【android 串口开发(一) 之生成so文件】
说到串口开发,不得不先明确一下以下概念。
接口的定义:
- 接口泛指实体把自己提供给外界的一种抽象化物(可以为另一实体),用以由内部操作分离出外部沟通方法,使其能被修改内部而不影响外界其他实体与其交互的方式。
串行接口的定义:
- 串行接口简称 串口,也称 串行通信接口 或 串行通讯接口(通常指COM接口)。是指数据一位一位地顺序传送,其特点是通信线路简单,只要一对传输线就可以实现双向通信,从而大大降低了成本,特别适用于远距离通信,但传送速度较慢。
串口通信的定义:
- 串口按位(bit)发送和接收字节。
串口通讯的定义:
- 串口通讯(Serial Communication), 是指外设和计算机间,通过数据信号线 、地线、控制线等,按位进行传输数据的一种通讯方式。一条信息的各位数据被逐位按顺序传送的通讯方式称为串行通讯。
【android 串口开发(二) 之 串口读写操作】
明确了概念以后,那么我们就回归正题。android的串口开发,很自然的就是要用到JNI的相关知识,通过JNI调用底层C代码。其实使用JNI直接进行串口设备的读写操作,网上参考的资料还是有不少的,而且 google也有开源项目 ,本文也是整理一下网上的资源,做些优化,也方便以后查阅。
说明:查阅了很多资料,很多生成so库的方法都比较旧了,用3.0以上的as,都不好使了。这里我们采用CMake方法。
一:生成SO库
1. 生成 .h结尾文件
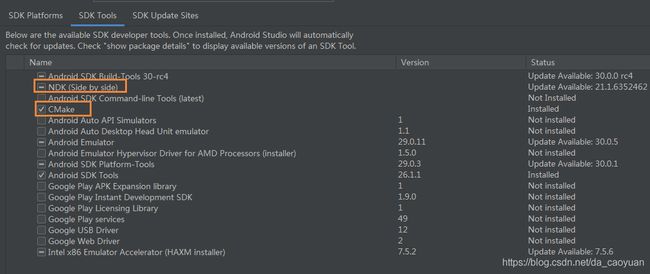
首现做一些准备工作,确保你的android studio已经下载了NDK和CMake。如图:
然后创建一个 SerialPort.java ,如图:
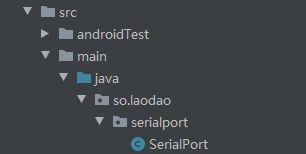
注意:包名一旦写好,以后都不要变动了。
SerialPort.java具体代码:
import android.util.Log;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileDescriptor;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.OutputStream;
/**
* Created by abc on 2017/2/21.
*/
public class SerialPort {
private static final String TAG = "SerialPort";
/*
* Do not remove or rename the field mFd: it is used by native method close();
*/
private FileDescriptor mFd;
private FileInputStream mFileInputStream;
private FileOutputStream mFileOutputStream;
public SerialPort(File device, int baudrate, int flags) throws SecurityException, IOException {
if (device == null) {
System.out.println("device is null");
return;
}
/* Check access permission */
if (!device.canRead() || !device.canWrite()) {
try {
/* Missing read/write permission, trying to chmod the file */
Process su;
su = Runtime.getRuntime().exec("/system/bin/su");
String cmd = "chmod 777 " + device.getAbsolutePath() + "\n" + "exit\n";
su.getOutputStream().write(cmd.getBytes());
if ((su.waitFor() != 0) || !device.canRead() || !device.canWrite()) {
throw new SecurityException();
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
throw new SecurityException();
}
}
mFd = open(device.getAbsolutePath(), baudrate, flags);
if (mFd == null) {
Log.e(TAG, "native open returns null");
throw new IOException();
}
mFileInputStream = new FileInputStream(mFd);
mFileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream(mFd);
}
// Getters and setters
public InputStream getInputStream() {
return mFileInputStream;
}
public OutputStream getOutputStream() {
return mFileOutputStream;
}
// JNI
private native static FileDescriptor open(String path, int baudrate, int flags);
public native void close();
static {
System.loadLibrary("serial_port");
}
}
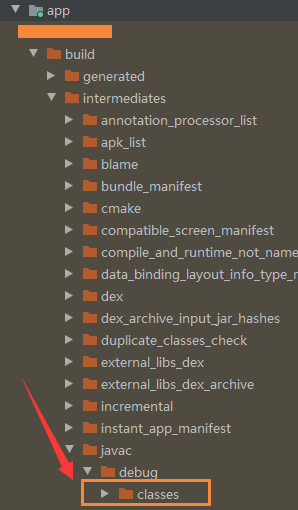
然后clean project 再rebuild project 生成class文件,
这时候打开如下图的文件夹看是否生成了classes文件夹,没有生成请重新再试一遍。
再打开Terminal输入指令
cd app/build/intermediates/javac/debug/classes
然后再输入指令
javah -jni so.laodao.serialport.SerialPort
注意 这里javah -jni后面跟的是 SerialPort.java 的全路径,如果javah报不存在之类的,是你的Java环境没有配置好。
这时候打开 debug/classes下面的文件发现多了一个以 .h 结尾文件

2.编写C文件
然后,将之前生成的文件,复制到jni文件夹中。再创建一个 SerialPort.c 文件。如图:

至于为什么会有红色箭头指向的类,有时间百度一下吧。如果不添加的话,有可能会报如下错误:
java.lang.UnsatisfiedLinkError: dlopen failed: cannot locate symbol tcgetattr referenced by libserial_port.so…
下面贴出 SerialPort.c 具体代码:
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include "so_laodao_serialport_SerialPort.h"
#include "android/log.h"
static const char *TAG = "serial_port";
#define LOGI(fmt, args...) __android_log_print(ANDROID_LOG_INFO, TAG, fmt, ##args)
#define LOGD(fmt, args...) __android_log_print(ANDROID_LOG_DEBUG, TAG, fmt, ##args)
