python excel复制数据保留单元格格式(.xls.xlsx)
最近帮朋友开发一个数据excel根据条件动态过率的功能.读取生成用pandas很方便,但是这里有一点比较麻烦的是得保留原来的单元格格式.这点操作起来就要麻烦一点了.下面总结了.xlsx和.xls处理
1.xlsx 文件处理
xlsx文件处理可以使用openpyxl库进行处理,比较简单,流程如下
1.获取原来的数据cell
2.进行value和style复制
import openpyxl
import copy
# 复制excel 保留格式
# file_path : 原文件地址
# out_file_path : 输出文件地址
# ids : 条件
def copy_xlsx(file_path,out_file_path,ids):
# 打开原表
workbook = openpyxl.load_workbook(file_path, data_only=True)
# 获取第一个sheet表
sheet = workbook.sheet_by_index(0)
# 创建一个新的 Excel 文件
new_workbook = openpyxl.Workbook()
new_sheet = new_workbook.active # 选择新工作表
# 复制数据和样式
i = 1 # openpyxl 行号从1开始
for row in sheet.iter_rows():
# todo 这里条件按需添加,可以去掉
if i ==1 or row[0].value in ids:
# 复制行
for source_cell in row:
target_cell = new_sheet.cell(row=i, column=source_cell.column,value = source_cell.value)
# 复制样式
if source_cell.has_style:
# 设置样式 得用 copy.copy() 不然会报错
target_cell._style = copy.copy(source_cell._style)
target_cell.font = copy.copy(source_cell.font)
target_cell.border = copy.copy(source_cell.border)
target_cell.fill = copy.copy(source_cell.fill)
target_cell.number_format = copy.copy(source_cell.number_format)
target_cell.protection = copy.copy(source_cell.protection)
target_cell.alignment = copy.copy(source_cell.alignment)
i += 1
# 保存新的 Excel 文件
new_workbook.save(out_file_path)
2. xls 文件处理
xls文件处理起来麻烦点,
首先得引入xlrd 只能进行读取,xlwt负责写入,xlutils相当中间人,可以简化很多操作
import xlrd
import xlwt
from xlutils.filter import process, XLRDReader, XLWTWriter
1.xlrd 获取workbook_rb, formatting_info=True 这个一定要加才能获取到格式,formatting_info模式是false是不获取格式.
2.通过 xlutils 获取到所有单元格格式
3.通过 xlwt 的 worksheet.write(i, col_num, cell.value,style) 写入value 及 style
import xlrd
import xlwt
from xlutils.filter import process, XLRDReader, XLWTWriter
# 创建 xls
def create_xls(savePath:str,ids):
# 创建一个新的 Excel 文件(写入模式)
workbook_rb = xlrd.open_workbook(path.get(),formatting_info=True) # 打开工作簿
# 这里是关键,获取所有样式列表
w = XLWTWriter()
process(XLRDReader(workbook_rb, 'unknown.xls'), w)
style_list = w.style_list
sheet = sheet = workbook.sheet_by_index(0)
new_workbook = xlwt.Workbook(encoding='utf-8')
new_worksheet = new_workbook.add_sheet('sheet1') # 添加一个新工作表,替换为你的工作表名称
# xlrd 的 index 从0开始
i=0
for row_num, row in enumerate(sheet.get_rows(), start=0):
if i ==0 or row[0].value in ids:
for col_num, cell in enumerate(row, start=0):
# 复制格式
style = style_list[cell.xf_index]
#获取当前单元格的style
new_worksheet.write(i, col_num, cell.value,style)
i+=1
new_workbook.save(savePath)
return savePath
经过测试,上述代码是可以的,但是有个小问题
w = XLWTWriter()
process(XLRDReader(workbook_rb, 'unknown.xls'), w)
style_list = w.style_list
这段代码我就想获取到style_list 但的东西有点多,这里其实是复制了一个新的workbook对象.新对象里面有原始workbook的所有信息.
