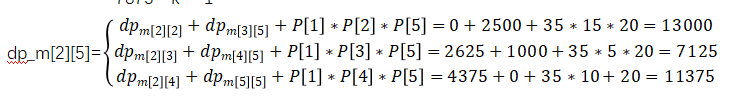大三上算法设计和分析 老师:付豪
目录
第一章:递归和分治
1.利用递归函数计算n!
2. 斐波那契数列(2018年贝壳网校招笔试)
3.(蓝桥杯2019年第十届真题)Fibonacci数列与黄金分割
4.(笔试真题)小明爬楼梯
5.整数因子分解问题:计算正整数n有多少种因子大于1的不同的分解式:
6.二分搜搜索
7.归并算法
8.排序算法
9.汉诺塔
10棋盘覆盖
第二章:回溯+DFS
1.走迷宫
2.全排列
3.油田问题
4.N皇后
回溯测试main主函数
============================我是分割线===============================
第一章:递归和分治
1.利用递归函数计算n!
#include
using namespace std;
int fib(int n);
int main()
{undefined
int n;
cin>>n;
cout< 2. 斐波那契数列(2018年贝壳网校招笔试)
2斐波那契数列是指这样的数列:数列的第一个和第二个数都为1,接下来每个数都等于前面2个数之和。给出一个正整数k,要求斐波那契数列中第k个数是多少?
输入描述:输入一行,包含一个正整数k。(0
using namespace std;
int fib(int n);
int main()
{undefined
int n;
cin>>n;
cout< 3.(蓝桥杯2019年第十届真题)Fibonacci数列与黄金分割
/*3.(蓝桥杯2019年第十届真题)
Fibonacci数列与黄金分割
题目:Fibonacci数列是非常著名的数列:F[1]=1,F[2]=1,对于i>3,F[i]=F[i-1]+F[i-2]。
Fibonacci数列有一个特殊的性质,前一项与后一项的比值,F[i]/F[i+1],会趋近于黄金分割。为了验证这一性质,给定正整数N,请你计算F[N]/F[N+1],并保留8位小数。
输入:一个正整数N。(1<=N<=2000000000)
输出:F[N]/F[N+1]。(答案保留8位小数)
样例输入:2
样例输出:0.50000000*/
#include
using namespace std;
int fib(int n);
int main()
{undefined
int n;
cin>>n;
cout< 4.(笔试真题)小明爬楼梯
4.(笔试真题)
小明爬楼梯,一次只能上1级或者2级台阶,一共有n级台阶,小明共有多少种方法上台阶?
输入:输入一行,包含一个正整数n。
输出:输出一行,包含一个正整数,表示小明上n级台阶的方法数。
样例输入:3
样例输出:4
#include
using namespace std;
int fib(int n);
int main()
{undefined
int n;
cin>>n;
cout< 5.整数因子分解问题:计算正整数n有多少种因子大于1的不同的分解式:
5.整数因子分解问题:计算正整数n有多少种因子大于1的不同的分解式:
例如:n=12,共有8种:
12=12 12=2*6 12=6*2 12=3*2*2
12=4*3 12=2*2*3 12=3*4 12=2*3*2
#include
using namespace std;
int f(int n)
{undefined
int count=0;
for(int i=2;i> n;
cout< 6.二分搜搜索
======================================================================================
#include
using namespace std;
int bs(int a[],int num)
{
int i=0,j=9;
while(i<=j)
{
int mid=(i+j)/2;
if(a[mid]=num) return mid;
else if(a[mid]>num) j=mid-1;
else i=mid+1;
}
return -1;
}
int bsc(int a[],int num,int i,int j)
{
int mid=(i+j)/2;
if(i>j) return -1;
else if (a[mid]=num) return mid;
else if (a[mid>num]) return bsc(a,num,i,mid-1)
else return return bsc(a,num,mid+1,j)
}
int main()
{
int a[]={1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10};
int num=2;
cout << bs(a,num) << endl;
cout << bsc(a,num,0,8)<< endl;
} 7.归并算法
#include
#include
using namespace std;
void MergeSort(int *a,int left,int right,int *b)
{
void Merge(int *a,int left,int right,int mid,int *b);
if(left < right)
{
int mid=(left+right)/2;
MergeSort(a,left,right,b);
MergeSort(a,mid+1,right,b);
Merge(a,left,right,mid,b);
}
}
void Merge(int *a,int left,int right,int mid,int *b)
{
int i=left,j=mid+1,k=0;
while(i<=mid && j<=right)
{
if(a[i] 8.排序算法
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
int arrLen;
int* initArr(){
//get a initial array
