【C# Programming】继承、接口
一、继承
1、派生
继承在相似而又不同的概念之间建立了类层次概念。 更一般的类称为基类,更具体的类称为派生类。派生类继承了基类的所有性质。
定义派生类要在类标识符后面添加一个冒号,接着添加基类名。
public class PdaItem
{
public string Name { get; set; }
public DateTime LastUpdated { get; set; }
}
// Define the Contact class as inheriting the PdaItem class
public class Contact : PdaItem
{
public string Address { get; set; }
public string Phone { get; set; }
}除非明确指定了基类,否则所有类都默认从object 派生。
2、基类和派生类的转型
由于派生建立了“属于”关系,所以总可以将派生类的值赋给基类型的变量。这称为隐式类型转换。 从基类型转换到派生类型,要求执行显式转型。方法是在原始引用名称前,将要转换成的目标类型放到圆括号中。
public static void Main()
{
// Derived types can be implicitly converted to base types
Contact contact = new Contact();
PdaItem item = contact;//隐式类型转换
// Base types must be cast explicitly to derived types 显示类型转换/强制类型转换
contact = (Contact)item;
// ...
}
3、自定义转换
类型之间的转换并不限于单一继承链中的类型,不同类型相互之间也能进行转换,关键是两个类型之间提供转型操作符。 C# 允许显式或隐式转型操作符。 例如:
class GPSCoordinates
{
public static implicit operator UTMCoordinates(GPSCoordinates coordinates)
{
// ...
return null;//return the new UTMCoordinates object
}
}
class UTMCoordinates { /*… */}
如果需要显式转换,可将implict 换成 explict。
4、private 访问修饰符
派生类继承了除构造器和析构器之外的所有基类成员,到那时私有成员只能在声明它们的那个类型中才能访问,派生类不能访问基类的私有成员。
public class PdaItem
{
private string _Name;
// ...
}
public class Contact : PdaItem
{
// ...
}
public class Program
{
public static void ChapterMain()
{
Contact contact = new Contact();
// ERROR: ‘PdaItem. _Name’ is inaccessible due to its protection level
//contact._Name = "Inigo Montoya"; //uncomment this line and it will not compile
}
}
5、protected 访问修饰符
基类中受保护的成员只能由基类以及派生链中的其他类访问。
public class Program
{
public static void Main()
{
Contact contact = new Contact();
contact.Name = "Inigo Montoya";
// ERROR: ‘PdaItem.ObjectKey’ is inaccessible due to its protection level
//contact.ObjectKey = Guid.NewGuid(); //uncomment this line and it will not compile
}
}
public class PdaItem { protected Guid ObjectKey { get; set; } }
public class Contact : PdaItem
{
void Save()
{
// Instantiate a FileStream using .dat for the filename.
FileStream stream = System.IO.File.OpenWrite(ObjectKey + ".dat");
}
void Load(PdaItem pdaItem)
{
// ERROR: ‘pdaItem.ObjectKey’ is inaccessible due to its protection level
//pdaItem.ObjectKey =...;
Contact contact = pdaItem as Contact;
if(contact != null)
contact.ObjectKey = new Guid();//...;
}
public string Name { get; set; }
}
6、单继承
- 继承链中的类理论是无限的。但是C#是单继承语言,意味着一个类不能从两个类中直接派生。
- 在极少数需要多继承类结构时, 一般的解决方法是使用聚合(aggregation)即一个类包含另一个类的实例。
7、密封类
密封类要求使用sealed 修饰符,这样做的结果时不能从它们派生其他类。
public sealed class CommandLineParser
{
// ...
}
// ERROR: Sealed classes cannot be derived from
public sealed class DerivedCommandLineParser
//: CommandLineParser //uncomment this line and it will not compile
{
// ...
