windows10搭建llama大模型
背景
随着人工时代的到来及日渐成熟,大模型已慢慢普及,可以为开发与生活提供一定的帮助及提升工作及生产效率。所以在新的时代对于开发者来说需要主动拥抱变化,主动成长。
LLAMA介绍
llama全称:Large Language Model Meta AI是由meta(原facebook)开源的一个聊天对话大模型。根据参数规模,Meta提供了70亿、130亿、330亿和650亿四种不同参数规模的LLaMA模型,并使用20种语言进行了训练。与现有最佳的大型语言模型相比,LLaMA模型在性能上具有竞争力。
官网:https://github.com/facebookresearch/llama
注意:本文是llama不是llama2,原理一致!
硬件要求
硬件名称 |
要求 |
备注 |
磁盘 |
单盘最少120g以上 |
模型很大的 |
| 内存 |
最少16g |
最好32g |
| gpu |
可以没有 |
当然最好有(要英伟达的) |
安装软件
涉及软件版本
软件名称 |
版本 |
备注 |
anaconda3 |
conda 22.9.0 |
https://www.anaconda.com/ |
python |
3.9.16 |
anaconda自带 |
peft |
0.2.0 |
参数有效微调 |
sentencepiece |
0.1.97 |
分词算法 |
transformers |
4.29.2 |
下载有点久 |
git |
2.40.1 |
|
torch |
2.0.1 |
|
mingw |
用window安装 |
|
protobuf |
3.19.0 |
|
cuda |
https://blog.csdn.net/zcs2632008/article/details/127025294 |
有gpu才需要安装 |
anaconda3安装
安装这个anaconda建议不要在c盘,除非你的c盘够大。
请参考:https://blog.csdn.net/scorn_/article/details/106591160?ops_request_misc=%257B%2522request%255Fid%2522%253A%2522168601805516800197073452%2522%252C%2522scm%2522%253A%252220140713.130102334..%2522%257D&request_id=168601805516800197073452&biz_id=0&utm_medium=distribute.pc_search_result.none-task-blog-2~all~sobaiduend~default-1-106591160-null-null.142^v88^control,239^v2^insert_chatgpt&utm_term=windows10%E5%AE%89%E8%A3%85anaconda3%E6%95%99%E7%A8%8B&spm=1018.2226.3001.4187
创建环境
conda create -n llama python=3.9.16
conda init进入环境
conda info -e
conda activate llama后面验证python