cout << "Input array's length:";
cin >> arrLen;
int *arr = new int[arrLen];
srand((unsigned)time(NULL));
for(int i = 0; i < arrLen; i++)
arr[i] = rand()%arrLen;
return arr;
}
void printArr(int *a, int len){
//print array
for(int i = 0; i < len; i++)
cout << a[i] << " ";
cout << endl;
}
int* bubbleSort(int *a, int len){
//bubble sort
for(int i = len-1; i > 0; i--)
for(int j = 0; j < i; j++)
if(a[j] > a[j+1]){
int temp = a[j];
a[j] = a[j+1];
a[j+1] = temp;
}
return a;
}
int* selectionSort(int *a, int len){
//selection sort
for(int i = 0; i < len; i++){
int index = i;
for(int j = i+1; j < len; j++){
if(a[j] < a[index]) index = j;
}
int temp = a[i];
a[i] = a[index];
a[index] = temp;
}
return a;
}
int* mergeSort(int *a,int left, int right, int *b){
//merge sort
void mSort(int *a, int left, int right, int mid,int *b);
if(left < right){
int mid = (left + right) / 2;
mergeSort(a,left, mid,b);
mergeSort(a,mid+1,right,b);
mSort(a,left,right,mid,b);
return a;
}
return a;
}
void mSort(int *a, int left, int right, int mid,int *b){
int i = left, j = mid+1,k = 0;
while(i <= mid && j <= right){
if(a[i] < a[j]) b[k++] = a[i++];
else b[k++] = a[j++];
}
while(i <= mid) b[k++] = a[i++];
while(j <= right) b[k++] = a[j++];
for(int x = 0; x < k; x++) a[left+x] = b[x];
}
int* quickSort(int *a, int left, int right){
//quick sort
int qSort(int *a, int left, int right);
if(left < right){
int mid = qSort(a,left,right);
quickSort(a,left,mid-1);
quickSort(a,mid+1,right);
return a;
}
return a;
}
int qSort(int *a, int left, int right){
int i = left, j = right+1, x= a[left];
while(true){
while(a[++i] < x && i <= right);
while(a[--j] > x);
if(i >= j) break;
int temp = a[i];
a[i] = a[j];
a[j] = temp;
}
a[left] = a[j];
a[j] = x;
return j;
}
int main(){
DWORD time_start,time_end;
long time_total;
//init array
int *a = initArr();
int *b = new int[arrLen];
int *temp = new int[arrLen];
//print array
//printArr(a,arrLen);
//1.bubble sort
cout << "1.Bubble sort: \n";
memcpy(temp,a,arrLen*sizeof(int));
time_start = GetTickCount();
//printArr(bubbleSort(temp,arrLen),arrLen);
//bubbleSort(temp,arrLen);
time_end = GetTickCount();
time_total = time_end - time_start;
cout << "time_start:" << time_start/1000.0 << "s \n" << "time_end:" << time_end / 1000.0 << "s \n" << "time_total:" << time_total/1000.0 << "s \n" << endl;
//2.selection sort
cout << "2.Selection sort: \n";
memcpy(temp,a,arrLen*sizeof(int));
time_start = GetTickCount();
//printArr(selectionSort(temp,arrLen),arrLen);
//selectionSort(temp,arrLen);
time_end = GetTickCount();
time_total = time_end - time_start;
cout << "time_start:" << time_start/1000.0 << "s \n" << "time_end:" << time_end / 1000.0 << "s \n" << "time_total:" << time_total/1000.0 << "s \n" << endl;
