【数据结构】Java实现常用数据结构
【数据结构】Java算法基础
一、前言
KMP算法
汉诺塔
八皇后(分治算法)
马踏棋盘算法(骑士周游问题)图的深度优先算法+贪心算法优化
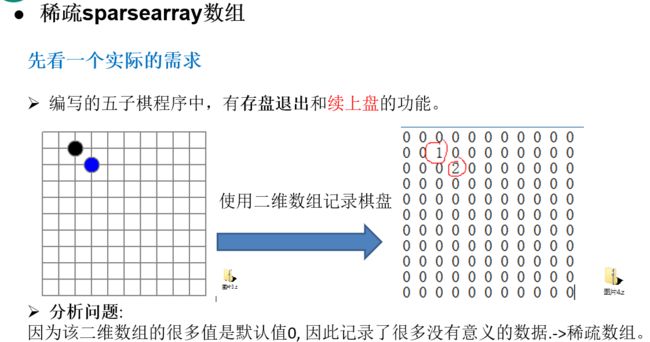
第一章、稀疏数组和队列
1.1 稀疏数组
基本介绍
当一个数组中大部分元素为0,或者为同一个值的数组时,可以使用稀疏数组来保存该数组。
稀疏数组的处理方法是:
-
记录数组一共有几行几列,有多少个有效值
-
把具有不同值的有效元素的行列及值记录在一个小规模的数组中,从而缩小程序的规模

package zy.code.sparsearray;
/**
* 稀疏数组
*/
public class SparseArray {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建一个原始二维数组
// 11 *11 的棋盘大小,1表示黑棋子,2表示蓝棋子
int chessArr[][] = new int[11][11];
chessArr[1][2] = 1;
chessArr[2][3] = 2;
chessArr[4][5] = 2;
for (int[] row : chessArr){
for (int data : row){
System.out.printf("%d\t",data);
}
System.out.println();;
}
//计算有效值
int val = 0;
for (int i=0; i<11;i++){
for (int j=0;j<11;j++){
if (chessArr[i][j] != 0){
val++;
}
}
}
System.out.printf("原来二维有效值有 %d 个\n",val);
/**
* 二维数组 转 稀疏数组的思路
* 1. 遍历 原始的二维数组,得到有效数据的个数 sum
* 2. 根据sum 就可以创建 稀疏数组 sparseArr int[sum + 1] [3]。加一是因为第一列放的是原二维数组有几行几列、几个有效值。
* 3. 将二维数组的有效数据数据存入到 稀疏数组
*/
//创建稀疏数组
int spareArr[][] = new int[val+1][3];
spareArr[0][0] = 11;
spareArr[0][1] = 11;
spareArr[0][2] = val;
//定义一个稀疏数组的行计数器
int spare_row = 0;
for (int i = 0; i<11; i++){
for (int j = 0; j <11; j++){
if (chessArr[i][j] != 0){
spare_row++;
spareArr[spare_row][0] = i;
spareArr[spare_row][1] = j;
spareArr[spare_row][2] = chessArr[i][j];
}
}
}
// 遍历稀疏数组
System.out.println("转换后的稀疏数组为:");
for (int i = 0; i < spareArr.length; i ++){
System.out.printf("%d\t%d\t%d\t\n",spareArr[i][0],spareArr[i][1],spareArr[i][2]);
}
System.out.println();
/**
* 稀疏数组 转 原始的二维数组的思路
*
* 1. 先读取稀疏数组的第一行,根据第一行的数据,创建原始的二维数组大小,比如上面的 chessArr2 = int [11][11]
* 2. 在读取稀疏数组后几行的数据,并赋给 原始的二维数组 即可.
*/
int row_count = spareArr[0][0];
int column_count = spareArr[0][1];
int chessArr_val = spareArr[0][2];
//创建原数组大小
int chessArr2[][] = new int[row_count][column_count];
//遍历稀疏数组并赋值
for (int i = 1; i<= chessArr_val; i ++){
int r = spareArr[i][0];
int c = spareArr[i][1];
int v = spareArr[i][2];
chessArr2[r][c] = v;
}
//输出还原数组
System.out.println("原来的二维数组为:");
for (int[] row : chessArr2){
for (int data : row){
System.out.printf("%d\t",data);
}
System.out.println();;
}
}
}
作业:
- 抽取出普通二维数组与稀疏数组的转换,封装成工具类
- 使用 I/O 流基础,序列化对象保存到磁盘文件中
/**
* 抽取普通二维数组与稀疏数组的转换。封装成工具方法
*/
public class SpareArryUtil {
/**
* 普通二维数组转换为稀疏数组
*/
public static int[][] arrayTYoSpare(int[][] chessArr){
//计算有效值
int val = 0;
for (int i=0; i<11;i++){
for (int j=0;j<11;j++){
if (chessArr[i][j] != 0){
val++;
}
}
}
//创建稀疏数组
int spareArr[][] = new int[val+1][3];
spareArr[0][0] = 11;
spareArr[0][1] = 11;
spareArr[0][2] = val;
//定义一个稀疏数组的行计数器
int spare_row = 0;
for (int i = 0; i<11; i++){
for (int j = 0; j <11; j++){
if (chessArr[i][j] != 0){
spare_row++;
spareArr[spare_row][0] = i;
spareArr[spare_row][1] = j;
spareArr[spare_row][2] = chessArr[i][j];
}
}
}
return spareArr;
}
/**
* 稀疏数组还原回普通二维数组
*/
public static int[][] spareToArray(int[][] spareArr){
int row_count = spareArr[0][0];
int column_count = spareArr[0][1];
int chessArr_val = spareArr[0][2];
//创建原数组大小
int chessArr2[][] = new int[row_count][column_count];
//遍历稀疏数组并赋值
for (int i = 1; i<= chessArr_val; i ++){
int r = spareArr[i][0];
int c = spareArr[i][1];
int v = spareArr[i][2];
chessArr2[r][c] = v;
}
return chessArr2;
}
}
/**
* 将对象序列化到磁盘文件
*/
public class SerializeObjToFile {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("G:\\test\\data\\spareArr.data"));
int chessArr[][] = new int[11][11];
chessArr[1][2] = 1;
chessArr[2][3] = 2;
chessArr[4][5] = 2;
int[][] spareArr = SpareArryUtil.arrayTYoSpare(chessArr);
int[][] chessArr2 = SpareArryUtil.spareToArray(spareArr);
/**
* 序列化对象到磁盘
*/
oos.writeObject(spareArr);
oos.flush();
oos.close();
}
}
1.2 数组模拟队列
(1)队列的数据结构:
当我们将数据存入队列时称为 ”addQueue”,addQueue 的处理需要有两个步骤:
-
尾指针后移:rear = rear+1 , 当 front == rear 【空】
-
判断尾指针 rear 小于数组队列的最大下标 [ maxSize - 1 ],则将数据存入 rear所指的数组元素中,否则无法存入数据。
注意:
-
rear == maxSize - 1; [ 队列满 ]
-
rear 是队列最后 [含]
-
front 是队列最前元素 [不含]
-
class ArrayQueue(arrMaxSize: Int) {
val maxSize: Int = arrMaxSize //队列的最大容量,等于数组的最大容量
val array = new Array[Int](arrMaxSize) //数组的最大容量
var front: Int = -1 //队首初始值
var rear: Int = -1 //队尾初始值
}
//初始化队列
val queue = new ArrayQueue(3)
代码实现:
public class ArrayQueueDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//测试一把
//创建一个队列
ArrayQueue queue = new ArrayQueue(3);
char key = ' '; //接收用户输入
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);//
boolean loop = true;
//输出一个菜单
while(loop) {
System.out.println("s(show): 显示队列");
System.out.println("e(exit): 退出程序");
System.out.println("a(add): 添加数据到队列");
System.out.println("g(get): 从队列取出数据");
System.out.println("h(head): 查看队列头的数据");
key = scanner.next().charAt(0);//接收一个字符
switch (key) {
case 's':
queue.showQueue();
break;
case 'a':
System.out.println("输出一个数");
int value = scanner.nextInt();
queue.addQueue(value);
break;
case 'g': //取出数据
try {
int res = queue.getQueue();
System.out.printf("取出的数据是%d\n", res);
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO: handle exception
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
break;
case 'h': //查看队列头的数据
try {
int res = queue.headQueue();
System.out.printf("队列头的数据是%d\n", res);
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO: handle exception
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
break;
case 'e': //退出
scanner.close();
loop = false;
break;
default:
break;
}
}
System.out.println("程序退出~~");
}
}
// 使用数组模拟队列-编写一个ArrayQueue类
class ArrayQueue {
private int maxSize; // 表示数组的最大容量
private int front; // 队列头
private int rear; // 队列尾
private int[] arr; // 该数据用于存放数据, 模拟队列
// 创建队列的构造器
public ArrayQueue(int arrMaxSize) {
maxSize = arrMaxSize;
arr = new int[maxSize];
front = -1; // 指向队列头部,分析出front是指向队列头的前一个位置.
rear = -1; // 指向队列尾,指向队列尾的数据(即就是队列最后一个数据)
}
// 判断队列是否满
public boolean isFull() {
return rear == maxSize - 1;
}
// 判断队列是否为空
public boolean isEmpty() {
return rear == front;
}
// 添加数据到队列
public void addQueue(int n) {
// 判断队列是否满
if (isFull()) {
System.out.println("队列满,不能加入数据~");
return;
}
rear++; // 让rear 后移
arr[rear] = n;
}
// 获取队列的数据, 出队列
public int getQueue() {
// 判断队列是否空
if (isEmpty()) {
// 通过抛出异常
throw new RuntimeException("队列空,不能取数据");
}
front++; // front后移
return arr[front];
}
// 显示队列的所有数据
public void showQueue() {
// 遍历
if (isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("队列空的,没有数据~~");
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
System.out.printf("arr[%d]=%d\n", i, arr[i]);
}
}
// 显示队列的头数据, 注意不是取出数据
public int headQueue() {
// 判断
if (isEmpty()) {
throw new RuntimeException("队列空的,没有数据~~");
}
return arr[front + 1];
}
}
数组模拟队列的问题:
- 假溢出

1.3 循环队列
优化思路如下:
- front 变量的含义做一个调整: front 就指向队列的第一个元素, 也就是说 arr[front] 就是队列的第一个元素
- front 的初始值 = 0
- rear 变量的含义做一个调整:rear 指向队列的
最后一个元素的后一个位置. 因为希望空出一个空间做为约定.
- rear 的初始值 = 0
- 当队列满时,条件是 (rear + 1) % maxSize == front 【满】
- 对队列为空的条件, rear == front 【空】
- 当我们这样分析, 队列中有效的数据的个数 count == (rear + maxSize - front) % maxSize // rear = 1 front = 0
- 我们就可以在原来的队列上修改得到,一个环形队列

