Spring MVC:REST
Spring MVC
- REST
-
- RESTful 风格的四种请求方式实现
- 附
REST
REST( Representational State Transfer ,表述性状态传递),是 Roy Fielding 博士在2000年提出的一种软件架构风格(即描述了一个架构样式的网络系统,如 web 应用程序)。REST 是一种针对网络应用的设计和开发方式,可以降低开发的复杂性,提高系统的可伸缩性。
RESTful 是一种网络应用程序的设计风格和开发方式,基于 HTTP ,可以使用 XML 格式定义或 JSON 格式定义。RESTful 适用于移动互联网厂商作为业务接口的场景,实现第三方 OTT 调用移动网络资源的功能,动作类型为新增、变更、删除所调用资源。
REST 是一组架构约束条件和原则。而满足这些约束条件和原则的应用程序或设计则是 RESTful 。
RESTful 特点
1、每一个 URI( Uniform Resource Identifier ,统一资源标识符)代表1种资源
2、客户端使用 GET 、POST 、PUT 、DELETE 4个表示操作方式的动词对服务端资源进行操作
- GET 用于获取资源
- POST 用于新增资源
- PUT 用于更新资源
- DELETE 用于删除资源
3、通过操作资源的表现形式来操作资源
4、资源的表现形式是 XML 或者 HTML
5、客户端与服务端之间的交互在请求之间是无状态的,从客户端到服务端的每个请求都必须包含理解请求所必需的信息
RESTful 风格的四种请求方式实现
在 HTTP 协议中,GET 、POST 、PUT 、DELETE 4个表示操作方式的动词,而对应的操作为 GET 用于获取资源,POST 用于新增资源,PUT 用于更新资源,DELETE 用于删除资源。
在 Spring MVC 中,可以使用占位符的方式实现 RESTful 风格。
实现结果
/某路径/731 ——— HTTP GET :得到 id = 731 的一条数据
/某路径/731 ——— HTTP PUT :更新 id = 731 的一条数据
/某路径/731 ——— HTTP DELETE :删除 id = 731 的一条数据
/某路径 ————— HTTP POST :新增一条数据
简单示例:
首先,使用 @RequestMapping 注解映射请求中的 method 参数实现四种请求方式的调用
package cn.edu.springmvcdemo.controller;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
@Controller
public class RestfulDemo {
@RequestMapping("/restful")
public String restfulTest(){
return "restful";
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/getTest",method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String getTest(){
System.out.println("执行了 getTest 方法!!!");
return "accessing";
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/putTest",method = RequestMethod.PUT)
public String putTest(){
System.out.println("执行了 putTest 方法!!!");
return "redirect:/restful";
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/deleteTest",method = RequestMethod.DELETE)
public String deleteTest(){
System.out.println("执行了 deleteTest 方法!!!");
return "redirect:/restful";
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/postTest",method = RequestMethod.POST)
public String postTest(){
System.out.println("执行了 postTest 方法!!!");
return "accessing";
}
}
接着,在 web.xml 中配置过滤器来指定的 post 请求转变为所需的 put 或 delete 请求
<filter>
<filter-name>HiddenHttpMethodFilterfilter-name>
<filter-class>org.springframework.web.filter.HiddenHttpMethodFilterfilter-class>
filter>
<filter-mapping>
<filter-name>HiddenHttpMethodFilterfilter-name>
<url-pattern>/*url-pattern>
filter-mapping>
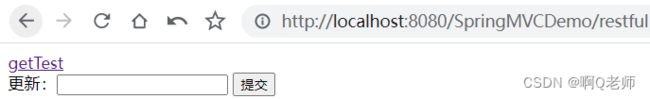
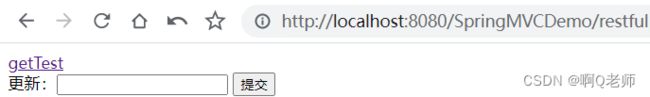
然后,创建 restful.jsp ,以 GET 请求和 put 请求为例
<%--
Created by IntelliJ IDEA.