}
8、virtual 修饰符
- C#支持重写(override)实例方法和属性,但不支持重写字段或者任何静态成员,为了重写,在基类中必须将允许重写的每个成员标记为virtual。
public class PdaItem
{
public virtual string Name { get; set; }
}
public class Contact : PdaItem
{
public override string Name
{
get {
return $"{ FirstName } { LastName }";
}
set {
string[] names = value.Split(' ‘);
FirstName = names[0];
LastName = names[1];
}
}
public string FirstName { get; set; }
public string LastName { get; set; }
}
- C# 应用于派生类的override 关键字是必须的,C# 不允许隐式重写。为了重写,基类和派生类成员签名必须一致。
9、new 修饰符
如果重写方法没有使用override 关键字,则编译器会报告警告消息, 一种方法是添加override关键字,另一种方法是使用new 修饰符。
warning CS0108: 'Program.DerivedClass.DisplayName()' hides inherited member 'Program.BaseClass.DisplayName()'. Use the new keyword if hiding was intended.
warning CS0114: 'Program.SuperSubDerivedClass.DisplayName()' hides inherited member 'Program.SubDerivedClass.DisplayName()'. To make the current member override that implementation, add the override keyword. Otherwise add the new keyword.
new 修饰符在基类面前隐藏了派生类重新声明的成员,这时是搜索继承链,找到使用new 修饰符的那个成员前的成员,然后调用该成员,例如:
public class Program{
public class BaseClass{
public void DisplayName() => Console.WriteLine("BaseClass");
}
public class DerivedClass : BaseClass{
// Compiler WARNING: DisplayName() hides inherited member. Use the new keyword if hiding was intended.
public virtual void DisplayName() => Console.WriteLine("DerivedClass");
}
public class SubDerivedClass : DerivedClass{
public override void DisplayName() =>Console.WriteLine("SubDerivedClass");
}
public class SuperSubDerivedClass : SubDerivedClass{
public new void DisplayName() => Console.WriteLine("SuperSubDerivedClass");
}
public static void Main()
{
SuperSubDerivedClass superSubDerivedClass = new SuperSubDerivedClass();
SubDerivedClass subDerivedClass = superSubDerivedClass;
DerivedClass derivedClass = superSubDerivedClass;
BaseClass baseClass = superSubDerivedClass;
superSubDerivedClass.DisplayName();
subDerivedClass.DisplayName();
derivedClass.DisplayName();
baseClass.DisplayName();
}
}
10、sealed 修饰符
虚成员也可以密封,这样做会禁止子类重写继承链中高层基类的虚成员, 例如:
class A
{
public virtual void Method()
{
}
}
class B : A
{
public override sealed void Method()
{
}
}
class C : B
{
// ERROR: Cannot override sealed members
//public override void Method()
//{
//}
}
11、base 成员
重写成员时, 可以使用base关键字调用该成员的基类版本。 base 表示当前类的基类。
public class Address
{
public string StreetAddress;
public string City;
public string State;
public string Zip;
public override string ToString()
{
return $"{ StreetAddress + NewLine }"
+ $"{ City }, { State } { Zip }";
}
}
public class InternationalAddress : Address {
public string Country;
public override string ToString() => base.ToString() +NewLine + Country;
}
12、构造器
当构造派生类的对象时, 基类的构造函数首先被调用。如果基类没有默认构造函数,则需要在派生类的构造函数中显示调用基类的构造函数,例如:
public class PdaItem
{
public PdaItem(string name)
{
Name = name;
}
public string Name { get; set; }
}
public class Contact : PdaItem
{
public Contact(string name) :
base(name)
{
Name = name;
}
public new string Name { get; set; }
// ...