代码实现:
package zy.code.queue;
/**
* 数组实现循环队列
*/
public class CircleArrayQueue {
private int maxSize;//最大容量为数组大小
private int front;//队首指向第一个元素,初始值为0
private int rear;//队尾指向最后一个元素的下一个位置,初始值为0
private int[] arr;//存储队列元素
/**
* 队列初始化
* @param maxSize
*/
public CircleArrayQueue(int maxSize) {
this.maxSize = maxSize;
this.front = 0;
this.rear = 0;
this.arr = new int[maxSize];
}
/**
* 判断是否已满
*/
public boolean isFull(){
if ((rear + 1) % maxSize == front) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
/**
* 判空
*/
public boolean isEmpty(){
if (this.front == this.rear){
return true;
}
return false;
}
/**
* 添加数据
*/
public void addQueue(int n){
if (isFull()){
System.out.println("队列满,不能添加数据。");
return;
}
arr[rear] = n;//添加元素
rear = (rear + 1) % maxSize;//指针后移
}
/**
* 取数据
*/
public int getQueue(){
if(isEmpty()){
throw new RuntimeException("队列空,不能取数据。");
}
// 先把队头元素保存在一个临时变量
// 然后对头指针后移
// 返回临时变量
int temp = arr[front];
front = (front + 1 ) % maxSize;
return temp;
}
/**
* 显示队列数据
*/
public void showQueue(){
if(isEmpty()){
System.out.println("队列空,没有数据可以显示。");
}
//怎么遍历数组?
int count = size();
for (int i = front; i < front + count; i++){
//从队头开始遍历,真正的下标可能会超出数组大小,必须转换为循环后的真正下标
int index = i % maxSize;
int val = arr[index];
System.out.printf("arr[%d] = %d\n",index,val);
}
}
/**
* 取出队列有效元素的个数
*/
public int size(){
return (rear + maxSize - front) % maxSize;
}
/**
* 查看第一个元素
*/
public int headQueue(){
if(isEmpty()){
throw new RuntimeException("队列空,不能取数据。");
}
return arr[front];
}
}
package zy.code.queue;
import java.util.Scanner;
/**
* 测试循环队列
*/
public class CircleQueueTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//测试一把
//创建一个队列
CircleArrayQueue queue = new CircleArrayQueue(3);
char key = ' '; //接收用户输入
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);//
boolean loop = true;
//输出一个菜单
while(loop) {
System.out.println("s(show): 显示队列");
System.out.println("e(exit): 退出程序");
System.out.println("a(add): 添加数据到队列");
System.out.println("g(get): 从队列取出数据");
System.out.println("h(head): 查看队列头的数据");
key = scanner.next().charAt(0);//接收一个字符
switch (key) {
case 's':
queue.showQueue();
break;
case 'a':
System.out.println("输出一个数");
int value = scanner.nextInt();
queue.addQueue(value);
break;
case 'g': //取出数据
try {
int res = queue.getQueue();
System.out.printf("取出的数据是%d\n", res);
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO: handle exception
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
break;
case 'h': //查看队列头的数据
try {
int res = queue.headQueue();
System.out.printf("队列头的数据是%d\n", res);
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO: handle exception
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
break;
case 'e': //退出
scanner.close();
loop = false;
break;
default:
break;
}
}
System.out.println("程序退出~~");
}
}
第二章、链表
2.1 链表的介绍
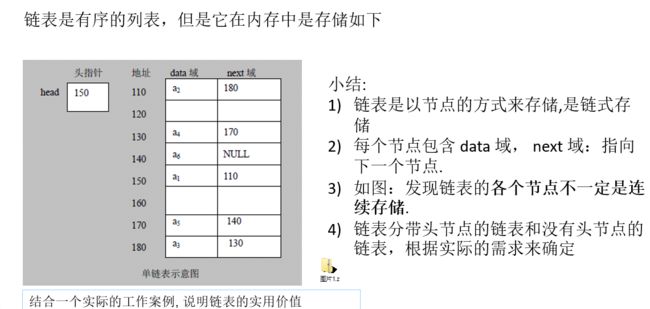
2.2 单链表
单链表是单方向的
/**
* 单链表结点的结构定义
*/
public class HeroNode {
public int no;//英雄排名
public String name;//姓名
public String nickname;//昵称
public HeroNode next;//指向下一个节点的指针
public HeroNode(int no, String name, String nickname) {
this.no = no;
this.name = name;
this.nickname = nickname;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
// 不打印 next,只打印该节点的data信息
return "HeroNode [no=" + no + ", name=" + name + ", nickname=" + nickname + "]";
}
}
/**
* 单链表
*/
public class SingleLinkedList {
private HeroNode head = new HeroNode(0,"","");
//返回头节点
public HeroNode getHead() {
return head;
}
/**
* 删除一个节点
* 1. 遍历节点找到要删除的节点编号
* 2. 要得到待删除节点的前一个节点,让 fore.next ---> temp.next
*/
public void delete(int no){
if (head.next == null){
System.out.println("链表为空,不能更新....");
return;
}
HeroNode temp = head.next;
HeroNode fore = head;//指向temp的前一个节点
boolean flag = false; //是否找到要删除的结点的标志
while (temp != null){
if(temp.no == no){
flag = true;
break;
}
// 没有找到也没有到尾部,指针后移
fore = temp;
temp = temp.next;
}
if (flag){
// 找到匹配节点temp,删除
fore.next = temp.next;
}else{
System.out.printf("删除失败,没有匹配 %d 号的节点\n",no);
}
}
/**
* 更新结点
*/
public void update(HeroNode heroNode){
if (head.next == null){
System.out.println("链表为空,不能更新....");
return;
}
HeroNode temp = head.next;
boolean flag = false;
while (temp != null){
if (temp.no == heroNode.no){
flag = true;
break;
}
//指针后移
temp = temp.next;
}
if (flag){
temp.name = heroNode.name;
temp.nickname = heroNode.nickname;
}else{
System.out.println("遍历完本单链表,未发现有可修改的匹配项....");
}
}
/**
* 插入新节点
* 1. 考虑节点排名顺序,默认从小到大排序,
* 2. 插入的新节点依次与遍历节点比较,如果遍历节点比新节点大,在之前插入
*/
public void addByOrder(HeroNode heroNode){
HeroNode temp = head;
boolean flag = false;//判断节点排名是否相等的标志
while (temp.next != null && temp.next.no <= heroNode.no){
if (temp.next.no == heroNode.no){
flag = true;
}
//指针后移
temp = temp.next;
}
if (!flag){
// 在temp之后、n之前插入。先连接尾部再连接前部
heroNode.next = temp.next;
temp.next = heroNode;
}
}
/**
* 追加新的节点
* 1. 不考虑排名问题时,只在单链表尾端进行追加
* 2. 遍历单链表,让最后一个节点的next指向新节点
*/
public void add(HeroNode heroNode){
// 由于head头节点是固定的,不能指向其他节点,所以这里创建一个临时指针进行遍历
HeroNode temp = this.head;
while (temp.next != null){
temp = temp.next;
}
// 遍历到结尾,追加
temp.next = heroNode;
}
/**
* 显示单链表
* 单向遍历
*/
public void list(){
//判断链表是否为空
if (head.next == null){
System.out.println("链表为空....");
return;
}
// 使用辅助节点来遍历
HeroNode temp = head.next;
while (temp != null){
System.out.println(temp);
temp = temp.next;
}
}
}
package zy.code.linkedlist;
import java.util.Stack;
/**
* 面试题基础练习
*/
public class SingleLinkedListUtil {
/**
* 【新浪面试题】获取单链表的长度(不含头结点)
*/
public static int getSize(HeroNode head){
if (head.next == null){
System.out.println("该单链表为空");
return 0;
}
HeroNode temp = head.next;
int size = 0;
while (temp != null){
size++;
temp = temp.next;
}
return size;
}
/**
* 【新浪面试题】获取倒数第 k 个节点(不包含头结点在内)
*/
public static HeroNode getLastIndexNode(HeroNode head,int k){
if (head.next == null){
System.out.println("该单链表为空");
return null;
}
// 获取该链表的长度
int size = SingleLinkedListUtil.getSize(head);
HeroNode temp = head.next;
// 从头顺序遍历 size - k 个
for (int i = 0; i < size - k; i++){
temp = temp.next;
}
return temp;
}
/**
* 【腾讯面试题】反转单链表
* 思路:
* 1. 先定义一个节点 reverseHead = new HeroNode();
* 2. 从头到尾遍历原来的链表,每遍历一个节点,就将其取出,并放在新的链表reverseHead 的最前端.(前插法)
* 3. 原来的链表的head.next = reverseHead.next
*/
public static HeroNode reverse(HeroNode head){
if (head.next == null || head.next.next == null){
System.out.println("该单链表为空或只有一个结点");
return head;
}
HeroNode cur = head.next;
HeroNode next = null;
HeroNode reverseHead = new HeroNode(0,"","");
while (cur != null){
// 先保存cur的下一个节点
next = cur.next;
// 改变cur,采用前插法,插入反转链表
cur.next = reverseHead.next;
reverseHead.next = cur;
// 原指针后移
cur = next;
}
// 最后将原来的头指针替换为反转后链表的头指针
head.next = reverseHead.next;
return head;
}
/**
* 【百度面试题】
* 逆序打印单链表 【百度,要求方式 1:反向遍历 。 方式2:Stack栈】
* 注意:
* 1. 只需要逆序打印,无需改变原链表的结构
* 2. 可以使用栈,顺序遍历结点并压栈,然后打印栈即可
*/
public static void reversePrint(HeroNode head){
if (head.next == null){
return;
}
Stack<HeroNode> stack = new Stack<HeroNode>();
HeroNode temp = head.next;
while (temp != null){
stack.push(temp);
temp = temp.next;
}
//遍历栈
while (stack.size() > 0){
System.out.println(stack.pop());
}
}
}
2.3 双向链表
使用带head头的双向链表实现 –水浒英雄排行榜
管理单向链表的缺点分析:
1)单向链表,查找的方向只能是一个方向,而双向链表可以向前或者向后查找。
2)单向链表不能自我删除,需要靠辅助节点 ,而双向 链表,则可以自我删除,所以前面我们单链表删除 时节点,总是要保存好待删除结点的上一个一节点。
分析 双向链表的遍历,添加,修改,删除的操作思路===》代码实现
# 遍历 方和 单链表一样,只是可以向前,也可以向后查找
# 添加 (默认添加到双向链表的最后)
先找到双向链表的最后这个节点,两步
temp.next = newHeroNode
newHeroNode.pre = temp;
# 修改 思路和 原来的单向链表一样.
# 删除
(1) 因为是双向链表,因此,我们可以实现自我删除某个节点
(2) 直接找到要删除的这个节点,比如temp(两步)
- temp.pre.next = temp.next
- temp.next.pre = temp.pre;
代码:
/**
* 双向链表的结点结构
*/
public class DoubleHeroNode {
public int no;//英雄排名
public String name;//姓名
public String nickname;//昵称
public DoubleHeroNode next;//指向下一个节点的指针
public DoubleHeroNode pre;//指向上一个结点的指针
public DoubleHeroNode(int no, String name, String nickname) {
this.no = no;
this.name = name;
this.nickname = nickname;
}
public String toString() {
// 不打印 next,只打印该节点的data信息
return "HeroNode [no=" + no + ", name=" + name + ", nickname=" + nickname + "]";
}
}
package zy.code.linkedlist;
/*
双向链表的数据结构
*/
public class DoubleLinkedList {
DoubleHeroNode head = new DoubleHeroNode(0,"","");
DoubleHeroNode getHead(){
return head;
}
/**
* 顺序遍历双向链表
*/
public void list(){
//判断链表是否为空
if (head.next == null){
System.out.println("链表为空....");
return;
}
// 使用辅助节点来遍历
DoubleHeroNode temp = head.next;
while (temp != null){
System.out.println(temp);
temp = temp.next;
}
}
/**
* 追加新的节点
* 1. 不考虑排名问题时,只在单链表尾端进行追加
* 2. 遍历单链表,让最后一个节点的next指向新节点
*/
public void add(DoubleHeroNode heroNode){
// 由于head头节点是固定的,不能指向其他节点,所以这里创建一个临时指针进行遍历
DoubleHeroNode temp = this.head;
while (temp.next != null){
temp = temp.next;
}
// 遍历到结尾,追加
temp.next = heroNode;
heroNode.pre = temp;
}
/**
* 更新结点
*/
public void update(DoubleHeroNode heroNode){
if (head.next == null){
System.out.println("链表为空,不能更新....");
return;
}
DoubleHeroNode temp = head.next;
boolean flag = false;
while (temp != null){
if (temp.no == heroNode.no){
flag = true;
break;
}
//指针后移
temp = temp.next;
}
if (flag){
temp.name = heroNode.name;
temp.nickname = heroNode.nickname;
}else{
System.out.println("遍历完本单链表,未发现有可修改的匹配项....");
}
}
/**
* 删除一个节点
* 1. 遍历节点找到要删除的节点编号
* 2. 待删除结点的 next、pre指针修改
*/
public void delete(int no){
if (head.next == null){
System.out.println("链表为空,不能更新....");
return;
}
DoubleHeroNode temp = head.next;
boolean flag = false; //是否找到要删除的结点的标志
while (temp != null){
if(temp.no == no){
flag = true;
break;
}
// 指针后移
temp = temp.next;
}
if (flag){
// 找到匹配节点temp,执行删除操作
if (temp.next == null){
// 要删除的结点是最后一个
temp.pre.next = temp.next;
}else{
temp.pre.next = temp.next;
temp.next.pre = temp.pre;
}
}else{
System.out.printf("删除失败,没有匹配 %d 号的节点\n",no);
}
}
/**
* 插入新节点
* 1. 考虑节点排名顺序,默认从小到大排序,
* 2. 插入的新节点依次与遍历节点比较,如果遍历节点比新节点大,在之前插入
*/
public void addByOrder(DoubleHeroNode heroNode){
DoubleHeroNode temp = head;
boolean flag = false;//判断节点排名是否相等的标志
while (temp.next != null && temp.next.no <= heroNode.no){
if (temp.next.no == heroNode.no){
flag = true;//已存在相同结点,不需要插入
break;
}
//指针后移
temp = temp.next;
}
if (!flag){
//第一步:先连键
heroNode.next = temp.next;
heroNode.pre = temp;
//第二步:断掉原来的键
if (temp.next == null){
//若temp是最后一个元素,在temp之后结尾插入
temp.next = heroNode;
}else{
// 在中间插入的话,是在temp、temp.next 之间插入
temp.next.pre = heroNode;
temp.next = heroNode;
}
}else{
System.out.println("链表种已存在相同结点,请不要重复插入");
}
}
}
2.4 单项环形链表(josephu问题)
环形链表结点的构建
/**
* 以丢手帕问题为例
* 一个小朋友就是一个结点
*/
public class BoyNode {
public int no;// 编号
public BoyNode next; // 指向下一个节点,默认null
public BoyNode(int no) {
this.no = no;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "BoyNode[" +
"no=" + no +
']';
}
}
单项环形链表结构
/**
* 单向环形链表
*/
public class CircleSingleLinkedList {
private BoyNode first =null;
public BoyNode getFirst() {
return first;
}
/**
* 添加多个结点
*/
public void addBoys(int nums){
if (nums < 1){
System.out.println("nums 值不正确,至少添加1个小朋友");
return;
}
// cur为辅助指针,向后移动遍历
BoyNode cur = null;
for (int i = 1; i <= nums; i++){
// 创建小孩并编号
BoyNode boy = new BoyNode(i);
if (i == 1){
//创建第一个结点时构建环形
first = boy;
boy.next = first;//一个人也可以形成一个环
cur = first;
}else{
//添加的结点加入这个环
cur.next = boy;
boy.next = first;
cur = boy;//cur 移动到新的节点上
}
}
}
/**
* 遍历打印环形单链表
* 1. 先让一个辅助指针(变量) curBoy,指向first节点
* 2. 然后通过一个while循环遍历 该环形链表即可 curBoy.next == first 结束
*/
public void show(){
// 判断
if (first == null){
System.out.println("环形单链表为空....");
return;
}
BoyNode cur = first;
while (true){
System.out.printf("小孩编号:%d\n",cur.no);
if (cur.next == first){
break;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
}

