docker搭建redis哨兵集群和分片集群
搭建哨兵集群
环境准备拉取镜像
搭建目标 : 一主而从三哨兵集群
docker pull redis:6.2.6创建文件夹及配置文件
我这里在/usr/local/docker/redis目录下
在 redis-master、redis-slave1、redis-slave2 下分别建立data、 redis.conf、 sentinel.conf
redis配置文件
在从节点上配置所属于哪个父集群(找爹行动)
- replicaof 39.106.53.30 6379(redis5.0之后)
- slaveof 39.106.53.30 6379(5.0之前的命令)
# master redis.conf
save 3600 1
save 300 100
save 60 10000
appendonly no
protected-mode no
port 6379
# redis-slave1 redis.conf
save 3600 1
save 300 100
save 60 10000
appendonly no
bind 0.0.0.0
port 6380
protected-mode no
replicaof 39.106.53.30 6379
# redis-slave2 redis.conf
save 3600 1
save 300 100
save 60 10000
appendonly no
bind 0.0.0.0
port 6381
protected-mode no
replicaof 39.106.53.30 6379sentinel配置
# master 配置
port 26379
dir /tmp
sentinel monitor mymaster 39.106.53.30 6379 2
sentinel down-after-milliseconds mymaster 30000
sentinel failover-timeout mymaster 60000
# slave1 配置
port 26380
dir /tmp
sentinel monitor mymaster 39.106.53.30 6379 2
sentinel down-after-milliseconds mymaster 30000
sentinel failover-timeout mymaster 60000
# slave2 配置
port 26381
dir /tmp
sentinel monitor mymaster 39.106.53.30 6379 2
sentinel down-after-milliseconds mymaster 30000
sentinel failover-timeout mymaster 60000编写docker-compose.yml
version: '3'
services:
master:
image: redis:6.2.6
container_name: redis-master
command: redis-server /etc/redis/redis.conf
ports:
- 6379:6379
volumes:
- /usr/local/docker/redis/redis-master/data:/data
- /usr/local/docker/redis/redis-master/redis.conf:/etc/redis/redis.conf
slave1:
image: redis:6.2.6
container_name: redis-slave1
volumes:
- /usr/local/docker/redis/redis-slave1/data:/data
- /usr/local/docker/redis/redis-slave1/redis.conf:/etc/redis/redis.conf
command: redis-server /etc/redis/redis.conf
ports:
- 6380:6380
depends_on:
- master
slave2:
image: redis:6.2.6
container_name: redis-slave2
volumes:
- /usr/local/docker/redis/redis-slave2/data:/data
- /usr/local/docker/redis/redis-slave2/redis.conf:/etc/redis/redis.conf
