用原生JS实现虚拟列表
最近在开发需求的时候,有用到 Antd 的虚拟列表组件 rc-virtual-list ,粗略地看了一下源码,于是萌生了自己写一个虚拟列表的想法。
当一个列表需要渲染大量数据的时候是非常耗时的,而且在列表滚动的过程中会出现卡顿的现象。即使用上懒加载解决了列表初始化时渲染过慢的问题,但是每次拉取下一页数据的时候都会造成列表的重新渲染。随着拉取的数据越来越多,列表渲染时间长、卡顿的问题依然存在。
这个时候虚拟列表就派上用场了。虚拟列表的实现原理简单来说,就是列表并不会把所有的数据都渲染出来,而是通过监听滚动事件然后实时计算当前是哪几条数据显示在页面上,然后只渲染用户可以看见的这几条数据。
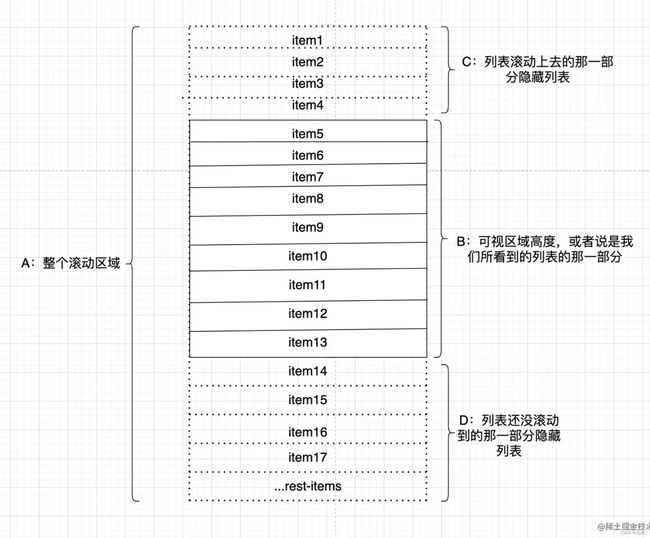
在网上找了张图可以说明的更生动些:
定高虚拟列表
实现虚拟列表需要两层的div:
<style>
.list-container {
overflow: auto;
border: 1px solid black;
height: 500px;
}
style>
<body>
<div class="list-container">
<div class="list-container-inner">div>
div>Ï
body>
外层的div用来固定高度,也就是图上展示的B区域。内层的div用来装列表元素,也就是图上展示的A区域。给外层的div设置 overflow: auto ,这样当列表元素数量超过B区域的高度时就会出现滚动条。
接下来,我们需要监听外层div的滚动事件,实时计算出显示在可视区域上的第一个元素的坐标 startIndex 和 最后一个元素的坐标 endIndex。假设列表每个元素的高度都是60px,那么 startIndex 就等于外层 div 顶部卷起来的长度除以列表元素的高度,而 endIndex 就等于 startIndex + 可视区域能展示的元素个数 :
const itemHeight = 60
const height = 500
const startIndex = Math.floor(outerContainer.scrollTop / itemHeight)
const endIndex = startIndex + Math.ceil(height / itemHeight)
然后用 startIndex 和 endIndex 去截取数据,并渲染在内层 div 上:
const viewData = data.slice(startIndex, endIndex + 1)
const innerContainer = document.querySelector('.list-container-inner')
innerContainer.innerHTML = ''
for(let i = 0; i < viewData.length; i++) {
const item = document.createElement('div')
item.innerHTML = viewData[i]
innerContainer.appendChild(item)
}
最后一步,虽然我们只需要渲染在可视区域上的元素,但是我们还需要给内层的 div 设置 padding-top 和 padding-bottom ,替代那些不需要渲染的元素。由此保证虚拟列表是可以滚动的,而且滚动条位置和列表元素位置是相对应的。 padding-top 等于 startIndex 之前的元素高度和, padding-bottom 等于 endIndex 之后的元素高度和:
const paddingTop = startIndex * itemHeight
const paddingBottom = (data.length - endIndex) * itemHeight
innerContainer.setAttribute('style', `padding-top: ${paddingTop}px; padding-bottom: ${paddingBottom}px`)
完整代码:
<style>
.list-container {
overflow: auto;
border: 1px solid black;
height: 500px;
}
style>
<body>
<div class="list-container">
<div class="list-container-inner">div>
div>
<script>
/** --------- 一些基本变量 -------- */
const itemHeight = 60
const height = 500
/** --------- 生成数据 -------- */
const initData = () => {
const data = []
for(let i = 0; i < 15; i++) {
data.push({content: `内容:${i}`, height: itemHeight, color: i % 2 ? 'red' : 'yellow'})
}
return data
}
const data = initData()
const contentHeight = itemHeight * data.length
const outerContainer = document.querySelector('.list-container')
const scrollCallback = () => {
// 获取当前要渲染的元素的坐标
const scrollTop = Math.max(outerContainer.scrollTop, 0)
const startIndex = Math.floor(scrollTop / itemHeight)
const endIndex = startIndex + Math.ceil(height / itemHeight)
const innerContainer = document.querySelector('.list-container-inner')
// 从data取出要渲染的元素并渲染到容器中
const viewData = data.slice(startIndex, endIndex + 1)
innerContainer.innerHTML = ''
for(let i = 0; i < viewData.length; i++) {
const item = document.createElement('div')
const itemData = viewData[i]
item.innerHTML = itemData.content
item.setAttribute('style', `height: ${itemData.height}px; background: ${itemData.color}`)
innerContainer.appendChild(item)
}
// 未渲染的元素由padding-top和padding-bottom代替,保证滚动条位置正确
const paddingTop = startIndex * itemHeight
const paddingBottom = (data.length - endIndex) * itemHeight
innerContainer.setAttribute('style', `padding-top: ${paddingTop}px; padding-bottom: ${paddingBottom}px`)