Josephu 问题为:设编号为1,2,… n的n个人围坐一圈,约定编号为k(1<=k<=n)的人从1开始报数,数到m 的那个人出列,它的下一位又从1开始报数,数到m的那个人又出列,依次类推,直到所有人出列为止,由此产生一个出队编号的序列
n = 5 // 共有5个人
k = 1 // 从第1个人开始报数
m = 2 // 数到2出列
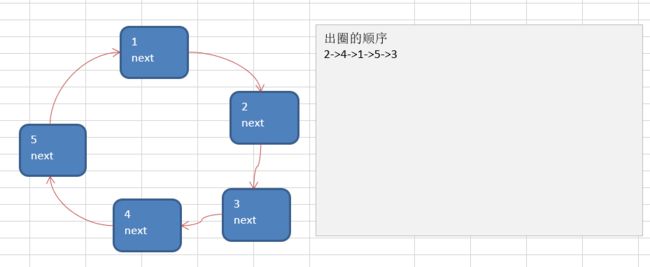
思路:
构建一个单向的环形链表思路
\1. 先创建第一个节点, 让 first 指向该节点,并形成环形
\2. 后面当我们每创建一个新的节点,就把该节点,加入到已有的环形链表中即可.
遍历环形链表
\1. 先让一个辅助指针(变量) curBoy,指向first节点
\2. 然后通过一个while循环遍历 该环形链表即可 curBoy.next == first 结束


出圈游戏代码实现:
/**
* 出圈游戏
* nums : 总共人数
* startNum : 从几号开始
* m : 数到几(数几个)
*/
public void playjosephu(int nums,int startNum,int m){
//参数校验
if (nums < 1 || startNum <0 || m > nums){
System.out.println("参数设定有问题");
return;
}
//创建辅助指针,该指针一直指向first的后一个,first向后移动始终指向报数者
BoyNode helper = first;
// 遍历到环的最后一个人,并让helper指向最后一个人
while (helper.next != first){
helper = helper.next;
}
//根据第一个报数的人,移动first、helper的默认位置
//比如,第一个报数的是3号,指针还需要再往后移动2次
for (int i = 0; i < startNum - 1; i++){
first = first.next;
helper = helper.next;
}
while (helper != first){
//报数
//从1数到m,为什么是数 m-1 次?因为从1到m,还需要循环m-1个人,指针才会指向那个“出圈者”
for (int j = 0; j < m - 1; j++){
first = first.next;
helper = helper.next;
}
//出圈
System.out.printf("%d 号出圈\n",first.no);
first = first.next;
helper.next = first;
}
//循环游戏结束后,最终会只剩下一个人
System.out.printf("最后剩下的一个人的编号是:%d\n",first.no);
}
第三章、栈
3.1 数组模拟栈结构

/**
* 数组模拟栈
*/
public class ArrayStack {
int maxSize; //最大容量
int[] stack; //栈数组存放数据
int top = -1; //栈顶的索引
public ArrayStack(int maxSize) {
this.maxSize = maxSize;
this.stack = new int[maxSize];
}
/**
* 判断栈满
*/
public boolean isFull(){
return top == maxSize - 1;
}
/**
* 判断栈空
*/
public boolean isEmpty(){
return top == - 1;
}
/**
* 入栈
*/
public void push(int val){
if (isFull()){
System.out.println("栈满");
return;
}
top++;
stack[top] = val;
}
/**
* 出栈
* @return
*/
public int pop(){
if (isEmpty()){
throw new RuntimeException("栈空,没有数据");
}
int val = stack[top];
top--;
return val;
}
/**
* 遍历(从栈顶到栈底)
*/
public void list(){
if (isEmpty()){
System.out.println("栈空,没有数据");
return;
}
for (int i = top; i >= 0;i--){
System.out.printf("stack[%d]=%d\n",i,stack[i]);
}
}
}
3.2 栈的表达式计算
-
通过一个 index 值(索引),来遍历我们的表达式
-
如果我们发现是一个数字****, 就直接入数栈
-
如果发现扫描到是一个符号, 就分如下情况
如果当前符号优先级 小于 栈顶符号,弹出栈顶符号以及数字栈的两个数字进行运算,将结果再压入数字栈。
栈顶符号参与运算就算销毁了,那么再比较当前符号和新的栈顶,重复重复
直到当前栈顶优先级大于 栈顶符号,压入栈。
该练习只做到了两位数与加减乘除运算。没有考虑小括号、多位数的情况。只适用于栈的初步操作练习。如果想实现完整的计算器案例,还需要向后学习前缀、中缀、后缀表达式、逆波兰表达式的知识。
并且这种算法,只是对中缀表达式直接操作,中缀表达式很难被计算机操作,运用起来情况复杂

/**
* 基于数组栈的计算器
*/
public class Calculator {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String expression = "10*10-1";
ArrayStack numStack = new ArrayStack(30);
ArrayStack oprStack = new ArrayStack(30);
//定义相关变量
int index = 0;//用于扫描字符串表达式
char ch =' ';//保存每次扫描的元素
int num1 = 0;
int num2 = 0;
int opr = 0;
int result = 0;
String keepNum = "";
//循环遍历表达式字符串
for (index = 0; index < expression.length(); index++){
ch = expression.charAt(index);
if (oprStack.isOpr(ch)){
//是操作符
if (!oprStack.isEmpty()){
//符号栈不为空
// 一直比较优先级,直到当前符号大于栈顶
//43+ 42* 45-
while (!oprStack.isEmpty() && oprStack.priority(ch) <= oprStack.priority(oprStack.peekTop()) ){
//弹出当前栈顶符号一个
opr = oprStack.pop();
//弹出数字站两个
num1 = numStack.pop();
num2 = numStack.pop();
//计算
result = oprStack.calculate(num1, num2, opr);
//结果压入数字栈
numStack.push(result);
}
//直到当前符号优先级大时,将当前符号压栈
oprStack.push(ch);
}else{
//符号栈为空,直接压栈
oprStack.push(ch);
}
}else{
//不是操作符,是数字(注意:ch是char 类型)
// numStack.push(ch - 48);// 0的ASCII码是48
//多位数问题
keepNum += ch;
if (index == expression.length() - 1){
numStack.push(ch - 48);// 0的ASCII码是48
}else{
if (!oprStack.isOpr(expression.charAt(index+1))){
// 如果下一位还是数字
keepNum += expression.charAt(index+1);
int i = Integer.parseInt(keepNum);
//多位数入栈
numStack.push(i);
//清空keepNum
keepNum = "";
//多位数压栈后,扫描索引必须移位
index++;
}else{
//如果下一位是操作符
int j = Integer.parseInt(keepNum);
numStack.push(j);
keepNum = "";
}
}
}
}
//表达式扫描完毕,对两个栈中的元素进行操作
while (!oprStack.isEmpty()){
opr = oprStack.pop();
num1 = numStack.pop();
num2 = numStack.pop();
result = oprStack.calculate(num1, num2, opr);
numStack.push(result);
}
// 数字栈最后只剩一个最终结果
System.out.printf("表达式:%s = %d\n",expression,numStack.pop());
}
}
3.3 前缀中缀后缀表达式
前缀表达式
又称为波兰表达式,是一种操作符在前、数字在后的表达式。



[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-X2hcnk60-1600153298274)(G:\图片\blog\image-20200725110231867.png)]


