【C++】STL之string
提示:文章写完后,目录可以自动生成,如何生成可参考右边的帮助文档
文章目录
- 前言
- string类的内部
-
-
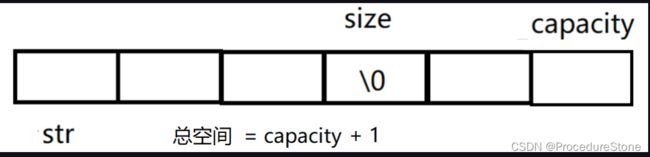
- 成员变量:
-
- string的模拟实现
-
- **六个默认成员函数**
- **iterator**
- **capacity**
- **modify**
- element access
- **String operations**
- Non-member function overloads
前言
本文将介绍如何实现string,从而提高对string类的理解
string类的内部
成员变量:
string的模拟实现
六个默认成员函数
构造函数
string(const char* str = "")
:_size(strlen(str))
, _capacity(_size)
, _str(new char[_capacity+1])
{
memcpy(_str, str, _size + 1);
}
注意点:
- 未赋值的string,其实里面有\0 , 因此
const char* str = "" - 注意初始化列表的规则, 声明顺序对应初始化顺序
- 拷贝采用memset而不是strcpy,因为string里面的str中间可以有\0
拷贝构造
string(const string& str)
{
_size = str._size;
_capacity = str._capacity;
_str = new char[_capacity];
memcpy(_str, str._str, str._size + 1);
}
析构函数
~string()
{
delete[] _str;
_str = nullptr;
_size = 0;
_capacity = 0;
}
赋值运算符重载
void swap(string& tmp)
{
std::swap(_str, tmp._str);
std::swap(_size, tmp._size);
std::swap(_capacity, tmp._capacity);
}
string& operator=(const string& str)
{
if (this != &str)
{
string tmp(str);
this->swap(tmp);
}
return *this;
}
//更简短的写法
string& operator=(string tmp)
{
swap(tmp);
}
iterator
string的迭代器是字符指针
typedef char* iterator
typedef const char* const_iterator
begin() - 字符数组的地址
iterator begin()
{
return _str;
}
const_iterator begin() const
{
return _str;
}
end() - 字符数组地址 + size 即 ‘\0’
iterator end()
{
return _str + _size;
}
const_iterator end() const
{
return _str + _size;
}
capacity
reserve
注意:
windows : 不能比原来的容量低
linux: 除非多余的空间无数据, 否则不能比size低
void reserve(size_t n)
{
if (n > _capacity)
{
char* tmp = new char[n + 1];
memcpy(tmp, _str, _size + 1);
delete[] _str;
_str = tmp;
_capacity = n;
}
}
resize
注意:
window: 任意
linux:
void resize(size_t n, char c = '\0')
{
if (n > _size)
{
if (n >= _capacity)
{
reserve(n + 4);
}
for (size_t i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
_str[i + _size] = c;
}
_size = n;
_str[n] = '\0';
}
else
{
_size = n;
_str[_size] = '\0';
}
}
modify
operator+=
string& operator+=(char c)
{
if (_size == _capacity)
{
reserve(_capacity == 0 ? 4 : _capacity * 2);
}
_str[_size] = c;
++_size;
_str[_size] = '\0';
return *this;
}
string& operator+=(const char* str)
{
size_t len = strlen(str);
if (_size + len >= _capacity)
{
reserve(_size + len);
}
memcpy(_str + _size, str, len + 1);
_size += len;
return *this;
}
注意:+=是需要返回本身
insert
string& insert(size_t pos, size_t n, char c)
{
assert(pos <= _size);
if (_size + n > _capacity)
{
reserve(_size + n);
}
//后移
size_t end = _size;
while (end >= pos && end != npos)
{
_str[end + n] = _str[end];
--end;
}
for (size_t i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
_str[pos + i] = c;
}
_size += n;
return *this;
}
string& insert(size_t pos, const char* str)
{
assert(pos <= _size);
size_t len = strlen(str);
if (_size + len > _capacity)
{
reserve(_size + len);
}
//后移
size_t end = _size;
while (end >= pos && end != npos)
{
_str[end + len] = _str[end];
--end;
}
for (size_t i = 0; i < len; i++)
{
_str[pos + i] = str[i];
}
_size += len;
return *this;
}
注意:出现负数与无符号数的冲突
size_t end = _size; while (end >= pos && end != npos)
当pos = 0时,end会出现为-1的情况,但end为无符号数,因此end = max_size_t死循环
- 强转 -
end >=(int)pos - npos -
size_t npos = -1, while(end >= pos && end != npos
element access
operator【】
//access
char& operator[](size_t pos)
{
assert(pos <= _size);
return _str[pos];
}
const char& operator[](size_t pos) const
{
assert(pos <= _size);
return _str[pos];
}
有个典型错误:
reserve()之后, 直接访问。因为operator【】是看size
String operations
c_str
const char* c_str() const
{
return _str;
}
find
size_t find(char c, size_t pos = 0)
{
assert(pos < _size);
for (size_t i = pos; i < _size; i++)
{
if (_str[i] == c)
{
return i;
}
}
return npos;
}
size_t find(const char* str, size_t pos = 0)
{
assert(pos < _size);
const char* ptr = strstr(_str, str);
if (ptr) return ptr - _str;
else return npos;
}
substr
string substr(size_t pos = 0, size_t len = npos) const
{
assert(pos < _size);
size_t n = len;
if (len == npos || pos + len >= _size)
{
n = _size - pos;
}
string tmp;
tmp.reserve(n);
tmp._size = n;
tmp[n] = '\0';
memcpy(tmp._str, _str + pos, n);
return tmp;
}
Non-member function overloads
operator<<
标准:
- string的打印规则与字符串不一样,而是以size为终结
std::ostream& operator<<(std::ostream& out, const sfw::string& str)
{
for (auto it : str)
{
out << it;
}
return out;
}
operator>>
标准:
- 过滤前面的空格和换行
注意: - 流提取不会提取
' ' 和 \n, 因此需使用输入流的成员函数get(), - 每次提取会对原来进行覆盖
std::istream& operator>>(std::istream& in, sfw::string& str)
{
str.clear();
//清除缓冲区
char c = in.get();
while(!(c != '\n' && c != ' '))
{
c = in.get();
}
//读取,分批次读取
char bag[128];
int i = 0;
while (c != '\n' && c != ' ')
{
bag[i++] = c;
if (i == 127)
{
bag[i] = '\0';
str += bag;
i = 0;
}
c = in.get();
}
if (i)
{
bag[i] = '\0';
str += bag;
}
return in;
}
relation operator
注意:
对于比较 : 只用写出 == 以及 >(<), 其余根据逻辑关系调用就可以了
//operator==
bool operator==(const string& str) const
{
if (_size != str._size) return false;
size_t i = 0;
while (i < _size)
{
if (_str[i] != str._str[i]) return false;
i++;
}
return true;
}
//operator>
bool operator>(const string& str) const
{
size_t sz = min(str._size, _size);
for (size_t i = 0; i < sz; i++)
{
if (_str[i] > str._str[i]) return true;
}
return _size > str._size;
}