User: dell
Date: 2023/7/31
Time: 21:50
To change this template use File | Settings | File Templates.
--%>
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<body>
<%-- <a>标签默认为 GET 请求 --%>
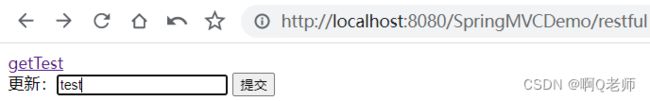
<a href="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/getTest">getTesta>
<form action="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/putTest" method="post">
<%-- 将 post 请求转变为 put 请求,name 属性值必须为 _method ,delete 请求同理 --%>
<input type="hidden" name="_method" value="put" />
更新:<input type="text" />
<input type="submit" value="提交" />
form>
body>
html>
再创建 accessing.jsp
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<body>
<h2>成功执行!h2>
body>
html>
最后,测试结果
1.点击 getTest 链接
跳转成功,执行 GET 请求
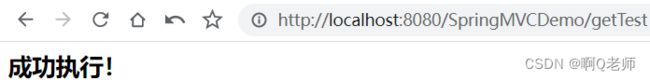
结果如图:
附
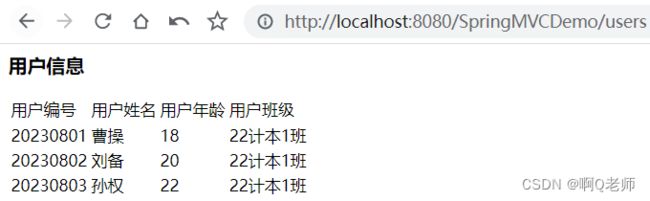
下面实现 Spring + Spring MVC + JDBCTemplate 的整合,并通过 RESTful 风格获取所有用户信息。
简单示例:
首先,在 pom.xml 中添加依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframeworkgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-txartifactId>
<version>5.3.25version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframeworkgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-aspectsartifactId>
<version>5.3.25version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframeworkgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-jdbcartifactId>
<version>5.3.25version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet.jspgroupId>
<artifactId>javax.servlet.jsp-apiartifactId>
<version>2.3.3version>
<scope>providedscope>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.mchangegroupId>
<artifactId>c3p0artifactId>
<version>0.9.5.2version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.mchangegroupId>
<artifactId>mchange-commons-javaartifactId>
<version>0.2.20version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysqlgroupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-javaartifactId>
<version>8.0.25version>
dependency>
接着,在 resources 中创建 spring 配置文件 applicationContext.xml ,并在 web.xml 中配置 contextLoaderListener 和加入 spring 配置文件
<context-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocationparam-name>
<param-value>classpath:applicationContext.xmlparam-value>
context-param>
<listener>
<listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListenerlistener-class>
listener>
然后,对 spring 配置文件 applicationContext.xml 和 springmvc 配置文件 springmvc.xml 进行配置。这里要防止两个配置文件在扫描包时有重合现象
<context:component-scan base-package="cn.edu.springmvcdemo" >
<context:exclude-filter type="annotation" expression="org.springframework.stereotype.Controller" />
<context:exclude-filter type="annotation" expression="org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ControllerAdvice" />
context:component-scan>
<context:component-scan base-package="cn.edu.springmvcdemo" use-default-filters="false">
<context:include-filter type="annotation" expression="org.springframework.stereotype.Controller" />
<context:include-filter type="annotation" expression="org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ControllerAdvice" />
context:component-scan>
注:Spring IoC 容器与 Spring MVC IoC 容器为父子关系,即全局变量和局部变量的关系
再在 resources 目录下创建 jdbc.properties ,并对 spring 配置文件 applicationContext.xml 进行连接 MySQL 数据库的基本信息的配置
jdbc.driverClass=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
jdbc.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/springmvcdemo?useSSL=false&serverTimezone=UTC
jdbc.user=root
jdbc.password=0123
acquireIncrement=5
initialPoolSize=10
minPoolSize=5
maxPoolSize=100
maxStatements=2
maxStatementsPerConnection=5
<context:property-placeholder location="classpath:jdbc.properties" />
<bean id="dataSource" class="com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource">