}
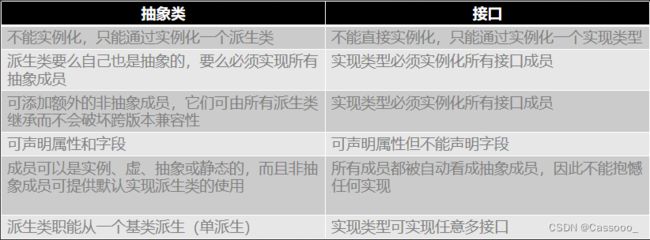
13、抽象类
抽象类是仅供派生的类,无法实例化抽象类,只能实例化从它派生的类。不抽象,可以实例化的类称为具体类。
抽象类代表抽象的实体。一个类要从抽象类成功派生,必须为抽象类中的抽象方法提供具体实现. C#要求为类定义添加abstract 修饰符。
public abstract class PdaItem
{
public PdaItem(string name)
{
Name = name;
}
public virtual string Name { get; set; }
}
public class Program
{
public static void Main()
{
PdaItem item;
// ERROR: Cannot create an instance of the abstract class
//item = new PdaItem("Inigo Montoya"); //uncomment this line and it will not compile
}
}
14、抽象成员
不可实例化只是抽象类的一个较次要的特征,其主要特征是包含抽象成员。抽象成员是没有实现的方法或属性。其作用是强制所有派生类实现。
public abstract class PdaItem{
public PdaItem(string name)
{
Name = name;
}
public virtual string Name { get; set; }
public abstract string GetSummary();
}
public class Contact : PdaItem{
public Contact(string name) : base(name) {}
public override string Name
{
get{
return $"{ FirstName } { LastName }";
}
set{
string[] names = value.Split(' ‘);
FirstName = names[0];
LastName = names[1];
}
}
public string FirstName { get; set; }
public string LastName { get; set; }
public string Address { get; set; }
public override string GetSummary() =>$"FirstName: { FirstName + NewLine }"
+ $"LastName: { LastName + NewLine }" + $"Address: { Address + NewLine }";
}
public class Appointment : PdaItem
{
public Appointment(string name) :
base(name)
{
Name = name;
}
public DateTime StartDateTime { get; set; }
public DateTime EndDateTime { get; set; }
public string Location { get; set; }
// ...
public override string GetSummary()
{
return $"Subject: { Name + NewLine }"
+ $"Start: { StartDateTime + NewLine }"
+ $"End: { EndDateTime + NewLine }"
+ $"Location: { Location }";
}
}
相同签名的成员在不同类中的不同实现,称为多态性(polymorphism).抽象成员是实现多态的一个手段
public class Program{
public static void Main()
{
PdaItem[] pda = new PdaItem[3];
Contact contact = new Contact("Sherlock Holmes");
contact.Address = "221B Baker Street, London, England";
pda[0] = contact;
Appointment appointment = new Appointment("Soccer tournament");
appointment.StartDateTime = new DateTime(2008, 7, 18);
appointment.EndDateTime = new DateTime(2008, 7, 19);
appointment.Location = "Estádio da Machava";
pda[1] = appointment;
contact = new Contact("Anne Frank");
contact.Address = "Apt 56B, Whitehaven Mansions, Sandhurst Sq, London";
pda[2] = contact;
List(pda);
}
public static void List(PdaItem[] items)
{
// Implemented using polymorphism. The derived type knows the specifics of implementing GetSummary().
foreach(PdaItem item in items)
{
Console.WriteLine("________");
Console.WriteLine(item.GetSummary());
}
}
}
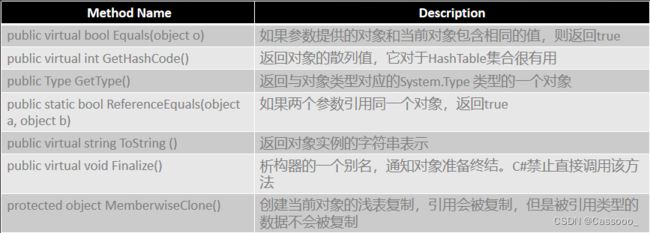
15、System.Object
任何对象,不管是自定义类型,还是系统内建类型,都最终从Sytem.Object派生。因此,都定义了如下方法:
16、使用 is 操作符验证基础类型
C# 允许在继承链中向下转型。C#提供了is 操作符判断基础类型。它允许验证一个数据项是否是属于特定类型
public class AnObject
{
public static void Save(object data)
{
if(data is string)
{
data = Encrypt((string)data);
}
// ...
