lodash -- 前端格式化、模块化工具库(附:防抖节流函数)
目录
-
- 一、介绍
- 二、安装和引用
- 三、常用的方法
-
- 01 判断类型
- 02 转换类型
- 03 操作数组
- 04 遍历集合
- 05 函数(防抖、节流)
一、介绍
lodash是一个JS库,一个让
javascript使用起来更简单的工具,它可以对Number,String,Object,Array等进行简单或复杂的操作,减少代码量
二、安装和引用
$ npm i -g npm
$ npm i --save lodash
- 项目中引用
const _ = require('lodash')
return (value) => {
_.isBoolean(value)
}
- 全局挂载
import lodash from "lodash";
Vue.prototype._ = lodash
三、常用的方法
01 判断类型
isNumber– 判断值是否为数字类型
_.isNumber(10); //true
_.isNumber('10'); //false
isString– 判断值是否为字符串类型
_.isString('string'); //true
_.isString(5); //false
isObject– 判断值是否为对象
_.isObject({}); //true
_.isObject([1,2,4]); //true
_.isObject(null); //false
isArray– 判断值是否为对象
_.isArray([1,2,4]); //true
_.isObject('fdsa'); //false
isUndefined– 判断值是否是undefined
_.isUndefined(void 0); //true
_.isUndefined(null); //false
isNull– 判断值是否是null
_.isNull(null); //true
_.isNull(void 0); //false
isFunction– 判断值是否是fuction
_.isFunction(_); // true
_.isFunction(/abc/); // false
02 转换类型
toArray– 转换值为数组
_.toArray({ 'a': 1, 'b': 2 }); // 返回[1, 2]
_.toArray('abc'); // 返回['a', 'b', 'c']
_.toArray(1); //[]
_.toArray(null); //[]
toInteger– 转换值为整数
_.toInteger(3.2); // 返回3
_.toInteger('3.2'); // 返回3
toString– 转换值为字符串
_.toString(3.2); // 返回'3.2'
_.toString(null); // 返回 ''
_.toString([1, 2, 3]); // 返回 '1,2,3'
03 操作数组
_.concat– 创建一个新数组,将array与任何数组或值拼接在一起。
const array = [1];
const other = _.concat(array, 2, [3], [[4]]); // 不会改变原数组
console.log(other); // 返回[1, 2, 3, [4]]
console.log(array); // 返回[1]
_.drop– 去除array前面的n个元素(n默认值为1), 返回的是一个新数组
_.drop([1, 2, 3]);// => [2, 3] n默认为1,所以去掉第一位
_.drop([1, 2, 3], 2);// => [3]
_.drop([1, 2, 3], 5);// => []
_.drop([1, 2, 3], 0);// => [1, 2, 3]
_.uniq– 获得去重后的新数组
_.uniq([2, 1, 2]); // => [2, 1];
_.reverse– 将数组的元素顺序反转,返回一个新数组
const array = [1, 2, 3];
_.reverse(array); // => [3, 2, 1]
_.pull– 移除在数组中指定的值(传参)
const array = [1, 2, 3, 1, 2, 3];
_.pull(array, 2, 3); // => [1, 1]
04 遍历集合
forEach遍历数组或对象
_.forEach(collection, [iteratee=_.identity]),collection传入的是需要遍历的数组或对象,iteratee为返回类型,提供三个参数,value,index|key,collection
遍历数组:
const arr = ['cake', 'fruit', 'rice', 'soup']
// 以下为两种写法,返回值一样
_(arr).forEach((value, index, collection) => {
console.log(value, index, collection);
});
_.forEach(arr, (value, index, collection) => {
console.log(value, index, collection);
});
// value为数组每一项的值,index是对应的索引,collection是整个数组
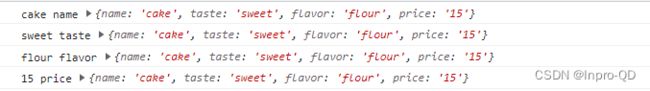
遍历对象:
const arr = {name:'cake', taste:'sweet', flavor:'flour', price:'15'}
// 以下为两种写法,返回值一样
_(arr).forEach((value, key, collection) => {
console.log(value, key, collection);
});
_.forEach(arr, (value, key, collection) => {
console.log(value, key, collection);
});
// value为对象每一属性的值,key是对应的属性名,collection是整个对象
05 函数(防抖、节流)
- 防抖函数
_.debounce(func, [wait=0], [options=])
防抖函数,通俗来讲,就是在某段时间内,不管触发多少次函数,只认最后一次,例如:淘宝搜索栏,但你打完最后一个字,才会触发搜索功能。
loadash的debounce函数接收三个参数,第一个参数是要执行的函数体,第二参数是设置的时间范围,第三参数可传入选项leading(默认为false,用来设置function是否在延迟开始之前调用) 、trailing(默认为true,用来设置function是否在延迟结束后调用)、maxWait(function允许被延迟的最大值)
这里是在Vue项目中使用的示例:
<template>
<button @click="clickBtn">防抖</button>
</template>
<script>
const _ = require('lodash')
export default {
methods: {
clickBtn:_.debounce(
// 这里最好别用箭头函数(官网给的示例为箭头函数),因为这里使用箭头函数,
// this会指向lodash方法的作用域,没法调用组件内其他函数
function () {
console.log(111)
},1000)
}
clickBtn:_.debounce(function () {
console.log(111)
}, 1000, {'leading': true,'trailing': false}
})
}
}
</script>
连续点击按钮多次,一秒之后只打印一个111
clickBtn:_.debounce(function () {
console.log(111)
}, 1000, {'leading': true,'trailing': false}
})
设置
leading为true,在点击按钮后立马打印111,且在规定时间内只打印一次
- 节流函数
_.throttle(func, [wait=0], [options=])
同理,节流函数就是在定义的一段时间内,不管触发多少次函数,只执行一次回调(只认第一次触发)。
throttle也是接收三个参数,但是第三参数options只有两个选项:leading、trailing,默认都为true
示例:
<template>
<button @click="clickBtn">节流</button>
</template>
<script>
const _ = require('lodash')
export default {
methods: {
clickBtn:_.throttle(function() {
console.log(111)
},2000)
}
}
</script>
因为
throttle的leading和trailing都默认为true,所以在第一次点击时会立即打印111,并且在设置时间内(代码为2秒),再次点击按钮,则会在两秒之后打印111。想要实现不同的节流效果,自行设置leading、trailing即可