//3.merge sort
cout << "3.Merge sort: \n";
memcpy(temp,a,arrLen*sizeof(int));
time_start = GetTickCount();
//printArr(mergeSort(temp,0,arrLen-1,b),arrLen);
mergeSort(temp,0,arrLen-1,b);
time_end = GetTickCount();
time_total = time_end - time_start;
cout << "time_start:" << time_start/1000.0 << "s \n" << "time_end:" << time_end / 1000.0 << "s \n" << "time_total:" << time_total/1000.0 << "s \n" << endl;
//4.quick sort
cout << "4.Quick sort: \n";
memcpy(temp,a,arrLen*sizeof(int));
time_start = GetTickCount();
//printArr(quickSort(temp,0,arrLen-1),arrLen);
quickSort(temp,0,arrLen-1);
time_end = GetTickCount();
time_total = time_end - time_start;
cout << "time_start:" << time_start/1000.0 << "s \n" << "time_end:" << time_end / 1000.0 << "s \n" << "time_total:" << time_total/1000.0 << "s \n" << endl;
delete a;
delete b;
delete temp;
} 9.汉诺塔
# include
void hanoi ( int n, char a, char b, char c ) //这里代表将a柱子上的盘子借助b柱子移动到c柱子
{ if (1 == n) //如果是一个盘子直接将a柱子上的盘子移动到c
{
printf("%c-->%c\n",a,c);
}
else
{
hanoi ( n-1, a, c, b ) ; //将a柱子上n-1个盘子借助c柱子,移动到b柱子
printf("%c-->%c\n",a , c) ; //再直接将a柱子上的最后一个盘子移动到c
hanoi ( n-1, b, a, c ) ; //然后将b柱子上的n-1个盘子借助a移动到c
}
}
int main ()
{ int n ;
printf( "Input the number of diskes:") ;
scanf("%d",&n) ;
hanoi ( n, 'A' , 'B' , 'C' ) ;
} 10棋盘覆盖
#include
#include
using namespace std;
int board[100][100];
int t=0;
void Board(int tr,int tc,int dr,int dc,int s)
{
if(s==1)return;
int temp = ++t;
s/=2;
if(dr= tc+s)Board(tr,tc+s,dr,dc,s);
else{
board[tr+s-1][tc+s]=temp;
Board(tr,tc+s,tr+s-1,tc+s,s);
}
if(dr>= tr+s && dc< tc+s)Board(tr,tc,dr,dc,s);
else{
board[tr+s][tc+s-1]=temp;
Board(tr+s,tc,tr+s,tc+s-1,s);
}
if(dr>= tr+s && dc>= tc+s)Board(tr,tc,dr,dc,s);
else{
board[tr+s][tc+s]=temp;
Board(tr+s,tc+s,tr+s,tc+s,s);
}
}
int main()
{
Board(1,1,1,1,4);
for(int i=1;i<=4;i++)
{
for(int j=1;j<=4;j++)
{
cout << board[i][j] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
} 第二章:回溯+DFS
1.走迷宫
int **map;// 地图数组
int **t; //解空间数组
int n,m,start_x,start_y,end_x,end_y;//n行
int dir[4][2]={{0,1},{-1,0},{0,-1},{1,0}};// 四个方向
int c;// 计算有几种结果
void dfs(int x,int y){
//到终点
if(x==end_x&&y==end_y){
cout<<"=================="<=0&&newX=0&&newY>n>>m;// 输入迷宫大小
//数组内存空间分配
map=new int *[n];
t=new int *[n];
for(i=0;i>map[i][j];
t[i][j]=0;
}
}
cout<<"起点坐标和终点坐标"<>start_x>>start_y>>end_x>>end_y;
t[start_x][start_y]=1;
dfs(start_x,start_y);
/*测试代码
输入迷宫大小
5 5
输入迷宫具体数值
0 1 1 0 0
0 1 0 0 1
0 0 0 0 0
1 0 0 0 1
0 1 1 0 0
起点坐标和终点坐标
3 2 2 2
==================
0 0 0 0 0
0 0 1 1 0
0 0 1 1 0
0 0 1 1 0
0 0 0 0 0
==================
0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0