}
private static object Encrypt(string data)
{
return null;
}
}17、使用 as 操作符进行转换
as 操作符尝试将对象转换为特定类型,如果对象不能转换,as 操作符返回null. 因而转型失败不会引发异常
class Program
{
static object Print(IDocument document)
{
if(document != null)
{
// Print document...
}
return null;
}
static void Main()
{
object data = new object();
// ...
Print(data as Document);
}
}
internal class Document : IDocument
{
}
internal interface IDocument
{
}
二、接口
1、概述
- 和抽象类不同,接口能将实现细节和提供的服务完全隔离开。接口的关键特点是既不包含实现,也不包含数据。
- 按照惯例,接口名采用Pascal大小写风格,以大写字母I 作为前缀
- interface Ixxxx { //... }
- 接口声明的成员描述了在实现该接口的类型中必须能够访问的成员
interface IFileCompression
{
void Compress(string targetFileName, string[] fileList);
void Uncompress(
string compressedFileName, string expandDirectoryName);
}
- 如果接口要求派生类包含特定数据,会声明属性而不是字段
interface IListable {
string[] ColumnValues // Return the value of each column in the row.
{
get;
}
}
public abstract class PdaItem{
public PdaItem(string name) {
Name = name;
}
public virtual string Name { get; set; }
}
class Contact : PdaItem, Ilistable{
public Contact(string firstName, string lastName, string address, string phone)
: base(null)
{
FirstName = firstName;
LastName = lastName;
Address = address;
Phone = phone;
}
public string FirstName { get; set; }
public string LastName { get; set; }
public string Address { get; set; }
public string Phone { get; set; }
public string[] ColumnValues {
get {
return new string[] { FirstName, LastName, Phone, Address };
}
}
public static string[] Headers {
get { return new string[] {"First Name", "Last Name ", "Phone ", "Address" };
}
}2、接口实现
- 声明类以实现接口, 类似于从基类派生:要实现的接口和基类名称以逗号分隔,基类在前,接口顺序任意。 类可以实现多个接口,但只能从一个基类直接派生。例如:
public class Contact : PdaItem, IListable, IComparable
{
public Contact(string name) : base(name) {}
#region IComparable Members
public int CompareTo(object obj)
{
int result;
Contact contact = obj as Contact;、
if(obj == null)
result = 1; // This instance is greater than obj.
else if(obj.GetType() != typeof(Contact))
throw new ArgumentException($"The parameter is not a of type { nameof(Contact) }", nameof(obj));
else if(Contact.ReferenceEquals(this, obj))
result = 0;
else {
result = LastName.CompareTo(contact.LastName);
if(result == 0)
result = FirstName.CompareTo(contact.FirstName);
}
return result;
}
#endregion
string[] IListable.ColumnValues{
get {
return new string[] {FirstName, LastName, Phone, Address};
}
}
protected string LastName { get; set; }
protected string FirstName { get; set; }
protected string Phone { get; set; }
protected string Address { get; set; }
}
- 一旦某个类声明自己要实现的接口,接口所有成员都必须实现,抽象类允许提供接口成员的抽象实现。
- 接口的另一特征是永远不能实例化。不能用new 创建接口,所以接口没有构造器或者析构器。只有实例化实现接口的类型,才能使用接口实例。接口不能包含静态成员
- 在类型中实现接口成员时有两种方式: 显式 和隐式
3、显示成员实现
显式声明的接口成员需要在成员名前附加接口前缀, 例如:
public class Contact : PdaItem, IListable, IComparable {
//….
string[] IListable.ColumnValues{
get {
return new string[] {FirstName, LastName, Phone, Address};
}
}
}
显式实现的接口只能通过接口本身调用,因此需要将对象转型为接口。 显式实现的接口成员直接和接口关联,因此不允许使用virtual, override, 或者public 来修饰他们。 例如:
public class Program
{
public static void Main()
{
string[] values;
Contact contact1, contact2 = null;
// ERROR: Unable to call ColumnValues() directly on a contact.
