【C++】类的声明 与 类的实现 分开 ② ( 头文件导入多次报错 | 头文件的作用 | 类的声明 | 类的实现 | 代码示例 - 类的使用 )
文章目录
- 一、头文件导入多次报错
-
- 1、头文件没有 #pragma once 报错
- 2、头文件加上 #pragma once 编译成功
- 二、头文件的作用
- 三、类的声明
- 四、类的实现
- 五、代码示例 - 类的使用
-
- main 入口程序代码
- 头文件代码
- 类实现代码
一、头文件导入多次报错
1、头文件没有 #pragma once 报错
在 .cpp 源码文件中 , 使用 #include "Student.h" 代码 , 包含头文件 ,
使用
#include "Student.h"
#include "Student.h"
代码 的作用 , 相当于将 Student.h 头文件中的所有内容 , 拷贝了 2 次 ,
其效果类等同于 :
class Student
{
};
class Student
{
};
编译时会报如下 " “Student”:“class”类型重定义 " 错误 :
1>------ 已启动生成: 项目: HelloWorld, 配置: Debug Win32 ------
1>Student.cpp
1>Y:\002_WorkSpace\002_VS\HelloWorld\HelloWorld\Student.h(15,1): error C2011: “Student”:“class”类型重定义
1>Y:\002_WorkSpace\002_VS\HelloWorld\HelloWorld\Student.h(14): message : 参见“Student”的声明
1>已完成生成项目“HelloWorld.vcxproj”的操作 - 失败。
========== 生成: 成功 0 个,失败 1 个,最新 0 个,跳过 0 个 ==========
2、头文件加上 #pragma once 编译成功
在头文件中 , 加上了 #pragma once 代码 , 即使在代码中 , 导入了 2 次头文件 , 也可以正常编译 , 不会报错 ;
#include "Student.h"
#include "Student.h"
二、头文件的作用
在 .h 头文件中 , 只是对 变量 / 类 / 函数 , 进行声明 , 不实现它们 ;
导入 .h 头文件 的 作用是可以访问这些 变量 / 类 / 函数 的 声明 ;
在 实际 开发中 , 有两种情况下是需要导入 .h 头文件 的 :
- 以 实现 声明的 变量 / 类 / 函数 为目的 , 自己开发函数库 给别人用 ;
- 以 使用 声明的 变量 / 类 / 函数 为目的 , 使用别人开发的函数库 , 导入了头文件 , 即可访问头文件中声明的 变量 / 类 / 函数 ;
三、类的声明
在 Student.h 头文件中 , 定义 class Student 类 , 只声明该类 , 以及类的 成员属性 和 成员函数 ;
不实现 成员函数 ;
成员函数 在 对应的 Student.cpp 中实现 ;
代码示例 :
// 确保 该头文件 只包含一次
#pragma once
/*
// C 语言中可使用如下宏定义确保 头文件 只被包含一次
#ifndef Student_H
#define Student_H
// 源码主要内容
#endif // !Student_H
*/
class Student
{
private:
int age;
char name[64];
public:
void setAge(int age);
int getAge();
};
四、类的实现
在 Student.cpp 源码中 , 导入 Student.h 头文件 , 这是 创建 Student 类时自动生成的 ;
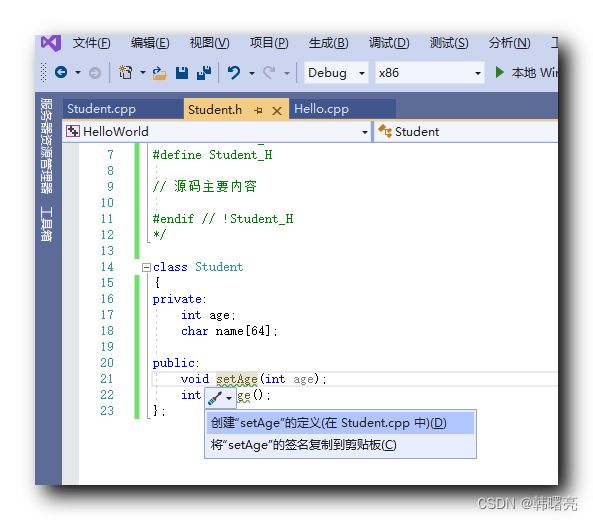
在类中声明成员函数 void setAge(int age); , 如果没有实现该成员函数 , 鼠标移动上去后 , 会报如下错误 ;
选第一个选项 , 即可在 Student.cpp 中生成实现该函数的代码 ;
void setAge(int age);
int getAge();
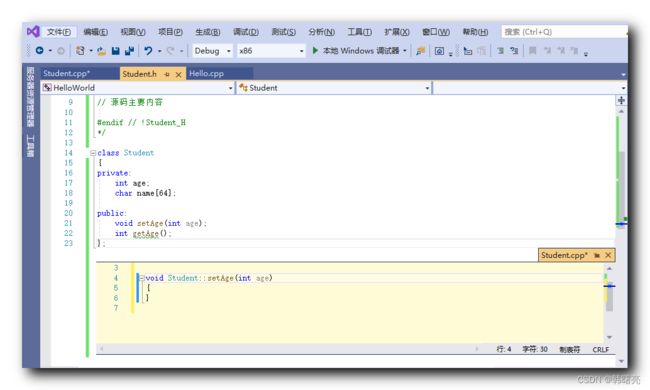
对应的 Student.cpp 中的方法如下 :
void Student::setAge(int age)
{
m_age = age;
}
int Student::getAge()
{
return m_age;
}
在 void Student::setAge(int age) 方法中 , 可以直接访问 Student 中的成员 , 使用 域作用符 等同于 类内部的环境 ;
五、代码示例 - 类的使用
首先 , 导入 Student.h 头文件 , 其中声明了类 , 可以直接使用类 ;
// 导入自定义类
#include "Student.h"
然后 , 直接在 main 函数中使用 Student 类即可 ; 先声明类 , 为类成员赋值 , 然后打印类的成员 ;
Student s;
s.setAge(18);
cout<< s.getAge() << endl;
main 入口程序代码
代码示例 :
// 导入标准 io 流头文件 其中定义了 std 命名空间
#include 执行结果 :
头文件代码
// 确保 该头文件 只包含一次
#pragma once
/*
// C 语言中可使用如下宏定义确保 头文件 只被包含一次
#ifndef Student_H
#define Student_H
// 源码主要内容
#endif // !Student_H
*/
class Student
{
private:
int m_age;
char m_name[64];
public:
void setAge(int age);
int getAge();
};
类实现代码
#include "Student.h"
void Student::setAge(int age)
{
m_age = age;
}
int Student::getAge()
{
return m_age;
}