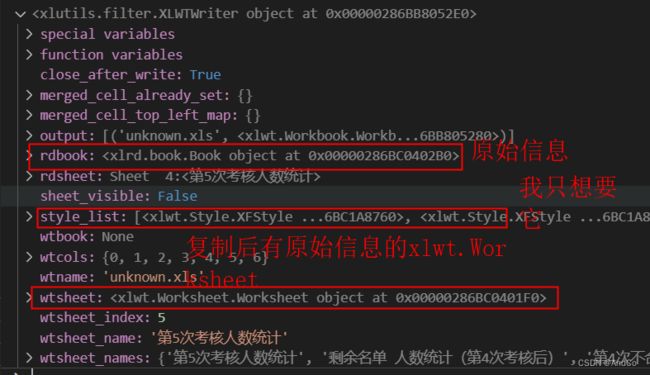
可以看到它包含的 原始 xlrd.book信息 ,xlwt.worksheet 信息(他已经将xlrd.book原始信息进行复制),style_list信息.
这个如果只是对于我们想获取style_list,那么这里信息有点太多.
因此我们能不能只获取style_list呢,我们通过XLWTWriter源码查询下style_list是如何获取的.看下能不能一探究竟.
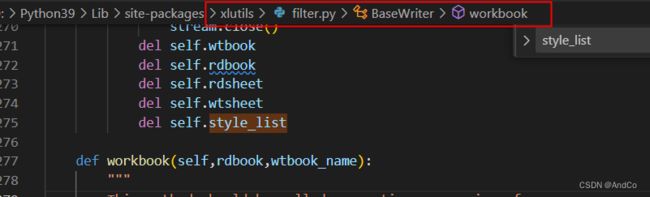
通过过w.style_list进入源码查看,我们发现在xlutils.filter.BaseWriter.workbook 进行了定义.
接着我们找下style_list是如何进行赋值的,查询下发现如下代码self.style_list.append(wtxf),这个就是赋值代码.

让我们看下它是如何实现的,核心代码就是下面这个,大致流程就是
1.创建一个 xlwt.Style.XFStyle() 对象 wtxf
2.从rdbook中获取到格式信息 rdbook.xf_list
3.对 wtxf 进行各种赋值
if not rdbook.formatting_info:
return
for rdxf in rdbook.xf_list:
wtxf = xlwt.Style.XFStyle()
#
# number format
#
wtxf.num_format_str = rdbook.format_map[rdxf.format_key].format_str
#
# font
#
wtf = wtxf.font
rdf = rdbook.font_list[rdxf.font_index]
wtf.height = rdf.height
wtf.italic = rdf.italic
wtf.struck_out = rdf.struck_out
wtf.outline = rdf.outline
wtf.shadow = rdf.outline
wtf.colour_index = rdf.colour_index
wtf.bold = rdf.bold #### This attribute is redundant, should be driven by weight
wtf._weight = rdf.weight #### Why "private"?
wtf.escapement = rdf.escapement
wtf.underline = rdf.underline_type ####
# wtf.???? = rdf.underline #### redundant attribute, set on the fly when writing
wtf.family = rdf.family
wtf.charset = rdf.character_set
wtf.name = rdf.name
#
# protection
#
wtp = wtxf.protection
rdp = rdxf.protection
wtp.cell_locked = rdp.cell_locked
wtp.formula_hidden = rdp.formula_hidden
#
# border(s) (rename ????)
#
wtb = wtxf.borders
rdb = rdxf.border
wtb.left = rdb.left_line_style
wtb.right = rdb.right_line_style
wtb.top = rdb.top_line_style
wtb.bottom = rdb.bottom_line_style
wtb.diag = rdb.diag_line_style
wtb.left_colour = rdb.left_colour_index
wtb.right_colour = rdb.right_colour_index
wtb.top_colour = rdb.top_colour_index
wtb.bottom_colour = rdb.bottom_colour_index
wtb.diag_colour = rdb.diag_colour_index
wtb.need_diag1 = rdb.diag_down
wtb.need_diag2 = rdb.diag_up
#
# background / pattern (rename???)
#
wtpat = wtxf.pattern
rdbg = rdxf.background
wtpat.pattern = rdbg.fill_pattern
wtpat.pattern_fore_colour = rdbg.pattern_colour_index
wtpat.pattern_back_colour = rdbg.background_colour_index
#
# alignment
#
wta = wtxf.alignment
rda = rdxf.alignment
wta.horz = rda.hor_align
wta.vert = rda.vert_align
wta.dire = rda.text_direction
# wta.orie # orientation doesn't occur in BIFF8! Superceded by rotation ("rota").
wta.rota = rda.rotation
wta.wrap = rda.text_wrapped
wta.shri = rda.shrink_to_fit
wta.inde = rda.indent_level
# wta.merg = ????
#
self.style_list.append(wtxf)
拿到这个代码后就简单了,我们就是照着封装一下,就是使用了.这样我们只要能够获取到rdbook (也就是xlrd获取到的book),就是获取到style_list了.无需获取到其他我们不关注的信息.
