基于哈希表对unordered_map和unordered_set的封装
本章完整代码gitee仓库:对unordered_map和unordered_set的封装、unordered_map和unordered_set源码
文章目录
- 1. 哈希表的改造
- 1.1 模板参数的改造
- 1.2 增加迭代器
- 1.3 返回值的修改
- 2. 对unordered_set的封装
- 3. 对unordered_map的封装
- 4. 关于哈希表的长度
1. 哈希表的改造
unordered_map和unordered_set底层都是哈希表的开散列方式。
我们还是像封装map和set类似,先对哈希表改造一下
1.1 模板参数的改造
K:关键码类型T:对于unordered_map,T,就是有个键值对;对于unordered_set,T就是KKeyOfT:取出元素(主要是为了unordered_map设计)HashFunc:仿函数,将key转换成整数,才能进行取模
template<class K,class T,class KeyOfT,class HashFunc = DefaultHashFunc<K>>
class HashTable
{}
1.2 增加迭代器
多增了Ptr和Ref两个模板参数,用来控制是普通迭代器还是const迭代器
//前置声明
template<class K, class T, class KeyOfT, class HashFunc>
class HashTable;
template<class K, class T, class Ptr, class Ref, class KeyOfT, class HashFunc>
struct HTIterator
{
typedef HashNode<T> Node;
typedef HTIterator<K, T, Ptr, Ref, KeyOfT, HashFunc> Self;
//参考list迭代器
typedef HTIterator<K, T, T*, T&, KeyOfT, HashFunc> Iterator;
Node* _node;
//迭代器里面并不用修改哈希表内容,直接设置为const
const HashTable<K, T, KeyOfT, HashFunc>* _pht;
HTIterator(Node* node, const HashTable<K, T, KeyOfT, HashFunc>* pht)
:_node(node)
,_pht(pht)
{}
//通过迭代器为拷贝构造
//const迭代器为构造
HTIterator(const Iterator&it)
:_node(it._node)
, _pht(it._pht)
{}
Ref operator*()
{
return _node->_data;
}
Ptr operator->()
{
return &_node->_data;
}
Self& operator++()
{
if (_node->_next)
{
_node = _node->_next;
}
else
{
HashFunc hf;
KeyOfT kot;
//当前位置
size_t hashi = hf(kot(_node->_data)) % _pht->_table.size();
//下一个位置
++hashi;
//找到不为空的桶
while (hashi < _pht->_table.size())
{
if (_pht->_table[hashi])
{
_node = _pht->_table[hashi];
return *this;
}
else
{
++hashi;
}
}
_node = nullptr;
}
return *this;
}
bool operator!=(const Self& s)
{
return _node != s._node;
}
};
1.3 返回值的修改
Insert:
在哈希表里面,我们插入操作的返回值是bool类型,如果要进行封装,我们需要返回指向元素的迭代器(因为unordered_map还要支持[])
pair<iterator,bool> Insert(const T& data)
{
KeyOfT kot;
iterator ret = Find(kot(data));
if (ret!=end())
return make_pair(ret,false);
HashFunc hf;
//扩容 -- 扩容的时候会稍微慢一点 ---^(扩容)-----^(扩容)----------^(扩容)-----.....