command: redis-server /etc/redis/redis.conf
ports:
- 6381:6381
depends_on:
- master
sentinel1:
image: redis:6.2.6
container_name: redis-sentinel1
command: redis-sentinel /usr/local/etc/redis/sentinel.conf
ports:
- 26379:26379
volumes:
- /usr/local/docker/redis/redis-master/sentinel.conf:/usr/local/etc/redis/sentinel.conf
depends_on:
- master
- slave1
- slave2
sentinel2:
image: redis:6.2.6
container_name: redis-sentinel2
command: redis-sentinel /usr/local/etc/redis/sentinel.conf
ports:
- 26380:26380
volumes:
- /usr/local/docker/redis/redis-slave1/sentinel.conf:/usr/local/etc/redis/sentinel.conf
depends_on:
- master
- slave1
- slave2
sentinel3:
image: redis:6.2.6
container_name: redis-sentinel3
command: redis-sentinel /usr/local/etc/redis/sentinel.conf
ports:
- 26381:26381
volumes:
- /usr/local/docker/redis/redis-slave1/sentinel.conf:/usr/local/etc/redis/sentinel.conf
depends_on:
- master
- slave1
- slave2执行docker-compose
docker-compose up -d 查看集群信息
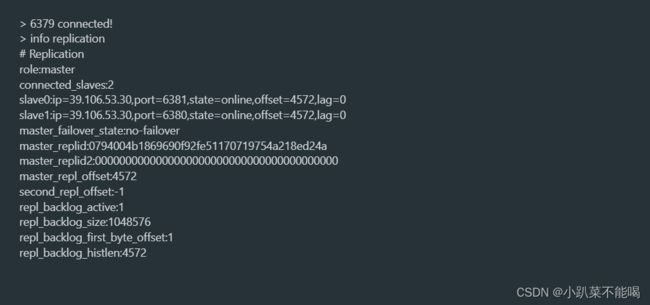
查看集群信息
查看集群信息 info replication
 测试数据同步
测试数据同步
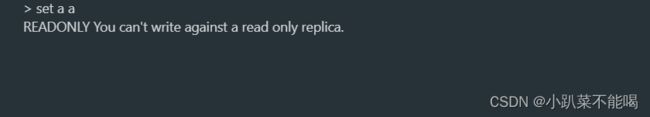
本次搭建的集群,在从节点是只读形式,只有主节点才能够写,在主节点写入 set test test
set k v,查看所有从节点信息,在从节点中写,会提示只读副本
在主节点中写,发现在所有从节点中都存在数据,数据同步成功
 主从集群同步原理
主从集群同步原理
主从同步第一次同步是全量同步:
master如何判断slave是不是第一次来同步数据:
Replication ld: 简称replid,是数据集的标记,id一致则说明是同一数据集。每一个master都有唯一的replid,slave则会继承master节点的replid
ofset:偏移量,随着记录在repl_bak_log中的数据增多而逐渐增大。slave完成同步时也会记录当前同步的ofset如果slave的offset小于master的offset,说明slave数据落后于master,需要更新
因此slave做数据同步,必须向master声明自己的replication id 和offset,master才可以判断到底需要同步哪些数据
但如果slave重启后同步,则执行增量同步
repl_bak_log大小有上限,写满后会覆盖最早的数据。如果slave断开时间过久,导致尚未备份的数据被覆盖,则无法基于log做增量同步,只能再次全量同步
全量同步流程
增量同步流程
spring boot整合集群并配置读写分离
引入依赖
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-data-redis
配置集群
由于哨兵模式的节点不固定,所以配置哨兵集群,监听的redis集群由哨兵去找
server:
port: 9000
spring:
redis:
sentinel:
master: mymaster
nodes:
- 39.106.53.30:26379
- 39.106.53.30:26380
- 39.106.53.30:26381测试集群同步
这里的ReadFrom是配置Redis的读取策略:
- MASTER:从主节点读取.