3.4 逆波兰计算器
package zy.code.stack;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Stack;
/**
* 逆波兰表达式的计算器
*/
public class PolandNotation {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String infixExpression = "1+((2+3)*4)-11+20*300";
List<String> infixList = infixStringToList(infixExpression);
System.out.println("前缀表达式" + infixList);
List<String> sufixList = infixToSuffixList(infixList);
System.out.println("后缀表达式" + sufixList);
int calResult = calculate(sufixList);
System.out.println("逆波兰计算器计算结果为 :" + calResult);//6010
}
/**
* 中缀表达式转后缀表达式
*/
public static List<String> infixToSuffixList(List<String> infixList){
// 初始化两个栈,一个处理操作符号栈,一个中间栈
Stack<String> stack = new Stack<String>();
List<String> sufList = new ArrayList<>();//中间栈可以用列表代替
// 遍历中缀表达式
for (String str : infixList){
//如果是数字,直接输出
if (str.matches("\\d+")){
sufList.add(str);
}else{
//如果是操作符号
if (stack.isEmpty() || str.equals("(")){
//栈空或者是左括号
stack.push(str);
}else{
//找不空,其他符号
if (str.equals(")")){
//如果是右括号
while ( !(stack.peek().equals("("))){
//遍历弹出括号之间的符号
String pop_str = stack.pop();
sufList.add(pop_str);
}
stack.pop();//弹出左括号
}else{
//不是右括号,比较优先级
while (!stack.isEmpty() && !(stack.peek().equals("(")) && Operation.getPriority(str) <= Operation.getPriority(stack.peek())){
sufList.add(stack.pop());
}
stack.push(str);
}
}
}
}
//遍历完表达式后,将符号栈剩余的字符出栈,并输出到中间栈
while (!stack.isEmpty()){
sufList.add( stack.pop());
}
return sufList;
}
/**
* 中缀表达式字符串转换成数组
*/
public static List<String> infixStringToList(String infixExpression){
List<String> list = new ArrayList<String>();
int i = 0;//遍历字符串的索引
char ch = ' ';//获取字符串的每一个字符
String str = "";//拼接对位数字符
// 遍历表达式
while ( i < infixExpression.length() ){
ch = infixExpression.charAt(i);
if (ch < 48 || ch > 57){
// 是个操作符号
list.add("" + ch);
i++;
}else{
//是个数字
while (i < infixExpression.length() && infixExpression.charAt(i) >= 48 && infixExpression.charAt(i) <= 57){
//有下一个,且下一个还是数字
str += infixExpression.charAt(i);
i++;
}
list.add(str);
str = "";//清空多位数拼接字符串,以便于下次拼接使用
}
}
return list;
}
/**
* 以空格分割字符串转 List
*/
public static List<String> stringToList(String suffixExpression){
String[] split = suffixExpression.split(" ");
List<String> list = new ArrayList<String>();
for (String str:split){
list.add(str);
}
return list;
}
/**
* 后缀表达式的计算
*/
public static int calculate(List<String> list){
int result = 0;
Stack<String> stack = new Stack<String>();
for (String str :list){
// 正则表达式,如果该字符串匹配的是多位整数
if (str.matches("\\d+")){
//数字压栈
stack.push(str);
}else{
// 字符串匹配操作符号
int num1 = Integer.parseInt(stack.pop());
int num2 = Integer.parseInt(stack.pop());
switch (str){
case "+":
result = num2 + num1;
break;
case "-":
result = num2 - num1;
break;
case "*":
result = num2 * num1;
break;
case "/":
result = num2 / num1;
break;
default:
break;
}
// 将计算结果入栈
stack.push("" + result);
}
}
// 将栈中的最后数字就是计算结果
return Integer.parseInt(stack.pop());
}
}
package zy.code.stack;
/**
* 操作符优先级定义
*/
public class Operation {
private static int ADD = 1;
private static int SUB = 1;
private static int MUL = 2;
private static int DIV = 2;
//写一个方法,返回对应的优先级数字
public static int getPriority(String operation) {
int result = 0;
switch (operation) {
case "+":
result = ADD;
break;
case "-":
result = SUB;
break;
case "*":
result = MUL;
break;
case "/":
result = DIV;
break;
default:
System.out.println("不存在该运算符" + operation);
break;
}
return result;
}
}
第四章、递归
4.1 递归的基本概念
- 递归用于解决什么样的问题
1)各种数学问题如: 8皇后问题 , 汉诺塔, 阶乘问题, 迷宫问题, 球和篮子的问题(google编程大赛)
2)各种算法中也会使用到递归,比如快排,归并排序,二分查找,分治算法等.
3)将用栈解决的问题–>递归代码比较简洁,但是时间复杂度很高
- 递归需要遵守的重要规则
执行一个方法时,就创建一个新的受保护的独立空间(栈空间)
方法的局部变量是独立的,不会相互影响, 比如n变量
如果方法中使用的是引用类型变量(比如数组),就会共享该引用类型的数据.
递归必须向退出递归的条件逼近,否则就是无限递归,出现StackOverflowError,死龟了
当一个方法执行完毕,或者遇到return,就会返回,遵守谁调用,就将结果返回给谁,同时当方法执行完毕或者返回时,该方法也就执行完毕。

4.2 阶乘问题
4.3迷宫问题
/**
* 迷宫
*/
public class MiGong {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建迷宫地图
// 先创建一个二维数组,模拟迷宫
// 地图
int[][] map = new int[8][7];
// 使用1 表示墙
// 上下全部置为1
for (int i = 0; i < 7; i++) {
map[0][i] = 1;
map[7][i] = 1;
}
// 左右全部置为1
for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++) {
map[i][0] = 1;
map[i][6] = 1;
}
//设置挡板, 1 表示
map[3][1] = 1;
map[3][2] = 1;
// map[1][2] = 1;
// map[2][2] = 1;
// 输出地图
System.out.println("地图的情况");
for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 7; j++) {
System.out.print(map[i][j] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
//使用递归回溯给小球找路
setWay(map, 1, 1);
//输出新的地图, 小球走过,并标识过的递归
System.out.println("小球走过,并标识过的 地图的情况");
for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 7; j++) {
System.out.print(map[i][j] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
//使用递归回溯来给小球找路
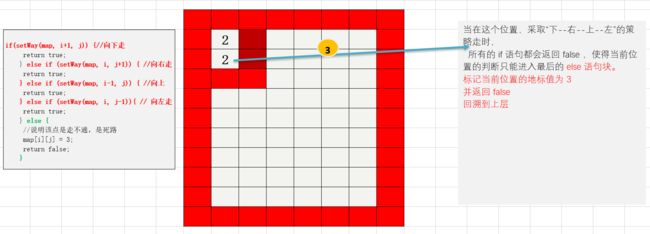
//说明
//1. map 表示地图
//2. i,j 表示从地图的哪个位置开始出发 (1,1)
//3. 如果小球能到 map[6][5] 位置,则说明通路找到.
//4. 约定: 当map[i][j] 为 0 表示该点没有走过 当为 1 表示墙 ; 2 表示通路可以走 ; 3 表示该点已经走过,但是走不通
//5. 在走迷宫时,需要确定一个策略(方法) 下->右->上->左 , 如果该点走不通,再回溯
public static boolean setWay(int[][] map,int i,int j){
if (map[6][5] == 2){
// 目标到达
return true;
}else{
if (map[i][j] == 0){
// 该点还没有走过
map[i][j] = 2;//走该点
if (setWay(map,i+1,j)){//向下走
return true;
}else if(setWay(map,i,j+1)){//向右走
return true;
}else if (setWay(map,i-1,j)){//向上走
return true;
}else if (setWay(map,i,j-1)){//向左走
return true;
}else{
//都走过来都返回false,说明该点不通
map[i][j] = 3;
return false;
}
}else{
// 该点== 1、3都是走不通
return false;
}
}
}
}

4.34八皇后问题(回溯算法)


/**
* 递归穷举法:八皇后问题
* 递归的判断至少有一万多次
*/
public class Queen8 {
int max = 8;
int[] arr = new int[max];
int count = 0;
public static void main(String[] args) {
Queen8 queen8 = new Queen8();
//从第一个皇后开始探索
queen8.check(0);
System.out.printf("总共的摆放组合有 %d 个\n",queen8.count);
}
/**
* 放置第 n 个皇后
* check方法中有一个循环,每递归一层都会有一个for循环
* 如果底层完毕,就会回溯上一层
* 上一层就会接着for循环,而新的循环又会产生一个新的递归,新的递归树里面皇后的位置会改变,产生不同的结果
*/
public void check(int n){
if (n == max){
//当n等于最大数时,说明所有的皇后已经摆放完毕,这个递归的出口到了。
print();//打印目前的arr数组
return;//结束递归,返回上层
}
//从第0列开始试着放置皇后
for (int i = 0;i < max;i++){
//先试着放置皇后
arr[n] = i;
if (judge(n)){
//不冲突,该位置暂时可以放置,继续放置下一个皇后,即开始递归
check(n+1);
}
//冲突,当前位置暂时不可以放置,继续试着放置到下一列
}
}
/**
* 判断第n个皇后的摆放位置是否正确
*/
public boolean judge(int n){
for (int i = 0;i < n; i++){
if (arr[i] == arr[n] || Math.abs(i-n) == Math.abs(arr[i]-arr[n])){
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
/**
* 写一个方法,可以将皇后摆放的位置输出
*/
private void print() {
count++;
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
System.out.print(arr[i] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
0 4 7 5 2 6 1 3
0 5 7 2 6 3 1 4
0 6 3 5 7 1 4 2
0 6 4 7 1 3 5 2
1 3 5 7 2 0 6 4
1 4 6 0 2 7 5 3
1 4 6 3 0 7 5 2
1 5 0 6 3 7 2 4
1 5 7 2 0 3 6 4
1 6 2 5 7 4 0 3
1 6 4 7 0 3 5 2
1 7 5 0 2 4 6 3
2 0 6 4 7 1 3 5
2 4 1 7 0 6 3 5
2 4 1 7 5 3 6 0
2 4 6 0 3 1 7 5
2 4 7 3 0 6 1 5
2 5 1 4 7 0 6 3
2 5 1 6 0 3 7 4
2 5 1 6 4 0 7 3
2 5 3 0 7 4 6 1
2 5 3 1 7 4 6 0
2 5 7 0 3 6 4 1
2 5 7 0 4 6 1 3
2 5 7 1 3 0 6 4
2 6 1 7 4 0 3 5
2 6 1 7 5 3 0 4
2 7 3 6 0 5 1 4
3 0 4 7 1 6 2 5
3 0 4 7 5 2 6 1
3 1 4 7 5 0 2 6
3 1 6 2 5 7 0 4
3 1 6 2 5 7 4 0
3 1 6 4 0 7 5 2
3 1 7 4 6 0 2 5
3 1 7 5 0 2 4 6
3 5 0 4 1 7 2 6
3 5 7 1 6 0 2 4
3 5 7 2 0 6 4 1
3 6 0 7 4 1 5 2
3 6 2 7 1 4 0 5
3 6 4 1 5 0 2 7
3 6 4 2 0 5 7 1
3 7 0 2 5 1 6 4
3 7 0 4 6 1 5 2
3 7 4 2 0 6 1 5
4 0 3 5 7 1 6 2
4 0 7 3 1 6 2 5
4 0 7 5 2 6 1 3
4 1 3 5 7 2 0 6
4 1 3 6 2 7 5 0
4 1 5 0 6 3 7 2
4 1 7 0 3 6 2 5
4 2 0 5 7 1 3 6
4 2 0 6 1 7 5 3
4 2 7 3 6 0 5 1
4 6 0 2 7 5 3 1
4 6 0 3 1 7 5 2
4 6 1 3 7 0 2 5
4 6 1 5 2 0 3 7
4 6 1 5 2 0 7 3
4 6 3 0 2 7 5 1
4 7 3 0 2 5 1 6
4 7 3 0 6 1 5 2
5 0 4 1 7 2 6 3
5 1 6 0 2 4 7 3
5 1 6 0 3 7 4 2
5 2 0 6 4 7 1 3
5 2 0 7 3 1 6 4
5 2 0 7 4 1 3 6
5 2 4 6 0 3 1 7
5 2 4 7 0 3 1 6
5 2 6 1 3 7 0 4
5 2 6 1 7 4 0 3
5 2 6 3 0 7 1 4
5 3 0 4 7 1 6 2
5 3 1 7 4 6 0 2
5 3 6 0 2 4 1 7
5 3 6 0 7 1 4 2
5 7 1 3 0 6 4 2
6 0 2 7 5 3 1 4
6 1 3 0 7 4 2 5
6 1 5 2 0 3 7 4
6 2 0 5 7 4 1 3
6 2 7 1 4 0 5 3
6 3 1 4 7 0 2 5
6 3 1 7 5 0 2 4
6 4 2 0 5 7 1 3
7 1 3 0 6 4 2 5
7 1 4 2 0 6 3 5
7 2 0 5 1 4 6 3
7 3 0 2 5 1 6 4
总共的摆放组合有 92 个
Process finished with exit code 0
第五章、算法时间、空间复杂度
5.1 时间复杂度