//这里的扩容不能和开放定址法一样采用将旧表元素重新插入新表
//因为这里涉及到开节点,新表开新节点,旧表释放旧节点,浪费
if (_n == _table.size())
{
size_t newSize = _table.size() * 2;
vector<Node*> newTable;
newTable.resize(newSize,nullptr);
//遍历旧表,将节点牵过来
for (size_t i = 0; i < _table.size(); i++)
{
Node* cur = _table[i];
while (cur)
{
Node* next = cur->_next;
//头插到新表
size_t newHashi = hf(kot(cur->_data)) % newSize;
cur->_next = newTable[newHashi];
newTable[newHashi] = cur;
cur = next;
}
_table[i] = nullptr;
}
_table.swap(newTable);
}
size_t hashi = hf(kot(data)) % _table.size();
//头插
Node* newNode = new Node(data);
newNode->_next = _table[hashi];
_table[hashi] = newNode;
++_n;
return make_pair(iterator(newNode, this), true);
}
Find:
Find操作原先是返回一个节点,现在返回的是迭代器
iterator Find(const K& key)
{
HashFunc hf;
KeyOfT kot;
size_t hashi = hf(key) % _table.size();
Node* cur = _table[hashi];
while (cur)
{
if (kot(cur->_data) == key)
{
return iterator(cur, this);
}
cur = cur->_next;
}
return end();
}
2. 对unordered_set的封装
unordered_set的key是是不允许的修改的,所以迭代器都是底层都是const_iterator
namespace my_UnorderedSet
{
template<class K>
class unordered_set
{
struct SetKeyOfT
{
const K& operator()(const K& key)
{
return key;
}
};
public:
typedef typename hash_bucket::HashTable<K, K, SetKeyOfT>::const_iterator iterator;
typedef typename hash_bucket::HashTable<K, K, SetKeyOfT>::const_iterator const_iterator;
iterator begin() const
{
return _ht.begin();
}
iterator end() const
{
return _ht.end();
}
pair<iterator, bool> insert(const K& key)
{
//强转
//return _ht.Insert(key);
//稳定写法
pair<typename hash_bucket::HashTable<K, K, SetKeyOfT>::iterator, bool> ret = _ht.Insert(key);
return pair<iterator, bool>(ret.first, ret.second);
}
iterator find(const K& key)
{
return _ht.Find(key);
}
bool erase(const K& key)
{
return _ht.Erase(key);
}
private:
hash_bucket::HashTable<K, K,SetKeyOfT> _ht;
};
}
3. 对unordered_map的封装
unordered_map的key也是不允许修改的,通过控制pair里面的key值,来禁止对key值的修改(const限制)
