = new HashSet<>();
tuples3.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("aaa", 11.1));
tuples3.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("ccc", 41.20));
tuples3.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("ddd", 61.5));
tuples3.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("fff", 11.6));
operations.add("zs-key-3", tuples3);
Long result = operations.unionAndStore("zs-key-1", Arrays.asList("zs-key-2","zs-key-3"), "zs-key-new");
System.out.println("result = " + result);
Set<ZSetOperations.TypedTuple<String>> tuples = operations.rangeWithScores("zs-key-new", 0, -1);
for (ZSetOperations.TypedTuple<String> next : tuples) {
System.out.println(next.getValue() + " - " + next.getScore());
}
输出结果:
result = 6
fff - 23.2
aaa - 33.3
eee - 61.5
bbb - 62.400000000000006
ddd - 82.9
ccc - 112.5
Long unionAndStore(K key, Collection:多个集合取并集,并将并集结果保存到指定缓存键中,使用指定聚合函数获取并集元素。
- 参数:
- key:缓存键
- otherKeys:其他缓存键集合
- destKey:目标缓存键
- aggregate:聚合函数
- 返回值:返回结果集数量
示例:
ZSetOperations<String, String> operations = redisTemplate.opsForZSet();
Set<ZSetOperations.TypedTuple<String>> tuples1 = new HashSet<>();
tuples1.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("aaa", 11.1));
tuples1.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("bbb", 41.20));
tuples1.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("ccc", 71.3));
tuples1.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("ddd", 21.4));
operations.add("zs-key-1", tuples1);
Set<ZSetOperations.TypedTuple<String>> tuples2 = new HashSet<>();
tuples2.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("aaa", 31.1));
tuples2.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("bbb", 21.20));
tuples2.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("ddd", 61.5));
tuples2.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("fff", 11.6));
operations.add("zs-key-2", tuples2);
Set<ZSetOperations.TypedTuple<String>> tuples3 = new HashSet<>();
tuples3.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("aaa", 21.1));
tuples3.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("ccc", 41.20));
tuples3.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("ddd", 41.5));
tuples3.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("fff", 61.6));
operations.add("zs-key-3", tuples3);
Long result1 = operations.unionAndStore("zs-key-1", Arrays.asList("zs-key-2", "zs-key-3"), "zs-key-new",
RedisZSetCommands.Aggregate.MIN);
System.out.println("result1 = " + result1);
Set<ZSetOperations.TypedTuple<String>> tupleSet1 = operations.rangeWithScores("zs-key-new", 0, -1);
for (ZSetOperations.TypedTuple<String> next : tupleSet1) {
System.out.println(next.getValue() + " - " + next.getScore());
}
Long result2 = operations.unionAndStore("zs-key-1", Arrays.asList("zs-key-2", "zs-key-3"), "zs-key-new",
RedisZSetCommands.Aggregate.MAX);
System.out.println("result2 = " + result2);
Set<ZSetOperations.TypedTuple<String>> tupleSet2 = operations.rangeWithScores("zs-key-new", 0, -1);
for (ZSetOperations.TypedTuple<String> next : tupleSet2) {
System.out.println(next.getValue() + " - " + next.getScore());
}
输出结果:
result1 = 6
aaa - 11.1
fff - 11.6
bbb - 21.2
ddd - 21.4
ccc - 41.2
eee - 61.5
result2 = 6
aaa - 31.1
bbb - 41.2
ddd - 61.5
eee - 61.5
fff - 61.6
ccc - 71.3
Long unionAndStore(K key, Collection:多个集合取并集,并将并集结果保存到指定缓存键中,使用指定聚合函数和权重来计算和获取并集元素,权重值会和元素的分数相乘。
- 参数:
- key:缓存键
- otherKeys:其他缓存键集合
- destKey:目标缓存键
- aggregate:聚合函数
- weights:权重
- 返回值:返回结果集数量
示例:
ZSetOperations<String, String> operations = redisTemplate.opsForZSet();
Set<ZSetOperations.TypedTuple<String>> tuples1 = new HashSet<>();
tuples1.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("aaa", 11.1));
tuples1.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("bbb", 41.20));
tuples1.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("ccc", 71.3));
tuples1.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("ddd", 21.4));
operations.add("zs-key-1", tuples1);
Set<ZSetOperations.TypedTuple<String>> tuples2 = new HashSet<>();
tuples2.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("aaa", 31.1));
tuples2.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("bbb", 21.20));
tuples2.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("ddd", 61.5));
tuples2.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("fff", 11.6));