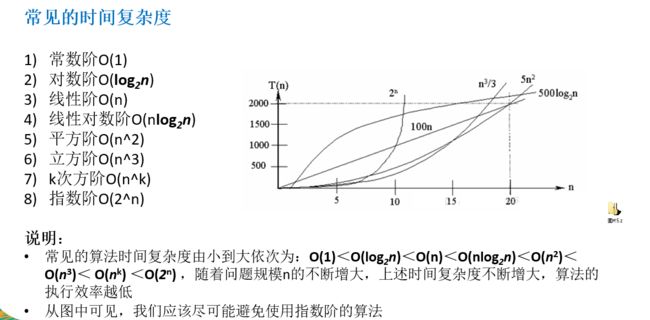



5.2 空间复杂度

5.3 排序算法的复杂度
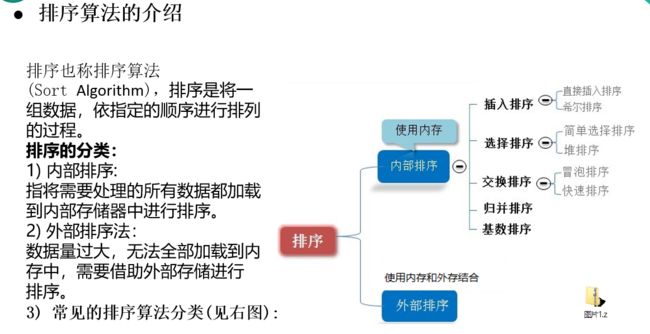

第六章、排序算法
6.1 冒泡排序
每次都是比较相邻元素,然后交换。
第一趟排序,会将最大的放到倒数第一。
第二趟排序,将次大的放到倒数第二。
以此类推,直到某一趟排序没有发生交换,就说明排好了。
public static void bubble(int[] arr){
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length - 1; i++){
System.out.println("第"+ (i+1) + "趟排序");
boolean flag = false;
for (int j = 0; j < arr.length - 1 - i; j++){
if (arr[j] > arr[j+1]){
int temp = arr[j+1];
arr[j+1] = arr[j];
arr[j] = temp;
flag = true;
}
}
if (!flag){
break;
}
}
}
6.2 选择排序
每一趟排序都找到最小的元素,与之交换
从左到右扫描,第一趟以第一个位置为基准,只要后面元素比基准小,就交换,第一趟下来最小的会放在最前面。
第二趟以第二个数为基准,从后面再依次找更小的替换之。
以此类推,选择排序是从左到右实现的。(冒泡排序是从右到左实现的。)
public static void select(int[] arr){
for (int i = 0;i < arr.length - 1;i++){
for (int j = i + 1; j < arr.length; j++){
if (arr[j] < arr[i]){
//选取更小的往前替换
int temp = arr[j];
arr[j] = arr[i];
arr[i] = temp;
}
}
}
}
另一种写法
//选择排序
public static void selectSort(int[] arr) {
//选择排序时间复杂度是 O(n^2)
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length - 1; i++) {
int minIndex = i;
int min = arr[i];
for (int j = i + 1; j < arr.length; j++) {
if (min > arr[j]) { // 说明假定的最小值,并不是最小
min = arr[j]; // 重置min
minIndex = j; // 重置minIndex
}
}
// 将最小值与放在arr[i]交换
if (minIndex != i) {
arr[minIndex] = arr[i];
arr[i] = min;
}
//System.out.println("第"+(i+1)+"轮后~~");
//System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr));// 1, 34, 119, 101
}
}
6.3 插入排序
public static void insertSort(int[] arr){
for (int i = 1; i < arr.length; i++){
if (arr[i] < arr[i-1]){
//将当前元素插入到前面,依次判断前面的元素大小,越小越往前,直到比某个数大
int temp = arr[i];
int j;
for (j = i -1; j >= 0 && temp < arr[j] ; j--){
//让小数插入,大数后移
arr[j+1] = arr[j];
}
//当temp >= arr[j]时扫描结束,在arr[j]的后面插入temp
arr[j+1] = temp;
}
}
}
思想解析:

6.4 希尔排序



有一群小牛, 考试成绩分别是 {8,9,1,7,2,3,5,4,6,0} 请从小到大排序. 请分别使用
1)希尔排序时, 对有序序列在插入时采用交换法, 并测试排序速度.
2)希尔排序时, 对有序序列在插入时采用移动法, 并测试排序速度
/**
* 希尔排序
*/
public class ShellSort {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {8,9,1,7,2,3,5,4,6,0};
shellSort2(arr);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr));
}
/**
* 希尔排序之交换法
*/
public static void shellSort(int[] arr){
for (int gap = arr.length/2; gap > 0; gap/= 2){
for (int i = gap; i < arr.length; i++){
int j = i;//用于分组扫描
//同组以每隔一个步长扫描上一个元素并比较大小
while (j-gap >= 0 && arr[j-gap] > arr[j]){
//交换
int temp = arr[j];
arr[j] = arr[j-gap];
arr[j-gap] = temp;
//j继续向前扫描同组上一个元素
j -= gap;
}
}
}
}
/**
* 希尔排序之移动法
*/
public static void shellSort2(int arr[]){
for (int gap = arr.length/2; gap > 0; gap /= 2){
for (int i = gap; i < arr.length; i++){
int j = i;//用于分组扫描
int temp = arr[j];//用于保存待插入的无序数
while (j - gap >= 0 && arr[j-gap] > temp){
//大数后移
arr[j] = arr[j-gap];//以步长为单位进行后移
j -= gap;
}
//将待插入元素放到 j-gap 的后面
arr[j] = temp;
}
}
}
}
6.5 快速排序
快速排序法介绍
快速排序,是对冒泡排序的一种改进。
基本思想是:通过一趟排序将数组分割成独立的两部分,其中一部分的所有数据都比另外一部分的所有数据都要小,然后再按此方法对这两部分数据分别进行快速排序,整个排序过程可以递归进行,以此达到整个数据变成有序序列

/**
* 快速排序
*/
public class QuickSort {
public static void main(String[] args) {
}
/**
* 快排,左右标兵法
*/
public static void quickSort(int[] arr,int left, int right){
int l = left;
int r= right;
int pivot = arr[(left + right) / 2];//pivot 中轴值
int temp = 0;//用作交换时的中间变量
while (l < r){
//左标兵从前往后找大数,右标兵从后往前找小数
while (arr[l] < pivot){//大数法则
l++;
}
while (arr[r] > pivot){//小数法则
r--;
}
if (l > r){
break;//在找数过程中,左右标兵碰面了,表示找数失败
}
//找数成功,交换左右标兵的值
temp = arr[l];
arr[l] = arr[r];
arr[r] = temp;
//注意一个bug,当数组中存在两个相等的pivot时,要避免死循环
//比较交换完的元素是否有等于pivot,防止两个相等的pivot进入死循环
if (arr[l] == pivot){
r--;//交换完的元素可以跳过
}
if (arr[r] == pivot){
l++;
}
}
//如果一趟下来,l==r,必须l++,r--,将数组左右区分开
if (l == r){
l++;
r--;
}
//向左递归
quickSort(arr,left,r);
//向右递归
quickSort(arr,l,right);
}
}
另一种快排方式:以首位为基准
/**
* 实现快速排序算法,用于对节点进行排序
*
* @param nodes
* @param start
* @param end
*/
private static void subSort(List<Node> nodes, int start, int end) {
if (start < end) {
// 以第一个元素作为分界值
Node base = nodes.get(start);
// i从左边搜索,搜索大于分界值的元素的索引
int i = start;
// j从右边开始搜索,搜索小于分界值的元素的索引
int j = end + 1;
while (true) {
// 找到大于分界值的元素的索引,或者i已经到了end处
while (i < end && nodes.get(++i).weight >= base.weight)
;
// 找到小于分界值的元素的索引,或者j已经到了start处
while (j > start && nodes.get(--j).weight <= base.weight)
;
if (i < j) {
swap(nodes, i, j);
} else {
break;
}
}
swap(nodes, start, j);
//递归左边子序列
subSort(nodes, start, j - 1);
//递归右边子序列
subSort(nodes, j + 1, end);
}
}
/**
* 将指定集合中的i和j索引处的元素交换
*
* @param nodes
* @param i
* @param j
*/
private static void swap(List<Node> nodes, int i, int j) {
Node tmp;
tmp = nodes.get(i);
nodes.set(i, nodes.get(j));
nodes.set(j, tmp);
}
public static void quickSort(List<Node> nodes){
subSort(nodes, 0, nodes.size()-1);
}
6.6 归并排序
概述:
归并排序采用一种分而治之的思想,把一个长数组拆分成一个个的小区域,直到不能再拆分为止,
合并前,借助一个中间数组 remp,将待合并数组从中间分开,左边是左分解数组,右边是右分解数组
合并时,是取较小的元素先存放到 temp数组,这样保持temp数组从小到大的排序,当待合并数组合并完成时,再将temp数组拷贝给arr(索引必须在分解后的范围内)
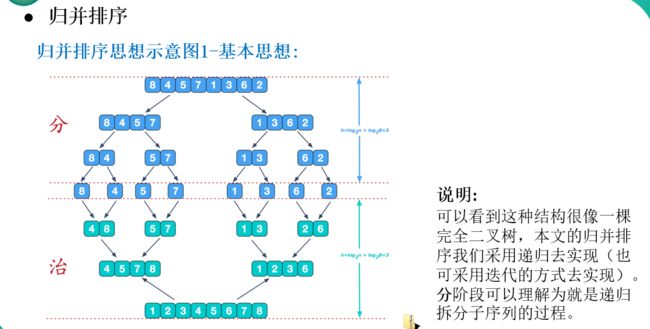

/**
* 归并排序:采取分而治之的思想
*/
public class MergetSort {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = { 8, 4, 5, 7, 1, 3, 6, 2 };
int[] temp = new int[arr.length];
mergeSort(arr,0,arr.length-1,temp);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr));
}
/**
* 分而治之思想,使用递归去分割数组,然后再合并
* @param arr
* @param left
* @param right
* @param temp
*/
public static void mergeSort(int[] arr,int left,int right,int[] temp){
if (left < right){
int mid = (left+right)/2;
//向左递归分解
mergeSort(arr,left,mid,temp);
//向右递归分解
mergeSort(arr,mid+1,right,temp);
//合并
merge(arr,left,mid,right,temp);
}
}
/**
* 合并算法
* @param arr 排序的原始数组
* @param left 左边有序序列的初始索引
* @param mid 中间索引
* @param right 右边索引
* @param temp 做中转的数组
*/
public static void merge(int[] arr,int left,int mid,int right,int[] temp){
int i = left;
int j = mid + 1;
int t = 0;//用于对temp数组的遍历
//1.
//先把左右两边(有序)的数据按照规则填充到temp数组
//直到左右两边的有序序列,有一边处理完毕为止
while (i <= mid && j <= right){
if (arr[i] <= arr[j]){
temp[t] = arr[i];
t++;
i++;
}else{
temp[t] = arr[j];
t++;
j++;
}
}
//2.//把有剩余数据的一边的数据依次全部填充到temp
while (i <= mid){
temp[t] = arr[i];
t++;
i++;
}
while (j <= right){
temp[t] = arr[j];
t++;
j++;
}
//3.
//将temp数组的元素拷贝到arr
//注意,并不是每次都拷贝所有
//第一次合并 tempLeft = 0 , right = 1 // tempLeft = 2 right = 3 // tL=0 ri=3
t = 0;
int tempindex = left;
while (tempindex <= right){
arr[tempindex] = temp[t];
t++;
tempindex++;
}
}
}
6.7 桶排序(基数排序)
基数排序基本思想
- 将所有待比较数值统一为同样的数位长度,数位较短的数前面补零。然后,从最低位开始,依次进行一次排序。这样从最低位排序一直到最高位排序完成以后, 数列就变成一个有序序列。
2)这样说明,比较难理解,下面我们看一个图文解释,理解基数排序的步骤


