Mybatis框架学习
什么是mybatis?
mybatis是一款用于持久层的、轻量级的半自动化ORM框架,封装了所有jdbc操作以及设置查询参数和获取结果集的操作,支持自定义sql、存储过程和高级映射
mybatis用来干什么?
用于处理java和数据库的交互
使用mybatis的好处
- 与JDBC相比,减少了50%以上的代码量。
- MyBatis灵活,不会对应用程序或者数据库的现有设计强加任何影响,SQL可以写在XML里(还可以以注解方式写到Java代码中),从程序代码中彻底分离,降低耦合度,便于统一管理和优化,可重用。
- 提供XML标签,支持编写动态SQL语句(XML中使用 if, else 等)
使用mybatis
下载Mybatis的jar包:Releases · mybatis/mybatis-3 (github.com)
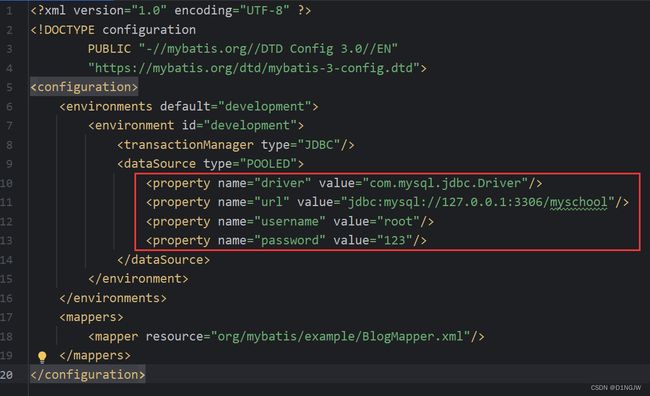
创建xml文件:mybatis-config.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE configuration
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN"
"https://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd">
<configuration>
<environments default="development">
<environment id="development">
<transactionManager type="JDBC"/>
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<property name="driver" value="${driver}"/>
<property name="url" value="${url}"/>
<property name="username" value="${username}"/>
<property name="password" value="${password}"/>
</dataSource>
</environment>
</environments>
<mappers>
<mapper resource="org/mybatis/example/BlogMapper.xml"/>
</mappers>
</configuration>
修改内容:
SqlSessionFactoryBuilder
通过SqlSessionFactoryBuilder可创建多个SqlSessionFactory实例
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(new FileInputStream("mybatis-config.xml"));
SqlSessionFactory
通过SqlSessionFactory创建多个会话,SqlSession对象,每个会话就相当于我不同的地方登陆一个账号去访问数据库。
一般SqlSessionFactory只需要创建一次
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(new FileInputStream("mybatis-config.xml"));
SqlSession
使用 MyBatis 的主要 Java 接口就是 SqlSession。你可以通过这个接口来执行命令,获取映射器实例和管理事务。SqlSession实例可直接执行已映射的sql语句。
确保SqlSession关闭的标准模式:
//try-with-resource
try(SqlSession session = sqlSessionFactory.openSession()) {
}
XML映射语句
基于XML映射语句,便可满足sqlsession的调用
例如简单的select语句
DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="TestMapper">
<select id="selectEmployee" resultType="com.test.entity.Employee">
select * from employee where id = #{id}
select>
mapper>
参数符号:#{id},这就告诉 MyBatis 创建一个预处理语句(PreparedStatement)参数,在 JDBC 中,这样的一个参数在 SQL 中会由一个?来标识,并被传递到一个新的预处理语句中.