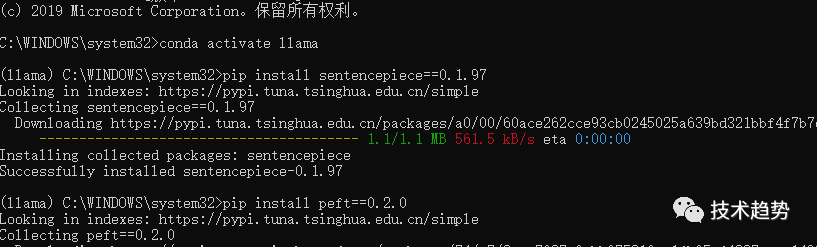
peft安装
pip install peft==0.2.0transformers安装
注意:这个会很大~有点久~
conda install transformers==4.29.2安装git
https://blog.csdn.net/dou3516/article/details/121740303
安装torch
pip install torch==2.0.1安装mingw
win+r输入powershell
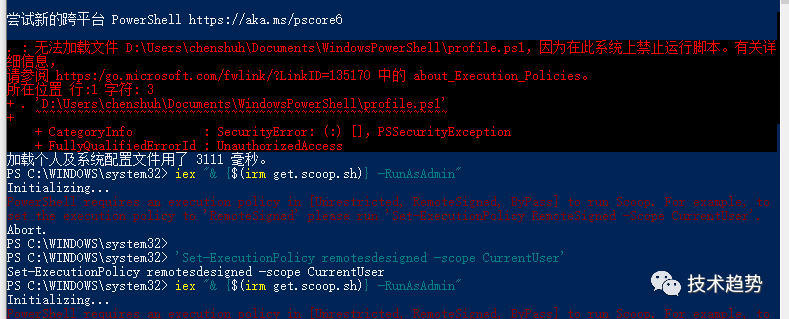
遇到禁止执行脚本问题:(如果没有异常请跳出这步)
参考
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_43999496/article/details/115871373
配置权限
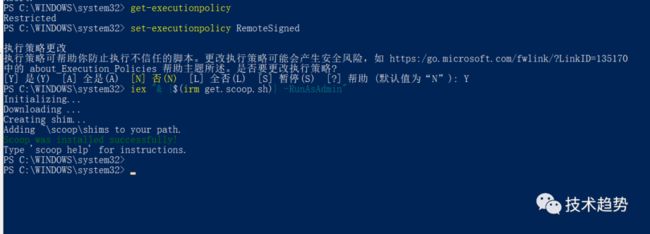
get-executionpolicy
set-executionpolicy RemoteSigned然后输入Y
安装 mingw
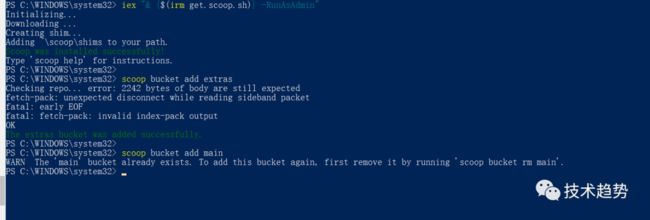
iex "& {$(irm get.scoop.sh)} -RunAsAdmin"安装好后分别运行下面两个命令(添加库):
scoop bucket add extrasscoop bucket add main输入命令安装mingw
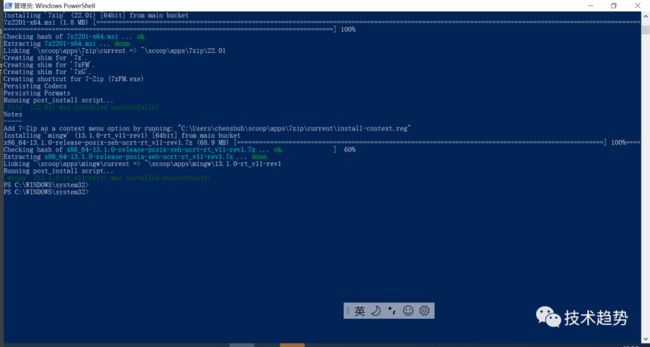
scoop install mingw安装:protobuf
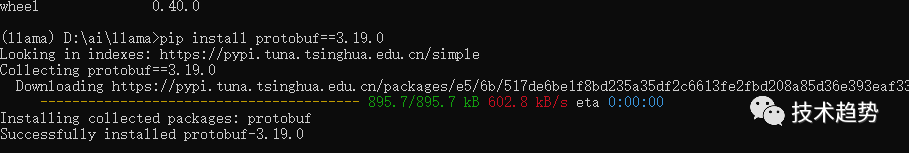
pip install protobuf==3.19.0项目配置
下载代码
需要下载两个模型, 一个是原版的LLaMA模型, 一个是扩充了中文的模型, 后续会进行一个合并模型的操作
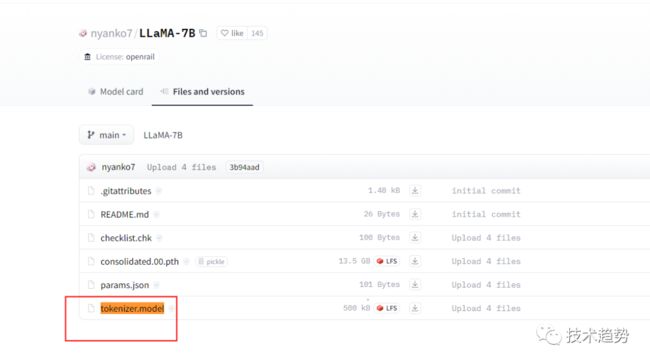
原版模型下载地址(要代理):https://ipfs.io/ipfs/Qmb9y5GCkTG7ZzbBWMu2BXwMkzyCKcUjtEKPpgdZ7GEFKm/
备用:nyanko7/LLaMA-7B at main
下载不了的话,请关注【技术趋势】回复llama1获取。
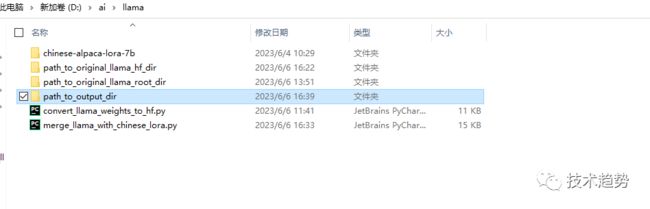
创建文件夹
git lfs install下载中文模型
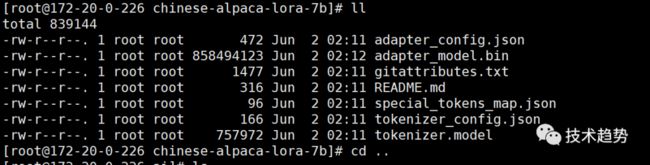
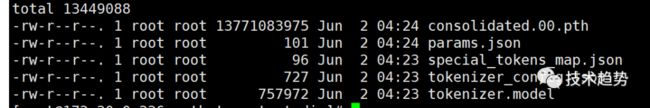
git clone https://huggingface.co/ziqingyang/chinese-alpaca-lora-7b补充Linux图:
下载羊驼模型(有点大)
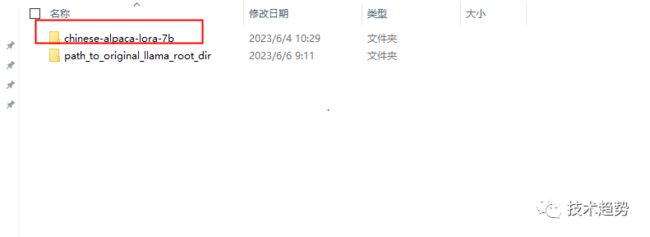
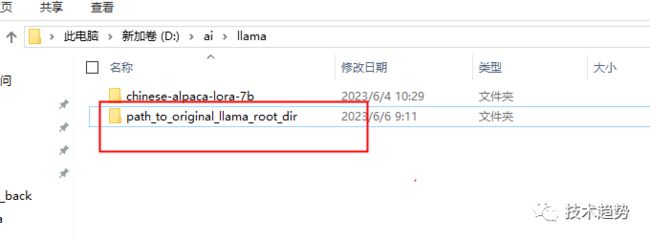
先建一个文件夹:path_to_original_llama_root_dir