operations.add("zs-key-2", tuples2);
Set<ZSetOperations.TypedTuple<String>> tuples3 = new HashSet<>();
tuples3.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("aaa", 21.1));
tuples3.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("ccc", 41.20));
tuples3.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("ddd", 41.5));
tuples3.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("fff", 61.6));
operations.add("zs-key-3", tuples3);
Long result1 = operations.unionAndStore("zs-key-1", Arrays.asList("zs-key-2", "zs-key-3"), "zs-key-new",
RedisZSetCommands.Aggregate.MIN, RedisZSetCommands.Weights.of(2, 3, 5));
System.out.println("result1 = " + result1);
Set<ZSetOperations.TypedTuple<String>> tupleSet1 = operations.rangeWithScores("zs-key-new", 0, -1);
for (ZSetOperations.TypedTuple<String> next : tupleSet1) {
System.out.println(next.getValue() + " - " + next.getScore());
}
Long result2 = operations.unionAndStore("zs-key-1", Arrays.asList("zs-key-2", "zs-key-3"), "zs-key-new",
RedisZSetCommands.Aggregate.MAX, RedisZSetCommands.Weights.of(2, 3, 5));
System.out.println("result2 = " + result2);
Set<ZSetOperations.TypedTuple<String>> tupleSet2 = operations.rangeWithScores("zs-key-new", 0, -1);
for (ZSetOperations.TypedTuple<String> next : tupleSet2) {
System.out.println(next.getValue() + " - " + next.getScore());
}
输出结果:
result1 = 6
aaa - 22.2
fff - 34.8
ddd - 42.8
bbb - 63.599999999999994
ccc - 142.6
eee - 184.5
result2 = 6
bbb - 82.4
aaa - 105.5
eee - 184.5
ccc - 206.0
ddd - 207.5
fff - 308.0
Cursor:根据匹配规则查询结果集
- 参数:
- key:缓存键
- 返回值:返回结果集
示例:
ZSetOperations<String, String> operations = redisTemplate.opsForZSet();
Set<ZSetOperations.TypedTuple<String>> tuples1 = new HashSet<>();
tuples1.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("aaa", 11.1));
tuples1.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("aab", 41.20));
tuples1.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("aac", 71.3));
tuples1.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("bba", 21.4));
tuples1.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("bbb", 51.4));
tuples1.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("bbaa", 67.3));
tuples1.add(new DefaultTypedTuple<>("bcaab", 85.2));
operations.add("zs-key", tuples1);
Cursor<ZSetOperations.TypedTuple<String>> cursor1 = operations.scan("zs-key", ScanOptions.NONE);
while (cursor1.hasNext()){
ZSetOperations.TypedTuple<String> next = cursor1.next();
System.out.println(next.getValue() + " - " + next.getScore());
}
System.out.println("----------");
Cursor<ZSetOperations.TypedTuple<String>> cursor2 = operations.scan("zs-key", ScanOptions.scanOptions().match("aa*").build());
while (cursor1.hasNext()){
ZSetOperations.TypedTuple<String> next = cursor2.next();
System.out.println(next.getValue() + " - " + next.getScore());
}
输出结果:
aaa - 11.1
fff - 11.6
bba - 21.4
ddd - 21.4
aab - 41.2
bbb - 51.4
eee - 61.5
bbaa - 67.3
aac - 71.3
ccc - 71.3
bcaab - 85.2
----------
三、RedisUtil 工具类封装
@Component
public class RedisUtil {
private static RedisTemplate<String, Object> redisTemplate;
@Autowired
public RedisUtil(RedisTemplate<String, Object> redisTemplate) {
RedisUtil.redisTemplate = redisTemplate;
}
// region redis common method
/**
* common method:删除缓存键key对应的缓存
*
* @param key 缓存键
*/
public static void delete(String key) {
try {
redisTemplate.delete(key);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* common method:批量删除缓存键集合keys对应的缓存
*
* @param keys 缓存键集合
*/
public static void delete(Collection<String> keys) {
try {
redisTemplate.delete(keys);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* common method:缓存键key对应的缓存是否存在
*
* @param key 缓存键
*/
public static Boolean hasKey(String key) {
try {
return redisTemplate.hasKey(key);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return false;
}
}
/**
* common method:获取所有满足正则匹配的缓存键
*
* @param pattern 匹配规则
*/
public static Set<String> keys(String pattern) {
try {
return redisTemplate.keys(pattern);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
}
}
/**
* common method:重命名缓存键
*
* @param oldKey 旧缓存键
* @param newKey 新缓存键
*/
public static void rename(String oldKey, String newKey) {
try {
redisTemplate.rename(oldKey, newKey);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
// endregion
// region redis String
/**
* String 类型缓存:添加缓存
*
* @param key 缓存键
* @param value 缓存值