这样代码就是可以简单搞成这样,效率会提高不少,只需引入xlrd,xlwt
import xlrd
import xlwt
# 获取到表的所有单元格格式
def get_style_list(rdbook:xlrd.Book):
style_list=[]
if not rdbook.formatting_info:
return
for rdxf in rdbook.xf_list:
wtxf = xlwt.Style.XFStyle()
#
# number format
#
wtxf.num_format_str = rdbook.format_map[rdxf.format_key].format_str
#
# font
#
wtf = wtxf.font
rdf = rdbook.font_list[rdxf.font_index]
wtf.height = rdf.height
wtf.italic = rdf.italic
wtf.struck_out = rdf.struck_out
wtf.outline = rdf.outline
wtf.shadow = rdf.outline
wtf.colour_index = rdf.colour_index
wtf.bold = rdf.bold # This attribute is redundant, should be driven by weight
wtf._weight = rdf.weight # Why "private"?
wtf.escapement = rdf.escapement
wtf.underline = rdf.underline_type
# wtf.???? = rdf.underline #### redundant attribute, set on the fly when writing
wtf.family = rdf.family
wtf.charset = rdf.character_set
wtf.name = rdf.name
#
# protection
#
wtp = wtxf.protection
rdp = rdxf.protection
wtp.cell_locked = rdp.cell_locked
wtp.formula_hidden = rdp.formula_hidden
#
# border(s) (rename ????)
#
wtb = wtxf.borders
rdb = rdxf.border
wtb.left = rdb.left_line_style
wtb.right = rdb.right_line_style
wtb.top = rdb.top_line_style
wtb.bottom = rdb.bottom_line_style
wtb.diag = rdb.diag_line_style
wtb.left_colour = rdb.left_colour_index
wtb.right_colour = rdb.right_colour_index
wtb.top_colour = rdb.top_colour_index
wtb.bottom_colour = rdb.bottom_colour_index
wtb.diag_colour = rdb.diag_colour_index
wtb.need_diag1 = rdb.diag_down
wtb.need_diag2 = rdb.diag_up
#
# background / pattern (rename???)
#
wtpat = wtxf.pattern
rdbg = rdxf.background
wtpat.pattern = rdbg.fill_pattern
wtpat.pattern_fore_colour = rdbg.pattern_colour_index
wtpat.pattern_back_colour = rdbg.background_colour_index
#
# alignment
#
wta = wtxf.alignment
rda = rdxf.alignment
wta.horz = rda.hor_align
wta.vert = rda.vert_align
wta.dire = rda.text_direction
# wta.orie # orientation doesn't occur in BIFF8! Superceded by rotation ("rota").
wta.rota = rda.rotation
wta.wrap = rda.text_wrapped
wta.shri = rda.shrink_to_fit
wta.inde = rda.indent_level
# wta.merg = ????
#
style_list.append(wtxf)
return style_list
# 创建 xls
def copy_xls(file_path:str, savePath: str, ids):
# 创建一个新的 Excel 文件(写入模式)
workbook_rb = xlrd.open_workbook(file_path, formatting_info=True) # 打开工作簿
# 这里是关键,获取所有样式列表
style_list = get_style_list(workbook_rb)
# 获取第一个sheet
sheet = sheet = workbook_rb.sheet_by_index(0)
new_workbook = xlwt.Workbook(encoding='utf-8')
new_worksheet = new_workbook.add_sheet('sheet1') # 添加一个新工作表,替换为你的工作表名称
# xlrd 的 index 从0开始
i = 0
for row in sheet.get_rows():
# todo 这里条件按需添加,可以去掉
if i == 0 or row[0].value in ids:
for col_num, cell in enumerate(row, start=0):
# 复制格式
style = style_list[cell.xf_index]
# 获取当前单元格的style
new_worksheet.write(i, col_num, cell.value, style)
i += 1
new_workbook.save(savePath)
return savePath
参考:
https://www.cnblogs.com/KeenLeung/p/14101049.html
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_39804265/article/details/105127786
