【前端性能优化】长列表优化
1 什么是长列表?
1.1 概念
前端的业务开发中会遇到一些数据量较大且无法使用分页方式来加载的列表,我们一般把这种列表叫做长列表。
1.2 参考案例
比如淘宝网的商品列表页,一个手机屏可以容纳10个左右商品。如果每次只请求10个商品,一次请求10个商品和50个商品,数据返回所需要的时间相差不大。对于mysql优化,强调的也是减少查询的次数。所以说如果每次只请求10条数据对服务端来说压力会比较大,前端的长列表优化就变得比较重要。
2 优化方案
完整渲染的长列表基本上很难达到业务上的要求的,非完整渲染的长列表一般有两种方式:
2.1 懒渲染
2.1.1 懒渲染概念
就是常见的无线滚动,每次只渲染一部分(比如10条),等剩余部分滚到可见区域,再渲染一部分。
2.1.2 原理
用数组保存所有的数据,根据一屏幕能渲染的数量大致算出一次性渲染的数量,比如10,然后将数据源数组10个分为一组生产一个二维数组。列表后面跟着一个dom,监听滚动事件,当这个dom滚动到可视区域时,取出二维数组中数据来渲染。
2.1.3 参考实践
- 根据一屏幕数量分割源数组,splitArray方法。
- 记录渲染了几组数据 groupIdx,默认0
- 记录已经渲染的数据 componentList
- 添加滚动事件
- 在滚动事件中,判断列表后面的dom是否进入可视区域。
components/LazyLoad/index.js
import React, { useEffect, useState, useRef, useMemo } from 'react';
import PropTypes from 'prop-types';
// import loadable from '@loadable/component';
import { splitArray } from '../../utils/index';
import './index.css'
// const RenderComponentByType = loadable(() => import('../RenderComponentByType/index'));
function LazyLoadC({ dataSource }) {
const clientHeight = document.documentElement.clientHeight || document.body.clientHeight; // 视窗高
const componentGroups = useMemo(() => splitArray(dataSource, 10), [dataSource]); // 分割数组
const groupLen = componentGroups.length;
const [groupIdx, setGroupIdx] = useState(0);
const [componentList, setComponentList] = useState([]); // 当前视窗,页面组件数据
const bottomDomRef = useRef(null);
useEffect(() => {
const firstScreenData = componentGroups.length > 0 ? componentGroups[0] : [];
setComponentList(firstScreenData);
setGroupIdx(1);
}, [componentGroups]); // 第一屏渲染
useEffect(() => {
const handleScroll = () => {
const { top } = bottomDomRef.current.getBoundingClientRect();
if (top < clientHeight && groupIdx < groupLen) {
setComponentList(componentList.concat(componentGroups[groupIdx]));
setGroupIdx(groupIdx + 1);
}
};
window.addEventListener('scroll', handleScroll);
return () => {
window.removeEventListener('scroll', handleScroll);
};
}, [clientHeight, componentGroups, componentList, groupIdx, groupLen]);
return (
{componentList.map((item) =>
 {item.name}
{item.text}
)}
Loading
);
};
LazyLoadC.defaultProps = {
dataSource: Array(10000).fill().map((val, idx) => {
return {
id: idx,
name: 'John Doe',
image: 'http://via.placeholder.com/40',
text: '回家范德萨花费巨大啥返回的数据撒繁华大街上返回的数据撒,回复'
}
})
};
export default LazyLoadC;
{item.name}
{item.text}
)}
Loading
);
};
LazyLoadC.defaultProps = {
