java中的路径
在命令行运行java时,主要有2种路径。
第一种是工作路径;另一种是类所在的路径(classpath)。
第一种也就是运行java XXX.class命令时所在的路径。此路径可通过
System.getProperty("user.dir") 来获取。而第二种可以通过类加载器获取
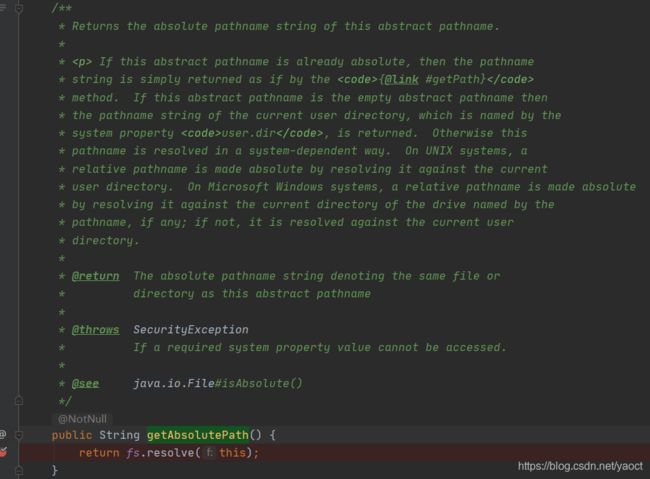
1.1 在java.io.File类中的相对路径就是基于工作路径,源码:
java.io.File#getAbsolutePath
java.io.WinNTFileSystem#resolve(java.io.File)
@Override
public String resolve(File f) {
String path = f.getPath();
int pl = f.getPrefixLength();
if ((pl == 2) && (path.charAt(0) == slash))
return path; /* UNC */
if (pl == 3)
return path; /* Absolute local */
if (pl == 0)
return getUserPath() + slashify(path); /* Completely relative */
if (pl == 1) { /* Drive-relative */
String up = getUserPath();
String ud = getDrive(up);
if (ud != null) return ud + path;
return up + path; /* User dir is a UNC path */
}
if (pl == 2) { /* Directory-relative */
String up = getUserPath();
String ud = getDrive(up);
if ((ud != null) && path.startsWith(ud))
return up + slashify(path.substring(2));
char drive = path.charAt(0);
String dir = getDriveDirectory(drive);
String np;
if (dir != null) {
/* When resolving a directory-relative path that refers to a
drive other than the current drive, insist that the caller
have read permission on the result */
String p = drive + (':' + dir + slashify(path.substring(2)));
SecurityManager security = System.getSecurityManager();
try {
if (security != null) security.checkRead(p);
} catch (SecurityException x) {
/* Don't disclose the drive's directory in the exception */
throw new SecurityException("Cannot resolve path " + path);
}
return p;
}
return drive + ":" + slashify(path.substring(2)); /* fake it */
}
throw new InternalError("Unresolvable path: " + path);
}其中当pl==0是为相对路径,pl==1是是磁盘所在根路径。getUserPath方法获取到的就是根路径
java.io.WinNTFileSystem#getUserPath
private String getUserPath() {
/* For both compatibility and security,
we must look this up every time */
return normalize(System.getProperty("user.dir"));
}1.2 springboot配置类底层也是取此相对路径
2.
另一种是类所在的路径,可以通过类加载器获取
2.1
java.lang.ClassLoader#getResource
/**
* Finds the resource with the given name. A resource is some data
* (images, audio, text, etc) that can be accessed by class code in a way
* that is independent of the location of the code.
*
* The name of a resource is a '/'-separated path name that
* identifies the resource.
*
*
This method will first search the parent class loader for the
* resource; if the parent is null the path of the class loader
* built-in to the virtual machine is searched. That failing, this method
* will invoke {@link #findResource(String)} to find the resource.
*
* @apiNote When overriding this method it is recommended that an
* implementation ensures that any delegation is consistent with the {@link
* #getResources(java.lang.String) getResources(String)} method.
*
* @param name
* The resource name
*
* @return A URL object for reading the resource, or
* null if the resource could not be found or the invoker
* doesn't have adequate privileges to get the resource.
*
* @since 1.1
*/
public URL getResource(String name) {
URL url;
if (parent != null) {
url = parent.getResource(name);
} else {
url = getBootstrapResource(name);
}
if (url == null) {
url = findResource(name);
}
return url;
}java.lang.Class#getResource 底层也是调用了类加载器的方法,但是会检测第一个字符是否为‘/’,如果无‘/’,则加上包名,源码:
/**
* Add a package name prefix if the name is not absolute Remove leading "/"
* if name is absolute
*/
private String resolveName(String name) {
if (name == null) {
return name;
}
if (!name.startsWith("/")) {
Class c = this;
while (c.isArray()) {
c = c.getComponentType();
}
String baseName = c.getName();
int index = baseName.lastIndexOf('.');
if (index != -1) {
name = baseName.substring(0, index).replace('.', '/')
+"/"+name;
}
} else {
name = name.substring(1);
}
return name;
}2.2
org.springframework.util.ResourceUtils#getFile(java.lang.String)底层如果路径以"classpath"为前缀,也是调用了类加载器的方法。源码:
/**
* Resolve the given resource location to a {@code java.io.File},
* i.e. to a file in the file system.
