数据结构与算法分析-排序
作者:xiabodan 出处:http://blog.csdn.net/xiabodan
排序算法(Sorting Algorithm)是计算机算法的一个组成部分。也是程序=算法+数据结构中的一部分(算法)。
实验平台:raspberry 2 B + Ubuntu Mate
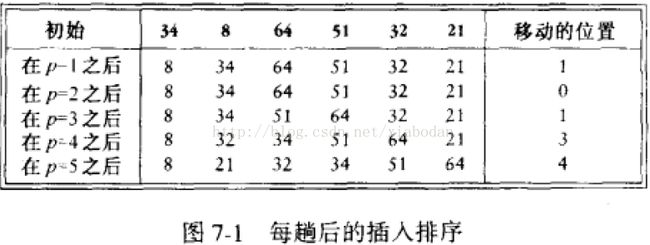
插入排序
//插入排序
//stable
//O(N^2) comparisons and swaps
//Adaptive: O(n) time when nearly sorted
//Very low overhead
void insertion(elementtype A[],int n)
{
int p = 0 ;
int j = 0 ;
for(p=1;p0&&A[j-1]>tem;j--)
{
A[j] = A[j-1];
}
A[j] = tem;
}
}
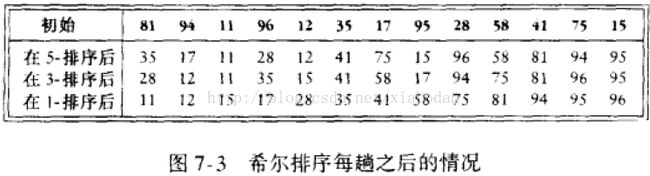
希尔排序
//希尔排序
//O(N^3/2) unstable
//Adaptive: O(N.lg(N)) time when nearly sorted
//Very low overhead
void shell(elementtype A[],int n)
{
int i,j,inc;
elementtype tem;
for(inc=N/2;inc>0;inc /=2)
{
for(i=inc;i=inc;j-=inc)
{
if(tem 冒泡排序
//冒泡排序
//O(N^2) stable
//Adaptive: O(N) time when nearly sorted
//Very low overhead
void bubble(elementtype A[],int n)
{
int flag = 1;
int i,j;
for(i=0;ii;j--)
{
if(A[j]
选择排序
选择排序,外循环i从A【0】-A【N-1】,内循环从A【i+1】-A【N-1】,内循环负责找出A【i+1】-A【N-1】中比A【i】小的元素,并用一个k去标记它的位置,在内循环结束的时候将A【i】与A【k】互换,那么A【i+1】-A【N-1】中比A【i】小的元素A【k】就被放在了A【i】这个位置。也就是选择一个最小的放在A【i】这个位置。选择排序的比较次数是O(N^2),但是交换次数却只有O(N)。因为内循环每次仅仅是标记最小元素,并没有实时的去交换元素。
//选择排序
//Not stable
//O(1) extra space
//Θ(n2) comparisons
//Θ(n) swaps
//Not adaptive
void selection(elementtype A[],int n)
{
int i,j;
int k;
for(i=0;i
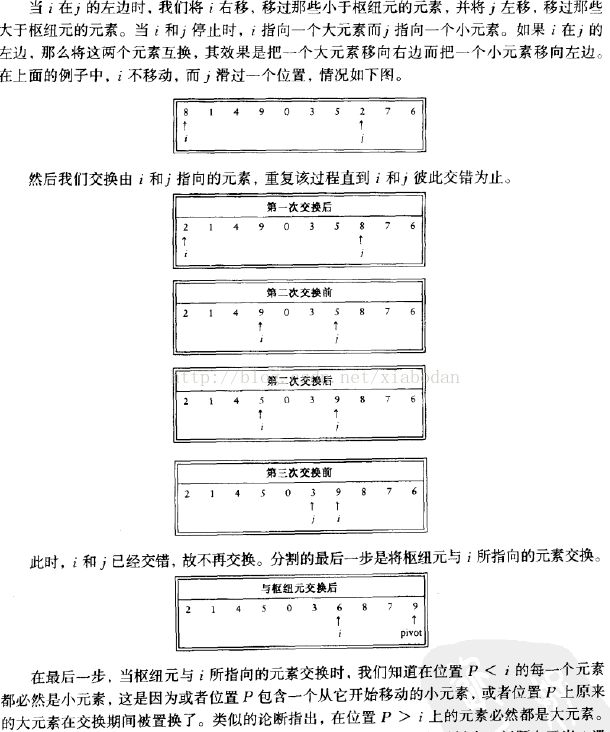
快速排序
另外一个问题是枢纽元素pivot的选择,选择枢纽元素pivot的方法有很多,一种常用的就是三数中值算法。也就是选取集合A首尾以及中位元素,然后选取这三个数的中位数作为枢纽元素pivot。
//快速排序
//not Stable
//O(lg(n)) extra space (see discussion)
//O(n2) time, but typically O(n·lg(n)) time
//Not adaptive
#define CUT 3
elementtype median3(elementtype A[],int left ,int right)
{
int center = (left +right) / 2;
if(A[left]>A[center])
swap(&A[left],&A[center]);
if(A[left]>A[right])
swap(&A[left],&A[right]);
if(A[center]>A[right])
swap(&A[center],&A[right]);
swap(&A[center],&A[right-1]);
return A[right-1];
}