// values = contact1.ColumnValues;
// First cast to IListable.
values = ((IListable)contact2).ColumnValues;
// ...
}
}
4、隐式成员实现
隐式实现只要求成员是公共的且签名与接口成员的签名相符。接口成员实现不需要override 关键字或者其他任何表明该成员与接口关联的指示符。
由于成员是像其他类成员那样声明的,所以可以像调用其它类成员那样直接调用隐式实现的成员。 result = contact1.CompareTo(contact2);
隐式实现上,显式实现不允许的许多修饰符是必须或者可选的。例如: 隐式实现必须式public.而且还可选择virtual.具体取决于派生类是否可以重写。去掉virtual 导致成员密封。
5、显式接口实现与隐式接口实现的比较
选择显示实现还是隐式实现的基本原则:
- 如果成员是类的辅助成员,则必要设计成类的直接可见成员
- 假设接口成员的用途在实现类中不明确,就可以考虑显式成员
- 显式接口成员不会在类型的声明空间添加具名元素。所以,假如类型有一个潜在的与之相冲突的成员。那么另一个是显式的接口成员, 就可以与之同名
6、接口继承
- 一个接口可以从另一个接口派生, 派生的接口将继承“基接口”的所有成员。例如:
interface IReadableSettingsProvider
{
string GetSetting(string name, string defaultValue);
}
interface ISettingsProvider : IReadableSettingsProvider
{
void SetSetting(string name, string value);
}
class FileSettingsProvider : ISettingsProvider{
public void SetSetting(string name, string value) { /*.. */ }
public string GetSetting(string name, string defaultValue)
{
return name + defaultValue; // just returning this for the example
}
}
- 假如显式实现GetSetting,必须通过IReadableSettingsProvider
- 即使类实现的接口是从基接口派生的,这个类任然可以可以声明自己要实现这两个接口。例如:
interface IReadableSettingsProvider
{
string GetSetting(string name, string defaultValue);
}
interface ISettingsProvider : IReadableSettingsProvider
{
void SetSetting(string name, string value);
}
class FileSettingsProvider : ISettingsProvider, IReadableSettingsProvider{
public void SetSetting(string name, string value) { /*.. */ }
public string GetSetting(string name, string defaultValue)
{
return name + defaultValue; // just returning this for the example
}
}
7、多接口继承
接口也能从多个接口继承,而且语法与类的继承和实现语法一致 。
interface IReadableSettingsProvider
{
string GetSetting(string name, string defaultValue);
}
interface IWriteableSettingsProvider
{
void SetSetting(string name, string value);
}
interface ISettingsProvider : IReadableSettingsProvider,
IWriteableSettingsProvider
{
}
8、接口上的扩展方法
扩展方法的一个重要特点是除了能作用于类,还能作用于接口,语法和作用于类一致。方法的第一个参数是要扩展的接口,该参数必须附加this 修饰符。
class Program
{
public static void Main()
{
Contact[] contacts = new Contact[6];
contacts[0] = new Contact("Dick", "Traci", "123 Main St., Spokane, WA 99037", "123-123-1234");
contacts.List(Contact.Headers); // Classes are implicitly converted totheir supported interfaces.
Console.WriteLine();
//…..
}
}
static class Listable
{
public static void List( this IListable[] items, string[] headers)
{
//....
}
}
9、通过接口实现多继承
虽然类职能从一个基类派生。但是可以实现任意数量的接口
interface IPerson {
string FirstName {get; set; }
string LastName{get; set; }
}
public class Person : IPerson {
public string FirstName { get; set; }
public string LastName { get; set; }
}
public class Contact : PdaItem, IPerson {
public Contact(string name)
: base(name) {}
private Person Person
{
get { return _Person; }
set { _Person = value; }
}
private Person _Person;
public string FirstName
{
get { return _Person.FirstName; }
set { _Person.FirstName = value; }
}
public string LastName {
get { return _Person.LastName; }
set { _Person.LastName = value; }
}
}