LINUX 文件操作
目录
一、查看文件内容
1、cat
2、head
3、tail
4、more
5、less
二、过滤文件内容显示
三、切割显示
四、排序显示
五、其他显示命令
1、uniq
2、tr
六、文本内容
七、复制、移动文件
1、复制文件
2、移动文件
八、查找文件路径
九、压缩和解压文件
1、zip和unzip
2、gzip和gunzip
十、tar归档
一、查看文件内容
1、cat
查看文本文件的内容。
基本语法
cat [选项] 文件路径选项:
-n :对输出的文件内容中的所有行标注行号;
-b :对输出文件内容中的非空行标注行号;
例如:
[root@node1 test]# cat -n a.txt
1 11
2 44
3
4 33
5
6 66
7
8 55
9
[root@node1 test]# cat -b a.txt
1 11
2 44
3 33
4 66
5 55
2、head
默认查看文档的前10行。
基本语法
head -数字 文件路径例如
[root@node1 test]# head a.txt
11
44
33
66
55
[root@node1 test]# head -5 a.txt
11
44
33
3、tail
默认查看文件后10行。
基本语法
tail [选项] 文件路径选项:
-数字(num) :指定查看文挡后num行的内容。
-f :不停的去读取和显示文件最小的内容,这样有实施监视的效果。Ctrl+C键终止显示和追踪。
例如:
[root@node1 test]# tail -4 a.txt
66
55
4、more
分页查看文件内容,按回车键翻滚,按空格键向下翻页,按b键向上翻页,文件末尾more会自动退出。
基本语法
more [选项] 文件路径例如
5、less
与more功能类似,按q退出。
基本语法
less [选项] 文件路径选项:
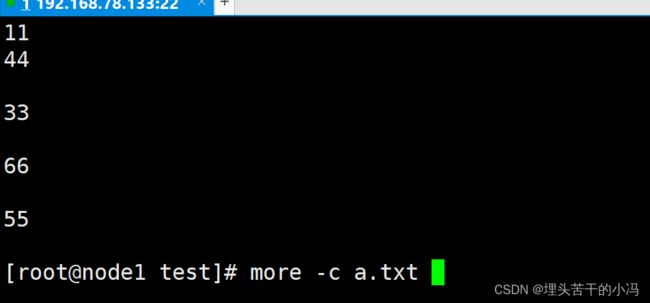
-c :从顶部清屏然后显示文件
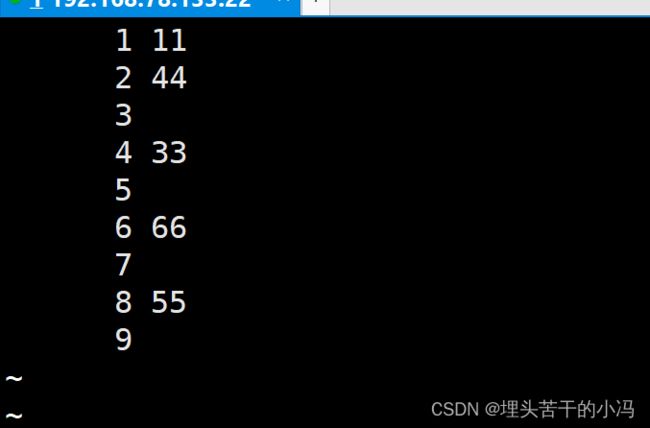
-N :在每行前添加行号输出
例如
less -c a.txt
less -cN a.txt
二、过滤文件内容显示
grep:在指定的普通文件中查找并显示含有指定字符串的行,也可以结合管道符一起使用。
基本语法
grep [选项] 关键字符串 文件路径常用选项:
-c : 显示找到的行数
-i :忽略大小写
-n :显示行号
-v :反向选择,仅列出没有关键字符串的行
特殊字符:
^[a] :匹配以a开始的行
^[ab] :匹配以a或b开始的行
^[^ab] :匹配不以a或b开始的行
^[0-9] :匹配以数字开始的行
a$ :匹配以a结尾的行
^$ :过滤空白行
例如
[root@node1 test]# grep ^1 a.txt
11
[root@node1 test]# grep 1$ a.txt
11
[root@node1 test]# grep ^$ a.txt
[root@node1 test]# grep ^[1-3] a.txt
11
33
[root@node1 test]# grep ^[12345] a.txt
11
44
33
55
三、切割显示
cut用于按列提取文本内容。
基本语法
cut [选项] 文件名称-c :指定提取字符位置列表
-f :指定提取的字段列表,默认以水平制表符分隔,字段之间可以指定分隔符分隔
-d :指定字段的分隔符,默认为水平制表符分隔
-n :取消字符分隔符的解释,视为普通字符
-s :只输出包含分隔符的行
例如
查看/etc/passwd文件中前5行以 : 分隔,第1列字段的值。
[root@node1 test]# cut -d: -f1 /etc/passwd | head -5
root
bin
daemon
adm
lp
四、排序显示
sort命令用于文本内容进行排序显示。
基本语法
sort [选项] 文件名称常用选项:
-f :忽略大小写
-b :忽略缩进与空格
-n :以数值型排序
-r :反向排序
-u :去重排序
-t :指定间隔符
-k :设置字段范围
例如
[root@node1 test]# sort a.txt --直接排序,不跟选项,默认升序
11
33
44
55
66
[root@node1 test]# sort -u a.txt --去重排序
11
33
44
55
66
[root@node1 test]# sort -ur a.txt --去重倒排序
55
44
33
11
五、其他显示命令
1、uniq
uniq命令用于去除文本中连续的重复行,可以和其他命令结合使用。
基本语法
uniq [选项] 文件名称例如
[root@node1 test]# cat a.txt --原文件内容
aa
aa
aa
cc
cc
aa
dd
dd
gg
kk
[root@node1 test]# uniq a.txt --去重查看