namespace my_UnorderedMap
{
template<class K,class V>
class unordered_map
{
struct MapKeyOfT
{
const K& operator()(const pair<const K, V>& kv)
{
return kv.first;
}
};
public:
typedef typename hash_bucket::HashTable<K, pair<const K,V>, MapKeyOfT>::iterator iterator;
typedef typename hash_bucket::HashTable<K, pair<const K,V>, MapKeyOfT>::const_iterator const_iterator;
iterator begin()
{
return _ht.begin();
}
iterator end()
{
return _ht.end();
}
const_iterator begin() const
{
return _ht.begin();
}
const_iterator end() const
{
return _ht.end();
}
pair<iterator, bool> insert(const pair<K,V>& kv)
{
return _ht.Insert(kv);
}
V& operator[](const K& key)
{
pair<iterator, bool> ret = _ht.Insert(make_pair(key, V()));
return ret.first->second;
}
iterator find(const K& key)
{
return _ht.Find(key);
}
bool erase(const K& key)
{
return _ht.Erase(key);
}
private:
hash_bucket::HashTable<K, pair<const K, V>, MapKeyOfT> _ht;
};
}
4. 关于哈希表的长度
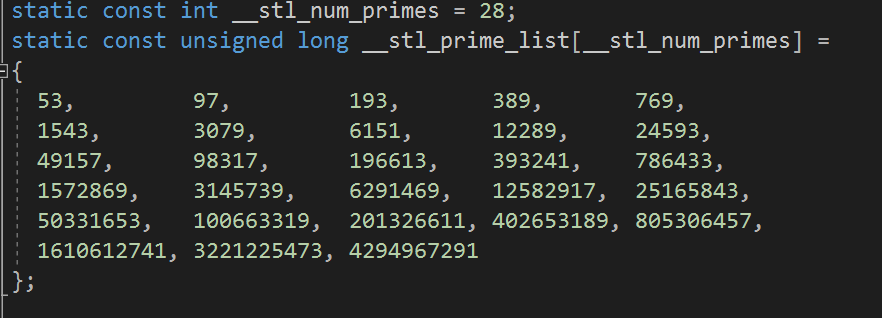
有人提出来过,哈希表的长度最好是用素数,SGI库里面就采用的这种方式,提前准备好一份质数表,要扩容的时候,就扩到二倍附近的那个质数
我们也可以放一份质数表到我们的哈希表里面
//质数表
size_t GetNextPrime(size_t prime)
{
const int PRIMECOUNT = 28;
static const size_t primeList[PRIMECOUNT] =
{
53ul, 97ul, 193ul, 389ul, 769ul,
1543ul, 3079ul, 6151ul, 12289ul, 24593ul,
49157ul, 98317ul, 196613ul, 393241ul, 786433ul,
1572869ul, 3145739ul, 6291469ul, 12582917ul,
25165843ul,
50331653ul, 100663319ul, 201326611ul, 402653189ul,
805306457ul,
1610612741ul, 3221225473ul, 4294967291ul
};
size_t i = 0;
for (; i < PRIMECOUNT; ++i)
{
if (primeList[i] > prime)
return primeList[i];
}
return primeList[i];
}
然后初始化的时候,我们就用这个质数表提供的长度
HashTable()
{
_table.resize(GetNextPrime(1), nullptr);
}
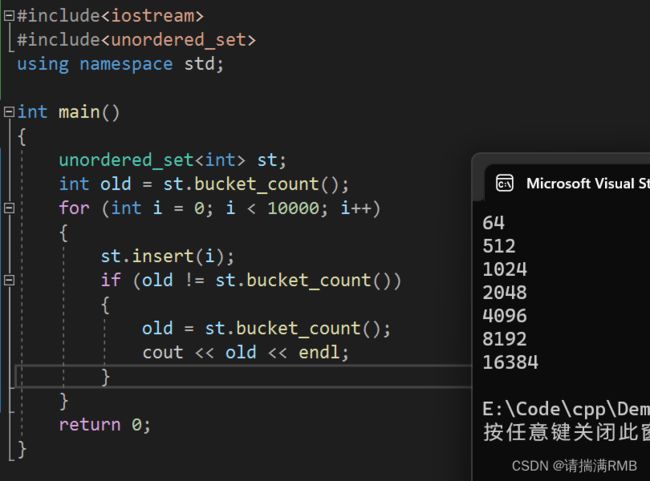
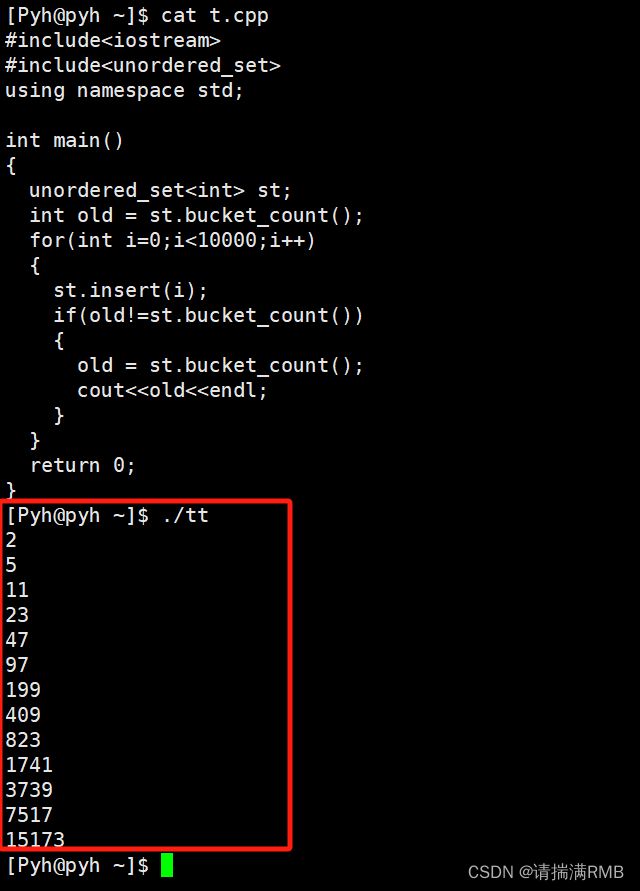
当然了,这个也没有具体的数据作为支撑,VS2022并没有采用这种方式,g++采用的是这种方式,具体采用哪种方式,看自己的喜好
VS2022:
g++:
那么本次分享就到这里,我们下期再见,如果还有下期的话