Shamir门限方案的秘钥分享(包括逆元求解)
Shamir门限方案的秘钥分享(不要求支持大数)
题目描述
【实验目的】
- 通过基于Shamir门限方案的密钥分割及恢复的演示,理解密钥分割的重要性,理解密钥分割的基本原理和作用,掌握基于Shamir门限方案的密钥分割软件的使用
【实验原理】
秘密共享体制为将秘密分给多人掌管提供了可能。例如重要场所的通行、遗嘱的生效等都必须由两人或多人同时参与才能生效,这时都需要将秘密分给多人掌管并同时参与才能恢复。在实际应用中,秘密共享的要求多种多样、形形色色,每一种解决问题的方案都可成为一种体制。1979年,Shamir在提出秘密分享思想的同时,利用拉格朗日插值多项式理论设计出了一个具体的(t,n)秘密分享方案。1979年以后,人们通过对秘密共享问题的分析研究,构建出了许多类型的秘密共享体制。具有代表性和一般性的除了有Shamir提出的(t,n)门限体制,还有Blakley提出的矢量体制,Asmuth和Bloom提出的同余类体制,Karnin提出的矩阵法体制等。
一般地,一个由秘密分发者D和参与者P1,P2,…,Pn构成的(t,n)秘密分享体制包含下面两个协议:
(1) 秘密分发协议:在这个协议中,秘密分发者D在n个参与者中分享秘密s,每个参与者Pi获得一个碎片si,i=1,2,…,n。
(2) 秘密重构协议:在这个协议中,任意不少于t个参与者一起合作,以自己的碎片为输入,重构原秘密s。
一个安全的(t,n)秘密分享体制必须同时提供两个性质:一方面,任意t个参与者通过提供自己的碎片能够协作地恢复出原秘密s;另一方面,任意少于t个参与者即便拥有自己的碎片也无法计算关于原秘密s的任何信息。一般称这里的t为门限值。
Shamir提出的基于LaGrange插值公式的密钥分存思想是,利用有限域GF§上的t-1次多项式
h(x)= at- 1xt- 1+ … + a1x+ a0 mod p (1)
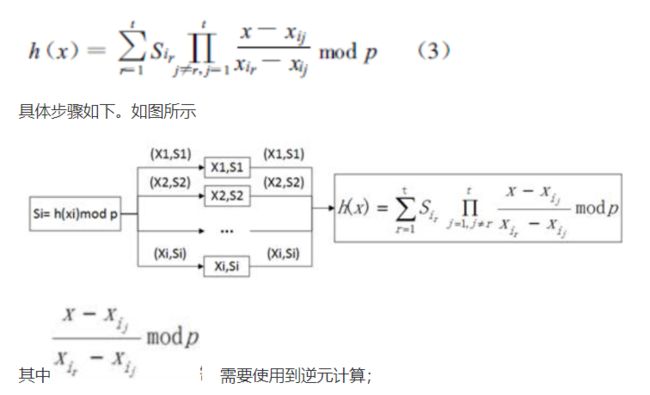
构造秘密共享的(t,n)门限体制。其中,所选的随机素数p要大于最大可能的秘密数S和参与者总数n,并且公开;S=h(0)=a0,而at-1,at-2,… ,a1为选用的随机系数,这些都需要保密,在生成n个秘密份额之后即可销毁。通过计算多项式h(x)对n个不同xi的取值就给出每个人的秘密份额:
Si= h(xi)mod p,i= 1,2,3,… ,n (2)
每一(xi,Si)对就是曲线h上的一个点,可看作是用户的标识符。由于任意t个点都可唯一地确定相应的t- 1次多项式,所以,秘密S可以从t个秘密份额重构。给定任意t个秘密份额Si1,Si2,… ,Sit,由LaGrange插值公式重构的多项式为
关于逆元,可以参看https://blog.csdn.net/wcxyky/article/details/103366577其中有些例子不够完善,请谨慎选取,小心验证。
具体例子:
n=5, t=3, p=17; 随机选取K=13,a1=10,a2=2;
于是有
输入
大素数p
子秘钥总数n
门限值t
输出
设置的密钥与恢复的密钥的差值
输入样例1
1006000813
10
3
输出样例1
0
AC代码
import java.util.*;
/**
* @author xzx
* @date 2022/10/29
*/
public class Main {
static class Point {
public long x;
public long y;
public Point(long x, long y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
}
private static long k;
private static long a1;
private static long a2;
public static void main(String[] args) {
//处理输入
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
long p = scanner.nextInt();
long n = scanner.nextInt();
long t = scanner.nextInt();
long key = calculate(p, n, t);
//System.out.println("恢复的密钥:"+key);
long dis = key - k;
System.out.println(dis);
}
/**
* 推演
*
* @param prime 大素数p
* @param total 子秘钥总数n
* @param threshold 门限值t
* @return
*/
private static long calculate(long prime, long total, long threshold) {
randomGenerateParams();
List<Long> points = getTotalPoint(total, prime);
List<Point> list = getThresholdPoint(prime, total, threshold, points);
return getKey(list, prime);
}
/**
* 恢复密钥
*
* @param list 选取的点
* @param prime mod
* @return
*/
private static long getKey(List<Point> list, long prime) {
long res = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
Point point = list.get(i);
long val = point.y;
for (int j = 0; j < list.size(); j++) {
if (i == j) {
continue;
}
val *= list.get(j).x;
val %= prime;
long inv = getInv(point.x - list.get(j).x, prime);
//System.out.println(point.x - list.get(j).x + "关于" + prime + "的逆元是:" + inv);
val *= inv;
val %= prime;
}
res += val;
res %= prime;
}
return res;
}
/**
* 求解逆元
*
* @param a
* @param mod
* @return
*/
static long getInv(long a, long mod) {
return qkpow(a, mod - 2, mod);
}
/**
* 费马小定理/欧拉定理
*
* @param a
* @param p
* @param mod
* @return
*/
static long qkpow(long a, long p, long mod) {
long t = 1, tt = a % mod;
while (p != 0) {
if ((p & 1) != 0) t = t * tt % mod;
tt = tt * tt % mod;
p >>= 1;
}
return t < 0 ? t + mod : t;
}
/**
* 解密的时候随机选取t个点(不重复)
*
* @param prime
* @param total
* @param threshold
* @param points
* @return
*/
private static List<Point> getThresholdPoint(long prime, long total, long threshold, List<Long> points) {
boolean[] used = new boolean[(int) total + 1];
Point[] list = new Point[(int) threshold];
Random random = new Random();
for (int i = 0; i < threshold; i++) {
while (true) {
int x = random.nextInt((int) total) + 1;
if (!used[x]) {
used[x] = true;
list[i] = new Point(x, points.get(x));
break;
}
}
}
return Arrays.asList(list);
}
/**
* 获取total个点
*
* @param total
* @param prime
* @return
*/
private static List<Long> getTotalPoint(long total, long prime) {
Long[] points = new Long[(int) total + 1];
for (int i = 1; i <= total; i++) {
long y = (k + a1 * i + a2 * i * i) % prime;
//System.out.println("(x" + i + ", y" + i + ") = " + "(" + i + ", " + y + ")");
points[i] = y;
}
return Arrays.asList(points);
}
/**
* 随机选取K,a1,a2
*/
private static void randomGenerateParams() {
Random random = new Random();
// 1-20
k = random.nextInt(20) + 1;
//System.out.println("设置的密钥: " + k);
// 1-10
a1 = random.nextInt(10) + 1;
a2 = random.nextInt(2) + 1;
}
}