*/
public static void set(String key, Object value) {
try {
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set(key, value);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* String 类型缓存:添加缓存并指定过期时间
*
* @param key 缓存键
* @param value 缓存值
* @param expireTime 过期时间
* @param timeUnit 时间单位
*/
public static void set(String key, Object value, long expireTime, TimeUnit timeUnit) {
try {
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set(key, value, expireTime, timeUnit);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* String 类型缓存:添加缓存并指定过期时间
*
* @param key 缓存键
* @param value 缓存值
* @param duration 持续时间,Java 8中的类,如 Duration.ofSeconds(5000);
*/
public static void set(String key, Object value, Duration duration) {
try {
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set(key, value, duration);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* String 类型缓存:修改缓存,从指定位置offset开始,修改键为key的缓存的值
* 例如:set("kkk", "new", 4), key:value = "kkk":"this is value" -> key:value = "kkk":"thisnew value"
*
* @param key 缓存键
* @param value 缓存值
* @param offset 指定位置
*/
public static void set(String key, Object value, long offset) {
try {
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set(key, value, offset);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* String 类型缓存:用于设置Redis中位图(bitmaps)的指定偏移量的值。
* 位图是由位(0或1)组成的数据结构,可以用于表示某个事件的状态或者进行位运算。
*
* @param key 缓存键
* @param offset 要设置的位置,以比特为单位。
* @param value 要设置的值,0 或 1。
*/
public static void setBit(String key, long offset, boolean value) {
try {
redisTemplate.opsForValue().setBit(key, offset, value);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* String 类型缓存:添加缓存,缓存键key不存在则添加,key存在则添加失败
*
* @param key 缓存键
* @param value 缓存值
*/
public static void setIfAbsent(String key, Object value) {
try {
redisTemplate.opsForValue().setIfAbsent(key, value);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* String 类型缓存:添加缓存并指定过期时间,缓存键key不存在则添加,key存在则添加失败
*
* @param key 缓存键
* @param value 缓存值
* @param expireTime 过期时间
* @param timeUnit 时间单位
*/
public static void setIfAbsent(String key, Object value, long expireTime, TimeUnit timeUnit) {
try {
redisTemplate.opsForValue().setIfAbsent(key, value, expireTime, timeUnit);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* String 类型缓存:添加缓存并指定过期时间,缓存键key不存在则添加,key存在则添加失败
*
* @param key 缓存键
* @param value 缓存值
* @param duration 持续时间,Java 8中的类,如 Duration.ofSeconds(5000);
*/
public static void setIfAbsent(String key, Object value, Duration duration) {
try {
redisTemplate.opsForValue().setIfAbsent(key, value, duration);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* String 类型缓存:批量添加缓存
*
* @param map 缓存内容,key:value
*/
public static void multiSet(Map<String, Object> map) {
try {
redisTemplate.opsForValue().multiSet(map);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* String 类型缓存:批量添加缓存,map中只要有一个缓存键key不存在则添加失败
*
* @param map 缓存内容,key:value
*/
public static void multiSetIfAbsent(Map<String, Object> map) {
try {
redisTemplate.opsForValue().multiSetIfAbsent(map);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* String 类型缓存:为键key的缓存指定新值value,并获取缓存key的旧值
*
* @param key 缓存键
* @param value 新缓存值
*/
public static void getAndSet(String key, Object value) {
try {
redisTemplate.opsForValue().getAndSet(key, value);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* String 类型缓存:获取缓存
*
* @param key 缓存键
*/
public static Object get(String key) {
try {
return redisTemplate.opsForValue().get(key);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
}
}
/**
* String 类型缓存:获取缓存的一部分,指定开始和结束位置
*
* @param key 缓存键
* @param start 开始位置
* @param end 结束位置
*/
public static String get(String key, long start, long end) {
try {
return redisTemplate.opsForValue().get(key, start, end);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
}
}
/**
* String 类型缓存:获取缓存的位图数据
*
* @param key 缓存键
* @param offset 偏移位置
*/
public static Boolean getBit(String key, long offset) {
try {
return redisTemplate.opsForValue().getBit(key, offset);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
}
}
// endregion
// region redis hash
/**
* Hash 类型缓存:添加缓存
*
* @param key 缓存键
* @param hashKey hash 键
* @param value hash 值
*/
public static void hSet(String key, Object hashKey, Object value) {
try {
redisTemplate.opsForHash().put(key, hashKey, value);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* Hash 类型缓存:批量添加缓存