#define LOGE(fmt, args...) __android_log_print(ANDROID_LOG_ERROR, TAG, fmt, ##args)
static speed_t getBaudrate(jint baudrate)
{
switch(baudrate) {
case 0: return B0;
case 50: return B50;
case 75: return B75;
case 110: return B110;
case 134: return B134;
case 150: return B150;
case 200: return B200;
case 300: return B300;
case 600: return B600;
case 1200: return B1200;
case 1800: return B1800;
case 2400: return B2400;
case 4800: return B4800;
case 9600: return B9600;
case 19200: return B19200;
case 38400: return B38400;
case 57600: return B57600;
case 115200: return B115200;
case 230400: return B230400;
case 460800: return B460800;
case 500000: return B500000;
case 576000: return B576000;
case 921600: return B921600;
case 1000000: return B1000000;
case 1152000: return B1152000;
case 1500000: return B1500000;
case 2000000: return B2000000;
case 2500000: return B2500000;
case 3000000: return B3000000;
case 3500000: return B3500000;
case 4000000: return B4000000;
default: return -1;
}
}
/*
* Class: android_serialport_SerialPort
* Method: open
* Signature: (Ljava/lang/String;II)Ljava/io/FileDescriptor;
*/
JNIEXPORT jobject JNICALL Java_so_laodao_serialport_SerialPort_open
(JNIEnv *env, jclass thiz, jstring path, jint baudrate, jint flags)
{
int fd;
speed_t speed;
jobject mFileDescriptor;
/* Check arguments */
{
speed = getBaudrate(baudrate);
if (speed == -1) {
/* TODO: throw an exception */
LOGE("Invalid baudrate");
return NULL;
}
}
/* Opening device */
{
jboolean iscopy;
const char *path_utf = (*env)->GetStringUTFChars(env, path, &iscopy);
LOGD("Opening serial port %s with flags 0x%x", path_utf, O_RDWR | flags);
fd = open(path_utf, O_RDWR | flags);
LOGD("open() fd = %d", fd);
(*env)->ReleaseStringUTFChars(env, path, path_utf);
if (fd == -1)
{
/* Throw an exception */
LOGE("Cannot open port");
/* TODO: throw an exception */
return NULL;
}
}
/* Configure device */
{
struct termios cfg;
LOGD("Configuring serial port");
if (tcgetattr(fd, &cfg))
{
LOGE("tcgetattr() failed");
close(fd);
/* TODO: throw an exception */
return NULL;
}
cfmakeraw(&cfg);
cfsetispeed(&cfg, speed);
cfsetospeed(&cfg, speed);
if (tcsetattr(fd, TCSANOW, &cfg))
{
LOGE("tcsetattr() failed");
close(fd);
/* TODO: throw an exception */
return NULL;
}
}
/* Create a corresponding file descriptor */
{
jclass cFileDescriptor = (*env)->FindClass(env, "java/io/FileDescriptor");
jmethodID iFileDescriptor = (*env)->GetMethodID(env, cFileDescriptor, "", "()V");
jfieldID descriptorID = (*env)->GetFieldID(env, cFileDescriptor, "descriptor", "I");
mFileDescriptor = (*env)->NewObject(env, cFileDescriptor, iFileDescriptor);
(*env)->SetIntField(env, mFileDescriptor, descriptorID, (jint)fd);
}
return mFileDescriptor;
}
/*
* Class: cedric_serial_SerialPort
* Method: close
* Signature: ()V
*/
JNIEXPORT void JNICALL Java_so_laodao_serialport_SerialPort_close
(JNIEnv *env, jobject thiz)
{
jclass SerialPortClass = (*env)->GetObjectClass(env, thiz);
jclass FileDescriptorClass = (*env)->FindClass(env, "java/io/FileDescriptor");
jfieldID mFdID = (*env)->GetFieldID(env, SerialPortClass, "mFd", "Ljava/io/FileDescriptor;");
jfieldID descriptorID = (*env)->GetFieldID(env, FileDescriptorClass, "descriptor", "I");
jobject mFd = (*env)->GetObjectField(env, thiz, mFdID);
jint descriptor = (*env)->GetIntField(env, mFd, descriptorID);
LOGD("close(fd = %d)", descriptor);
close(descriptor);
}
termios.h 具体代码:
/*
* Copyright (C) 2008 The Android Open Source Project
* All rights reserved.