void Qsort(elementtype A[],int left, int right)
{
int i,j;
elementtype pivot;
if(left + CUT<= right)
{
pivot = median3(A,left,right); //select middle element as pivot
i = left;j = right-1;
for(;;)
{
while(A[++i]pivot){}
if(i
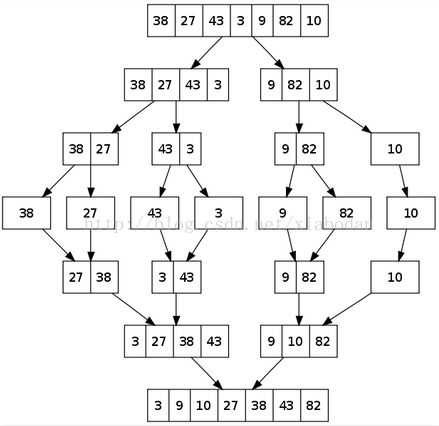
归并排序
//归并排序
//Stable
//(n) extra space for arrays (as shown)
//(lg(n)) extra space for linked lists
//(n·lg(n)) time
//Not adaptive
//Does not require random access to data
void Merge(elementtype A[],elementtype TA[],int lpos,int rpos,int rightend)
{
int leftend = rpos-1;
int numelement = rightend -lpos + 1;
int tpos = lpos;
while(lpos<=leftend && rpos<=rightend)
if(A[lpos] <= A[rpos])
TA[tpos++] = A[lpos++];
else
TA[tpos++] = A[rpos++];
while(lpos<=leftend)
TA[tpos++] = A[lpos++];
while(rpos<=rightend)
TA[tpos++] = A[rpos++];
int i = 0;
for(i=0;i
typedef int elementtype;
#define N 10//other function used for debug
void print(elementtype A[],int n)
{
int i = 0;
printf("after sorting\n");
for(i=0;ivoid swap(elementtype *a,elementtype *b)
{
elementtype tem = *a;
*a = *b;
*b = tem;
}未完待续.......
总结:
冒泡和插入是慢慢找到最大或最小的放在第一个去;选择直接找到最大或者最小放到第一个;归并、快排都用了devide-merge-conquer(分治策略),期间还是会用到前面提到的那几种最基本的算法;堆排序用了选择排序的思想;桶排序用了空间换时间的方法;万变不离其宗。
参考:
数据结构与算法分析-C语言描述[M],机械工业出版社
博客园 vamei的博客:http://www.cnblogs.com/vamei/archive/2013/03/12/2948847.html
天津城市学院一个精品课程:http://sjjp.tjuci.edu.cn/sjjg/datastructure/ds/web/paixu/paixu8.1.1.1.htm
国外一个排序网站有动画,分析,为代码: http://www.sorting-algorithms.com/
一个在国内不算太有名的国外网站,里面的内容貌似不止算法:
Programming problems and Competitions :: HackerRank
一个俄罗斯的ACM竞赛网站,不定期有算法比赛:
Codeforces
据说是某个Top2大学为后台的算法网站,比较简单,而且一直在定期更新算法入门教程,有定期比赛:
hihoCoder
hdu主办的ACM算法竞赛网站,定期有比赛:
Welcome to BestCoder
宇宙级题库:
UOJ - Universal Online Judge
北大:http://poj.org/
杭电:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/
华中科技大学:http://acm.hust.edu.cn/vjudge/toIndex.action