*
* @param key 缓存键
* @param map hash 键值对
*/
public static void hSet(String key, Map<Object, Object> map) {
try {
redisTemplate.opsForHash().putAll(key, map);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* Hash 类型缓存:添加缓存,hash 键不存在则添加,否则添加失败
*
* @param key 缓存键
* @param hashKey hash 键
* @param value hash 值
*/
public static void hSetIfAbsent(String key, Object hashKey, Object value) {
try {
redisTemplate.opsForHash().putIfAbsent(key, hashKey, value);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* Hash 类型缓存:获取缓存
*
* @param key 缓存键
* @param hashKey hash 键
*/
public static Object hGet(String key, Object hashKey) {
try {
return redisTemplate.opsForHash().get(key, hashKey);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
}
}
/**
* Hash 类型缓存:批量获取缓存
*
* @param key 缓存键
* @param hashKeys hash 键
*/
public static List<Object> hGet(String key, Collection<Object> hashKeys) {
try {
return redisTemplate.opsForHash().multiGet(key, hashKeys);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
}
}
/**
* Hash 类型缓存:获取缓存键下的所有缓存,以键值对的方式返回
*
* @param key 缓存键
*/
public static Map<Object, Object> hEntries(String key) {
try {
return redisTemplate.opsForHash().entries(key);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
}
}
/**
* Hash 类型缓存:获取缓存键key下的所有hash键
*
* @param key 缓存键
*/
public static Set<Object> hKeys(String key) {
try {
return redisTemplate.opsForHash().keys(key);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
}
}
/**
* Hash 类型缓存:获取缓存键key下的所有hash值
*
* @param key 缓存键
*/
public static List<Object> hValues(String key) {
try {
return redisTemplate.opsForHash().values(key);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
}
}
/**
* Hash 类型缓存:删除缓存
*
* @param key 缓存键
* @param hashKeys hash 键列表
*/
public static void hDelete(String key, Object... hashKeys) {
try {
redisTemplate.opsForHash().delete(key, hashKeys);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* Hash 类型缓存:缓存键key下的hash键是否存在
*
* @param key 缓存键
* @param hashKey hash 键
*/
public static Boolean hHasKey(String key, Object hashKey) {
try {
return redisTemplate.opsForHash().hasKey(key, hashKey);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
}
}
/**
* Hash 类型缓存:缓存键key下hash键对应的hash值的长度
*
* @param key 缓存键
* @param hashKey hash 键
*/
public static Long hLengthOfValue(String key, Object hashKey) {
try {
return redisTemplate.opsForHash().lengthOfValue(key, hashKey);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
}
}
/**
* Hash 类型缓存:获取缓存键key下的所有缓存的大小
*
* @param key 缓存键
*/
public static Long hSize(String key) {
try {
return redisTemplate.opsForHash().size(key);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
}
}
/**
* Hash 类型缓存:匹配获取键值对
*
* @param key 缓存键
* @param scanOptions hash 值
*/
public static Cursor<Map.Entry<Object, Object>> hScan(String key, ScanOptions scanOptions) {
try {
return redisTemplate.opsForHash().scan(key, scanOptions);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
}
}
/**
* Hash 类型缓存:使缓存键key下的hash键对应的值以long类型增加delta
* 如果指定的哈希表或字段不存在,那么将会创建一个新的哈希表和字段,并指定值为delta
*
* @param key 缓存键
* @param hashKey hash 键
*/
public static Long hIncrement(String key, Object hashKey, long delta) {
try {
return redisTemplate.opsForHash().increment(key, hashKey, delta);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
}
}
/**
* Hash 类型缓存:使缓存键key下的hash键对应的值以double类型增加delta
* 如果指定的哈希表或字段不存在,那么将会创建一个新的哈希表和字段,并指定值为delta
*
* @param key 缓存键
* @param hashKey hash 键
*/
public static Double hIncrement(String key, Object hashKey, double delta) {
try {
return redisTemplate.opsForHash().increment(key, hashKey, delta);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
}
}
// endregion
// region redis list
/**
* List 类型缓存:向队列头部添加缓存
*
* @param key 缓存键
* @param value 缓存值
*/
public static void lLeftSet(String key, Object value) {
try {
redisTemplate.opsForList().leftPush(key, value);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* List 类型缓存:缓存键key对应的缓存中,将值value添加到指定值pivot的前面
*
* @param key 缓存键
* @param pivot 指定值
* @param value 缓存值
*/
public static void lLeftSet(String key, Object pivot, Object value) {
try {
redisTemplate.opsForList().leftPush(key, pivot, value);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* List 类型缓存:批量向队列头部添加缓存
*
* @param key 缓存键
* @param values 缓存值列表
*/
public static void lLeftSet(String key, Object... values) {
try {