- MASTER PREFERRED:优先从master节点读取,master不可用才读取replica
- REPLICA: 从slave (replica)节点读取
- REPLICA PREFERRED: 优先从slave (replica)节点读取,所有的slave都不可用才读取master
package com.test.cluster.rediscluster;
import io.lettuce.core.ReadFrom;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.redis.LettuceClientConfigurationBuilderCustomizer;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
@SpringBootApplication
public class RedisClusterApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(RedisClusterApplication.class, args);
}
@Bean
public LettuceClientConfigurationBuilderCustomizer clientConfigurationBuilderCustomizer(){
return clientConfigurationBuilder -> clientConfigurationBuilder.readFrom(ReadFrom.REPLICA_PREFERRED);
}
}
编写controller
package com.test.cluster.rediscluster.controller;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.StringRedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
/**
* @Author sl
*/
@RestController
public class TestRedisSentinelController {
@Autowired
private StringRedisTemplate redisTemplate;
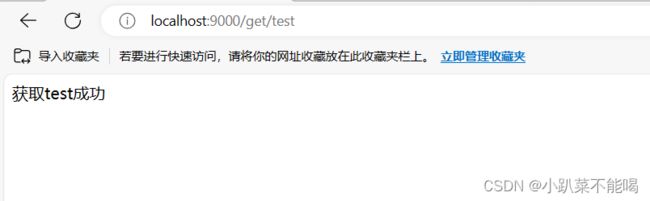
@RequestMapping("/get/{key}")
public String getKey(@PathVariable("key") String key){
String s = redisTemplate.opsForValue().get(key);
if(s!= null){
return "获取"+ s + "成功";
}
return "获取"+ key + "失败";
}
@RequestMapping("set/{key}/{value}")
public String setValue(@PathVariable("key")String key,@PathVariable("value") String value){
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set(key,value);
return "set" + key + "success";
}
}
设置key http://localhost:9000/set/china/yyds ,在80和81中,可以查到china的值
 搭建分片集群
搭建分片集群
redis 哨兵模式虽然提供了 redis⾼可⽤、高并发读的解决方案,但是在海量数据应用场景下,仍然存在海量数据存储问题和高并发写的问题。当只有⼀个 Master 对外提供服务时,如果数据量特别⼤,内存占⽤问题严重,数据的高并发写、数据备份和恢复都会⼤⼤降低效率,针对这些问题,redis 推出 Cluster 集群架构,该结构具有如下特点:
Redis Cluster 采用的去中心化的网络拓扑架构,没有中心节点,所有节点既是数据存储节点,也是控制节点
引入槽(slot)的概念,通过 CRC+hashslot 算法支持多个主节点(分片),每个主节点分别负责存储一部分数据,这样理论上可以支持无限主节点的水平扩容以便支持海量吞吐量
在 Cluster 集群里设置了 16384 个哈希槽(hash slot),在 master 节点上写键值对数据时,redis 先对每个键(key),用CRC16 算法对 key 进行运算,然后用 16384 对运算结果取模,余数作为插槽,每个槽在不同的节点下,形成了分片
内置类似哨兵的高可用机制,能够实现自动故障转移,保证每个主节点的高可用
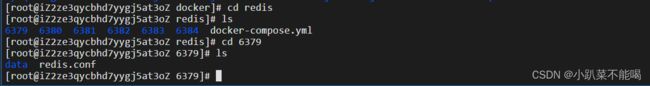
创建文件和映射
创建6379-6384的文件夹,目录为data ,redis.conf
编写redis.conf
port 6379
daemonize no
cluster-enabled yes
# reids维护
cluster-config-file nodes_6379.conf
tcp-keepalive 300
timeout 0
appendonly yes
logfile "redis_6379.log"
bind 0.0.0.0
cluster-node-timeout 5000
protected-mode no
cluster-announce-ip 39.106.53.30
cluster-announce-bus-port 16379编写docker-compose
version: '3'
services:
node1:
image: redis:6.2.6
container_name: redis-node1
restart: always
ports:
- 6379:6379
- 16379:16379
volumes:
- /usr/local/docker/redis/6379/data:/data
- /usr/local/docker/redis/6379/redis.conf:/etc/redis/redis.conf
command:
redis-server /etc/redis/redis.conf
node2:
image: redis:6.2.6
container_name: redis-node2
restart: always
