RTP协议介绍以及C语言实现具有发送H.264视频功能的RTP服务器
RTP封装H.264视频规范以及C语言实现
以前上学时间做嵌入式开发板Hi3516A的流媒体项目,现在又突然想起来,不想学过就忘了浪费了,所以又自己实现了一遍读取本地视频文件发送RTP视频流的程序,算是总结一下。网上关于RTP的介绍实在是太多,但是多数都是抄来抄去没有系统性,还是贴上代码更容易理解。
RTP封装H.264码流规范
本文简单说明RTP结构和实现,详细说明请参考标准文档RTF6184: RTP Payload Format for H.264 Video。
RTP Header
- V(version): 当前版本设为2。
- P(padding): 载荷之后填充数据,用于要求固定长度RTP包场景,一般不用,设置为0。
- X(extension): 固定头部后面加头部扩展字段标志,一般不用,设为0。
- CC(CSRC count): CSRC字段长度
- M(marker): AU最后一个包标志位
- PT(payload): RTP载荷媒体数据类型,H264=96
- Sequence number: RTP包序列号,递增1。
- timestamp: 媒体采样时间戳,H264/HEVC统一采用90kHz采样时钟,如果使用帧率fps来设置时间戳,则递增数值为90000/fps。
- SSRC: 数据包同源标志,来自同一处的RTP包应采用固定统一数值。
- CSRC: 一般CC=0,不用此位。
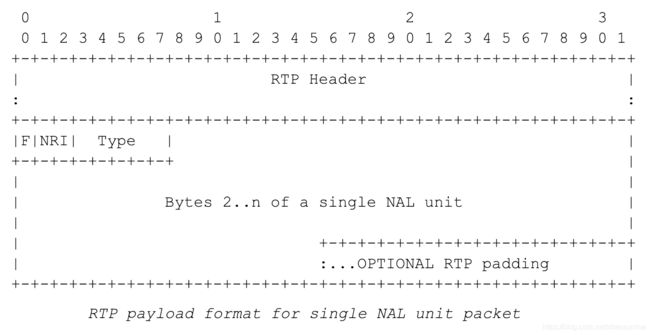
RTP Payload
RTP Packet = RTP Header + RTP payload.
RTP Payload结构一般分为3种:
- 单NALU分组(Single NAL Unit Packet): 一个分组只包含一个NALU。
- 聚合分组(Aggregation Packet): 一个分组包含多个NALU。
- 分片分组(Fragmentation Unit):一个比较长的NALU分在多个RTP包中。
各种RTP分组在RTP Header后面都跟着 F|NRI|Type 结构的NALU Header来判定分组类型。不同分组类型此字段名字可能不同,H264/HEVC原始视频流NALU也包含此结构的头部字段。

- F(forbidden_zero_bit):错误位或语法冲突标志,一般设为0。
- NRI(nal_ref_idc): 与H264编码规范相同,此处可以直接使用原始码流NRI值。
- Type:RTP载荷类型,1-23:H264编码规定的数据类型,单NALU分组直接使用此值,24-27:聚合分组类型(聚合分组一般使用24 STAP-A),28-29分片分组类型(分片分组一般使用28FU-A),30-31,0保留。
| NAL Unit Type | Packet Type | Packet Type Name |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | reserved | - |
| 1-23 | NAL unit | Single NAL unit packet |
| 24 | STAP-A | Single-time aggregation packet |
| 25 | STAP-B | Single-time aggregation packet |
| 26 | MTAP16 | Multi-time aggregation packet |
| 27 | MTAP24 | Multi-time aggregation packet |
| 28 | FU-A | Fragmentation unit |
| 29 | FU-B | Fragmentation unit |
| 30-31 | reserved | - |
单NALU分组
此结构的NALU Header结构可以直接使用原始码流NALU Header,所以单NALU分组Type = 1~23。
封装RTP包的时候可以直接把 查询到的NALU去掉起始码后的部分 当作单NALU分组的RTP包Payload部分。
聚合分组
通常采用STAP-A (Type=24)结构封装RTP聚合分组,下图为包含2个NALU的采用STAP-A结构的聚合分组。

- STAP-A NAL HDR: 也是一个NALU Header (F|NRI|Type)结构,1字节。比如可能值为0x18=00011000b,Type=11000b=24,即为STAP-A。所有聚合NALU的F只要有一个为1则设为1,NRI取所有NALU的NRI最大值。
- NALU Size: 表示此原始码流NALU长度,2字节。
- NALU HDR + NALU Date: 即为原始码流一个完整NALU。
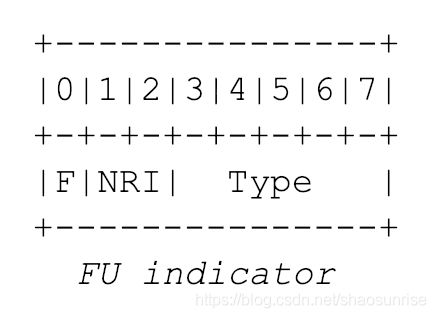
分片分组
通常采用无DON字段的FU-A结构封装RTP分片分组。各种RTP分组在RTP Header后面都跟着 F|NRI|Type 结构,来判定分组类型。

FU indicator
采用FU-A分组类型的话Type = 28,NRI与此NALU中NRI字段相同。
FU header

此结构中Type采用原始码流NALU中的Type字段,S=1表示这个RTP包为分片分组第一个分片,E=1表示为分片分组最后一个分片。除了首尾分片,中间的分片S&E都设为0。R为保留位,设为0。
RTP封装H.264码流示例程序
RTP Server示例程序
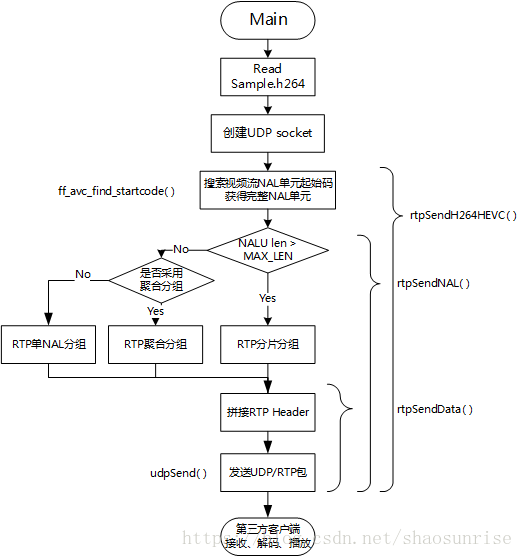
程序框架
这个示例程序是参考ffmpeg的代码,实现了读取一个Sample.h264裸流文件,(打算以后支持HEVC/H.265所以文件名有HEVC),通过ffmpeg内置的函数查找NAL单元起始码,从而获取一个完整的NALU。根据NALU长度选择RTP打包类型,然后再组装RTP头部信息,最终发送到指定IP和端口,本例发送到本机1234端口。本程序网络部分使用的是基于Linux/MacOS 的POSIX socket,Windows平台可以自己实现相应的函数进行代替。
程序文件概览
- main.c: 函数入口
- RTPEnc.c: RTP封装实现
- Network.c: UDP socket相关
- AVC.c: 查找NALU起始码函数,copy自ffmpeg
- Utils: 读取文件以及copy指定长度的内存数据
示例程序
main.c
#include RTPEnc.c
//
// Created by Liming Shao on 2018/5/10.
//
#include AVC.c
//
// Created by Liming Shao on 2018/5/10.
//
#include Network.c
//
// Created by Liming Shao on 2018/5/11.
//
#include Utils.c
//
// Created by Liming Shao on 2018/5/10.
//
#include 完整代码可以从Github上直接下载,地址:https://github.com/lmshao/RTP 。
RTP码流播放方法/SDP文件
本程序只是实现了发送RTP视频流的服务器端功能,可以使用第三方软件ffmpeg-ffplay/VLC进行播放。播放RTP流需要一个写有视频流信息的SDP文件(play.sdp),此程序使用的文件如下所示,具体关于SDP规范请自行查阅:
m=video 1234 RTP/AVP 96
a=rtpmap:96 H264/90000
a=framerate:25
c=IN IP4 127.0.0.1
s=Sample Video
VLC播放
使用VLC先打开此sdp文件,然后运行此服务端程序。
FFplay
ffplay是ffmpeg中独立的播放器程序。可以使用如下命令就行播放,同样是先执行播放命令,后运行RTP发送程序。
ffplay -protocol_whitelist "file,rtp,udp" play.sdp
附ffmpeg RTP发送命令:ffmpeg -re -i Sample.h264 -vcodec copy -f rtp rtp://127.0.0.1:1234
关于RTP时间戳问题
RTP协议要求时间戳应该使用90kHz的采样时钟,也就是说一秒钟的间隔应该设置时间差值为90000,25pfs恒定帧率的视频每一帧时间戳就为900000/25。这是对于视频文件而言的,对于实时采集的视频流,可以使用视频采集时刻作为时间戳。
因为本例使用的是.h264裸流文件,文件格式本身并没有时间戳信息,所以本例中可以不设置时间戳信息,也可以根据帧率设置时间戳信息,通过分析网络数据包发现FFmpeg RTP发送.h264视频时时间戳采用的是一个固定的随机数,并没有逐帧递增。
但是不设置时间戳信息的话,就会影响客户端解码播放。ffplay播放RTP流的时候,在没有RTP时间戳的情况下会根据接收的速度进行解码显示,VLC在没有RTP时间戳时,会先缓存一段时间的视频流,然后正常播放,可能是通过分析NALU视频流获取了显示时间信息。
关于RTP聚合分组STAP-A NAL HDR问题
RTP聚合分组的STAP-A NAL头部字段,RTP协议要求:
- The RTP timestamp MUST be set to the earliest of the NALU-times of all the NAL units to be aggregated.
- The type field of the NAL unit type octet MUST be set to the appropriate value, as indicated in Table 4. STAP-A type is 24.
- The F bit MUST be cleared if all F bits of the aggregated NAL units are zero; otherwise, it MUST be set.
- The value of NRI MUST be the maximum of all the NAL units carried in the aggregation packet.
通过分析,FFmpg在封装RTP聚合分组包的时候,并没有完全采用RTP协议规定的要求就行封装。比如F位和NRI位直接使用第一包的相关信息,好像也没影响视频播放。本示例程序方便起见时间戳采用的最后一个NAL的时间戳,有空再改进。
有任何问题欢迎交流。
代码可以从Github上直接下载,地址:https://github.com/lmshao/RTP 。