/**
* 基数排序
*/
public class RadixSort {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int arr[] = { 53, 3, 542, 748, 14, 214,10};
radixSory(arr);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr));
}
/**
* 获取数组中,最大数的位数
*/
public static int maxDigit(int[] arr){
int max=arr[0];
for (int i = 1; i < arr.length;i++){
if (arr[i] > max){
max = arr[i];
}
}
String maxStr = max + "";
return maxStr.length();
}
/**
* 基数排序
* @param arr
*/
public static void radixSory(int[] arr){
//创建一个桶二维数组,每一行代表一个桶,总共有10个桶
int[][] bucket = new int[10][arr.length];
//创建桶标志数组,标识该桶有多少个有效值
int[] bucketElementCounts = new int[10];
//获取最大有几位数
int maxDigit = maxDigit(arr);
double chu = (double) maxDigit;
chu = Math.pow(10,chu-1);//三位数,截取百位时要除以100,四位数则除以1000
for (int round = 1; round <= chu; round *= 10) {
//截取位数并放入对应桶
for (int j = 0; j < arr.length; j++) {
int digit = arr[j] / round % 10;
//将截取的位数放到对应下标的桶中
int BucketColumn = bucketElementCounts[digit];//得到对应桶中已经放入多少个元素
bucket[digit][BucketColumn] = arr[j];//放入
bucketElementCounts[digit]++;
}
//将桶中的元素再顺序放回arr数组
int index = 0;
for (int m = 0; m < bucket.length; m++) {
if (bucketElementCounts[m] != 0) {//如果改行有数据
//遍历该行
for (int n = 0; n < bucketElementCounts[m]; n++) {
arr[index++] = bucket[m][n];
}
}
//取出改行数据后,将改行数据清零
bucketElementCounts[m] = 0;//将计数器置零
}
}
}
}
该版本基数排序注意:
不支持负数、小数。如果有负数取模后会得到一个负数,比如 -118 ,取模后还是 -118 ,这时候会去找 -118 号桶,实际上并没有该桶,同数组会越界
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException: -8
at zy.code.sort.RadixSort.radixSory(RadixSort.java:57)
at zy.code.sort.RadixSort.main(RadixSort.java:14)
解决方案:可以在取模后,做一个取绝对值 abs的转换,存入桶中
6.8 排序总结

第七章、查找算法
7.1 线性查找
7.2 二分查找
首先进行二分查找前,数组必须是排好序的。
查找思路:
/**
* 二分查找:递归方式
*/
public class BinarySearch {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {1,12,12,12,12,12,45,78,100};
// int index = binarySearch(arr, 0, arr.length - 1, 45);
// System.out.println(index);
List<Integer> indexs = binarySearch2(arr, 0, arr.length - 1, 12);
System.out.println(indexs.toString());
}
/**
* 二分查找,只返回一个找到的索引
*/
public static int binarySearch(int[] arr,int left,int right,int value){
if (left > right){
return -1;
}
int mid = (left + right)/2;
int midValue = arr[mid];
if (value < midValue){
return binarySearch(arr,left,mid-1,value);
}else if(value > midValue){
return binarySearch(arr,mid+1,right,value);
}else{
return mid;
}
}
/**
* 二分查找,返回找到的所有匹配值索引
* 用数组保存索引并返回
*/
public static List<Integer> binarySearch2(int[] arr, int left, int right, int value){
if (left > right){
return new ArrayList<Integer>();
}
int mid = (left + right)/2;
int midValue = arr[mid];
if (value < midValue){
return binarySearch2(arr,left,mid-1,value);
}else if(value > midValue){
return binarySearch2(arr,mid+1,right,value);
}else{
List<Integer> indexlist = new ArrayList<>();
//分别向mid的左、右扫描
int temp = mid;
indexlist.add(mid);
//向左扫描
for (temp = mid -1; temp >=0 && arr[temp] == value; temp--){
indexlist.add(temp);
}
//向右扫描
for (temp = mid +1; temp < arr.length && arr[temp] == value; temp++){
indexlist.add(temp);
}
return indexlist;
}
}
}
7.3 插值查找
-
插值查找算法类似于二分查找,不同的是插值查找每次从自适应的mid位置处开始查找。
-
将折半查找中的求mid 索引的公式做一些改变
根据 差值占比,去确定 mid 的位置

int mid = left + (right – left) * (findVal – arr[left]) / (arr[right] – arr[left]);
注意:差值查找对于分布均匀的数组,比如等差数组的查找效率非常高,一次就能查找到。
但是对于散列程度较大的数组,他的查找效率不一定比二分查找要好。
/**
* 差值查找:依据公式计算mid的占比位置
* 如果是等差数组,不管查找什么,都是一次就找到
*/
public class DValueSearch {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建数组,如果该数组是一个等差数组,不管查找什么,都是一次就找到
int[] arr = new int[100];
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++){
arr[i] = i + 1;
}
int index = DValueSearch(arr, 0, arr.length - 1, 41);
System.out.println(index);
}
/**
* 差值查找算法
*/
public static int DValueSearch(int[] arr,int left,int right,int value){
System.out.println("差值查找了一次");
if (left > right || value < arr[0] || value > arr[arr.length-1]){
return -1;
}
int mid = left + (right - left) * (value - arr[left]) / (arr[right] - arr[left]);
int midValue = arr[mid];
if (value < midValue){
return DValueSearch(arr,left,mid-1,value);
}else if (value > midValue){
return DValueSearch(arr,mid+1,right,value);
}else{
return mid;
}
}
}
7.4 斐波那契黄金分割查找

代码思路:
- 第一步:拿到一个斐波那契数组
- 第二步:找到 对应的 f[k] ,使得 f[k] 的值大于等于 arr长度。这个 k值非常重要。
- 第三步:创建一个 中间数组temp,temp的大小等于黄金长度 f[k] ,而temp的数据来自arr
- 第四步:对temp数组操作
- 计算黄金分割点 mid = low + f [k-1] -1
- 比较findValue 与 temp[mid] 的daxiao
- 如果不等于黄金分割点的值,继续分割,重复第四步。
注意:重复第四步时, 对 k 的变化。
- 如果下次分割的是前半部分。前半部长度等于 f [k-1 ] ------>对应的 k–
- 如果下次分割的是后半部分。后半部长度等于 f [k-2] ------>对应的 k -= 2
/**
* 斐波那契查找:黄金分割点
*/
public class FibonacciSearch {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int [] arr = {1,8, 10, 89, 1000, 1234};
System.out.println("index=" + fibSearch(arr, 8));// 0
}
/**
* 获取一个长度为 n 的 斐波那契数组
*/
public static int[] fib(int m){
int[] f = new int[m];
f[0] = 1;
f[1] = 1;
for (int i = 2; i < m; i++){
f[i] = f[i-1] + f[i-2];
}
return f;
}
/**
* 斐波那契黄金分割点查找
* f[k] > arr.length ,f[k]为一个黄金长度,在查找前要将arr填充成黄金长度
*/
public static int fibSearch(int[] arr,int value){
int low = 0;
int high = arr.length-1;
int mid = 0;
int k = 0;
int[] f = fib(20);
//获取到斐波那契分割数值的下标.f[k]是一个黄金长度
while (f[k] < arr.length){
k++;
}
//f[k]的值可能大于数组arr的长度
// 为了使得数组个数要达到 f[k]-1,因此需要把原数组arr填充一下
//temp后面多出来的元素会默认用0填充
int[] temp = Arrays.copyOf(arr,f[k]);
//让temp比arr多出的元素,用arr最后一个元素填充
for (int i = high + 1; i < f[k]; i++){
temp[i] = arr[high];
}
//查找
while (low <= high){
mid = low + f[k - 1] - 1;//计算黄金分割点
if (value < temp[mid]){
high = mid - 1;
k--;//往前有f[k-1]个元素,为了下次循环,计算折断后的新的黄金分割点
}else if (value > temp[mid]){
low = mid + 1;
k -= 2;//往后有f[k-2] 个元素,计算折断后的新的黄金分割点
}else{
//找到,返回下标
if (mid <= high){
return mid;
}else{
return high;//还记得填充数组temp的长度其实是比arr大的吗
}
}
}
return -1;
}
}
第八章、哈希表
哈希表原理

谷歌上机题
看一个实际需求,google公司的一个上机题
有一个公司,当有新的员工来报道时,要求将该员工的信息加入(id,性别,年龄,住址.),当输入该员工的id时,要求查找到该员工的 所有信息
要求不使用数据库,尽量节省内存,速度越快越好。

/**
* 链表结点
* emp代表员工信息
*/
public class Emp {
public int id;
public String name;
public Emp next;
public Emp(int id, String name) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
}
}
/**
* 使用链表,模拟哈希表结构
*/
public class EmpLinkedList {
private Emp head;
public Emp getHead() {
return head;
}
/**
* 添加员工
* 1。假定 id是自增长的,添加时默认在链表尾部追加
*
* @param emp
*/
public void add(Emp emp){
if (head == null){
head = emp;
return;
}
//遍历到链表尾部
Emp temp = head;
while (temp.next != null){
temp = temp.next;
}
temp.next = emp;
}
/**
* 遍历链表
*/
public void list(){
if (head == null){
System.out.println("当前链表为空");
return;
}
System.out.println("当前链表的信息如下:");
Emp temp = head;
while (temp != null){
System.out.printf("emp[id=%d,name=%s] \t",temp.id,temp.name);
temp = temp.next;
}
}
/**
* 查找
*/
public Emp findById(int id){
if (head == null){
System.out.println("无法查找,因为当前链表为空");
return null;
}
Emp temp = head;
while (temp != null && temp.id != id){
temp = temp.next;
}
if (temp == null){
return null;
}else{
return temp;
}
}
}
/**
* 哈希表结构
*/
public class EmpHashTable {
private EmpLinkedList[] empLinkedListArray;//存放多条链表的数组结构
private int size;
public EmpHashTable(int size) {
this.size = size;
empLinkedListArray = new EmpLinkedList[size];//初始化哈希表的大小,即管理多少条链表
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++){
EmpLinkedList empLinkedList = new EmpLinkedList();
empLinkedListArray[i] = empLinkedList;
}
}
/**
* 散列函数
*/
public int hashFun(int id){
return id % size;
}
/**
* 添加员工
*/
public void add(Emp emp){
int linkedListIndex = hashFun(emp.id);
empLinkedListArray[linkedListIndex].add(emp);
}
/**
* 遍历哈希表
*/
public void list(){
for (int i = 0; i < empLinkedListArray.length;i++){
System.out.print(i + "号:");
empLinkedListArray[i].list();
System.out.println();
}
}
/**
* 根据id查找
*/
public void findById(int id){
int index = hashFun(id);
Emp emp = empLinkedListArray[index].findById(id);
if (emp != null){
System.out.printf("在 %d 号链表找到\t",index);
System.out.printf("emp[id=%d,name=%s] \n",emp.id,emp.name);
}else{
System.out.println("没有找到该员工");
}
}
}
测试类
/**
* 哈希表结构
* 1. 可以方便的管理多条链表
* 2. 根据 hash散列函数,计算添加对象应该加到哪一条链表当中去
*/
public class HashTableDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
EmpHashTable empHashTable = new EmpHashTable(7);
//写一个简单的菜单
String key = "";
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
while(true) {
System.out.println("================");
System.out.println("add: 添加雇员");
System.out.println("list: 显示雇员");
System.out.println("find: 查找雇员");
System.out.println("exit: 退出系统");
key = scanner.next();
switch (key) {
case "add":
System.out.println("输入id");
int id = scanner.nextInt();
System.out.println("输入名字");
String name = scanner.next();
//创建 雇员
Emp emp = new Emp(id, name);
empHashTable.add(emp);
break;
case "list":
empHashTable.list();
break;
case "find":
System.out.println("请输入要查找的id");
id = scanner.nextInt();
empHashTable.findById(id);
break;
case "exit":
scanner.close();
System.exit(0);
default:
break;
}
}
}
}
第九章、树与二叉树
9.1 二叉树的概念
为什么需要树这种数据结构呢?
- 对比 数组,它是顺序存储的有一定的顺序,检索时方便,但是插入、删除时要发生整体移动,效率低
- 对比 链表,他在物理上不是顺序的,插入、删除不用移动,但是在查找检索时。都要从头到尾去扫描,效率低。
- 树的示意图如如下,通过增删改、查,可以对比出树的效率优点