0 0 1 1 0
0 0 1 1 0
0 0 0 0 0
==================
0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0
0 0 1 0 0
0 0 1 0 0
0 0 0 0 0
==================
0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0
0 1 1 0 0
0 1 1 0 0
0 0 0 0 0
*/
}
2.全排列
#include
using namespace std;
//全排列
int n; //数值个数
int **num; //n行两列二维数组,第一列存数值,第二列存状态 0未选 1已选
int *res1; //存排列结果
int count1 = 0;
void dfs1(int i){
//判断是否n个数全部放入,即i == n
if(i == n){
count1++;
for(int j = 0; j < n; j++)
cout << res1[j] << " ";
cout << endl;
return;
}
//如果未全部放入,则依次遍历n个数
for(int j = 0; j < n; j++){
//判断第j个数是否可选
if(num[j][1] == 0){
res1[i] = num[j][0]; //将第j个数放入结果数组res的第i个位子
num[j][1] = 1; //将第j个数状态改为1,标记为已选,则不可被重复选中
dfs1(i+1); //递归下一个位子
num[j][1] = 0; //将第j个数状态改回0,可被下次选中
}
}
} 3.油田问题
//油田问题
int rows,columns; //油田大小行列数
char **map; //油田原始地图
int count2 = 0; //计数器,计数有多少片油田
int dir[8][2] = {{0,1},{-1,1},{-1,0},{-1,-1},{0,-1},{1,-1},{1,0},{1,1}}; //右、右上、上、左上、左、左下、下、右下8个方向矢量值
void dfs2(int x, int y){
map[x][y] = '*'; //将行列标(x,y)的值由'@'改为'*',标记为已查找过的油田
//以(x,y)搜索8个方向的相邻点
for(int i = 0; i < 8; i++){
int newX = x + dir[i][0], newY = y + dir[i][1]; //计算新坐标点的行列标
//判断是否遍历到油田:1.未越界 2.为油田
if(newX >= 0 && newX < rows && newY >= 0 && newY < columns && map[newX][newY] == '@')
dfs2(newX,newY); //将新坐标点的值改为'*',并继续向8个方向搜索
}
}
4.N皇后
//N皇后问题
int n_queen; //皇后个数
int **board; //原始棋盘:0表示未落子 1皇后
int count3 = 0;
bool check(int i, int j){
int j_left = j, j_right = j;
while(i > 0){
i--;
if(board[i][j] == 1) return false; //正上方
if(j_left > 0){ //左上方
j_left--;
if(board[i][j_left] == 1)
return false;
}
if(j_right < (n_queen-1)){ //右上方
j_right++;
if(board[i][j_right] == 1)
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
void dfs3(int i){
//判断N个皇后是否已全部放入,即i == n
if(i == n_queen){
count3++;
cout << "------------我是分割线----------------" << endl;
for(int x = 0; x < n_queen; x++){
for(int y = 0; y < n_queen; y++){
cout << board[x][y] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
return;
}
//否则所有皇后未被全部放入,则依次遍历n个点
for(int j = 0; j < n_queen; j++){
//判断当前第i个皇后是否能放入第j个点
if(check(i,j)){
board[i][j] = 1; //将第i个皇后(第i行)放入第j个位子
dfs3(i+1); //查找选择下一个皇后i+1的位子
board[i][j] = 0; //将第i个皇后撤出,供下一种情况可选择
}
}
}回溯测试main主函数
void main(){
int i,j;
cout << "全排列" << endl;
cin >> n; //设置数值个数
//根据数值个数分配内存空间
num = new int*[n];
res1 = new int[n];
for(i = 0; i < n; i++)
num[i] = new int[2];
//初始化赋值
for(i = 0; i < n; i++){
cin >> num[i][0];
num[i][1] = 0;
res1[i] = 0;
}
dfs1(0);
cout << "油田问题" << endl;
cin >> rows >> columns; //设置油田大小
//根据油田大小分配内存空间
map = new char*[rows];
for(i = 0; i < rows; i++)
map[i] = new char[columns];
//初始化赋值
for(i = 0; i < rows; i++)
for(j = 0; j < columns; j++)