ports:
- 6380:6380
- 16380:16380
volumes:
- /usr/local/docker/redis/6380/data:/data
- /usr/local/docker/redis/6380/redis.conf:/etc/redis/redis.conf
command:
redis-server /etc/redis/redis.conf
node3:
image: redis:6.2.6
container_name: redis-node3
restart: always
ports:
- 6381:6381
- 16381:16381
volumes:
- /usr/local/docker/redis/6381/data:/data
- /usr/local/docker/redis/6381/redis.conf:/etc/redis/redis.conf
command:
redis-server /etc/redis/redis.conf
node4:
image: redis:6.2.6
container_name: redis-node4
restart: always
ports:
- 6382:6382
- 16382:16382
volumes:
- /usr/local/docker/redis/6382/data:/data
- /usr/local/docker/redis/6382/redis.conf:/etc/redis/redis.conf
command:
redis-server /etc/redis/redis.conf
node5:
image: redis:6.2.6
container_name: redis-node5
restart: always
ports:
- 6383:6383
- 16383:16383
volumes:
- /usr/local/docker/redis/6383/data:/data
- /usr/local/docker/redis/6383/redis.conf:/etc/redis/redis.conf
command:
redis-server /etc/redis/redis.conf
node6:
image: redis:6.2.6
container_name: redis-node6
restart: always
ports:
- 6384:6384
- 16384:16384
volumes:
- /usr/local/docker/redis/6384/data:/data
- /usr/local/docker/redis/6384/redis.conf:/etc/redis/redis.conf
command:
redis-server /etc/redis/redis.conf执行docker-compose
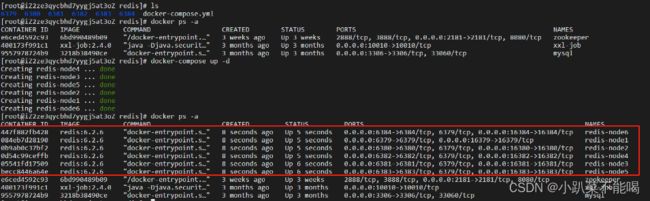
docker-compose up -d
集群启动
进入任意节点 docker exec -it redis-node1 /bin/bash
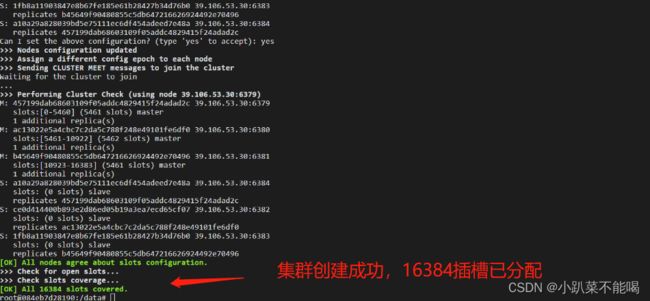
redis-cli --cluster create 39.106.53.30:6379 39.106.53.30:6380 39.106.53.30:6381 39.106.53.30:6382 39.106.53.30:6383 39.106.53.30:6384 --cluster-replicas 1--cluster-replicas 或者 --replicas 1 表示集群中每个master的副本数为1,此时 节点总数/(replicas+1)得到的就是master的数量,因此节点中前n个是master节点
查看集群信息
连接集群
以cluster方式连接集群,并set test test 值 ,在其他节点中有相同的值
 spring boot 整合分片集群
spring boot 整合分片集群
更改配置
server:
port: 9000
# 哨兵集群
#spring:
# redis:
# sentinel:
# master: mymaster
# nodes:
# - 39.106.53.30:26379
# - 39.106.53.30:26380
# - 39.106.53.30:26381
# 分片集群
spring:
redis:
cluster:
nodes:
- 39.106.53.30:6379
- 39.106.53.30:6380
- 39.106.53.30:6381
- 39.106.53.30:6382
- 39.106.53.30:6383
- 39.106.53.30:6384
测试controller
package com.test.cluster.rediscluster.controller;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.StringRedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
/**
* @Author sl
*/
@RestController
public class TestRedisClusterController {
@Autowired
private StringRedisTemplate redisTemplate;
@RequestMapping("/get/{key}")
public String getKey(@PathVariable("key") String key){
String s = redisTemplate.opsForValue().get(key);
if(s!= null){
return "获取"+ s + "成功";
}
return "获取"+ key + "失败";
}
@RequestMapping("set/{key}/{value}")
public String setValue(@PathVariable("key")String key,@PathVariable("value") String value){
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set(key,value);
return "set" + key + "success";
}
}