C++:unordered_map/unordered_set
"只有我,守着安静的沙漠。等待着花开。"
(一)unorderd系列容器;
(1)来源;
准确来说unordered系列关联式容器,是在C++ 11出来的。因为在C++98中引入了以红黑树为底层的map/set,但是当树的高度足够高,节点足够多时,查询的效率是不理想的。
本文中只对unordered_map和unordered_set进行介绍
unordered_multimap和unordered_multiset 和 multimap/multiset 异曲同工
(2)文档说明;
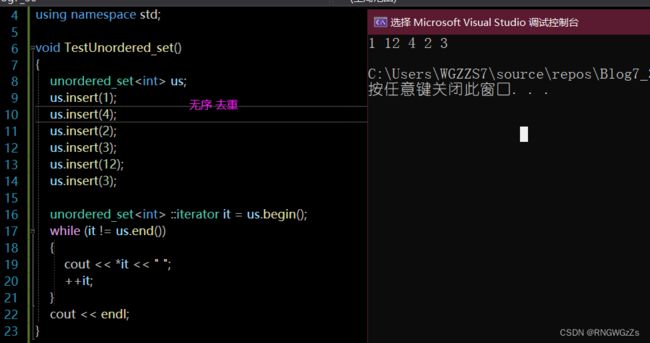
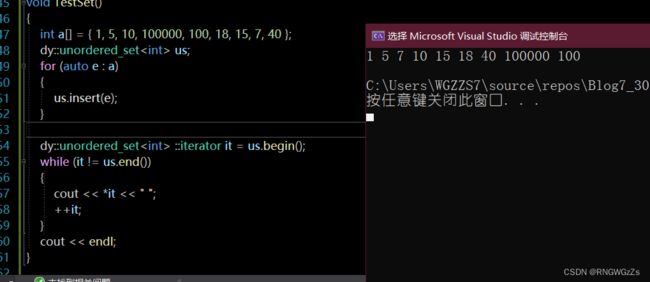
unordered_set;
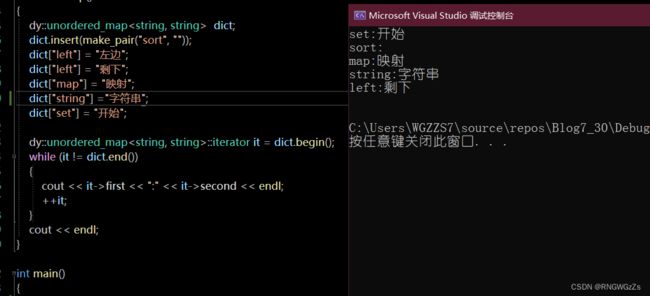
unordered_map;
(二)关联式容器模拟实现;
unorderd 系列 底层封装的 哈希结构;
(1)结构
template
class unordered_set
{
public:
struct SetOFT
{
K& operator()(const K& key)
{
return key;
}
};
private:
OpenHash::HashBuckets _us;
};
template
class unordered_map
{
public:
struct MapOFT
{
K& operator()(const pair& kv)
{
return kv.first;
}
};
private:
OpenHash::HashBuckets,MapOFT> _um;
}; 插入部分也要相应更改;
(2) 迭代器;
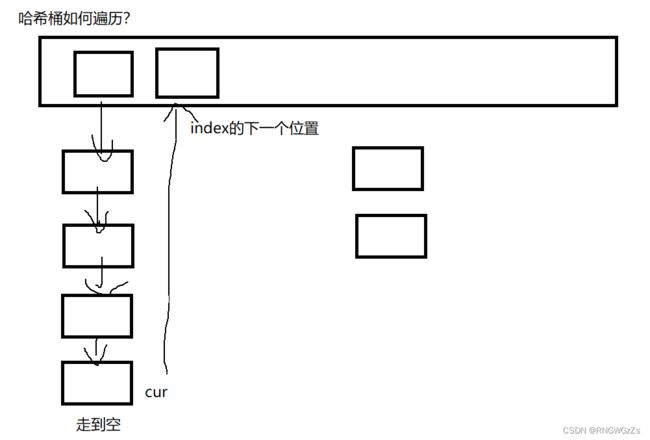
哈希并没有提供 双向 迭代器。因为其底层本身就是实现的是单链表。
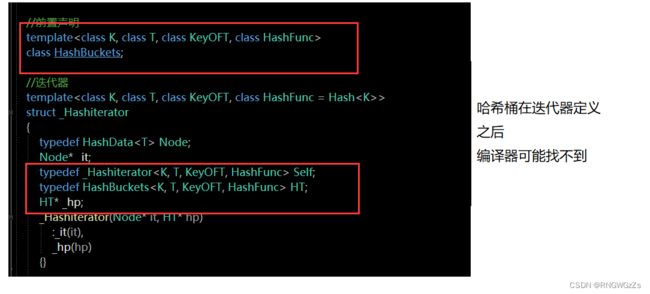
注意的坑;
template>
struct _Hashiterator
{
typedef HashData Node;
Node* _node;
typedef _Hashiterator Self;
typedef HashBuckets HT;
HT* _hp;
_Hashiterator(Node* node, HT* hp)
:_node(node),
_hp(hp)
{}
T& operator*()
{
return _node->_data;
}
T* operator->()
{
return &_node->_data;
}
Self& operator++()
{
if (_node->_next)
{
//这里说明 同一块区域的 节点还没走完
_node = _node->_next;
}
else
{
//需要换节点
//找到当前 index
size_t index = HashFunc()(KeyOFT()(_node->_data)) % _hp->_table.size();
++index;
//index 完就结束
while (index < _hp->_table.size())
{
if (_hp->_table[index])
{
//不为空 就说明 下面挂了节点
_node = _hp->_table[index];
return *this;
}
else
{
++index;
}
}
//说明已经没有节点了
_node = nullptr;
}
return *this;
}
bool operator !=(const Self& s)
{
return _node != s._node;
}
bool operator ==(const Self& s)
{
return _node == s._node;
}
};
①迭代器封装;
iterator begin()
{
size_t i = 0;
while (i < _table.size())
{
if (_table[i])
{
//this 可以作为 迭代器的哈希表传过去!