aa
cc
aa
dd
gg
kk
2、tr
tr指令从标准输入读取数据,经过替换或者删除后,将结果输出在标准输出。
基本语法
tr [选项] set1[set2]常用选项
-c :反选设定字符,也就是符合set1的部分不做处理,不符合的剩余部分才进行转换。
-d :删除指定字符
-s :缩减连续重复的字符成指定的单个字符。
例如
[root@node1 test]# cat a.txt | tr a-z A-Z |uniq
AA
CC
AA
DD
GG
KK
六、文本内容
wc命令用于统计指定文本文件的行数、字数或者字节数
基本语法
wc [选项] 文件名称常用选项
-l :只显示行数
-w:只显示单词数
-c :只显示字节数
例如
[root@node1 test]# wc -l a.txt
10 a.txt
[root@node1 test]# wc -w a.txt
10 a.txt
[root@node1 test]# wc -c a.txt
30 a.txt
[root@node1 test]# wc -lw a.txt
七、复制、移动文件
1、复制文件
基本语法
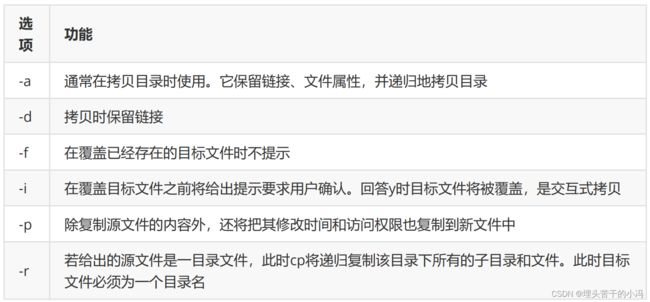
cp [选项] 源文件 目标文件常用选项:
例如
[root@node1 test]# cp a.txt aa.txt
[root@node1 test]# ls
aa.txt a.txt
2、移动文件
基本语法
mv [选项] 源文件名称 目标文件名称例如
[root@node1 test]# ls
aa.txt a.txt b
[root@node1 test]# mv a.txt ./b
[root@node1 test]# cd b/
[root@node1 b]# ls
a.txt
[root@node1 b]# cd -
/root/test
[root@node1 test]# ls
aa.txt b
八、查找文件路径
find 命令默认接的命令是-print,它默认以\n将找到的文件分隔。可以使用-print0来使用\0分隔,这样就不会分行了。但是一定要注意,-print0针对的是\n转\0,如果查找的文件本省就含有空格,则find后-print0仍然会显示空格。
基本语法
find 路径 [选项] 搜索内容 常用选项:
-name:按照文件名搜索
-iname:按照文件名搜索,不区分文件大小写
-inum:按照inode号搜索
例如
[root@node1 ~]# find /etc -name "host*"
/etc/host.conf
/etc/hosts
/etc/avahi/hosts
/etc/nvme/hostnqn
/etc/nvme/hostid
/etc/ansible/hosts
/etc/hostname
注:find功能比较强大,可以使用 man find 来进行查看他的其他选项功能。
九、压缩和解压文件
1、zip和unzip
基本语法
zip [选项] 压缩后的文件名 源文件名 ---压缩
unzip [选项] 文件名 ---解压zip常用选项:
-数字:指定压缩率
-r :将该目录下的所有文件一起压缩
-m :向压缩文件中添加一个新的压缩文件进去
-d :删除压缩中的某个文件
-x :压缩文件时排除某个文件 ---- zip test.zip *.zip -x test2.txt
例如
[root@node1 test]# zip b.zip b/
adding: b/ (stored 0%)
[root@node1 test]# ls
aa.txt b b.zip
[root@node1 test]# zip -r c.zip b
b/ b.zip
[root@node1 test]# zip -r c.zip b
b/ b.zip
[root@node1 test]# zip -r c.zip b/
adding: b/ (stored 0%)
adding: b/a.txt (deflated 27%)
adding: b/b.txt (deflated 55%)
adding: b/c.txt (deflated 67%)
adding: b/d.txt (deflated 71%)
[root@node1 test]#
[root@node1 test]#
[root@node1 test]# ls
aa.txt b b.zip c.zip
[root@node1 test]#
[root@node1 test]# zip -m b.zip aa.txt
adding: aa.txt (deflated 27%)
[root@node1 test]# ls
b b.zip c.zip
unzip常用选项:
-d :指定解压后存放目录
-v :查看压缩文件目录,不进行压缩
例如
[root@node1 test]# unzip b.zip
Archive: b.zip
inflating: aa.txt
