springboot
Springboot入门
Springboot入门
springboot 提供了一种快速使用spring项目的方式,而不是对spring功能的增强,本文参考
https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1Lq4y1J77x?p=12&vd_source=0882f549dac54045384d4a921596e234
可搭配视频教程查看
快速入门springboot
spring的缺点
配置繁琐
依赖繁琐
spring-boot的特点
自动配置
起步依赖,依赖传递
还有一些赋值功能,比如内嵌服务器,健康监测
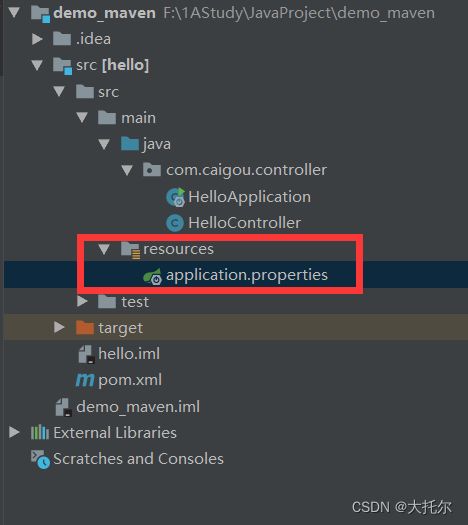
创建一个spring-boot项目
spring-boot使用jar的打包方式
spring和spring-boot的业务代码编写方式完全一样
通过运行spring-boot的入口类运行 web服务
修改配置文件以及代码
修改pom.xml
当项目的依赖发生变化时记得更新maven项目
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0modelVersion>
<groupId>com.caigougroupId>
<artifactId>helloartifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOTversion>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parentartifactId>
<version>2.1.3.RELEASEversion>
parent>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-webartifactId>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-testartifactId>
<scope>testscope>
dependency>
dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-pluginartifactId>
plugin>
plugins>
build>
project>
- 添加HelloController
package com.caigou.controller;
//import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
// 注意使用RestController 而不是Controller
@RestController
public class HelloController {
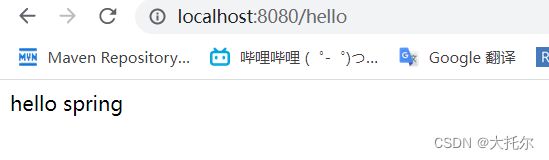
@RequestMapping("/hello")
public String hello(){
return "hello spring";
}
}
- 添加Application启动类
package com.caigou.controller;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@SpringBootApplication
public class HelloApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(HelloApplication.class, args);
}
}
快速生成springboot项目
springboot起步依赖原理分析
在spring-boot-starter-parent中组合了各种技术信息,组合搭配了一套最优技术版本
在各种starter中,定义了完成该功能所需要的坐标合集,其中大部分版本信息来自于父工程
我们的工程继承parent,引入starter,通过依赖传递可以方便的获取需要的jar包,不会存在版本冲突的问题
springboot配置
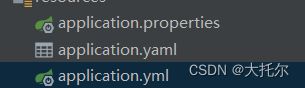
spring-boot是约定优于配置的,许多配置都有默认值,如果想更改这些配置的话,就要修改application.properties或者application.yml 文件
修改properties文件
# 更改服务端口
server.port=8081
# 自定义属性
name=abc
server:
port: 8085
当一个目录中存在三种配置文件时,application.properties 优先级大于application.yml, application.yml 优先级大于application.yaml
yml文件示例以及注意事项
yml简介,以存储数据为目标,受多种语言的支持
# 缩进要使用空格, 统一文件内变量不能重名
# 对象
person:
name: zhangsan
age: 18
# 对象行内写法
person1: {name: zhangsan, age: 18}
# 数组
city:
- beijing
- shanghai
# 数组行内
city1: [beijing,shanghai]
# 常量
msg1: '13513 \n 11351' # 不识别转义字符
msg2: "153135 \n 1531361" # 识别转义字符
# 参数引用
name: lisi
person2:
name: ${name}
读取自定义配置文件内容
- @Value 和 autowired_environment 的代码
以下是获取yml文件中自定义属性的代码,两种方式获取值的字符串写法都一样,environment只需要注入一个environment,@Value 需要注入多个值,如果注入值比较少的话使用@Value比较好
package com.caigou.controller;
//import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.core.env.Environment;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
// 注意使用RestController 而不是Controller
@RestController
public class HelloController {
@Value("${name}")
private String name;
@Value("${person.age}")