return iterator(_table[i], this);
}
++i;
}
return end();
}
iterator end()
{
return iterator(nullptr,this);
}
(3)插入+[];
①unordered_map
template
class unordered_map
{
struct MapOFT
{
K& operator()(const pair& kv)
{
return kv.first;
}
};
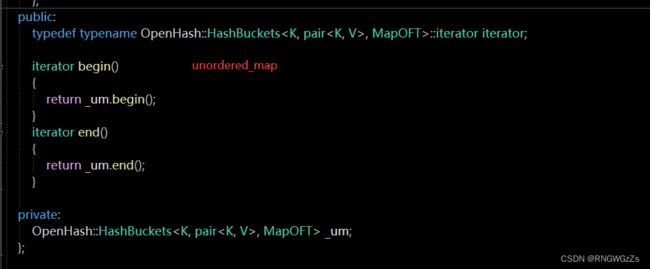
public:
typedef typename OpenHash::HashBuckets, MapOFT>::iterator iterator;
iterator begin()
{
return _um.begin();
}
iterator end()
{
return _um.end();
}
pair insert(const pair& kv)
{
return _um.insert(kv);
}
V& operator[](const K& key)
{
pair* ret = _um.insert(make_pair(key, V()));
return ret->first.second;
}
private:
OpenHash::HashBuckets, MapOFT> _um;
};
②unordered_set;
template
class unordered_set
{
struct SetOFT
{
K& operator()(const K& key)
{
return key;
}
};
public:
typedef typename OpenHash::HashBuckets::iterator iterator;
iterator begin()
{
return _us.begin();
}
iterator end()
{
return _us.end();
}
pair insert(const K& key)
{
return _us.insert(key);
}
private:
OpenHash::HashBuckets _us;
}; ③HashBuckets;
pair insert(const T& data)
{
HashFunc hf;
KeyOFT kot;
Node* ret = find(kot(data));
if (ret)
{
return make_pair(iterator(ret,this), false);
}
//哈希桶同样也需要 扩容
//当负载因子 为 1 到时候扩容
if (_n == _table.size())
{
vector NTable;
// NTable._table.resize(_table.size() * 2);
NTable.resize(GetNextPrime(_table.size()));
// 这里不是拷贝赋值 而是让旧表里的指针
//链接进新表
for (int i = 0; i < _table.size() ; i++)
{
if (_table[i])
{
//旧表节点
Node* cur = _table[i];
while (cur)
{
//记录 cur 的下一个 因为 头插 会改变cur->next
Node* next = cur->_next;
//重新计算映射位置
size_t index = hf(kot(data)) % NTable.size();
//头插
cur->_next = NTable[index];
NTable[index] = cur;
cur = next;
}
_table[i] = nullptr;
}
}
_table.swap(NTable);
}
//插入 哪个位置
size_t index = hf(kot(data)) % _table.size();
//去构建 一个节点nenode 以备插入
Node* newnode = new Node(data);
//插入选择头插 因为效率高
newnode->_next = _table[index];
_table[index] = newnode;
++_n;
return make_pair(iterator(newnode,this),true);
} unordered_set
unordered_map;
(4)成员函数;
//构造
HashBuckets() = default;//显示指定生成 默认构造
HashBuckets(const HashBuckets& HB)
{
_n = HB._n;
_table.resize(HB._table.size());
for (size_t i = 0;i < _table.size();++i)
{
Node* cur = HB._table[i];
while (cur)
{
Node* copy = new Node(cur->_data);
//再头插
copy->_next = _table[i];
_table[i] = copy;
cur = cur->_next;
}
}
}
//赋值
HashBuckets& operator=(HashBuckets hb)
{
_table.swap(hb._table);
swap(_n, hb._hp);
return *this;
}
本篇就到此为止,谢谢你的阅读
祝你好运~