[root@node1 test]# unzip b.zip -d file
Archive: b.zip
creating: file/b/
inflating: file/aa.txt
[root@node1 test]# ls
aa.txt b b.zip c.zip file
[root@node1 test]# cd file/
[root@node1 file]# ls
aa.txt b
[root@node1 test]# unzip -v b.zip
Archive: b.zip
Length Method Size Cmpr Date Time CRC-32 Name
-------- ------ ------- ---- ---------- ----- -------- ----
0 Stored 0 0% 09-10-2023 18:32 00000000 b/
30 Defl:N 22 27% 09-10-2023 18:03 885598db aa.txt
-------- ------- --- -------
30 22 27% 2 files
2、gzip和gunzip
基本语法
gzip [选项] 文件名称 --压缩
gunzip [选项] 文件名称 --解压gzip常用选项:
-r :压缩该目录下的所有文件
-c : 压缩并且原有文件存在
例如
[root@node1 test]# ls
aa.txt b file
[root@node1 test]# gzip aa.txt
[root@node1 test]# ls
aa.txt.gz b file
[root@node1 test]# gzip -r b/
[root@node1 test]# ls
aa.txt.gz b file
[root@node1 test]# cd b/
[root@node1 b]# ls
a.txt.gz b.txt.gz c.txt.gz d.txt.gz
还有其他压缩方式类似 bzip2和bunzip2、xz和unxz等
十、tar归档
基本语法
tar [选项] [args] ……常用选项
-c :创建.tar格式的包文件
-x :释放.tar格式的包文件
-t :查看包中的文件列表
-f (必选项):用于指定打包文件名,当与-c选项一起使用,创建tar包文件使用该选项指定的文件名;当-x选项一起使用时,则释放该选项指定的tar文件。
-v :标识在命令执行时显示详细提示信息
-p :打包时留文件及目录的权限
-C(大写):和-x选项一起使用,标识释放包时致电给释放的目标路径。
打包时排除某个文件
tar cf 文件名.tar --exculude=路径/文件 路径。
注:此处的路径前后需要保持一致,同一使用绝对路径或相对路径。
例如
创建(非压缩的)打包文件,将指定的一个或多个文件或目录备份生成为一个指定的包文件。
[root@node1 test]# tar -cvf file.tar
tar: Cowardly refusing to create an empty archive
Try 'tar --help' or 'tar --usage' for more information.
[root@node1 test]# tar -cvf file.tar file
file/
file/b/
file/aa.txt
[root@node1 test]# ls
aa.txt.gz b file file.tar列出包文件中的文件列表
[root@node1 test]# tar tf file.tar
file/
file/b/
file/aa.txt
创建带压缩的包文件,为节省存储空间,通常需要生成压缩格式的tar包文件,tar支持三种不同的压缩方式(.gz、.bz2、.xz)
.gz 对应选项是:czf/-czf
.bz2对应选项是:cjf/-cjf
.xz对应选项是:cJf/-cJf
[root@node1 test]# tar -czf b.tar.gz b/
[root@node1 test]# ls
aa.txt.gz b b.tar.gz file file.tar提取包文件到指定目录
[root@node1 test]# mkdir test_file
[root@node1 test]# ls
aa.txt.gz b b.tar.gz file file.tar test_file
[root@node1 test]# tar -xf b.tar.gz -C test_file/
[root@node1 test]# cd test_file/
[root@node1 test_file]# ls
b
格式如下:
tar xf/-xf/-xzf 文件名.tar.gz [-C 目标路径]
tar xf/-xf/-xjf 文件名.tar.bz2 [-C 目标路径]
tar xf/-xf/-xJf 文件名.tar.xz [-C 目标路径]