}
// 首屏渲染
scrollCallback()
// 监听外部容器的滚动事件
outerContainer.addEventListener('scroll', scrollCallback)
script>
body>
不定高虚拟列表
上面实现的是元素高度固定的虚拟列表,对于元素高度不固定的情况,虚拟列表实现起来会更复杂一些。
因为我们事先不知道元素的高度,所以在监听滚动事件的过程中,需要遍历一遍列表获取每个元素的高度,由此算出 startIndex 、 endIndex 等数据。不过在第一次渲染之前,因为元素没有渲染出来,我们拿不到元素的真实高度。所以这时候需要给元素一个最小高度 itemHeight ,通过 itemHeight 来计算 startIndex 和 endIndex,由此保证第一次渲染出来的元素能占满整个可视区域。
另外,当元素渲染出来以后,我们用一个字典去记录每个元素的真实高度,供下次滚动事件触发时 startIndex 和 endIndex 的计算。
startIndex 的算法是在遍历列表元素的过程中,逐步累加当前元素的高度得到 contentHeight ,当第一次出现 contentHeight 大于容器顶部卷起来的长度的时候,说明当前元素是列表可视区域的第一个元素,记为 startIndex。
endIndex 的算法是当第一次出现 contentHeight 大于 容器顶部卷起来的长度 + 容器高度 的时候,说明当前元素是列表可视区域的最后一个元素,记为 endIndex 。
完整代码:
<style>
.list-container {
overflow: auto;
border: 1px solid black;
height: 500px;
}
style>
<body>
<div class="list-container">
<div class="list-container-inner">div>
div>
<script>
/** --------- 一些基本变量 -------- */
const itemHeight = 60
const height = 500
/** --------- 生成数据 -------- */
const getRandomHeight = () => {
// 返回 [60, 150] 之间的随机数
return Math.floor(Math.random() * (150 - itemHeight + 1) + itemHeight)
}
const initData = () => {
const data = []
for(let i = 0; i < 15; i++) {
data.push({content: `内容:${i}`, height: getRandomHeight(), color: i % 2 ? 'red' : 'yellow'})
}
return data
}
const data = initData()
const cacheHeightMap = {}
const outerContainer = document.querySelector('.list-container')
const scrollCallback = () => {
let contentHeight = 0
let paddingTop = 0
let upperHeight = 0
let startIndex
let endIndex
const innerContainer = document.querySelector('.list-container-inner')
const scrollTop = Math.max(outerContainer.scrollTop, 0)
// 遍历所有的元素,获取当前元素的高度、列表总高度、startIndex、endIndex
for(let i = 0; i < data.length; i++) {
// 初始化的时候因为元素还没有渲染,无法获取元素的高度
// 所以用元素的最小高度itemHeight来进行计算,保证渲染的元素个数能占满列表
const cacheHeight = cacheHeightMap[i]
const usedHeight = cacheHeight === undefined ? itemHeight : cacheHeight
contentHeight += usedHeight
if (contentHeight >= scrollTop && startIndex === undefined) {
startIndex = i
paddingTop = contentHeight - usedHeight
}
if (contentHeight > scrollTop + height && endIndex === undefined) {
endIndex = i
upperHeight = contentHeight
}
}
// 应对列表所有元素没有占满整个容器的情况
if (endIndex === undefined) {
endIndex = data.length - 1
upperHeight = contentHeight
}
// 未渲染的元素的高度由padding-top和padding-bottom代替,保证滚动条位置正确
// 这里如果把设置pading的操作放在渲染元素之后,部分浏览器滚动到最后一个元素时会有问题
const paddingBottom = contentHeight - upperHeight
innerContainer.setAttribute('style', `padding-top: ${paddingTop}px; padding-bottom: ${paddingBottom}px`)
// 从data取出要渲染的元素并渲染到容器中
const viewData = data.slice(startIndex, endIndex + 1)
innerContainer.innerHTML = ''
const fragment = document.createDocumentFragment()
for(let i = 0; i < viewData.length; i++) {
const item = document.createElement('div')
const itemData = viewData[i]
item.innerHTML = itemData.content
item.setAttribute('style', `height: ${itemData.height}px; background: ${itemData.color}`)
fragment.appendChild(item)
}
innerContainer.appendChild(fragment)
// 存储已经渲染出来的元素的高度,供后面使用
const children = innerContainer.children
let flag = startIndex
for(const child of children) {
cacheHeightMap[flag] = child.offsetHeight
flag++
}
}
// 首屏渲染
scrollCallback()
// 监听外部容器的滚动事件
outerContainer.addEventListener('scroll', scrollCallback)
script>
body>
最后效果: