SpringMVC之自定义注解
目录
一.JAVA注解简介
1.1.Java注解分类
1.2.JDK元注解
二.自定义注解
1.1.如何自定义注解
1.2.自定义注解的基本案例
1.2.1.案例一(获取类与方法上的注解值)
1.2.2.案例二(获取类属性上的注解属性值)
1.2.3. 案例三(获取参数修饰注解对应的属性值)
三.Aop自定义注解的应用
好啦,今天的分享就到这了,希望能够帮到你呢!
一.JAVA注解简介
Java注解是Java语言中一种元数据的形式,它是在程序源代码中插入的特殊标记,用于给程序中的代码提供额外的信息。注解可以用来为类、方法、字段等程序元素添加标记,以表明这些元素应该如何被处理或解析。
Java注解是在编译时或运行时可以被读取和处理的。它们可以被用来提供编译器指令、在运行时进行跟踪和分析、生成代码和文档等。Java注解使用简单的语法进行声明,通常以
@符号开头,紧跟注解的名称和一组可选的参数。Java提供了一些内置的注解,比如
@Override用于标记一个方法重写了父类中的方法,@Deprecated用于标记一个已过时的方法或类,@SuppressWarnings用于抑制编译器警告等。此外,开发者也可以自定义注解来满足特定的需求。通过使用注解,开发者可以为自己的代码添加额外的信息,并通过工具或框架来读取和处理这些注解,以达到特定的目的。注解可以提高代码的可读性、维护性和可扩展性,是Java开发中一个非常有用的特性。
1.1.Java注解分类
JDK(Java Development Kit)提供了一些基本的注解和元注解,下面分别介绍它们的作用:
1.基本注解:
@Override:用于标记一个方法是重写父类中的方法,如果该方法没有正确地重写父类的方法,则会在编译时报错。@Deprecated:用于标记一个方法、类或字段已经过时,表示不推荐使用,编译器会在使用过时元素时发出警告。@SuppressWarnings:用于抑制编译器产生的警告,可以在特定的代码块或者整个方法中使用,让编译器忽略特定的警告。2.元注解:
@Target:用于指定注解可以应用的目标元素类型,如类、字段、方法等。@Retention:用于指定注解的保留策略,即注解在何时生效,包括源代码期、编译期和运行期。@Documented:用于指定注解是否会包含在生成的文档中。@Inherited:用于指定注解是否可以被子类继承。3.自定义注解:
- 自定义注解是根据业务需求定义的注解,可以通过
@interface关键字来声明,并可以在注解中定义元素和默认值。自定义注解的元素可以是基本类型、枚举、Class类型、String类型以及以上类型的一维数组。自定义注解可以通过@MyAnnotation的形式应用到目标元素上,如类、方法、字段等。可以通过反射机制读取和解析自定义注解,并根据注解的信息进行相应的处理。使用自定义注解可以增加代码的可读性和可维护性,同时也方便框架和工具对程序进行扩展和定制。
1.2.JDK元注解
@Retention:定义注解的保留策略
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.SOURCE) //注解仅存在于源码中,在class字节码文件中不包含
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.CLASS) //默认的保留策略,注解会在class字节码文件中存在,但运行时无法获得,
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) //注解会在class字节码文件中存在,在运行时可以通过反射获取到@Target:指定被修饰的Annotation可以放置的位置(被修饰的目标)
@Target(ElementType.TYPE) //接口、类
@Target(ElementType.FIELD) //属性
@Target(ElementType.METHOD) //方法
@Target(ElementType.PARAMETER) //方法参数
@Target(ElementType.CONSTRUCTOR) //构造函数
@Target(ElementType.LOCAL_VARIABLE) //局部变量
@Target(ElementType.ANNOTATION_TYPE) //注解
@Target(ElementType.PACKAGE) //包
注:可以指定多个位置,例如:
@Target({ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.TYPE}),也就是此注解可以在方法和类上面使用@Inherited:指定被修饰的Annotation将具有继承性
@Documented:指定被修饰的该Annotation可以被javadoc工具提取成文档.
二.自定义注解
1.1.如何自定义注解
要自定义注解,需要使用
@interface关键字来声明注解,并在注解中定义元素和默认值。以下是自定义注解的基本步骤:
使用
@interface关键字声明一个注解,如@interface MyAnnotation。在注解内部定义元素,并为元素指定默认值。注解的元素可以是基本类型、枚举、Class类型、String类型以及以上类型的一维数组。
在代码中应用自定义注解。可以在类、方法、字段等目标元素上使用自定义注解。
通过反射机制读取和解析自定义注解。可以使用Java的反射机制获取类、方法、字段的注解信息,根据注解的信息进行相应的处理。
自定义注解可以根据具体的业务需求灵活定义,并通过反射机制读取和处理注解的信息。注解可以提高代码的可读性、可维护性和可扩展性,是Java开发中一个有用且强大的特性。
以下是示例,演示了如何自定义一个简单的注解:主要在2.3.4上
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
public @interface MyAnnotation {
String value() default "";
int count() default 0;
}在上述例子中,
MyAnnotation注解包含两个元素,一个是value,类型为String,默认值为空字符串;另一个是count,类型为int,默认值为0。使用了
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)元注解指定了注解在运行时保留,使用了@Target(ElementType.METHOD)元注解指定了注解可以应用在方法上。
MyClass类使用了自定义注解@MyAnnotation,并为注解的元素value和count指定了具体的值:
@MyAnnotation(value = "Hello", count = 5)
public class MyClass {
@MyAnnotation(value = "World")
private String name;
@MyAnnotation(count = 3)
public void myMethod() {
// 方法体
}
} 通过getAnnotation()方法获取MyAnnotation注解的实例,然后可以读取注解的元素值。
Class clazz = MyClass.class;
MyAnnotation annotation = clazz.getAnnotation(MyAnnotation.class);
String value = annotation.value();
int count = annotation.count();自定义注解可以根据具体的业务需求灵活定义,并通过反射机制读取和处理注解的信息。注解可以提高代码的可读性、可维护性和可扩展性,是Java开发中一个有用且强大的特性。
1.2.自定义注解的基本案例
创建完项目之后,找到 pom.xml 配置文件 ,进行项目引用导入。
4.0.0
org.example
fzpzyssm
1.0-SNAPSHOT
war
fzpzyssm Maven Webapp
http://www.example.com
UTF-8
1.8
1.8
3.7.0
5.0.2.RELEASE
3.4.5
5.1.44
5.1.2
1.3.1
2.1.1
2.4.3
2.9.1
3.2.0
1.7.13
4.12
4.0.0
1.18.2
1.1.0
2.10.0
2.9.0
1.7.1.RELEASE
2.9.3
1.2
1.1.2
8.0.47
1.3.3
5.0.2.Final
1.3.2
org.springframework
spring-core
${spring.version}
org.springframework
spring-beans
${spring.version}
org.springframework
spring-context
${spring.version}
org.springframework
spring-orm
${spring.version}
org.springframework
spring-tx
${spring.version}
org.springframework
spring-aspects
${spring.version}
org.springframework
spring-web
${spring.version}
org.springframework
spring-test
${spring.version}
org.mybatis
mybatis
${mybatis.version}
mysql
mysql-connector-java
${mysql.version}
com.github.pagehelper
pagehelper
${pagehelper.version}
org.mybatis
mybatis-spring
${mybatis.spring.version}
org.springframework
spring-context-support
${spring.version}
org.mybatis.caches
mybatis-ehcache
${mybatis.ehcache.version}
net.sf.ehcache
ehcache
${ehcache.version}
redis.clients
jedis
${redis.version}
org.springframework.data
spring-data-redis
${redis.spring.version}
com.fasterxml.jackson.core
jackson-databind
${jackson.version}
com.fasterxml.jackson.core
jackson-core
${jackson.version}
com.fasterxml.jackson.core
jackson-annotations
${jackson.version}
org.apache.commons
commons-dbcp2
${commons.dbcp2.version}
commons-pool2
org.apache.commons
org.apache.commons
commons-pool2
${commons.pool2.version}
org.springframework
spring-webmvc
${spring.version}
org.slf4j
slf4j-api
${slf4j.version}
org.slf4j
jcl-over-slf4j
${slf4j.version}
runtime
org.apache.logging.log4j
log4j-api
${log4j2.version}
org.apache.logging.log4j
log4j-core
${log4j2.version}
org.apache.logging.log4j
log4j-slf4j-impl
${log4j2.version}
org.apache.logging.log4j
log4j-web
${log4j2.version}
runtime
com.lmax
disruptor
${log4j2.disruptor.version}
junit
junit
${junit.version}
javax.servlet
javax.servlet-api
${servlet.version}
provided
org.projectlombok
lombok
${lombok.version}
provided
jstl
jstl
${jstl.version}
taglibs
standard
${standard.version}
org.apache.tomcat
tomcat-jsp-api
${tomcat-jsp-api.version}
commons-fileupload
commons-fileupload
${commons-fileupload.version}
org.hibernate
hibernate-validator
${hibernate-validator.version}
org.apache.shiro
shiro-core
${shiro.version}
org.apache.shiro
shiro-web
${shiro.version}
org.apache.shiro
shiro-spring
${shiro.version}
fzpzyssm
src/main/java
**/*.xml
src/main/resources
*.properties
*.xml
org.apache.maven.plugins
maven-compiler-plugin
${maven.compiler.plugin.version}
${maven.compiler.source}
${maven.compiler.target}
${project.build.sourceEncoding}
org.mybatis.generator
mybatis-generator-maven-plugin
1.3.2
mysql
mysql-connector-java
${mysql.version}
true
maven-clean-plugin
3.1.0
maven-resources-plugin
3.0.2
maven-compiler-plugin
3.8.0
maven-surefire-plugin
2.22.1
maven-war-plugin
3.2.2
maven-install-plugin
2.5.2
maven-deploy-plugin
2.8.2
1.2.1.案例一(获取类与方法上的注解值)
创建 TranscationModel 直接C到包里接口:
package com.junlinyi.annotation.demo;
public enum TranscationModel {
Read, Write, ReadWrite;
}创建 MyAnnotation1 直接C到包里接口
package com.junlinyi.annotation.demo;
import java.lang.annotation.*;
/**
* MyAnnotation1注解可以用在类、接口、属性、方法上
* 注解运行期也保留
* 不可继承
*/
@Target({ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.FIELD,ElementType.METHOD})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface MyAnnotation1 {
String name();
}创建 MyAnnotation2 直接C到包里接口
package com.junlinyi.annotation.demo;
import java.lang.annotation.*;
/**
* MyAnnotation2注解可以用在方法上
* 注解运行期也保留
* 不可继承
*/
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface MyAnnotation2 {
TranscationModel model() default TranscationModel.ReadWrite;
}
创建 MyAnnotation3 直接C到包里接口
package com.junlinyi.annotation.demo;
import java.lang.annotation.*;
/**
* @author 君临沂
* @site www.junlinyi.jly
* @company 君氏集团
* @create 2023-09-14-18:48
*
* MyAnnotation3注解可以用在方法上
* 注解运行期也保留
* 可继承
*/
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Inherited
@Documented
public @interface MyAnnotation3 {
TranscationModel[] models() default TranscationModel.ReadWrite;
}
创建测试类进行自定义注解测试 Demo1
package com.junlinyi.annotation.demo;
/**
* @author 君临沂
* @site www.junlinyi.jly
* @company 君氏集团
* @create 2023-09-14-19:00
*
* 获取类与方法上的注解值
*/
@MyAnnotation1(name = "abc")
public class Demo1 {
@MyAnnotation1(name = "xyz")
public Integer age;
@MyAnnotation2(model = TranscationModel.Read)
public void list() {
System.out.println("list");
}
@MyAnnotation3(models = {TranscationModel.Read, TranscationModel.Write})
public void edit() {
System.out.println("edit");
}
}
创建测试类进行自定义注解测试 Demo1Test
package com.junlinyi.annotation.demo;
import org.junit.Test;
/**
* @author 君临沂
* @site www.junlinyi.jly
* @company 君氏集团
* @create 2023-09-14-19:01
*/
public class Demo1Test {
@Test
public void list() throws Exception {
// 获取类上的注解
MyAnnotation1 annotation1 = Demo1.class.getAnnotation(MyAnnotation1.class);
System.out.println(annotation1.name());//abc
// 获取方法上的注解
MyAnnotation2 myAnnotation2 = Demo1.class.getMethod("list").getAnnotation(MyAnnotation2.class);
System.out.println(myAnnotation2.model());//Read
// 获取属性上的注解
MyAnnotation1 myAnnotation1 = Demo1.class.getDeclaredField("age").getAnnotation(MyAnnotation1.class);
System.out.println(myAnnotation1.name());// xyz
}
@Test
public void edit() throws Exception {
MyAnnotation3 myAnnotation3 = Demo1.class.getMethod("edit").getAnnotation(MyAnnotation3.class);
for (TranscationModel model : myAnnotation3.models()) {
System.out.println(model);//Read,Write
}
}
}
执行其中的方法( edit)进行测试,输出结果如下 :
1.2.2.案例二(获取类属性上的注解属性值)
场景自定义注解 TestAnnotation
package com.junlinyi.annotation.demo2;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
/**
* @author 君临沂
* @site www.junlinyi.jly
* @company 君氏集团
* @create 2023-09-14-19:25
*/
//@Retention(RetentionPolicy.SOURCE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.FIELD)
public @interface TestAnnotation {
String value() default "默认value值";
String what() default "这里是默认的what属性对应的值";
}
创建测试类进行自定义注解的测试 Demo2
package com.junlinyi.annotation.demo2;
/**
* @author 君临沂
* @site www.junlinyi.jly
* @company 君氏集团
* @create 2023-09-14-19:48
*
* 获取类属性上的注解属性值
*/
public class Demo2 {
@TestAnnotation(value = "这就是value对应的值_msg1", what = "这就是what对应的值_msg1")
private static String msg1;
// 当没有在注解中指定属性名,那么就是value
@TestAnnotation("这就是value对应的值1")
private static String msg2;
@TestAnnotation(value = "这就是value对应的值2")
private static String msg3;
@TestAnnotation(what = "这就是what对应的值")
private static String msg4;
}
创建测试类进行自定义注解的测试 Demo2Test
package com.junlinyi.annotation.demo2;
import org.junit.Test;
/**
* @author 君临沂
* @site www.junlinyi.jly
* @company 君氏集团
* @create 2023-09-14-19:48
*/
public class Demo2Test {
@Test
public void test1() throws Exception {
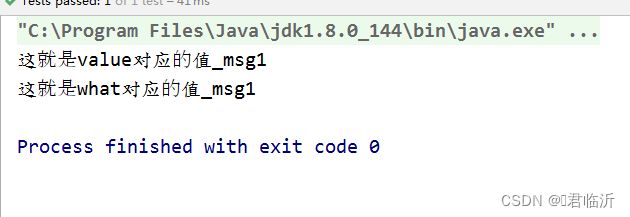
TestAnnotation msg1 = Demo2.class.getDeclaredField("msg1").getAnnotation(TestAnnotation.class);
System.out.println(msg1.value());
System.out.println(msg1.what());
}
@Test
public void test2() throws Exception{
TestAnnotation msg2 = Demo2.class.getDeclaredField("msg2").getAnnotation(TestAnnotation.class);
System.out.println(msg2.value());
System.out.println(msg2.what());
}
@Test
public void test3() throws Exception{
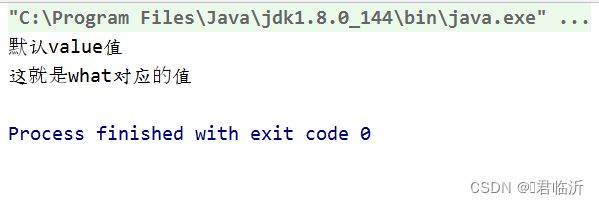
TestAnnotation msg3 = Demo2.class.getDeclaredField("msg3").getAnnotation(TestAnnotation.class);
System.out.println(msg3.value());
System.out.println(msg3.what());
}
@Test
public void test4() throws Exception{
TestAnnotation msg4 = Demo2.class.getDeclaredField("msg4").getAnnotation(TestAnnotation.class);
System.out.println(msg4.value());
System.out.println(msg4.what());
}
}
执行其中 test1 的方法进行测试,输出结果为 :
执行其中 test2 的方法进行测试,输出结果为 :
执行其中 test3 的方法进行测试,输出结果为 :
执行其中 test4 的方法进行测试,输出结果为 :
1.2.3. 案例三(获取参数修饰注解对应的属性值)
创建自定义注解 IsNotNull
package com.junlinyi.annotation.demo3;
import java.lang.annotation.*;
/**
* @author 君临沂
* @site www.junlinyi.jly
* @company 君氏集团
* @create 2023-09-14-19:50
*
* 非空注解:使用在方法的参数上,false表示此参数可以为空,true不能为空
*/
@Documented
@Target({ElementType.PARAMETER})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface IsNotNull {
boolean value() default false;
}
创建测试类 Demo3
package com.junlinyi.annotation.demo3;
/**
* @author 君临沂
* @site www.junlinyi.jly
* @company 君氏集团
* @create 2023-09-14-19:50
*
* 获取参数修饰注解对应的属性值
*/
public class Demo3 {
public void hello1(@IsNotNull(true) String name) {
System.out.println("hello:" + name);
}
public void hello2(@IsNotNull String name) {
System.out.println("hello:" + name);
}
}
创建测试类 Demo3Test进行方法测试
package com.junlinyi.annotation.demo3;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.lang.reflect.Parameter;
/**
* @author 君临沂
* @site www.junlinyi.jly
* @company 君氏集团
* @create 2023-09-14-19:50
*/
public class Demo3Test {
@Test
public void hello1() throws Exception {
Demo3 demo3 = new Demo3();
for (Parameter parameter : demo3.getClass().getMethod("hello1", String.class).getParameters()) {
IsNotNull annotation = parameter.getAnnotation(IsNotNull.class);
if(annotation != null){
System.out.println(annotation.value());//true
}
}
}
@Test
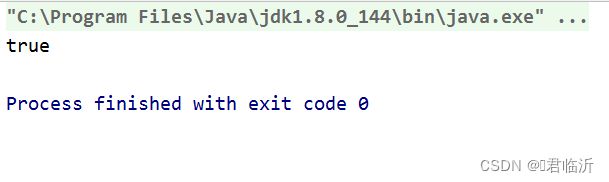
public void hello2() throws Exception {
Demo3 demo3 = new Demo3();
for (Parameter parameter : demo3.getClass().getMethod("hello2", String.class).getParameters()) {
IsNotNull annotation = parameter.getAnnotation(IsNotNull.class);
if(annotation != null){
System.out.println(annotation.value());//false
}
}
}
// @requestParam
// 默认情况下:传参为空,不会调用方法的,不为空会调用方法
// requice=false:啥也不传参也会调用方法
@Test
public void hello3() throws Exception {
// 模拟浏览器传递到后台的参数 解读@requestParam
String name = "junlinyi";
Demo3 demo3 = new Demo3();
Method method = demo3.getClass().getMethod("hello1", String.class);
for (Parameter parameter : method.getParameters()) {
IsNotNull annotation = parameter.getAnnotation(IsNotNull.class);
if(annotation != null){
System.out.println(annotation.value());//true
if (annotation.value() && !"".equals(name)){
method.invoke(demo3,name);
}
}
}
}
}
执行其中的方法( hello1 )进行测试,输出结果为 :
执行其中的方法( hello2 )进行测试,输出结果为 :
执行其中的方法( hello3 )进行测试,输出结果为 :
三.Aop自定义注解的应用
AOP(Aspect-Oriented Programming,面向切面编程)是一种编程范式,可以在程序运行期间通过动态代理方式实现对代码的横切关注点进行模块化管理。其中,自定义注解可以作为AOP的触发器,用于标记需要进行切面处理的目标对象或方法。
以下是一个示例,演示了如何使用自定义注解与AOP结合,实现日志记录的功能:
1 .定义自定义注解@MyLog,用于标记需要记录日志的方法:
package com.junlinyi.annotation.aop;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
/**
* @author 君临沂
* @site www.junlinyi.jly
* @company 君氏集团
* @create 2023-09-14-19:55
*
*/
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface MyLog {
String desc();
}
2 . 定义切面类MyLogAspect,在该类中定义增强逻辑,例如记录日志:
package com.junlinyi.aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Around;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Pointcut;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.util.Arrays;
/**
* @author 君临沂
* @site www.junlinyi.jly
* @company 君氏集团
* @create 2023-09-14-19:55
*
*/
@Component
@Aspect
public class MyLogAspect {
private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(MyLogAspect.class);
/**
* 只要用到了com.javaxl.p2.annotation.springAop.MyLog这个注解的,就是目标类
*/
@Pointcut("@annotation(com.junlinyi.annotation.aop.MyLog)")
private void MyValid() {
}
// @Before("MyValid()")
// public void before(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
// MethodSignature signature = (MethodSignature) joinPoint.getSignature();
// logger.debug("[" + signature.getName() + " : start.....]");
// System.out.println("[" + signature.getName() + " : start.....]");
//
// MyLog myLog = signature.getMethod().getAnnotation(MyLog.class);
// logger.debug("【目标对象方法被调用时候产生的日志,记录到日志表中】:"+myLog.desc());
// System.out.println("【目标对象方法被调用时候产生的日志,记录到日志表中】:" + myLog.desc());
// }
@Around("MyValid()")
public Object doAround(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp) throws Throwable {
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println(pjp.getTarget());
System.out.println(pjp.getThis());
Object[] args = pjp.getArgs();
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(args));
Object ob = pjp.proceed();// ob 为方法的返回值
System.out.println(ob);
logger.info("耗时 : " + (System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime));
return ob;
}
}
在上面的切面类中,使用@Aspect注解标记该类为切面类。@Pointcut("@annotation(com.CloudJun.annotation.aop.MyLog)")注解用于定义切点,表示匹配所有标记有@Log注解的方法。@Before注解表示在目标方法执行前执行增强逻辑。
3 . 创建一个控制器 LogController
package com.junlinyi.web;
import com.junlinyi.annotation.aop.MyLog;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
/**
* @author 君临沂
* @site www.junlinyi.jly
* @company 君氏集团
* @create 2023-09-14-19:56
*
*/
@Controller
public class LogController {
@RequestMapping("/myLog")
@MyLog(desc = "日志管理")
public void testLogAspect(HttpServletRequest request) {
request.getRemoteAddr();
request.getRemotePort();
System.out.println("这里随便来点啥");
}
}
自定义注解与AOP结合使用,可以实现各种不同的功能,如权限控制、性能监控、事务管理等。根据具体的业务需求,可以定义不同的注解,并在切面类中实现相应的增强逻辑。
测试:
处理中。。。。。