private int age;
@Value("${city[0]}")
private String city;
@Value("${msg1}")
private String msg1;
@Value("${msg2}")
private String msg2;
@Autowired
private Environment env;
@RequestMapping("/hello")
public String hello(){
System.out.println(name);
System.out.println(age);
System.out.println(city);
System.out.println(msg1);
System.out.println(msg2);
System.out.println(env.getProperty("person2.name"));
return "hello spring";
}
}
- 通过自定义bean
其中perfix用于指向配置文件中的自定义属性
package com.caigou.controller;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "person")
public class Person {
private String name;
private String age;
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getAge() {
return age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age='" + age + '\'' +
'}';
}
public void setAge(String age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
}
接着使用自动注入,便可以在代码中方便的使用属性
@Autowired
private Person person;
- 添加提示,修改pom.xml,在编写实体类和配置文件中会获得提示
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-configuration-processorartifactId>
<optional>trueoptional>
dependency>
springboot profile
不同环境的配置文件不一样,profile是用于动态配置切换的
profile配置方式
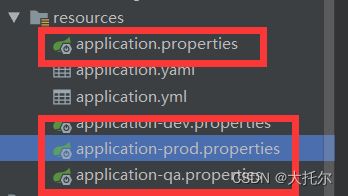
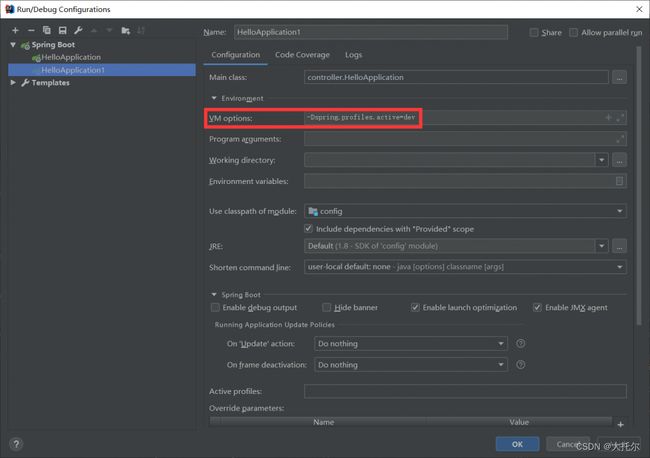
在主配置文件中添加如下代码,可选择使用的配置文件,等号后面的值,和文件application-后面的值要相同
spring.profiles.active=dev
---
server:
port: 8081
spring:
profiles: dev
---
server:
port: 8082
spring:
profiles: qa
---
server:
port: 8083
spring:
profiles: prod
---
spring:
profiles:
active: prod
不同配置的启动方式
java -jar springboot_jar包名 --spring.profiles.activate=dev
java -jar hello-1.0-SNAPSHOT.jar --spring.profiles.active=qa
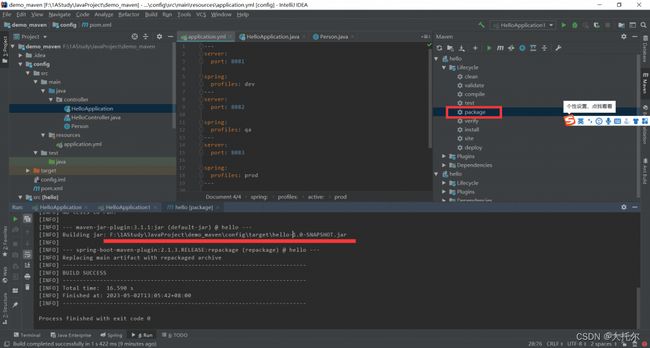
springboot 内部加载顺序
项目根目录config下的配置文件
项目根目录的配置文件
resources的config下的配置文件
resources下的配置文件
多个文件形成一个互补的关系,从上到下优先级依次降低,项目根目录config下的配置文件最牛
外部配置文件加载顺序
可以使用spring.config.application指定外部配置文件的位置,默认会加载jar包所在目录的外部配置文件,以及jar包config目录下的配置文件,外部配置文件的优先级要高于内部配置文件
spring boot 整合其他框架
- 编写业务代码
package controller;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service
public class UserService {
public void print(){
System.out.println("123");
}
}
- 编写测试方法
package controller;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringRunner;
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest(classes = HelloApplication.class)
public class UserServiceTest {
@Autowired
private UserService userService;
@Test
public void testPrint(){
userService.print();
}
}
spring boot整合redis
测试代码
package controller;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringRunner;
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest(classes = HelloApplication.class)
public class RedisTest {
@Autowired
private RedisTemplate redisTemplate;
@Test
public void setTest(){
redisTemplate.boundValueOps("name").set("zhangsan1");
}
@Test
public void getTest(){
Object name = redisTemplate.boundValueOps("name").get();
System.out.println(name);
}
}
修改配置文件
spring:
profiles: prod
redis:
host: 175.24.184.55
password: *********
spring boot 整合mybatis
- 添加依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis.spring.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-spring-boot-starterartifactId>
<version>2.1.0version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysqlgroupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-javaartifactId>
dependency>
- 编写Mapper,mapper包位于controller包下
package controller.mapper;
import domain.User;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Mapper;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Select;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
import java.util.List;
@Mapper
@Repository
public interface UserMapper {
@Select("select * from user")
List<User> findAll();
}
- 编写测试脚本
package controller;
import controller.mapper.UserMapper;
import domain.User;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringRunner;
import java.util.List;
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest(classes = HelloApplication.class)
public class UserTest {
@Autowired
private UserMapper userMapper;
@Test
public void testQueryAll(){
List<User> result = userMapper.findAll();
System.out.println(result);
}
}
- 写配置文件
spring:
datasource:
url: jdbc:mysql://ip:3306/caigou?useSSL=false&serverTimezone=UTC
username: root
password: HI79+=B8b1nr
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
使用xml配置文件
- 编写mapper
package controller.mapper;
import domain.User;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Mapper;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Property;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
import java.util.List;
@Mapper
@Repository
public interface UserXmlMapper {
List<User> findAll();
}
- 编写xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="controller.mapper.UserXmlMapper">
<!-- //namespace的值是dao接口的全限定名称(即在哪个包下面要全部写出来-->
<!-- //增删改查子标签的id要和接口中的方法名一样-->
<!--实现查询功能的select子标签-->
<select id="findAll" resultType="domain.User">
select * from user order by id desc
</select>
<!--实现插入功能的insert子标签-->
<!-- <insert id="insertStudent">-->
<!-- insert into student values(#{id},#{name},#{email},#{age})-->
<!-- </insert>-->
<!-- <!–实现修改功能的update子标签–>-->
<!-- <update id="updateEmp">-->
<!-- UPDATE emp SET name = #{name} WHERE id = #{id};-->
<!-- </update>-->
<!-- <!–实现删除功能的delete子标签–>-->
<!-- <delete id="deleteEmp">-->
<!-- DELETE FROM emp WHERE id = #{id};-->
<!-- </delete>-->
</mapper>
文件位于
mybatis:
mapper-locations: classpath:mapper/*Mapper.xml
spring boot高级.
spring-boot自动配置
condition, spring可以选择性的创建bean
spring boot 部署方式
打jar包
打war包
将jar包打包至服务器上,后台启动程序 https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_46504244/article/details/125628546
对部署好的springboot进行压测
可参考以下链接 https://blog.csdn.net/Loners_fan/article/details/127890332
ab -n 100 -c 100 http://172.16.1.6/
执行-n代表总请求数 -c 代表一次请求的发送的并发请求数
对于空负载的springboot web程序和python web程序两者在测试机器的表现是差不多的