cin >> map[i][j];
//遍历油田,每遇到一片新油田,计数器自增,且将新油田的值由'@'全部改为'*'
for(i = 0; i < rows; i++)
for(j = 0; j < columns; j++){
if(map[i][j] == '@'){
count2++;
dfs2(i,j);
}
}
cout << count2 << endl;
cout << "N皇后问题" << endl;
cin >> n_queen; //设置皇后个数,即棋盘大小
//根据棋盘大小分配内存空间
board = new int*[n_queen];
for(i = 0; i < n_queen; i++)
board[i] = new int[n_queen];
//初始化赋值
for(i = 0; i < n_queen; i++)
for(j = 0; j < n_queen; j++)
board[i][j] = 0;
dfs3(0);
cout << count3 << endl;
} 第三章贪心算法
1.0-1背包
#include
using namespace std;
struct Friut{
int id,w,v;
float pr,x;
};
Friut f[5];
void quickSort(Friut *f,int l,int r)
{
int qSort(Friut *f,int l,int r);
if(lx.pr&&i<=r);
while(f[--j].pr=j) break;
Friut t=f[i];
f[i]=f[j];
f[j]=t;
}
f[l]=f[j];
f[j]=x;
return j;
}
void choose(float c){
int i=0;
while(f[i].w<=c&&i<=4)
{
f[i].x=1;
c=c-f[i].w;
i--;
}
if(c>0) f[i].x=c/f[i].w;
}
int main()
{
for(int i=0;i<5;i++)
{
f[i].id=i+1;
cout<< " 输入吧";
cin >>f[i].w>>f[i].v;
f[i].pr=(float)f[i].v/f[i].w;
}
quickSort(f,0,4);
choose(10);
for(int i=0;i<5;i++)
{
cout< 第四章动态规划
1.单个矩阵连乘
2.矩阵连乘
一、
A{2*3} B{3*2}
A
1 2 3
4 5 6
B
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 1*1+2*2+3*3=14 ②1*4+2*5+3*6=32
③ 4*1+5*2+6*3=32 ④4*4+5*5+6*6=77
①A[1][1]*B[1][1]+A[1][2]*B[2][1]+A[1][3]*B[3][1]
②A[1][1]*B[1][2]+A[1][2]*B[2][2]+A[1][3]*B[3][2]
③A[2][1]*B[1][1]+A[2][2]*B[2][1]+A[2][3]*B[3][1]
④A[2][1]*B[1][2]+A[2][2]*B[2][2]+A[2][3]*B[3][2]
(AipBpj)ij =
二、结论:假设A矩阵是p*q矩阵,B矩阵是q*r矩阵,则结果C矩阵是q*r矩阵,循环p*q*r次,即乘法运算p*q*r次。
假设有A1,A2,A3三个矩阵,大小分别为A1{10*100},A2{100*5},A3{5*50}。
利用矩阵乘法结合律有两种相乘方式:
①(A1*A2)*A3=10*100*5+10*5*50=7500
②A1*(A2*A3)=100*5*50+10*100*50=75000
三、问题:不同的运算方式影响计算效率。在A1*A2*……*An矩阵相乘中找到最高效率的解。
A[1:n]的最优结果,假设到第k个矩阵为最优,则式子为A[1:k]*A[k+1:n]
计算次数=A[1:k]次数 + A[k+1:n]次数 + A[1:k]*A[k+1:n]次数
建立递推关系:
设计算A[i:j](1<=i<=j<=n)所需最少乘法次数为dp_m[i][j],用P[i]表示第i个矩阵的列数。则原问题的最优解是dp_m[1][n]。
- 当i==j时,只有一个矩阵Ai,无须计算,dp_m[i][j] = 0(1<=i<=n)
- 当i
四、综合可得递推式:
五、例:
A1{30*35} A2{35*15} A3{15*5} A4{5*10} A5{10*20} A6{20*25}
| dp_m |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
dp_s |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
|
| 1 |
0 |
15750 |
7875 |
9375 |
11875 |
15125 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
1 |
3 |
3 |
3 |
|
| 2 |
0 |
2625 |
4375 |
7125 |
10500 |
2 |
0 |
2 |
3 |
3 |
3 |
|||
| 3 |
0 |
750 |
2500 |
5375 |
3 |
0 |
3 |
3 |
3 |
|||||
| 4 |
0 |
1000 |
3500 |
4 |
0 |
4 |
5 |
|||||||
| 5 |
0 |
5000 |
5 |
0 |
5 |
|||||||||
| 6 |
0 |
6 |
0 |
dp_m[1][2] = dp_m[1][1] + dp_m[2][2] + P[0]*P[1]*P[2] = 0+0+30*35*15=15750 k==1
dp_m[2][3] = dp_m[2][2] + dp_m[3][3] + P[1]*P[2]*P[3] = 0+0+35*15*5=2625 k==2
= 7125 k==3
最优解分析:(A1*(A2*A3))*((A4*A5)*A6)
#