*
* Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without
* modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions
* are met:
* * Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright
* notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer.
* * Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above copyright
* notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer in
* the documentation and/or other materials provided with the
* distribution.
*
* THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS AND CONTRIBUTORS
* "AS IS" AND ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT
* LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS
* FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE
* COPYRIGHT OWNER OR CONTRIBUTORS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT,
* INCIDENTAL, SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING,
* BUT NOT LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES; LOSS
* OF USE, DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER CAUSED
* AND ON ANY THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY,
* OR TORT (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT
* OF THE USE OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF
* SUCH DAMAGE.
*/
#ifndef _TERMIOS_H_
#define _TERMIOS_H_
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
__BEGIN_DECLS
/* Redefine these to match their ioctl number */
#undef TCSANOW
#define TCSANOW TCSETS
#undef TCSADRAIN
#define TCSADRAIN TCSETSW
#undef TCSAFLUSH
#define TCSAFLUSH TCSETSF
static __inline__ int tcgetattr(int fd, struct termios *s)
{
return ioctl(fd, TCGETS, s);
}
static __inline__ int tcsetattr(int fd, int __opt, const struct termios *s)
{
return ioctl(fd, __opt, (void *)s);
}
static __inline__ int tcflow(int fd, int action)
{
return ioctl(fd, TCXONC, (void *)(intptr_t)action);
}
static __inline__ int tcflush(int fd, int __queue)
{
return ioctl(fd, TCFLSH, (void *)(intptr_t)__queue);
}
static __inline__ pid_t tcgetsid(int fd)
{
pid_t _pid;
return ioctl(fd, TIOCGSID, &_pid) ? (pid_t)-1 : _pid;
}
static __inline__ int tcsendbreak(int fd, int __duration)
{
return ioctl(fd, TCSBRKP, (void *)(uintptr_t)__duration);
}
static __inline__ speed_t cfgetospeed(const struct termios *s)
{
return (speed_t)(s->c_cflag & CBAUD);
}
static __inline__ int cfsetospeed(struct termios *s, speed_t speed)
{
s->c_cflag = (s->c_cflag & ~CBAUD) | (speed & CBAUD);
return 0;
}
static __inline__ speed_t cfgetispeed(const struct termios *s)
{
return (speed_t)(s->c_cflag & CBAUD);
}
static __inline__ int cfsetispeed(struct termios *s, speed_t speed)
{
s->c_cflag = (s->c_cflag & ~CBAUD) | (speed & CBAUD);
return 0;
}
static __inline__ void cfmakeraw(struct termios *s)
{
s->c_iflag &= ~(IGNBRK|BRKINT|PARMRK|ISTRIP|INLCR|IGNCR|ICRNL|IXON);
s->c_oflag &= ~OPOST;
s->c_lflag &= ~(ECHO|ECHONL|ICANON|ISIG|IEXTEN);
s->c_cflag &= ~(CSIZE|PARENB);
s->c_cflag |= CS8;
}
__END_DECLS
#endif /* _TERMIOS_H_ */
3.配置参数
好了,到此基本上完成一大半,万事俱备只欠东风。我们还需要一些关键步骤:用CMeke生成so文件。
首先,在项目(app)的build.gradel中的defaultConfig下添加:
externalNativeBuild {
cmake {
cppFlags ""
// abiFilters "armeabi-v7a", "x86", "arm64-v8a"
}
}
然后再在项目(app)的build.gradel 的 android 闭包下添加:
externalNativeBuild {
cmake {
path "CMakeLists.txt" //编译后so文件的名字
}
}
最后在创建 CMakeLists.txt文件,如图:

CMakeLists.txt 文件内容:
# For more information about using CMake with Android Studio, read the
# documentation: https://d.android.com/studio/projects/add-native-code.html
# Sets the minimum version of CMake required to build the native library.
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.4.1)
# Creates and names a library, sets it as either STATIC
# or SHARED, and provides the relative paths to its source code.
# You can define multiple libraries, and CMake builds them for you.
# Gradle automatically packages shared libraries with your APK.
#设置生成的so动态库最后输出的路径
set(CMAKE_LIBRARY_OUTPUT_DIRECTORY ${PROJECT_SOURCE_DIR}/../jniLibs/${ANDROID_ABI})
add_library( # Sets the name of the library.
