STM32F4X UCOSIII 消息队列
STM32F4X UCOSIII 消息队列
- 消息队列
-
- 消息队列的作用
- 消息队列工作机制
- 消息队列创建
- 消息发送
- 消息发送模式
-
- FIFO(先进先出)
- LIFO(后进先出)
- 消息接收
- 消息队列删除
- 消息队列常用函数
-
- 消息队列创建函数
- 消息队列发送函数
- 消息队列接收函数
- 消息队列删除函数
- UCOSIII 消息队列例程
消息队列
消息队列的作用
消息队列是一种常用于任务间通信的数据结构,用户可以自定义传输的消息结构。消息队列可以在任务与任务之间,中断与任务之间进行传输。。消息发送方需要把发送消息的数据指针传递给消息队列,接收方就通过消息队列获取数据。
消息队列工作机制
消息队列创建
消息队列在创建时,需要用户自定义消息队列可存放的数据个数,当消息队列创建成功时,消息队列的数据存放个数就不能改变。
消息发送
中断和任务都可以往消息队列里面发送消息,在消息发送之前,消息列队会先判断当前的消息队列列表里面是否已经满,当消息队列还没满的时候,会把要发送的数据放到消息队列的消息列表中,如果当前消息队列的列表已经满,则会返回一个错误代码,同时入队失败。
消息发送模式
UCOSIII的消息队列有两种入队模式,分别是FIFO(先进先出)模式和LIFO(后进先出)模式
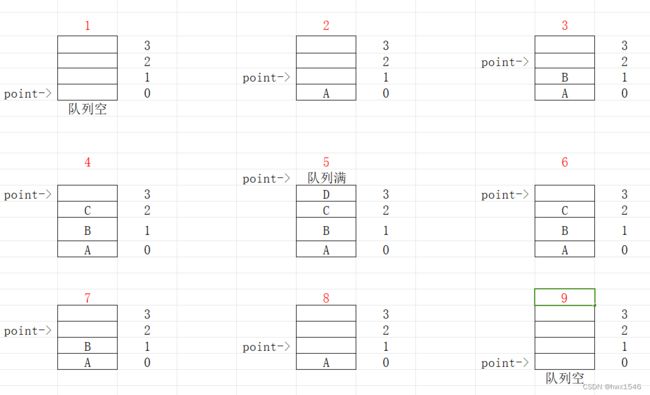
FIFO(先进先出)
- 1:定义了4个数据的队列,此时队列为空,队列指针指向队列底部
- 2:插入数据A,队列指针向上加1
- 3:插入数据B,队列指针向上加1
- 4:插入数据C,队列指针向上加1
- 5:插入数据D,此时队列已经满,不能再插入新数据
- 6:数据D出队,队列指针向下减1
- 7:数据C出队,队列指针向下减1
- 8:数据B出队,队列指针向下减1
- 9:数据A出队,此时队列为空
从上图可以知道,FIFO的数据特点就是先进来的数据先出去,后进来的数据后出去。
LIFO(后进先出)
- 1:定义了4个数据的队列,此时队列为空,队列指针指向队列顶部
- 2:插入数据A,队列指针向下减1
- 3:插入数据B,队列指针向下减1
- 4:插入数据C,队列指针向下减1
- 5:插入数据D,此时队列已经满,不能再插入新数据
- 6:数据D出队,队列指针向上加1
- 7:数据C出队,队列指针向上加1
- 8:数据B出队,队列指针向上加1
- 9:数据A出队,此时队列为空
- 从上图可以知道,LIFO的数据特点跟FIFO正好相反,LIFO是先进来的数据最后出去,后进来的数据最先出去。
消息接收
UCOSIII的消息接收也有两种模式,分别阻塞接收和超时接收模式
- 阻塞接收模式:当消息队列中没有数据的时候,接收数据的任务进入阻塞状态,除非消息队列中有消息,否则阻塞的任务不会退出。
- 超时接收:接收数据的任务可以设置超时时间,当消息队列中没有数据的时候,接收数据的任务进入阻塞状态,如果阻塞时间超过了设置的超时时间,阻塞的任务会主动退出,并返回一个接收错误的标志位。
消息队列删除
当消息队列不再使用时,可以调用消息队列删除函数,删除消息队列,此时消息队列中的所有数据都会删除,删除后的消息队列不能再次使用。
消息队列删除也有两种方式,分别是立刻删除和等待没有任务挂起删除
- 立刻删除:不管有没有任务在等待消息队列,都立刻删除
- 等待没有任务挂起删除:如果有任务在等待消息队列数据,暂时不删除消息队列,直到没有任务等待再删除
消息队列常用函数
消息队列创建函数
/*
p_q:消息队列指针
p_name:消息队列名字
max_qty:接收的最大消息个数
p_err:错误代码
*/
void OSQCreate (OS_Q *p_q,
CPU_CHAR *p_name,
OS_MSG_QTY max_qty,
OS_ERR *p_err)
消息队列发送函数
/*
p_q:消息队列指针
p_void:发送的消息的指针
msg_size:发送的消息的大小
opt:用户选项
p_err:错误代码
*/
void OSQPost (OS_Q *p_q,
void *p_void,
OS_MSG_SIZE msg_size,
OS_OPT opt,
OS_ERR *p_err)
消息队列接收函数
/*
p_q:消息队列指针
timeout:超时时间
opt:用户选项
p_msg_size:接收到的消息的大小
p_ts:时间戳
p_err:错误代码
返回值:成功则返回获取到的消息指针,错误则返回0
*/
void *OSQPend (OS_Q *p_q,
OS_TICK timeout,
OS_OPT opt,
OS_MSG_SIZE *p_msg_size,
CPU_TS *p_ts,
OS_ERR *p_err)
消息队列删除函数
/*
p_q:消息队列指针
opt:用户选项
p_err:错误代码
*/
OS_OBJ_QTY OSQDel (OS_Q *p_q,
OS_OPT opt,
OS_ERR *p_err)
UCOSIII 消息队列例程
在例程中,任务1会每个500ms发送一次消息,任务2则会阻塞等待消息
/*
*********************************************************************************************************
* EXAMPLE CODE
*
* (c) Copyright 2013; Micrium, Inc.; Weston, FL
*
* All rights reserved. Protected by international copyright laws.
* Knowledge of the source code may not be used to write a similar
* product. This file may only be used in accordance with a license
* and should not be redistributed in any way.
*********************************************************************************************************
*/
/*
*********************************************************************************************************
*
* EXAMPLE CODE
*
* IAR Development Kits
* on the
*
* STM32F429II-SK KICKSTART KIT
*
* Filename : app.c
* Version : V1.00
* Programmer(s) : YS
*********************************************************************************************************
*/
/*
*********************************************************************************************************
* INCLUDE FILES
*********************************************************************************************************
*/
#include