redisTemplate.opsForList().leftPushAll(key, values);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* List 类型缓存:批量向队列头部添加缓存
*
* @param key 缓存键
* @param values 缓存值集合
*/
public static void lLeftSet(String key, Collection<Object> values) {
try {
redisTemplate.opsForList().leftPushAll(key, values);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* List 类型缓存:向队列头部添加缓存,只有缓存列表存在才成功,否则添加失败
*
* @param key 缓存键
* @param value 缓存值
*/
public static void lLeftSetIfPresent(String key, Object value) {
try {
redisTemplate.opsForList().leftPushIfPresent(key, value);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* List 类型缓存:向队列尾部添加缓存
*
* @param key 缓存键
* @param value 缓存值
*/
public static void lRightSet(String key, Object value) {
try {
redisTemplate.opsForList().rightPush(key, value);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* List 类型缓存:缓存键key对应的缓存中,将值value添加到指定值pivot的后面
*
* @param key 缓存键
* @param pivot 指定值
* @param value 缓存值
*/
public static void lRightSet(String key, Object pivot, Object value) {
try {
redisTemplate.opsForList().rightPush(key, pivot, value);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* List 类型缓存:批量向队列尾部添加缓存
*
* @param key 缓存键
* @param values 缓存值列表
*/
public static void lRightSet(String key, Object... values) {
try {
redisTemplate.opsForList().rightPushAll(key, values);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* List 类型缓存:批量向队列尾部添加缓存
*
* @param key 缓存键
* @param values 缓存值集合
*/
public static void lRightSet(String key, Collection<Object> values) {
try {
redisTemplate.opsForList().rightPushAll(key, values);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* List 类型缓存:向队列尾部添加缓存,只有缓存列表存在才成功,否则添加失败
*
* @param key 缓存键
* @param value 缓存值
*/
public static void lRightSetIfPresent(String key, Object value) {
try {
redisTemplate.opsForList().rightPushIfPresent(key, value);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* List 类型缓存:键key的缓存中,替换索引index对应的值为value
*
* @param key 缓存键
* @param index 指定索引,从0开始
* @param value 缓存值
*/
public static void lSet(String key, long index, Object value) {
try {
redisTemplate.opsForList().set(key, index, value);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* List 类型缓存:获取键key的缓存,指定开始索引和结束索引
*
* @param key 缓存键
* @param start 开始索引,从0开始
* @param end 结束索引,-1为最后一个
*/
public static List<Object> lRange(String key, long start, long end) {
try {
return redisTemplate.opsForList().range(key, start, end);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
}
}
/**
* List 类型缓存:从键key对应的缓存中取出索引为index的元素
*
* @param key 缓存键
* @param index 指定索引,索引超过实际缓存大小,返回null,不会报错
*/
public static Object lIndex(String key, long index) {
try {
return redisTemplate.opsForList().index(key, index);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
}
}
/**
* List 类型缓存:键key的缓存中,移除值value出现的前count个
*
* @param key 缓存键
* @param count 出现次数,次数大于出现的实际次数,移除所有该值,不会报错
* @param value 缓存值
*/
public static void lRemove(String key, long count, Object value) {
try {
redisTemplate.opsForList().remove(key, count, value);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* List 类型缓存:键key的缓存中,从头部取出第一个元素
*
* @param key 缓存键
*/
public static Object lLeftGet(String key) {
try {
return redisTemplate.opsForList().leftPop(key);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
}
}
/**
* List 类型缓存:键key的缓存中,从头部取出第一个元素
* 阻塞连接,直到元素可用或者时间超时
*
* @param key 缓存键
* @param expireTime 超时时间
* @param timeUnit 时间单位
*/
public static Object lLeftGet(String key, long expireTime, TimeUnit timeUnit) {
try {
return redisTemplate.opsForList().leftPop(key, expireTime, timeUnit);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
}
}
/**
* List 类型缓存:键key的缓存中,从头部取出第一个元素
* 阻塞连接,直到元素可用或者时间超时
*
* @param key 缓存键
* @param duration 持续时间
*/
public static Object lLeftGet(String key, Duration duration) {
try {
return redisTemplate.opsForList().leftPop(key, duration);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
}
}
/**
* List 类型缓存:键key的缓存中,从尾部取出第一个元素
*
* @param key 缓存键
*/
public static Object lRightGet(String key) {
try {
return redisTemplate.opsForList().rightPop(key);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
}
}
/**
* List 类型缓存:键key的缓存中,从尾部取出第一个元素
* 阻塞连接,直到元素可用或者时间超时
*
* @param key 缓存键
* @param expireTime 超时时间
* @param timeUnit 时间单位
*/
public static Object lRightGet(String key, long expireTime, TimeUnit timeUnit) {
try {