#此处填入library名称,就是生成so文件的名称
serial_port
# Sets the library as a shared library.
SHARED
# Provides a relative path to your source file(s). c文件或cpp文件的相对路径
src/main/jni/SerialPort.c
)
# Searches for a specified prebuilt library and stores the path as a
# variable. Because CMake includes system libraries in the search path by
# default, you only need to specify the name of the public NDK library
# you want to add. CMake verifies that the library exists before
# completing its build.
find_library( # Sets the name of the path variable.
log-lib
# Specifies the name of the NDK library that
# you want CMake to locate.
log)
# Specifies libraries CMake should link to your target library. You
# can link multiple libraries, such as libraries you define in this
# build script, prebuilt third-party libraries, or system libraries.
target_link_libraries( # Specifies the target library.
#此处填入library名称,就是生成so文件的名称
serial_port
# Links the target library to the log library
# included in the NDK.
${log-lib})
到这里基本上ok啦!说明CMakeLists.txt 文件中,我们只需要关注修改一下so文件的名称和c文件的相对路径,其他不需要修改。更多 CMakeLists 语法请看这篇文章:Android Studio中CMakeList的写法
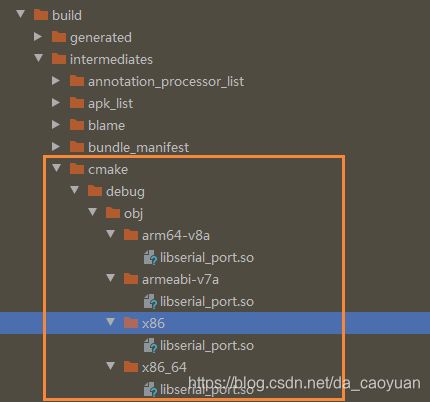
你现在就可以Make Project 或者 Rebuild Project 一下 ,之后会在这里会生成so库:

如果你不在CMakeLists.txt 中设置输出路径的话,
#设置生成的so动态库最后输出的路径
set(CMAKE_LIBRARY_OUTPUT_DIRECTORY ${PROJECT_SOURCE_DIR}/../jniLibs/${ANDROID_ABI})
不过你如果没有放到如上图一样到 jniLibs 文件夹中,而是放到了 libs文件夹下,
在项目(app)的build.gradel 的 android 闭包下添加,要添加如下代码:
sourceSets {
main {
jniLibs.srcDirs = ['libs']
}
}
然后删除咱们的jni文件试试,是否工程还能运行?
答案当然是能运行的!
打包so文件扩展:除了CMake生成so文件,你可以利用 Android.mk、Application.mk生成so文件。
(1)新建Android.mk、Application.mk两个文件
Android.mk:
LOCAL_PATH := $(call my-dir)
include $(CLEAR_VARS)
LOCAL_LDLIBS := -llog
LOCAL_MODULE := serial_port #输出so文件的名称
LOCAL_SRC_FILES := SerialPort.c #需要读取的C++源文件地址
include $(BUILD_SHARED_LIBRARY)
Application.mk:
APP_STL := gnustl_static
APP_CPPFLAGS := -frtti -fexceptions
APP_ABI := all #生成所有版本的so文件
APP_PLATFORM := android-8
(2)在build.gradle文件中条件配置代码
task ndkBuild(type: Exec, description: 'Compile JNI source via NDK') {
//配置ndk的路径
commandLine "D:\\studio_sdk\\ndk\\21.0.6113669\\build\\ndk-build.cmd",
//ndk默认的生成so的文件
'NDK_PROJECT_PATH=build/intermediates/ndk',
//配置的我们想要生成的so文件所在的位置
'NDK_LIBS_OUT=src/main/jniLibs',
//指定项目以这个mk的方式
'APP_BUILD_SCRIPT=src/main/jni/Android.mk',
//指定项目以这个mk的方式
'NDK_APPLOCATION_MK=src/main/jni/Application.mk'
}
tasks.withType(JavaCompile) {
//使用ndkBuild
compileTask -> compileTask.dependsOn ndkBuild
}
想看更多,更详细请看这篇文章:Android开发:JNI开发过程以及两种生成.so文件的方法
源码下载
CMake相关参考文章:
Android开发:JNI开发过程以及两种生成.so文件的方法
Android Studio中CMakeList的写法
Android-串口(通过jni技术生成自己的so)
google官方地址: https://github.com/cepr/android-serialport-api
android串口通信以及串口协议解析
android 串口编程
Android串口通信:串口读写实例
【Android应用开发】-(19)Android 串口编程原理和实现方式(附源码)