dataSource: Array(10000).fill().map((val, idx) => {
return {
id: idx,
name: 'John Doe',
image: 'http://via.placeholder.com/40',
text: '回家范德萨花费巨大啥返回的数据撒繁华大街上返回的数据撒,回复'
}
})
};
export default LazyLoadC;
index.css
.list {
padding: 10px;
}
.row {
border-bottom: 1px solid #ebeced;
text-align: left;
margin: 5px 0;
display: flex;
align-items: center;
}
.image {
margin-right: 10px;
width: 60px;
height: 60px;
}
.image img {
width: 100%;
height: 100%;
}
.content {
padding: 10px;
}
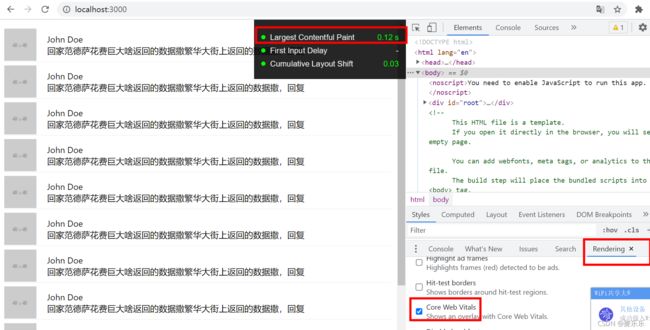
2.1.4 性能测试
LCP 0.12S
2.2 可视区域渲染
这种方式只渲染可见部分,不可见部分不渲染。
2.2.1 虚拟列表概念
虚拟列表(Virtual List),是一种长列表优化方案,是可视区渲染列表。其两个重要的概念:
- 可滚动区域:假设有1000条数据,每个列表项的高度是30,那么可滚动的区域的高度就是1000*30。当用户改变列表的滚动条的当前滚动值的时候,会造成可见区域的内容的变更。
- 可见区域:比如列表的高度是300,右侧有纵向滚动条可以滚动,那么视觉可见的区域就是可见区域。
2.2.2 虚拟列表原理:
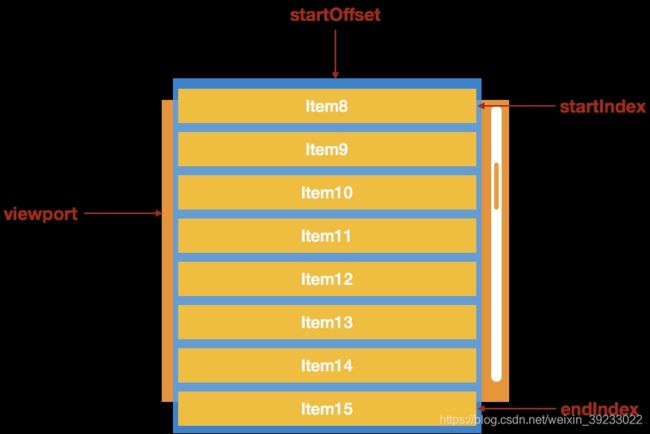
用数组保存所有列表元素的位置,只渲染可视区内的列表元素,当可视区滚动时,根据滚动的offset大小以及所有列表元素的位置,计算在可视区应该渲染哪些元素。
2.2.3 参考实现:
实现虚拟列表就是处理滚动条滚动后的可见区域的变更,具体实现步骤如下
- 计算当前可见区域起始数据的startIndex
- 计算当前可见区域结束数据的endIndex
- 计算当前可见区域的数据,并渲染到页面中
计算startIndex对应的数据在整个列表中的偏移位置startOffset,并设置到列表上
做了一个设定:每个列表项的高度都是30px。在这个约定下,核心JavaScript代码不超过10行,但是可以完整的实现可见区域的渲染和更新。
HTML、CSS如何实现,添加了这么几个样式:列表元素(.list-view)使用相对定位
使用一个不可见元素(.list-view-phantom)撑起这个列表,让列表的滚动条出现
列表的可见元素(.list-view-content)使用绝对定位,left、right、top设置为0
用react实现:
components/VirtualList/index.js
// index.js
import React from 'react';
import './index.css'
class VirtualList extends React.PureComponent {
scrollDom = null;
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = {
visibleData: [],
itemHeight: 50,
totalHeight: 800,
startOffset: '',
visibleCount: '',
start: 0,
end: null,
screenHeight: 0, // 可视区域高度
};
}
componentDidMount() {
const { itemHeight, start } = this.state;
const { listData } = this.props;
const screenHeight = this.scrollDom.clientHeight;
const visibleCount = Math.ceil(screenHeight/itemHeight);
const end = start + visibleCount;
this.setState({
totalHeight: listData.length * itemHeight,
screenHeight,
visibleCount,
end,
visibleData: listData.slice(start, end)
})
}
scrollEvent = (e) => {
const { visibleCount, itemHeight } = this.state;
const {listData} = this.props;
const scrollTop = this.scrollDom.scrollTop;
const start = Math.ceil(scrollTop/itemHeight);
const end = start + visibleCount;
this.setState({
start,
end,
visibleData: listData.slice(start, end),
startOffset: scrollTop - (scrollTop % itemHeight)