return redisTemplate.opsForList().rightPop(key, expireTime, timeUnit);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
}
}
/**
* List 类型缓存:键key的缓存中,从尾部取出第一个元素
* 阻塞连接,直到元素可用或者时间超时
*
* @param key 缓存键
* @param duration 持续时间
*/
public static Object lRightGet(String key, Duration duration) {
try {
return redisTemplate.opsForList().rightPop(key, duration);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
}
}
/**
* List 类型缓存:从键sourceKey的缓存尾部取出一个元素,并将此元素添加到键destinationKey的缓存头部
*
* @param sourceKey 数据缓存键
* @param destinationKey 目标缓存键
*/
public static Object lRightPopAndLeftPush(String sourceKey, String destinationKey) {
try {
return redisTemplate.opsForList().rightPopAndLeftPush(sourceKey, destinationKey);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
}
}
/**
* List 类型缓存:从键sourceKey的缓存尾部取出一个元素,并将此元素添加到键destinationKey的缓存头部
* 阻塞连接,直到元素可用或者时间超时
*
* @param sourceKey 数据缓存键
* @param destinationKey 目标缓存键
* @param expireTime 过期时间
* @param timeUnit 时间单位
*/
public static Object lRightPopAndLeftPush(String sourceKey, String destinationKey, long expireTime, TimeUnit timeUnit) {
try {
return redisTemplate.opsForList().rightPopAndLeftPush(sourceKey, destinationKey, expireTime, timeUnit);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
}
}
/**
* List 类型缓存:从键sourceKey的缓存尾部取出一个元素,并将此元素添加到键destinationKey的缓存头部
* 阻塞连接,直到元素可用或者时间超时
*
* @param sourceKey 数据缓存键
* @param destinationKey 目标缓存键
* @param duration 持续时间
*/
public static Object lRightPopAndLeftPush(String sourceKey, String destinationKey, Duration duration) {
try {
return redisTemplate.opsForList().rightPopAndLeftPush(sourceKey, destinationKey, duration);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
}
}
/**
* List 类型缓存:统计键key对应缓存的元素格式
*
* @param key 缓存键
*/
public static Long lSize(String key) {
try {
return redisTemplate.opsForList().size(key);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
}
}
/**
* List 类型缓存:截取键key对应的缓存,指定开始索引和结束索引
*
* @param key 缓存键
* @param start 开始索引
* @param end 结束索引
*/
public static void lTrim(String key, long start, long end) {
try {
redisTemplate.opsForList().trim(key, start, end);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
// endregion
// region redis set
/**
* Set 类型缓存:添加元素
*
* @param key 缓存键
* @param values 缓存值列表
*/
public static void sSet(String key, Object... values) {
try {
redisTemplate.opsForSet().add(key, values);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* Set 类型缓存:移除元素
*
* @param key 缓存键
* @param values 缓存值列表
*/
public static void sRemove(String key, Object... values) {
try {
redisTemplate.opsForSet().remove(key, values);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* Set 类型缓存:从键key的缓存中随机移除一个元素,并返回元素的值
*
* @param key 缓存键
*/
public static Object sPop(String key) {
try {
return redisTemplate.opsForSet().pop(key);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
}
}
/**
* Set 类型缓存:从键key的缓存中随机移除count个元素,并返回这些元素的值
*
* @param key 缓存键
* @param count 元素个数
*/
public static List<Object> sPop(String key, long count) {
try {
return redisTemplate.opsForSet().pop(key, count);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
}
}
/**
* Set 类型缓存:从键key的缓存中随机返回一个元素
*
* @param key 缓存键
*/
public static Object sRandomMember(String key) {
try {
return redisTemplate.opsForSet().randomMember(key);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
}
}
/**
* Set 类型缓存:从键key的缓存中随机返回count个元素,返回元素可重复
*
* @param key 缓存键
* @param count 元素个数
*/
public static List<Object> sRandomMembers(String key, long count) {
try {
return redisTemplate.opsForSet().randomMembers(key, count);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
}
}
/**
* Set 类型缓存:从键key的缓存中随机返回count个不重复的元素
* 超过元素总个数会返回所有元素,不报错
*
* @param key 缓存键
* @param count 元素个数
*/
public static Set<Object> sDistinctRandomMembers(String key, long count) {
try {
return redisTemplate.opsForSet().distinctRandomMembers(key, count);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
}
}
/**
* Set 类型缓存:判断指定元素在键key的缓存是否存在
*
* @param key 缓存键
* @param value 缓存值
*/
public static Boolean sExists(String key, Object value) {
try {
return redisTemplate.opsForSet().isMember(key, value);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
}
}
/**
* Set 类型缓存:统计键key的缓存元素个数
*
* @param key 缓存键
*/
public static Long sSize(String key) {
try {
return redisTemplate.opsForSet().size(key);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
}
}
/**