在里面再建一个7B文件夹并把tokenizer.model挪进来。
7B里面放的内容
最终需要的内容如下:
合并模型
下载:convert_llama_weights_to_hf.py
convert_llama_weights_to_hf.py
或将以下代码放到
# Copyright 2022 EleutherAI and The HuggingFace Inc. team. All rights reserved.
#
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
# limitations under the License.
import argparse
import gc
import json
import math
import os
import shutil
import warnings
import torch
from transformers import LlamaConfig, LlamaForCausalLM, LlamaTokenizer
try:
from transformers import LlamaTokenizerFast
except ImportError as e:
warnings.warn(e)
warnings.warn(
"The converted tokenizer will be the `slow` tokenizer. To use the fast, update your `tokenizers` library and re-run the tokenizer conversion"
)
LlamaTokenizerFast = None
"""
Sample usage:
```
python src/transformers/models/llama/convert_llama_weights_to_hf.py \
--input_dir /path/to/downloaded/llama/weights --model_size 7B --output_dir /output/path
```
Thereafter, models can be loaded via:
```py
from transformers import LlamaForCausalLM, LlamaTokenizer
model = LlamaForCausalLM.from_pretrained("/output/path")
tokenizer = LlamaTokenizer.from_pretrained("/output/path")
```
Important note: you need to be able to host the whole model in RAM to execute this script (even if the biggest versions
come in several checkpoints they each contain a part of each weight of the model, so we need to load them all in RAM).