MybatisUtil工具类
创建MybatisUtil工具类,以便集中创建SqlSession
public class MybatisUtil {
private static SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory;
static {
try {
sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(new FileInputStream("mybatis-config.xml"));
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* 获取一个新的会话
* @param autoCommit 是否开启自动提交(跟JDBC是一样的,如果不自动提交,则会变成事务操作)
* @return SqlSession对象
*/
public static SqlSession getSession(boolean autoCommit){
return sqlSessionFactory.openSession(autoCommit);
}
}
方便使用:
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws FileNotFoundException {
try(SqlSession session = MybatisUtil.getSession(true)) {
TestMapper mapper = session.getMapper(TestMapper.class);
}
}
}
映射器接口
映射器是一些用来绑定映射语句的接口。创建com.test.mapper包,创建接口TestMapper。
这样做好处是将映射器的结果快速转换为需要的实体类,通过XML中的namespace绑定接口
- 全限定名(比如 “com.test.mapper.TestMapper")将被直接用于查找及使用。
<mapper namespace="com.test.mapper.TestMapper">
<select id="selectEmployee" resultType="com.test.entity.Employee">
select * from employee
select>
mapper>
将接口与XML放在同包资源中,修改mybatis-config.xml文件
<mappers>
<mapper resource="com/test/mapper/TestMapper.xml"/>
mappers>
XML配置属性typeAliases
typeAliases,类型别名,简化Mapper的缩写
<configuration>
<typeAliases>
<typeAlias type="com.test.entity.Employee" alias="Employee"/>
typeAliases>
<environments default="development">
........
或直接扫描包,默认别名为小写的开头
<typeAliases>
<package name="com.test.entity"/>
typeAliases>
也可写注解来指定别名
@Alias("employee")
public class Employee {
...
}
ResultMap
当类中定义的字段与数据库的字段不统一时,用ResultMap来映射到对应的实体
column:数据库中的字段,property:java中编写的字段名称
<mapper namespace="com.test.mapper.TestMapper">
<resultMap id="Test" type="Employee">
<result column="id" property="xxx"/>
resultMap>
<select id="selectEmployee" resultMap="Test">
....
多个构造器如何选择
当有多个构造器,优先选择满足全部字段的构造器,如果没有则报错
![]()
如果只有一个构造器,不管满足几个字段,都会调用
那如果就是没有满足的呢?那就要用constructor
<mapper namespace="com.test.mapper.TestMapper">
<resultMap id="Test" type="Employee">
<constructor>
<arg column="id" javaType="Integer"/>
<arg column="name" javaType="String"/>
constructor>
<result column="id" property="xxx"/>
resultMap>
.......
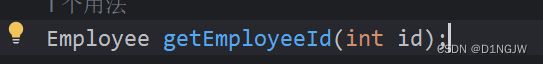
注意:这样写的话,构造器中形参需要对象类型,比如如果用int不用Interger,会报错:
![]()
另外,这样写的话构造器中的字段并不会映射到,因为映射器已经交给构造器来处理了。
bug:绑定错误
Exception in thread “main” org.apache.ibatis.binding.BindingException: Invalid bound statement (not found)
解决:select中id与接口绑定错误,记得要一致
增删改查
创建接口实例
TestMapper mapper = session.getMapper(TestMapper.class);
TestMapper.xml中编写sql语句
<mapper namespace="com.test.mapper.TestMapper">
<select id="getEmployeeId" resultType="Employee">
select * from employee where id = #{id}
select>
<insert id="addEmployee" parameterType="Employee">
insert into employee (id, name, sex, age, salary) values (#{id}, #{name}, #{sex}, #{age}, #{salary})
insert>
<delete id="deleteEmployee">
delete from employee where id = #{id}
delete>
mapper>
通过接口实例直接调用接口中的方法
update操作
mapper:
<update id="updateStudent" parameterType="student">
update student set sex = #{sex} where sid = #{sid}
update>
mapper接口:
int updateStudent(Student student);
测试:
Student student = mapper.getStudentSid(1940618805);