* Set 类型缓存:从键key的缓存中取出元素value添加到目标缓存键destKey的缓存中
*
* @param key 原缓存键
* @param value 缓存值
* @param destKey 目标缓存键
*/
public static Boolean sMove(String key, Object value, String destKey) {
try {
return redisTemplate.opsForSet().move(key, value, destKey);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
}
}
/**
* Set 类型缓存:比较并返回指定键和其他键对应的缓存中不同的元素
* 返回的元素为指定缓存键中不同的元素
*
* @param key 指定缓存键
* @param otherKey 其他缓存键
*/
public static Set<Object> sDifference(String key, String otherKey) {
try {
return redisTemplate.opsForSet().difference(key, otherKey);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
}
}
/**
* Set 类型缓存:比较并返回指定键和其他键对应的缓存中不同的元素
* 返回的元素为指定缓存键中不同的元素
*
* @param key 指定缓存键
* @param otherKeys 其他缓存键集合
*/
public static Set<Object> sDifference(String key, Collection<String> otherKeys) {
try {
return redisTemplate.opsForSet().difference(key, otherKeys);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
}
}
/**
* Set 类型缓存:比较缓存键集合中各个键对应的缓存中不同的元素
* 返回的元素为缓存键集合中第一个键对应的缓存中不同的元素
*
* @param keys 缓存键集合
*/
public static Set<Object> sDifference(Collection<String> keys) {
try {
return redisTemplate.opsForSet().difference(keys);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
}
}
/**
* Set 类型缓存:比较指定键和其他键对应的缓存中不同的元素,并将不同的元素另外缓存
* 缓存的元素为指定缓存键中不同的元素
*
* @param key 指定缓存键
* @param otherKey 其他缓存键
* @param destKey 目标缓存键
*/
public static void sDifferenceAndStore(String key, String otherKey, String destKey) {
try {
redisTemplate.opsForSet().differenceAndStore(key, otherKey, destKey);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* Set 类型缓存:比较指定键和其他键对应的缓存中不同的元素,并将不同的元素另外缓存
* 缓存的元素为指定缓存键中不同的元素
*
* @param key 指定缓存键
* @param otherKeys 其他缓存键集合
* @param destKey 目标缓存键
*/
public static void sDifferenceAndStore(String key, Collection<String> otherKeys, String destKey) {
try {
redisTemplate.opsForSet().differenceAndStore(key, otherKeys, destKey);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* Set 类型缓存:比较缓存键集合中各个键对应的缓存中不同的元素,并将不同的元素另外缓存
* 缓存的元素为缓存键集合中第一个键对应的缓存中不同的元素
*
* @param keys 缓存键集合
* @param destKey 目标缓存键
*/
public static void sDifferenceAndStore(Collection<String> keys, String destKey) {
try {
redisTemplate.opsForSet().differenceAndStore(keys, destKey);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* Set 类型缓存:比较并返回指定键和其他键对应的缓存中相同的元素
*
* @param key 指定缓存键
* @param otherKey 其他缓存键
*/
public static Set<Object> sIntersect(String key, String otherKey) {
try {
return redisTemplate.opsForSet().intersect(key, otherKey);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
}
}
/**
* Set 类型缓存:比较并返回指定键和其他键对应的缓存中相同的元素
*
* @param key 指定缓存键
* @param otherKeys 其他缓存键集合
*/
public static Set<Object> sIntersect(String key, Collection<String> otherKeys) {
try {
return redisTemplate.opsForSet().intersect(key, otherKeys);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
}
}
/**
* Set 类型缓存:比较缓存键集合中各个键对应的缓存中相同的元素
*
* @param keys 缓存键集合
*/
public static Set<Object> sIntersect(Collection<String> keys) {
try {
return redisTemplate.opsForSet().intersect(keys);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
}
}
/**
* Set 类型缓存:比较指定键和其他键对应的缓存中相同的元素,并将相同的元素另外缓存
*
* @param key 指定缓存键
* @param otherKey 其他缓存键
* @param destKey 目标缓存键
*/
public static void sIntersectAndStore(String key, String otherKey, String destKey) {
try {
redisTemplate.opsForSet().intersectAndStore(key, otherKey, destKey);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* Set 类型缓存:比较指定键和其他键对应的缓存中相同的元素,并将相同的元素另外缓存
*
* @param key 指定缓存键
* @param otherKeys 其他缓存键集合
* @param destKey 目标缓存键
*/
public static void sIntersectAndStore(String key, Collection<String> otherKeys, String destKey) {
try {
redisTemplate.opsForSet().intersectAndStore(key, otherKeys, destKey);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* Set 类型缓存:比较缓存键集合中各个键对应的缓存中相同的元素,并将相同的元素另外缓存
*
* @param keys 缓存键集合
* @param destKey 目标缓存键
*/
public static void sIntersectAndStore(Collection<String> keys, String destKey) {
try {
redisTemplate.opsForSet().intersectAndStore(keys, destKey);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* Set 类型缓存:比较并返回指定键和其他键对应的缓存中所有的元素,会去重
*
* @param key 指定缓存键
* @param otherKey 其他缓存键
*/
public static Set<Object> sUnion(String key, String otherKey) {
try {
return redisTemplate.opsForSet().union(key, otherKey);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
}
}
/**
* Set 类型缓存:比较并返回指定键和其他键对应的缓存中所有的元素,会去重
*
* @param key 指定缓存键