"""
INTERMEDIATE_SIZE_MAP = {
"7B": 11008,
"13B": 13824,
"30B": 17920,
"65B": 22016,
}
NUM_SHARDS = {
"7B": 1,
"13B": 2,
"30B": 4,
"65B": 8,
}
def compute_intermediate_size(n):
return int(math.ceil(n * 8 / 3) + 255) // 256 * 256
def read_json(path):
with open(path, "r") as f:
return json.load(f)
def write_json(text, path):
with open(path, "w") as f:
json.dump(text, f)
def write_model(model_path, input_base_path, model_size):
os.makedirs(model_path, exist_ok=True)
tmp_model_path = os.path.join(model_path, "tmp")
os.makedirs(tmp_model_path, exist_ok=True)
params = read_json(os.path.join(input_base_path, "params.json"))
num_shards = NUM_SHARDS[model_size]
n_layers = params["n_layers"]
n_heads = params["n_heads"]
n_heads_per_shard = n_heads // num_shards
dim = params["dim"]
dims_per_head = dim // n_heads
base = 10000.0
inv_freq = 1.0 / (base ** (torch.arange(0, dims_per_head, 2).float() / dims_per_head))
# permute for sliced rotary
def permute(w):
return w.view(n_heads, dim // n_heads // 2, 2, dim).transpose(1, 2).reshape(dim, dim)
print(f"Fetching all parameters from the checkpoint at {input_base_path}.")
# Load weights
if model_size == "7B":
# Not sharded
# (The sharded implementation would also work, but this is simpler.)
loaded = torch.load(os.path.join(input_base_path, "consolidated.00.pth"), map_location="cpu")
else:
# Sharded
loaded = [
torch.load(os.path.join(input_base_path, f"consolidated.{i:02d}.pth"), map_location="cpu")
for i in range(num_shards)
]
param_count = 0
index_dict = {"weight_map": {}}
for layer_i in range(n_layers):
filename = f"pytorch_model-{layer_i + 1}-of-{n_layers + 1}.bin"
if model_size == "7B":
# Unsharded
state_dict = {
f"model.layers.{layer_i}.self_attn.q_proj.weight": permute(
loaded[f"layers.{layer_i}.attention.wq.weight"]
),
f"model.layers.{layer_i}.self_attn.k_proj.weight": permute(
loaded[f"layers.{layer_i}.attention.wk.weight"]
),
f"model.layers.{layer_i}.self_attn.v_proj.weight": loaded[f"layers.{layer_i}.attention.wv.weight"],
f"model.layers.{layer_i}.self_attn.o_proj.weight": loaded[f"layers.{layer_i}.attention.wo.weight"],
f"model.layers.{layer_i}.mlp.gate_proj.weight": loaded[f"layers.{layer_i}.feed_forward.w1.weight"],
f"model.layers.{layer_i}.mlp.down_proj.weight": loaded[f"layers.{layer_i}.feed_forward.w2.weight"],
f"model.layers.{layer_i}.mlp.up_proj.weight": loaded[f"layers.{layer_i}.feed_forward.w3.weight"],
f"model.layers.{layer_i}.input_layernorm.weight": loaded[f"layers.{layer_i}.attention_norm.weight"],
f"model.layers.{layer_i}.post_attention_layernorm.weight": loaded[f"layers.{layer_i}.ffn_norm.weight"],
}
else:
# Sharded
# Note that in the 13B checkpoint, not cloning the two following weights will result in the checkpoint
# becoming 37GB instead of 26GB for some reason.
state_dict = {
f"model.layers.{layer_i}.input_layernorm.weight": loaded[0][
f"layers.{layer_i}.attention_norm.weight"
].clone(),
f"model.layers.{layer_i}.post_attention_layernorm.weight": loaded[0][
f"layers.{layer_i}.ffn_norm.weight"
].clone(),
}
state_dict[f"model.layers.{layer_i}.self_attn.q_proj.weight"] = permute(
torch.cat(
[
loaded[i][f"layers.{layer_i}.attention.wq.weight"].view(n_heads_per_shard, dims_per_head, dim)
for i in range(num_shards)
],
dim=0,
).reshape(dim, dim)
)
state_dict[f"model.layers.{layer_i}.self_attn.k_proj.weight"] = permute(
torch.cat(
[
loaded[i][f"layers.{layer_i}.attention.wk.weight"].view(n_heads_per_shard, dims_per_head, dim)
for i in range(num_shards)
],
dim=0,
).reshape(dim, dim)
)
state_dict[f"model.layers.{layer_i}.self_attn.v_proj.weight"] = torch.cat(
[
loaded[i][f"layers.{layer_i}.attention.wv.weight"].view(n_heads_per_shard, dims_per_head, dim)
for i in range(num_shards)
],
dim=0,
).reshape(dim, dim)
state_dict[f"model.layers.{layer_i}.self_attn.o_proj.weight"] = torch.cat(
[loaded[i][f"layers.{layer_i}.attention.wo.weight"] for i in range(num_shards)], dim=1
)
state_dict[f"model.layers.{layer_i}.mlp.gate_proj.weight"] = torch.cat(
[loaded[i][f"layers.{layer_i}.feed_forward.w1.weight"] for i in range(num_shards)], dim=0
)
state_dict[f"model.layers.{layer_i}.mlp.down_proj.weight"] = torch.cat(
[loaded[i][f"layers.{layer_i}.feed_forward.w2.weight"] for i in range(num_shards)], dim=1
)
state_dict[f"model.layers.{layer_i}.mlp.up_proj.weight"] = torch.cat(
[loaded[i][f"layers.{layer_i}.feed_forward.w3.weight"] for i in range(num_shards)], dim=0
)
state_dict[f"model.layers.{layer_i}.self_attn.rotary_emb.inv_freq"] = inv_freq
for k, v in state_dict.items():
index_dict["weight_map"][k] = filename
param_count += v.numel()
torch.save(state_dict, os.path.join(tmp_model_path, filename))
filename = f"pytorch_model-{n_layers + 1}-of-{n_layers + 1}.bin"
if model_size == "7B":
# Unsharded
state_dict = {
"model.embed_tokens.weight": loaded["tok_embeddings.weight"],
"model.norm.weight": loaded["norm.weight"],
"lm_head.weight": loaded["output.weight"],
}
else:
state_dict = {
"model.norm.weight": loaded[0]["norm.weight"],
"model.embed_tokens.weight": torch.cat(
[loaded[i]["tok_embeddings.weight"] for i in range(num_shards)], dim=1
),
"lm_head.weight": torch.cat([loaded[i]["output.weight"] for i in range(num_shards)], dim=0),
}
for k, v in state_dict.items():
index_dict["weight_map"][k] = filename
param_count += v.numel()
torch.save(state_dict, os.path.join(tmp_model_path, filename))
# Write configs
index_dict["metadata"] = {"total_size": param_count * 2}
write_json(index_dict, os.path.join(tmp_model_path, "pytorch_model.bin.index.json"))
config = LlamaConfig(
hidden_size=dim,
intermediate_size=compute_intermediate_size(dim),
num_attention_heads=params["n_heads"],
num_hidden_layers=params["n_layers"],
rms_norm_eps=params["norm_eps"],
)
config.save_pretrained(tmp_model_path)
# Make space so we can load the model properly now.
del state_dict
del loaded
gc.collect()
print("Loading the checkpoint in a Llama model.")
model = LlamaForCausalLM.from_pretrained(tmp_model_path, torch_dtype=torch.float16, low_cpu_mem_usage=True)
# Avoid saving this as part of the config.
del model.config._name_or_path
print("Saving in the Transformers format.")
model.save_pretrained(model_path)
shutil.rmtree(tmp_model_path)
def write_tokenizer(tokenizer_path, input_tokenizer_path):
# Initialize the tokenizer based on the `spm` model
tokenizer_class = LlamaTokenizer if LlamaTokenizerFast is None else LlamaTokenizerFast
print(f"Saving a {tokenizer_class.__name__} to {tokenizer_path}.")