})
}
render() {
const { visibleData, itemHeight, totalHeight, startOffset } = this.state;
return (
this.scrollDom = node} className="infinite-list-container" onScroll={this.scrollEvent}>
{
visibleData.map((item, index) => {item} )
}
);
}
}
export default VirtualList;
VirtualList.defaultProps = {
listData: new Array(10000).fill(1)
};
index.css
.infinite-list-container {
height: 100%;
overflow: auto;
position: relative;
-webkit-overflow-scrolling: touch;
}
.infinite-list-phantom {
position: absolute;
left: 0;
top: 0;
right: 0;
z-index: -1;
}
.infinite-list {
left: 0;
right: 0;
top: 0;
position: absolute;
text-align: center;
}
.infinite-list-item {
padding: 10px;
color: #555;
box-sizing: border-box;
border-bottom: 1px solid #999;
}App.js中引入:
import React from 'react';
import VirtualList from './components/VirtualList'
import './AppList.css'
// App.js
class App extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = {
};
}
render() {
return (
);
}
}
export default App2.2.4 性能测试:
即使有1万条数据,LCP也只需要0.13S
2.2.5 直接渲染
如果不做优化,直接渲染1万条数据:
components/Common/index.js
import React from 'react';
import './index.css';
const rowCount = 10000;
class Common extends React.Component {
constructor() {
super();
// 以下每条数据都包含 id、用户名、图片、随机生成4~8个字评论。
this.list = Array(rowCount).fill().map((val, idx) => {
return {
id: idx,
name: 'John Doe',
image: 'http://via.placeholder.com/40',
text: '回家范德萨花费巨大啥返回的数据撒繁华大街上返回的数据撒,回复'
}
});
}
renderRow(item) {
return (
 {item.name}
{item.text}
);
}
render() {
return (
{item.name}
{item.text}
);
}
render() {
return (
{/*  */}
*/}
Welcome to React
{this.list.map(this.renderRow.bind(this))}
);
}
}
export default Common;
index.css
.list {
padding: 10px;
}
.row {
border-bottom: 1px solid #ebeced;
text-align: left;
margin: 5px 0;
display: flex;
align-items: center;
}
.image {
margin-right: 10px;
width: 60px;
height: 60px;
}
.image img {
width: 100%;
height: 100%;
}
.content {
padding: 10px;
}
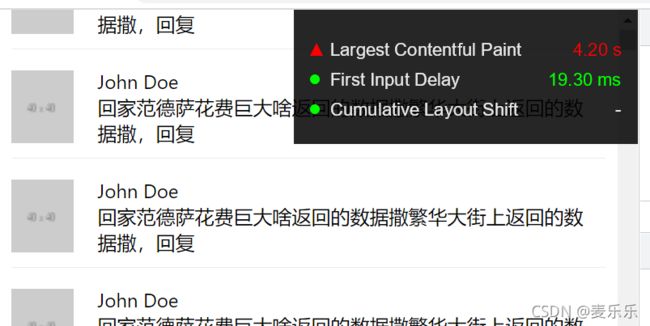
LCP渲染完成需要4.2S,能看到很明显的卡顿。
3 使用建议
3.1 react-virtualized
如果使用react开发,可以使用antdesign官网推荐的组件,结合 react-virtualized 实现滚动加载无限长列表,带有虚拟化(virtualization)功能,能够提高数据量大时候长列表的性能。
3.2 vue-virtual-scroll-list
如果使用vue开发,建议使用 vue-virtual-scroll-list,功能原理都是使用虚拟列表来优化长列表渲染。
当然也可以参照上面代码示例自己实现懒加载或者虚拟列表来优化长列表。另外也可以使用textarea来优化长列表,将首屏意外的数据放在textarea标签内部,滚动过程中取出渲染,写法类似懒渲染。
代码地址:https://github.com/artadmire/long-list