* @param otherKeys 其他缓存键集合
*/
public static Set<Object> sUnion(String key, Collection<String> otherKeys) {
try {
return redisTemplate.opsForSet().union(key, otherKeys);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
}
}
/**
* Set 类型缓存:比较缓存键集合中各个键对应的缓存中所有的元素,会去重
*
* @param keys 缓存键集合
*/
public static Set<Object> sUnion(Collection<String> keys) {
try {
return redisTemplate.opsForSet().union(keys);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
}
}
/**
* Set 类型缓存:比较指定键和其他键对应的缓存中所有的元素,会去重,并将合并的元素另外缓存
*
* @param key 指定缓存键
* @param otherKey 其他缓存键
* @param destKey 目标缓存键
*/
public static void sUnionAndStore(String key, String otherKey, String destKey) {
try {
redisTemplate.opsForSet().unionAndStore(key, otherKey, destKey);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* Set 类型缓存:比较指定键和其他键对应的缓存中所有的元素,会去重,并将合并的元素另外缓存
*
* @param key 指定缓存键
* @param otherKeys 其他缓存键集合
* @param destKey 目标缓存键
*/
public static void sUnionAndStore(String key, Collection<String> otherKeys, String destKey) {
try {
redisTemplate.opsForSet().unionAndStore(key, otherKeys, destKey);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* Set 类型缓存:比较缓存键集合中各个键对应的缓存中所有的元素,会去重,并将合并的元素另外缓存
*
* @param keys 缓存键集合
* @param destKey 目标缓存键
*/
public static void sUnionAndStore(Collection<String> keys, String destKey) {
try {
redisTemplate.opsForSet().unionAndStore(keys, destKey);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* Set 类型缓存:从键key的缓存中匹配查找元素
*
* @param key 缓存键
* @param scanOptions 匹配规则
*/
public static Cursor<Object> sScan(String key, ScanOptions scanOptions) {
try {
return redisTemplate.opsForSet().scan(key, scanOptions);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
}
}
// endregion
// region redis zset
/**
* ZSet 类型缓存:添加缓存
*
* @param key 缓存键
* @param value 缓存值
* @param score 分数
*/
public static void zsSet(String key, Object value, double score) {
try {
redisTemplate.opsForZSet().add(key, value, score);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* ZSet 类型缓存:批量添加缓存
* 示例:
* Set> tuples = new HashSet<>();
* ZSetOperations.TypedTuple
public static void zsSet(String key, Set<ZSetOperations.TypedTuple<Object>> tuples) {
try {
redisTemplate.opsForZSet().add(key, tuples);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* ZSet 类型缓存:删除缓存
*
* @param key 缓存键
* @param values 缓存值列表
*/
public static void zsRemove(String key, Object... values) {
try {
redisTemplate.opsForZSet().remove(key, values);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* ZSet 类型缓存:根据索引排序后,删除指定索引范围内的缓存,指定开始索引和结束索引
*
* @param key 缓存键
* @param start 开始索引
* @param end 结束索引
*/
public static void zsRemoveRange(String key, long start, long end) {
try {
redisTemplate.opsForZSet().removeRange(key, start, end);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* ZSet 类型缓存:根据分数排序后,删除指定范围内的缓存,指定最小分数和最大分数
*
* @param key 缓存键
* @param min 最小分数
* @param max 最大分数
*/
public static void zsRemoveRangeByScore(String key, double min, double max) {
try {
redisTemplate.opsForZSet().removeRangeByScore(key, min, max);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* ZSet 类型缓存:获取缓存元素,指定开始索引和结束索引
*
* @param key 缓存键
* @param start 开始索引
* @param end 结束索引
*/
public static Set<Object> zsRange(String key, long start, long end) {
try {
return redisTemplate.opsForZSet().range(key, start, end);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
}
}
/**
* ZSet 类型缓存:获取缓存元素,指定开始索引和结束索引,倒序排序
*
* @param key 缓存键
* @param start 开始索引
* @param end 结束索引
*/
public static Set<Object> zsReverseRange(String key, long start, long end) {
try {
return redisTemplate.opsForZSet().reverseRange(key, start, end);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
}
}
/**
* ZSet 类型缓存:从缓存中取出在范围range内的元素,并按照缓存元素value的字典顺序排序
*
* @param key 缓存键
* @param range 范围,内容为缓存元素value的值
*/
public static Set<Object> zsRangeByLex(String key, RedisZSetCommands.Range range) {
try {
return redisTemplate.opsForZSet().rangeByLex(key, range);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
}
}
/**
* ZSet 类型缓存:从缓存中取出在范围range内的元素,并按照缓存元素value的字典顺序排序
*
* @param key 缓存键
* @param range 范围,内容为缓存元素value的值
* @param limit 限制返回元素个数
*/
public static Set<Object> zsRangeByLex(String key, RedisZSetCommands.Range range, RedisZSetCommands.Limit limit) {
try {
return redisTemplate.opsForZSet().rangeByLex(key, range, limit);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
}