有关树的数学知识:
h 层的满二叉树,叶子结点个数:2 * h - 1 .(满二叉树的所有叶子结点都在最后一层)
9.2 二叉树的遍历

/**
* 二叉树的结点结构定义
*/
public class HeroNode {
public int no;
public String name;
public HeroNode left;
public HeroNode right;
public HeroNode(int no, String name) {
this.no = no;
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "HeroNode[no=" + no + "," + "name=" + name + "]";
}
}
/**
* 二叉树的遍历
*/
public class BinaryTree {
public HeroNode root = new HeroNode(0,"");
/**
* 前序遍历
*/
public static void preOrder(HeroNode root){
if (root != null){
System.out.println(root);
preOrder(root.left);
preOrder(root.right);
}
}
/**
* 中序遍历
*/
public static void inOrder(HeroNode root){
if (root != null){
inOrder(root.left);
System.out.println(root);
inOrder(root.right);
}
}
/**
* 后序遍历
*/
public static void postOrder(HeroNode root){
if (root != null){
postOrder(root.right);
System.out.println(root);
postOrder(root.left);
}
}
/**
* 前序查找
*/
public static HeroNode preOrderSearch(HeroNode root,int no){
HeroNode resultNode = null;
if (root != null){
if (root.no == no){
return root;
}
//向左遍历
resultNode = preOrderSearch(root.left, no);
if (resultNode != null){
return resultNode;
}
//向右遍历
resultNode = preOrderSearch(root.right,no);
}
return resultNode;
}
/**
* 中序查找
*/
public static HeroNode inOrderSearch(HeroNode root,int no){
HeroNode resultNode = null;
if (root != null){
//向左遍历
resultNode = inOrderSearch(root.left,no);
if (resultNode != null){
return resultNode;
}
if (root.no == no){
return root;
}
//向右递归
resultNode = inOrderSearch(root.right, no);
}
return resultNode;
}
/**
* 后序查找
*/
public static HeroNode postOrderSearch(HeroNode root,int no){
HeroNode resultNode = null;
if (root != null){
//向右递归
resultNode = postOrderSearch(root.right, no);
if (resultNode != null){
return resultNode;
}
//向左递归
resultNode = postOrderSearch(root.left,no);
if (resultNode != null){
return resultNode;
}
//比较自身
if (root.no == no){
return root;
}
}
return resultNode;
}
}
9.3 二叉树删除结点
删除时要注意:
- 二叉树的指针是单向的,在删除节点时,我们不能判断当前结点是否需要删除而删除之,而是需要 “ 断键”,找到父节点,判断它的子节点是否需要删除
- 在这里如果删除一个非叶节点会删除该子树的,鸡肋,但是以后学到二叉排序树时再做扩展、这里理解思路了就行
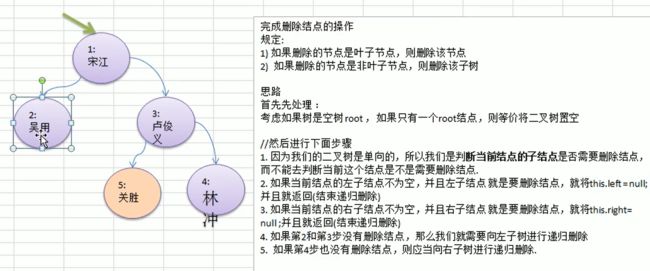
/**
* 删除结点
* 有点问题,无法删除根结点,理解思路为主
*/
public static void deleteNode(HeroNode root,int no){
if (root != null){
//判断左节点
if (root.left != null && root.left.no == no){
root.left = null;
return;
}
//判断右节点
if (root.right != null && root.right.no == no){
root.right = null;
return;
}
//向左递归
if (root.left != null){
deleteNode(root.left,no);
}
//向右递归
if (root.right != null){
deleteNode(root.right,no);
}
}
}

高级的删除节点方法,删除节点后,父节点的指针和哪个节点链接起来
9.4 顺序二叉树
将满二叉树与数组,两种存储方式的转换


/**
* 数组与二叉树的转换
*/
public class ArrBinaryTree {
private int[] arr;
public ArrBinaryTree(int[] arr) {
this.arr = arr;
}
/**
* 以前序遍历的方式输出数组元素
*/
public void preOrder(int index){
//参数判空
// 如果数组为空,或者arr.length = 0
if (arr == null || arr.length == 0){
System.out.println("数组为空,不能按照二叉树的前序遍历方式");
return;
}
//输出当前元素
System.out.println(arr[index]);
//向左子树递归
if (index * 2 + 1 < arr.length){
preOrder(2 * index + 1);
}
//向右递归
if (index * 2 + 2 < arr.length){
preOrder(index * 2 + 2);
}
}
}
顺序存储二叉树的重要性!
八大排序算法中的堆排序,就会使用到顺序存储二叉树, 关于堆排序,以后就会讲解到了。但是不要觉得现在的顺序存储简单就眼高手低了。
9.5 线索化二叉树
基本介绍:二叉树中有很多空指针,我们可以将空指针利用起来,指向当前结点的前驱或者后继。这样的二叉树就叫做线索化二叉树。

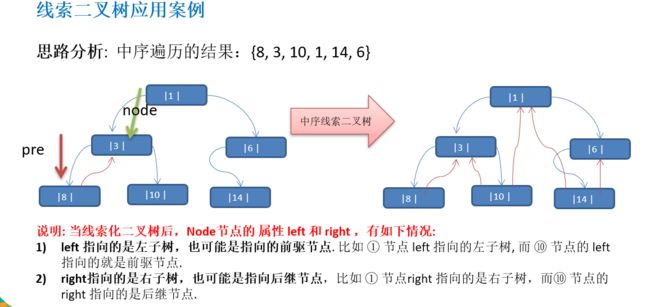
/**
* 线索化二叉树
*/
public class ThreadedBinaryTree {
private HeroNode root;
public HeroNode pre = null;//用于在线索化时保存好前一个结点
public void setRoot(HeroNode root) {
this.root = root;
}
public void threadByInOrder(){
this.threadByInOrder(root);
}
/**
* 线索化二叉树
* 以中序遍历的次序线索化
*/
public void threadByInOrder(HeroNode node){
if (node == null){
return;
}
//1.先线索化左子树
threadByInOrder(node.left);
//2.线索化当前结点
//2.1处理当前结点的前驱
if (node.left == null){
node.left = pre;
node.leftType = 1;//此时左指针的类型就变了
}
//2.2处理当前结点的后继(变相问题:处理上一个节点pre结点的后继)
//由于我们已经定义了pre,变相的问题就是让上一个结点pre的后继指向当前结点,递归进行时一个后继链就会生成
if (pre != null && pre.right == null){
pre.right = node;
pre.rightType = 1;
}
//3.处理完结点后,就可以表示当前结点已变成上一个结点了(线索化当前节点完成!)
pre = node;
//3.线索化右子树
threadByInOrder(node.right);
}
}
注意:在处理当前结点的后继时,实际是处理上一个节点的后继链,
因为我们无法预判下一个将访问哪一个,只能是递归退栈,才知道下一个访问哪一个

遍历线索化二叉树
思路:
首先找到线索的开始处(入口),按图索骥的顺着指针指向,找到下一个节点
/**
* 遍历线索化的二叉树(中序方式)
*/
public void threadedList(){
HeroNode node = root;
while (node != null){
//循环找到左子树的第一个leftType ==1的结点(或者左指针==null的结点),该节点就是线索化的初始位置
while (node.leftType == 0){
node = node.left;
}
//输出当前结点
System.out.println(node);
//循环找到当前结点的后继,并同时输出后继
while (node.rightType == 1){
node = node.right;
System.out.println(node);
}
//根据后继的线索遍历完之后,到一个既有左节点又有右节点的结点为止
//使用新的根结点,并遍历它的右子树
node = node.right;
}
}