<property name="driverClass" value="${jdbc.driverClass}" />
<property name="jdbcUrl" value="${jdbc.url}" />
<property name="user" value="${jdbc.user}" />
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}" />
<property name="acquireIncrement" value="${acquireIncrement}" />
<property name="initialPoolSize" value="${initialPoolSize}" />
<property name="minPoolSize" value="${minPoolSize}" />
<property name="maxPoolSize" value="${maxPoolSize}" />
<property name="maxStatements" value="${maxStatements}" />
<property name="maxStatementsPerConnection" value="${maxStatementsPerConnection}" />
bean>
<bean id="jdbcTemplate" class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource" />
bean>
<bean id="namedParameterJdbcTemplate" class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.namedparam.NamedParameterJdbcTemplate">
<constructor-arg type="javax.sql.DataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
bean>
配置完成后,创建名字为 springmvcdemo 的数据库,再创建名字为 user 的数据表和表信息
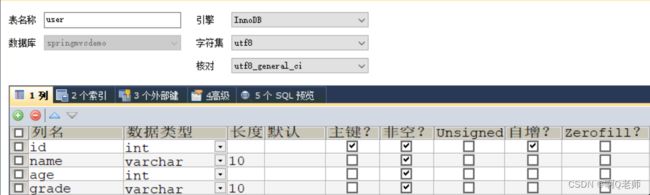

在 model 层中创建与数据表 user 一一映射的实体类 User
package cn.edu.springmvcdemo.model;
public class User {
private int id;
private String name;
private int age;
private String grade;
public User() {
super();
}
public User(int id, String name, int age, String grade) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.grade = grade;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getGrade() {
return grade;
}
public void setGrade(String grade) {
this.grade = grade;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User{" +
"id=" + id +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
", grade='" + grade + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
在 dao 层中创建接口 UserDao ,定义获取所有用户信息的方法
package cn.edu.springmvcdemo.dao;
import cn.edu.springmvcdemo.model.User;
import java.util.List;
public interface UserDao {
public List<User> selectAll();
}
同时,创建接口 UserDao 的实现类
package cn.edu.springmvcdemo.dao;
import cn.edu.springmvcdemo.model.User;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.BeanPropertyRowMapper;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.RowMapper;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
import java.util.List;
@Repository("userDao")
public class UserDaoImpl implements UserDao {
@Autowired
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
@Override
public List<User> selectAll() {
String sql = "SELECT `id`,`name`,`age`,`grade` FROM `user`;";
RowMapper<User> rowMapper = new BeanPropertyRowMapper<>(User.class);
List<User> list = jdbcTemplate.query(sql,rowMapper);
return list;
}
}
同理,在 sevice 层中创建接口 UserSevice ,定义获取所有用户信息的方法,而 UserSevice 的实现类则调用 UserDao 方法即可
在 controller 层中通过 RESTful 风格获取所有用户信息
package cn.edu.springmvcdemo.controller;
import cn.edu.springmvcdemo.model.User;
import cn.edu.springmvcdemo.service.UserService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.ui.ModelMap;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
import java.util.List;
@Controller
public class UserController {
@Autowired
private UserService userService;
@RequestMapping(value = "/users",method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String getSelectAll(ModelMap modelMap){
List<User> users = userService.selectAll();
modelMap.put("users",users);
return "user";
}
}
创建 user.jsp
<%@ taglib prefix="c" uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core" %>
<%--
Created by IntelliJ IDEA.
User: dell
Date: 2023/8/1
Time: 18:14
To change this template use File | Settings | File Templates.
--%>
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<body>
<h3>用户信息h3>
<table>
<tr>
<td>用户编号td>
<td>用户姓名td>
<td>用户年龄td>
<td>用户班级td>
tr>
<c:forEach var="user" items="${users}">
<tr>
<td>${user.id}td>
<td>${user.name}td>
<td>${user.age}td>
<td>${user.grade}td>
tr>
c:forEach>
table>
body>
html>