student.setSex("女");
mapper.updateStudent(student);
复杂查询
多表查询一对多:例如查询一个老师教多少个学生
collection:用于一对多关系,即实体里面放集合
<resultMap id="asTeacher" type="Teacher">
<id column="tid" property="tid"/>
<result column="tname" property="name"/>
<collection property="studentList" ofType="Student">
<id property="sid" column="sid"/>
<result column="name" property="name"/>
<result column="sex" property="sex"/>
collection>
resultMap>
<select id="getTeacherByTid" resultMap="asTeacher">
select *, teacher.name as tname from student inner join teach on student.sid = teach.sid
inner join teacher on teacher.tid where teach.tid = #{tid}
select>
id用于唯一标识一个老师
多表查询多对一:如果要求学生类增加一个老师属性,即根据教师id来找教师的所有学生
association:用于多对一关系
<resultMap id="test2" type="Student">
<id column="sid" property="sid"/>
<result column="name" property="name"/>
<result column="sex" property="sex"/>
<association property="teacher" javaType="Teacher">
<id column="tid" property="tid"/>
<result column="tname" property="name"/>
association>
resultMap>
<select id="selectStudent" resultMap="test2">
select *, teacher.name as tname from student left join teach on student.sid = teach.sid
left join teacher on teach.tid = teacher.tid where teach.tid = #{tid}
select>
事务处理
自动提交关闭:
SqlSession session = MybatisUtil.getSession(false)
手动提交
session.commit();
动态SQL
if
test 为if的条件,如果为真,则拼接if标签里面的and语句,如查询学号是偶数的男同学
<select id="getStudentSid" resultType="student">
select * from student where sid = #{sid}
<if test="sid % 2 == 0">
and sex = '男'
if>
select>
choose,when,otherwise
类似于switch,case,default
<select>
<choose>
<when test = "">
and...
when>
<when test = "">
and...
when>
<otherwise>
and...
otherwise>
choose>
select>
where
where元素只会在有子元素有返回的情况下才会插入where,并且如果子元素的开头是and,or,(显然sql语句中 where and…是语法错误的吧),where元素会将他们去除
select * from student
<where>
<if test="sid != null">
sid = #{sid}
if>
where>
set
<update id="updateStudent">
update student
<set>
<if test="name != null">
name = #{name}
if>
set>
where sid = #{sid}
update>
缓存机制
查询出的对象存入SqlSession的一级缓存,如果后续有相同操作,则之间从缓存中获取,不需要重新构造一个对象,提高效率
Student student = mapper.getStudentSid(1940618805);
Student student1 = mapper.getStudentSid(1940618805);
System.out.println(student1 == student); // true
但是,如果在该两次相同的操作中,对数据库内容进行了增,删,改操作,则会清除缓存
并且,每一个SqlSession会话的一级缓存是分开来的。即在不同的会话下,上述操作得到的不是同一个对象
一级缓存也叫做本地缓存,它只对一个会话的数据进行缓存。
要使用全局的缓存,是需要开启二级缓存。只需要在mapper文件中加上
<cache/>
<cache
eviction="FIFO"
flushInterval="60000"
size="512"
readOnly="true"/>
这个更高级的配置创建了一个 FIFO 缓存,每隔 60 秒刷新,最多可以存储结果对象或列表的 512 个引用,而且返回的对象被认为是只读的,因此对它们进行修改可能会在不同线程中的调用者产生冲突。
开启二级缓存后,不同会话中连续的相同操作也会直接从缓存中获取对象。(同样的,如果在这两次操作之间对数据库内容进行了增,删,改操作,则会清除缓存)
但是,多个会话时,只有当一个会话结束了才会将数据从一级缓存写入二级缓存:
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws FileNotFoundException {
try(SqlSession session1 = MybatisUtil.getSession(true);
SqlSession session2 = MybatisUtil.getSession(true)) {
TestMapper mapper1 = session1.getMapper(TestMapper.class);
TestMapper mapper2 = session2.getMapper(TestMapper.class);
Student student1 = mapper1.getStudentSid(1940618806);
Student student2 = mapper2.getStudentSid(1940618806);
System.out.println(student1 == student2); // false 获取对象时会话未结束,二级缓存没有内容
}
}
}