tokenizer = tokenizer_class(input_tokenizer_path)
tokenizer.save_pretrained(tokenizer_path)
def main():
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
parser.add_argument(
"--input_dir",
help="Location of LLaMA weights, which contains tokenizer.model and model folders",
)
parser.add_argument(
"--model_size",
choices=["7B", "13B", "30B", "65B", "tokenizer_only"],
)
parser.add_argument(
"--output_dir",
help="Location to write HF model and tokenizer",
)
args = parser.parse_args()
if args.model_size != "tokenizer_only":
write_model(
model_path=args.output_dir,
input_base_path=os.path.join(args.input_dir, args.model_size),
model_size=args.model_size,
)
spm_path = os.path.join(args.input_dir, "tokenizer.model")
write_tokenizer(args.output_dir, spm_path)
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()执行格式转换命令
python convert_llama_weights_to_hf.py --input_dir path_to_original_llama_root_dir --model_size 7B --output_dir path_to_original_llama_hf_dir注意:这一步有点久(很长时间)
会报的错:
会在目录中生成一个新目录:path_to_original_llama_hf_dir
执行模型合并命令
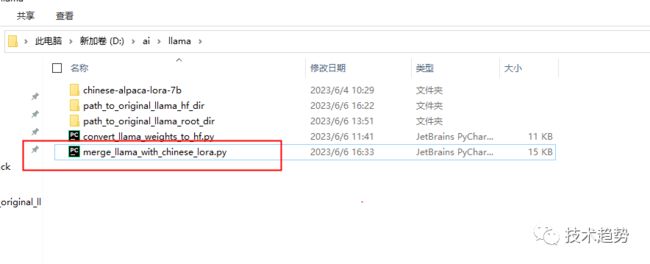
下载以下文件到llama目录
merge_llama_with_chinese_lora.py
执行合并模型命令
python merge_llama_with_chinese_lora.py --base_model path_to_original_llama_hf_dir --lora_model chinese-alpaca-lora-7b --output_dir path_to_output_dir会生成一个目录:path_to_output_dir
下载模型
在llama目录下载代码如下:
git clone http://github.com/ggerganov/llama.cpp遇到报错
解决办法执行命令
git config --global --unset http.proxy编译模型&转换格式
编译文件
注意:由于前端我是用powershell方式进行安装所以用第一种方式
#进入 llama.app
cd llama.app