* Does not check whether the file actually exists; simply returns
* the File that the given location would correspond to.
* @param resourceLocation the resource location to resolve: either a
* "classpath:" pseudo URL, a "file:" URL, or a plain file path
* @return a corresponding File object
* @throws FileNotFoundException if the resource cannot be resolved to
* a file in the file system
*/
public static File getFile(String resourceLocation) throws FileNotFoundException {
Assert.notNull(resourceLocation, "Resource location must not be null");
if (resourceLocation.startsWith(CLASSPATH_URL_PREFIX)) {
String path = resourceLocation.substring(CLASSPATH_URL_PREFIX.length());
String description = "class path resource [" + path + "]";
ClassLoader cl = ClassUtils.getDefaultClassLoader();
URL url = (cl != null ? cl.getResource(path) : ClassLoader.getSystemResource(path));
if (url == null) {
throw new FileNotFoundException(description +
" cannot be resolved to absolute file path because it does not exist");
}
return getFile(url, description);
}
try {
// try URL
return getFile(new URL(resourceLocation));
}
catch (MalformedURLException ex) {
// no URL -> treat as file path
return new File(resourceLocation);
}
}
3.1 springboot 获取resources路径
String resource = "AttendanceMachineCS\\AttendanceMachineCS.exe";
ClassPathResource classPathResource = new ClassPathResource(resource);
String command= null;
try {
command = classPathResource.getURL().getPath();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}参考:彻底搞懂Class.getResource和ClassLoader.getResource的区别和底层原理_zhangshk_的博客-CSDN博客
4.1 获取jar包中的资源
Java的类加载器ClassLoader提供了两个方法,用来对ClassPath里资源读取:getResource和getResourceAsStream
getResource
public URL getResource(String name)
访问资源的访问URL。需要注意的是,在IDEA开发工具里和打包成jar包,两个路径的形式是不一样的。
IDEA开发工具结果
在IDEA开发工具里,返回的是资源所在目录的绝对路径,类似:E:\\testproject\\resource\\myres.txt。这是一个标准的文件路径。
Jar包结果
在jar包里,返回的是jar包资源专有路径格式,类似:file:/E:/testproject.jar!/resource/myres.txt,但实际上此路径在文件系统中时不存在的。所以如果如果使用此路径构建File,会导致FileNotFoundException异常。
示例:
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
String myResPath = Test.class.getResource("resources/myres.txt").getFile();
File myResFile = new File(myResPath);
FileUtils.readFileToByteArray(myResFile);
}
其中Test来自另外一个jar包。此代码就会报FileNotFoundException异常。
getResourceAsStream(正确读取jar包内容的方法)
public InputStream getResourceAsStream(String name)
此方法返回读取指定资源的输入流,即直接获得jar包中文件的内容。如果要从jar包里读取资源的内容,这个才是正确的方法。
示例:
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
InputStream is = Test.class.getResourceAsStream("/resource/myres.txt");
BufferedReader br=new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(is));
String s="";
while((s=br.readLine())!=null)
System.out.println(s);
}
参考:从jar包读取资源文件的正确方法
5.1
1.this.getClass().getResource("") 得到的是当前类class文件的URI目录。不包括自己! 如:file:/D:/workspace/jbpmtest3/bin/com/test/ 2.this.getClass().getResource("/") 得到的是当前的classpath的绝对URI路径 。 如:file:/D:/workspace/jbpmtest3/bin/ 3.this.getClass() .getClassLoader().getResource("") 得到的也是当前ClassPath的绝对URI路径 。 如:file:/D:/workspace/jbpmtest3/bin/ 4.ClassLoader.getSystemResource("") 得到的也是当前ClassPath的绝对URI路径 。 如:file:/D:/workspace/jbpmtest3/bin/ 5.Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader ().getResource("") 得到的也是当前ClassPath的绝对URI路径 。 如:file:/D:/workspace/jbpmtest3/bin/ 6.ServletActionContext.getServletContext().getRealPath(“/”) Web应用程序 中,得到Web应用程序的根目录的绝对路径。这样,我们只需要提供相对于Web应用程序根目录的路径,就可以构建出定位资源的绝对路径。 如:file:/D:/workspace/.metadata/.plugins/org.eclipse.wst.server.core/tmp0/wtpwebapps/WebProject