通过下图的指示可以自己一步步分析一下,父节点(中间结点)必定会通过在循环遍历左子树的时候随着输出。

9.5 堆排序
博客园:堆排序详解
概念弄懂:什么是大顶堆、小顶堆
堆分为最大堆和最小堆,其实就是完全二叉树。最大堆要求节点的元素都要不小于其孩子,最小堆要求节点元素都不大于其左右孩子,两者对左右孩子的大小关系不做任何要求,其实很好理解。有了上面的定义,我们可以得知,处于最大堆的根节点的元素一定是这个堆中的最大值。
其实我们的堆排序算法就是抓住了堆的这一特点,每次都取堆顶的元素,将其放在序列最后面,然后将剩余的元素重新调整为最大堆,依次类推,最终得到排序的序列。
注意了,现在你应该了解堆排序的思想了,给你一串列表,你也能写出&说出堆排序的过程。
在写算法的过程中,刚开始我是很懵比。后来终于看懂了。
请特别特别注意: 初始化大顶堆时 是从最后一个有子节点开始由下往上调整最大堆。
而堆顶元素(最大数)与无序堆最后一个数交换后,需再次调整成大顶堆,此时是从上往下调整的。
不管是初始大顶堆的从下往上调整,还是堆顶堆尾元素交换,每次调整都是从父节点、左孩子节点、右孩子节点三者中选择最大者跟父节点进行交换,交换之后都可能造成被交换的孩子节点不满足堆的性质,因此每次交换之后要重新对被交换的孩子节点进行调整。我在算法中是用一个while循环来解决的
总结下:
就是你在交换时一定要注意的三个点
-
初始化大顶堆,
-
交换父节点与孩子节点之后,要注意新的孩子会不满足该子树的堆性质,要进行稳定
-
将堆顶与最后一个元素交换之后,
-
要注意新的堆顶会不满足该树的堆性质,要从上往下稳定。
-
初始化大顶堆只初始化一次,是由下往上的
-
调整大顶堆,在交换的过程会调整多次,是由上往下的。
代码如下,关键方法是 adjustHeap ,调整堆,每次调整都是向下得,和孩子乃至孙子比较。
package sortdemo;
import java.util.Arrays;
/**
* Created by chengxiao on 2016/12/17.
* 堆排序demo
*/
public class HeapSort {
public static void main(String []args){
int []arr = {9,8,7,6,5,4,3,2,1};
sort(arr);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr));
}
public static void sort(int []arr){
//1.构建大顶堆
for(int i=arr.length/2-1;i>=0;i--){
//从第一个非叶子结点从下至上,从右至左调整结构
adjustHeap(arr,i,arr.length);
}
//2.交换堆顶元素与末尾元素
for(int j=arr.length-1;j>0;j--){
swap(arr,0,j);//将堆顶元素与末尾元素进行交换
adjustHeap(arr,0,j);//重新对堆进行调整
}
}
/**
* 调整大顶堆(仅是调整过程,建立在大顶堆已构建的基础上)
* @param arr
* @param i
* @param length
*/
public static void adjustHeap(int []arr,int i,int length){
int temp = arr[i];//先取出当前元素i
//temp变量始终指向要调整的节点,向下调整的过程中,会将当前节点调整到一个最终位置。
for(int k=i*2+1;k<length;k=k*2+1){//从i结点的左子结点开始,也就是2i+1处开始
//如果左子结点小于右子结点,k指向右子结点
if(k+1<length && arr[k]<arr[k+1]){
k++;
}
//如果子节点大于父节点
if(arr[k] >temp){
arr[i] = arr[k];//要调整的节点的值被子节点覆盖
i = k;//更改arr[i]指向的位置和值是子节点
//?这样一来,子节点的值还是原来的子节点的值?没变呀?
//画图理解,本次循环时,待调整的节点会被孩子的值覆盖,待调整节点指向那个孩子,
//下次循环会对比孙子,如果孙子还比temp大,则孩子的值会被孙子替换,而孙子还是孙子,
//直到最终位置,循环结束孙子会被temp的值覆盖
}else{
break;
}
}
//循环向下遍历所有的子节点后,arr[i]最终指向最终要交换的子节点的位置与值
arr[i] = temp;//将temp值放到最终的位置
}
/**
* 交换元素
* @param arr
* @param a
* @param b
*/
public static void swap(int []arr,int a ,int b){
int temp=arr[a];
arr[a] = arr[b];
arr[b] = temp;
}
}
详细关注
//如果子节点大于父节点
if(arr[k] >temp){
arr[i] = arr[k];
i = k;
把较大得值赋给当前结点,
i指向k,继续向下比较,也许孙子系还有比待调整结点大得!
9.6 赫夫曼树
https://baijiahao.baidu.com/s?id=1663514710675419737&wfr=spider&for=pc
https://blog.csdn.net/bruce_6/article/details/38656413
权重:每个叶子结点有一个权重
路径长度:从根结点到该叶子结点所经过的边
结点的带权路径长度,是指树的根结点到该结点的路径长度,和该结点权重的乘积。
树的带权路径长度:在一棵树中,所有叶子结点的带权路径长度之和,被称为树的带权路径长度,也被简称为WPL。
public class HuffmanTree {
public static class Node<E> {
E data;
double weight;
Node leftChild;
Node rightChild;
public Node(E data, double weight) {
super();
this.data = data;
this.weight = weight;
}
public String toString() {
return "Node[data=" + data + ", weight=" + weight + "]";
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Node> nodes = new ArrayList<Node>();
nodes.add(new Node("A", 40.0));
nodes.add(new Node("B", 8.0));
nodes.add(new Node("C", 10.0));
nodes.add(new Node("D", 30.0));
nodes.add(new Node("E", 10.0));
nodes.add(new Node("F", 2.0));
Node root = HuffmanTree.createTree(nodes);
System.out.println(breadthFirst(root));
}
/**
* 构造哈夫曼树
*
* @param nodes
* 节点集合
* @return 构造出来的哈夫曼树的根节点
*/
private static Node createTree(List<Node> nodes) {
// 只要nodes数组中还有2个以上的节点
while (nodes.size() > 1) {
quickSort(nodes);
//获取权值最小的两个节点
Node left = nodes.get(nodes.size()-1);
Node right = nodes.get(nodes.size()-2);
//生成新节点,新节点的权值为两个子节点的权值之和
Node parent = new Node(null, left.weight + right.weight);
//让新节点作为两个权值最小节点的父节点
parent.leftChild = left;
parent.rightChild = right;
//删除权值最小的两个节点
nodes.remove(nodes.size()-1);
nodes.remove(nodes.size()-1);
//将新节点加入到集合中
nodes.add(parent);
}
return nodes.get(0);
}
/**
* 将指定集合中的i和j索引处的元素交换
*
* @param nodes
* @param i
* @param j
*/
private static void swap(List<Node> nodes, int i, int j) {
Node tmp;
tmp = nodes.get(i);
nodes.set(i, nodes.get(j));
nodes.set(j, tmp);
}
/**
* 实现快速排序算法,用于对节点进行排序
*
* @param nodes
* @param start
* @param end
*/
private static void subSort(List<Node> nodes, int start, int end) {
if (start < end) {
// 以第一个元素作为分界值
Node base = nodes.get(start);
// i从左边搜索,搜索大于分界值的元素的索引
int i = start;
// j从右边开始搜索,搜索小于分界值的元素的索引
int j = end + 1;
while (true) {
// 找到大于分界值的元素的索引,或者i已经到了end处
while (i < end && nodes.get(++i).weight >= base.weight)
;
// 找到小于分界值的元素的索引,或者j已经到了start处
while (j > start && nodes.get(--j).weight <= base.weight)
;
if (i < j) {
swap(nodes, i, j);
} else {
break;
}
}
swap(nodes, start, j);
//递归左边子序列
subSort(nodes, start, j - 1);
//递归右边子序列
subSort(nodes, j + 1, end);
}
}
public static void quickSort(List<Node> nodes){
subSort(nodes, 0, nodes.size()-1);
}
//广度优先遍历
public static List<Node> breadthFirst(Node root){
Queue<Node> queue = new ArrayDeque<Node>();
List<Node> list = new ArrayList<Node>();
if(root!=null){
//将根元素加入“队列”
queue.offer(root);
}
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
//将该队列的“队尾”元素加入到list中
list.add(queue.peek());
Node p = queue.poll();
//如果左子节点不为null,将它加入到队列
if(p.leftChild != null){
queue.offer(p.leftChild);
}
//如果右子节点不为null,将它加入到队列
if(p.rightChild != null){
queue.offer(p.rightChild);
}
}
return list;
}
}
9.7 赫夫曼编码
9.8 二叉排序树
9 .9 平衡二叉树
第十章、多路查找树
10.1 二叉树与B树
10.2 2-3树
10.3 B树、B+树
第十一章、图的搜索
11.1 图的常见概念
结点
边(弧)
邻接矩阵
邻接表


public class Graph {
private ArrayList<String> vertexList;
private int[][] edges;
private int numOfEdges;//边的数目
public Graph(int n) {
edges = new int[n][n];
vertexList = new ArrayList<String>(n);
numOfEdges = 0;
}
/**
* 插入结点
* @param vertex
*/
public void insertVertex(String vertex){
vertexList.add(vertex);
}
/**
* 插入边
* @param v1 表示点的下标
* @param v2 表示点的下标
* @param weight 边的权值
*/
public void insertEdge(int v1,int v2,int weight){
edges[v1][v2] = weight;
edges[v2][v1] = weight;//无向图
numOfEdges ++;
}
/**
* 返回结点个数
* @return
*/
public int getNumOfVertex(){
return vertexList.size();
}
/**
* 返回边数
* @return
*/
public int getNumOfEdges(){
return numOfEdges;
}
/**
* 根据索引返回图中的结点
* @param i
* @return
*/
public String getVertexByIndex(int i){
return vertexList.get(i);
}
/**
* 返回任意两节点之间边的权值
* @param v1
* @param v2
* @return
*/
public int getWeight(int v1,int v2){
return edges[v1][v2];
}
/**
* 打印当前图对应的邻接矩阵
*/
public void showGraph(){
for (int[] link : edges){
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(link));
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Graph graph = new Graph(5);
String[] vertexs = {"A","B","C","D","E"};
//添加结点
for (String vertex : vertexs){
graph.insertVertex(vertex);
}
//添加边
graph.insertEdge(0,1,1);
graph.insertEdge(0,2,1);
graph.insertEdge(1,2,1);
graph.insertEdge(1,3,1);
graph.insertEdge(1,4,1);
graph.showGraph();
}
11.2 图的深度优先搜索(递归)
含有图解:图的深度优先遍历和广度优先遍历
算法的思想:
从图中的某一个顶点x出发,访问x,然后遍历任何一个与x相邻的未被访问的顶点y,再遍历任何一个与y相邻的未被访问的顶点z……依次类推,直到到达一个所有邻接点都被访问的顶点为止;
然后,依次回退到尚有邻接点未被访问过的顶点,重复上述过程,直到图中的全部顶点都被访问过为止。
算法的实现:
使用邻接矩阵保存边,一维数组做是否访问过的标记
(1)先打印当前结点
(2)然后通过getFirstNeighbor方法得到当前结点的第一个邻接结点w,
- 若w存在,且没有访问过,则以w做递归,重复回到(1)
- 若w存在,且已经访问过,则w后移getNextNeighbor 访问当前结点的下一个邻接结点
public void dfs(){
//遍历所有结点进行深度搜索
for (int i = 0; i < getNumOfVertex(); i ++){
if (!isVisited[i]){
dfs(isVisited,i);
System.out.println();
}
}
}
public void dfs(boolean[] isVisited, int i){
System.out.print(getVertexByIndex(i) + " -> ");
isVisited[i] = true;
int w = getFirstNeighbor(i);
while (w != -1){
//存在邻接结点
if (!isVisited[w]){
//递归纵向深度遍历
dfs(isVisited,w);
}
//没有进入if语句或者递归结束回退,说明w都已被访问过
//得到i的另一个邻接结点
w = getNextNeighbor(i,w);
}
}
/**
* 获取结点下标i的第一个邻接结点
* @param i
* @return
*/
public int getFirstNeighbor(int i){
for (int j = 0; j < vertexList.size();j ++){
if (edges[i][j] > 0){
return j;
}
}
return -1;
}
/**
* 根据前一个邻接结点的下标来获取v1的下一个邻接结点
* @param v1 基准结点
* @param v2 邻接结点
* @return
*/
public int getNextNeighbor(int v1, int v2){
for (int j = v2 + 1; j < vertexList.size(); j++){
if (edges[v1][j] > 0){
return j;
}
}
return -1;
}
打印结果:
深度优先搜索路径:
A -> B -> C -> D -> E ->
11.3 图的深度优先搜索(借助堆栈)
参考资料:
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_38410730/article/details/79587759
11.4 图的广度优先搜索(1)
算法的思想
从图中的某一个顶点x出发,访问x,然后访问与x所相邻的所有未被访问的顶点x1、x2……xn,接着再依次访问与x1、x2……xn相邻的未被访问的所有顶点。依次类推,直至图中的每个顶点都被访问。
算法实现的思想
广度优先遍历背后基于队列,下面介绍一下具体实现的方法:
- 访问起始顶点,并将插入队列;
- 从队列中删除队头顶点,访问它的相邻结点,将与其相邻的未被访问的结点插入队列中;
- 重复第二步,直至队列为空。
未被访问的顶点怎么识别呢?利用visited数组来进行标记。
public void bfs(){
for (int i = 0; i < vertexList.size(); i ++){
if (!isVisited[i]){
bfs(isVisited,i);//根据当前结点作为基准进行广度优先遍历
System.out.println();
}
}
}
/**
* 广度优先搜索
* @param isVisited
* @param i 当前结点的下标
*/
public void bfs(boolean[] isVisited,int i){
//初始化一个队列
LinkedList<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();
System.out.print(getVertexByIndex(i) + " -> ");//打印当前结点
isVisited[i] = true;//标记已经访问过
queue.addLast(i);//将当前结点加入队列
//当队列不为空时,一直做如下操作
while (!queue.isEmpty()){
//取出队头结点
Integer u = queue.removeFirst();
//得到队头结点的第一个邻接点
int w = getFirstNeighbor(u);
while (w != -1){
if (!isVisited[w]){
//u的第一个邻接点没有访问过
System.out.print(getVertexByIndex(w) + "->");
isVisited[w] = true;
queue.addLast(w);//邻接结点入队
}
//u的第一个邻接点已经访问过,则获取下一个邻接点,继续循环再判断并入队
w = getNextNeighbor(u,w);
}
}
}
打印结果
广度优先搜索路径:
A -> B->C->D->E->
总结:
深度优先遍历。类似于栈,有递归与回退思想,是一种纵向的深度
广度优先遍历。借助队列,有分层的思想,是一种横向的宽度