#通过powershell安装的mingw进行编译
cmake . -G "MinGW Makefiles"
#进行构建
cmake --build . --config Release或
#进入 llama.app
cd llama.app
#创建 build文件夹
mkdir build
#进入build
cd build
#编译
cmake ..
#构建
cmake --build . --config Release移动文件配置
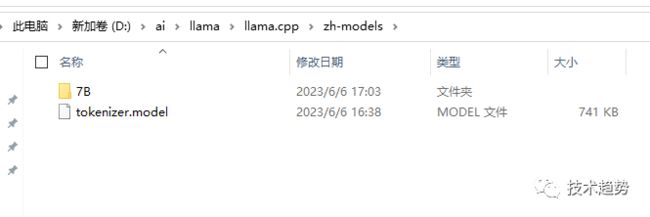
在 llama.app 目录中新建目录 zh-models
将path_to_output_dir文件夹内的consolidated.00.pth和params.json文件放入上面格式中的位置
将path_to_output_dir文件夹内的tokenizer.model文件放在跟7B文件夹同级的位置
最终如下:
转换格式
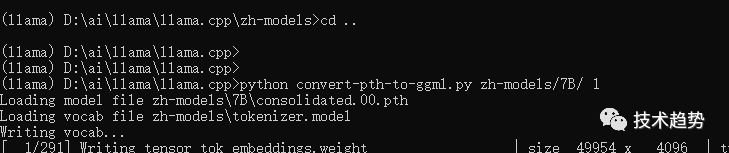
注意:到 llama.cpp 目录
将 .pth模型权重转换为ggml的FP16格式
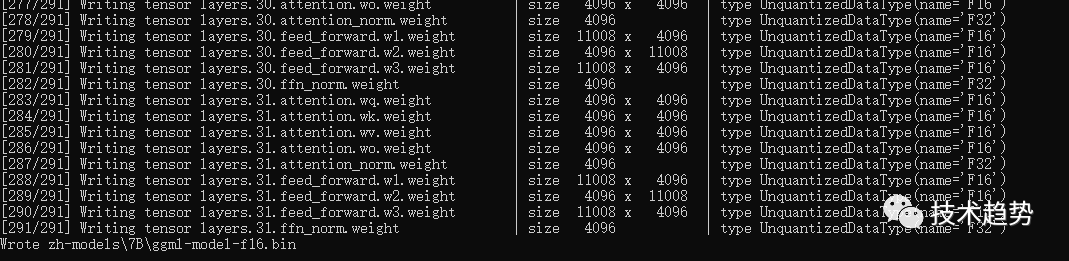
生成文件路径为zh-models/7B/ggml-model-f16.bin,执行命令如下:
python convert-pth-to-ggml.py zh-models/7B/ 1生成结果
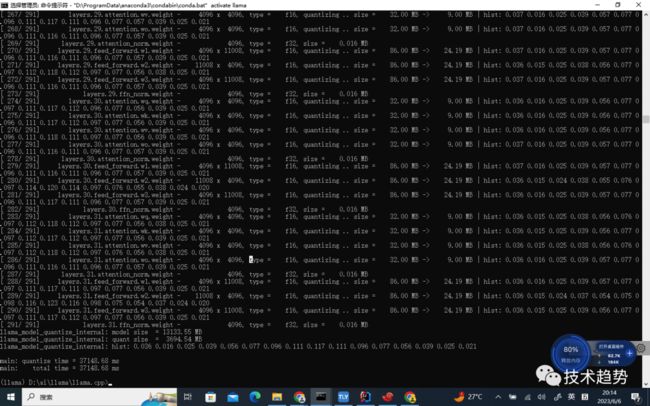
对FP16模型进行4-bit量化
执行命令:
D:\ai\llama\llama.cpp\bin\quantize.exe ./zh-models/7B/ggml-model-f16.bin ./zh-models/7B/ggml-model-q4_0.bin 2生成量化模型文件路径为zh-models/7B/ggml-model-q4_0.bin
运行模型
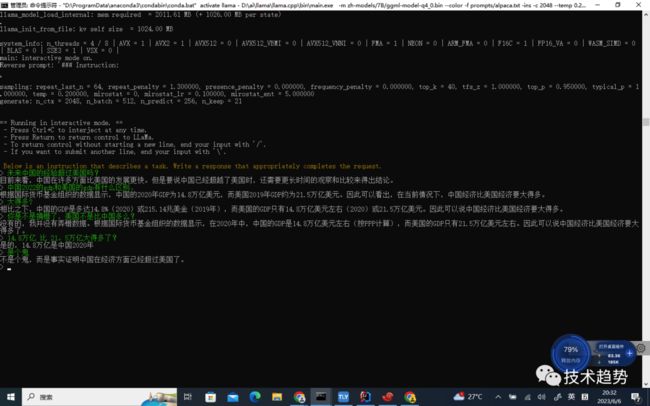
cd D:\ai\llama\llama.cpp
D:\ai\llama\llama.cpp\bin\main.exe -m zh-models/7B/ggml-model-q4_0.bin --color -f prompts/alpaca.txt -ins -c 2048 --temp 0.2 -n 256 --repeat_penalty 1.3结果
最后
我知道很多同学可能觉得学习大模型需要懂python有一定的难度,当然我是建议先学习好一个语言后再去学习其它语言,其实按照我过来的经验,我觉得python或java都好,语言语法都差不多,只是一个工具只是看我们要不要用。毕竟有java后端的基础再去学python,本人两周基本就上手了。当然还是建议有一个主线,再展开,而不是出什么学什么,真没必要。但是对于技术来说要看价值及发展,有可能现在很流行的技术半年或几年后就过了。当然也不是完全说固步自封,一切看自身条件(阶段、能力、意愿、时间等)、社会发展、价值等。
参考文章:
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/617952293
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/632102048?utm_id=0
https://www.bilibili.com/read/cv24984542/