protocol buffer协议的两种常用框架protobuf和nanopb
目录
目录
什么是protocol buffer
1.protobuf
1.1安装
1.2使用
2.nanopb(支持c语言)
2.1解压压缩包
2.2使用nanopb
3.3python解析nanopb生成的二进制数据
什么是protocol buffer
百度百科解释如下
protocolbuffer(以下简称PB)是google 的一种数据交换的格式,它独立于语言,独立于平台。google 提供了多种语言的实现:java、c#、c++、go 和 python,每一种实现都包含了相应语言的编译器以及库文件。
由于它是一种二进制的格式,比使用 xml 进行数据交换快许多。可以把它用于分布式应用之间的数据通信或者异构环境下的数据交换。
作为一种效率和兼容性都很优秀的二进制数据传输格式,可以用于诸如网络传输、配置文件、数据存储等诸多领域。
PB和json,xml比较:
一条消息数据,用protobuf序列化后的大小是json的10分之一,xml格式的20分之一,是二进制序列化的10分之一,总体看来PB的优势还是很明显的。
简单说来PB的主要优点就是:简单,快。缺点:可读性差
PB协议处理常用的两种框架protobuf和nanopb进行介绍
1.protobuf
protobuf是PB协议使用较广的一个框架,支持C++,JAVA,Python,Ruby,Go,PHP等多种语言,具体如下:
1.1安装
(1)protobuf源码git地址
https://gitcode.net/mirrors/google/protobuf?utm_source=csdn_github_accelerator
(2)protobuf各发行版本地址
https://github.com/protocolbuffers/protobuf/tags
例如下载protobuf-all-3.6.1.tar.gz
![]()
tar -zxvf protobuf-all-3.6.1.tar.gz
cd protobuf-3.6.1
检测安装环境和生成Makefile
./configure --prefix=/home/tiger/protobuf-3.6.1/protobuf 
编译和安装
make && make install

安装完成后在目录/home/tiger/protobuf-3.6.1/protobuf下可以看到三个文件夹:
![]()
bin:存放protoc可执行程序
include:调用protobuf所需头文件
lib:调用protobuf所需库文件
查看protoc版本:
cd bin
./protoc --version
1.2使用
参考文章:
java中使用protobuf总结
python中读写Protobuf总结
python中protobuf和json互相转换应用
2.nanopb(支持c语言)
protobuf支持多种语言,但是却不支持纯C语言,而且protobuf的使用笨重,在一些内存紧张的嵌入式设备上不能使用,nanopb是谷歌协议缓冲数据格式的一个纯C实现。它的目标是32位微控制器,但也适用于其他嵌入式系统的严格(< 10kB ROM,< 1kB RAM)内存限制。
源码下载地址如下:
https://jpa.kapsi.fi/nanopb/download/
2.1解压压缩包
此处以版本0.3.9.4为例子进行说明
tar -zxvf nanopb-0.3.9.4-linux-x86.tar.gz
2.2使用nanopb
cd nanopb-0.3.9.4-linux-x86
如下7个文件是nanopb用来处理protocol buffer协议的核心文件
pb_common.c
pb_common.h
pb_decode.c
pb_decode.h
pb_encode.c
pb_encode.h
pb.h定义协议:
metric.proto
syntax = "proto3";
package com.union.fun;
option optimize_for = LITE_RUNTIME;
enum MetricStatus {
UNKNOWN = 0;
IDLE = 1;
BUSY = 2;
}
message Metric {
string name = 1;// [nanopb.max_length = 40];
string type = 2;
float value = 3;
repeated string tags = 4;// [(nanopb).max_length = 40, (nanopb).max_count = 5];
int32 id = 5;
repeated string remarks = 6;
MetricStatus status = 7;
bytes version = 8;
}
metric.options
com.union.fun.Metric.name max_length:40
com.union.fun.Metric.tags max_size:40 max_count:5
生成实现文件:
生成器根据metric.proto生成对应的实现文件和头文件metric.pb.h 和 metric.pb.c
/home/tiger/nanopb-0.3.9.4-linux-x86/generator-bin/protoc --nanopb_out=. metric.proto
查看各个字段名称
/home/tiger/nanopb-0.3.9.4-linux-x86/generator-bin/protoc --nanopb_out=-v:. metric.proto
C++方式如下:
/home/tiger/nanopb-0.3.9.4-linux-x86/generator-bin/protoc --cpp_out=./ metric.proto
1)string类型使用注意
在nanopb中,string类型在生成c语言文件的时候,会有两种结构,一种是指定了最大长度的,一种是没有指定最大长度.指定了最大长度的string,会生成char[] 数组类型,
没有指定最大长度的,会生成pb_callback_t类型.具体的可以参照nanopb文档(https://jpa.kapsi.fi/nanopb/docs/concepts.html#compiling-proto-files-for-nanopb)
2).proto中optimize_for的参数
option optimize_for = LITE_RUNTIME;
optimize_for是文件级别的选项,Protocol Buffer定义三种优化级别SPEED/CODE_SIZE/LITE_RUNTIME。缺省情况下是SPEED。
SPEED: 表示生成的代码运行效率高,但是由此生成的代码编译后会占用更多的空间。
CODE_SIZE: 和SPEED恰恰相反,代码运行效率较低,但是由此生成的代码编译后会占用更少的空间,通常用于资源有限的平台,如Mobile。
LITE_RUNTIME: 生成的代码执行效率高,同时生成代码编译后的所占用的空间也是非常少。这是以牺牲Protocol Buffer提供的反射功能为代价的。因此我们在C++中链接Protocol Buffer库时仅需链接libprotobuf-lite,而非libprotobuf。
在Java中仅需包含protobuf-java-2.4.1-lite.jar,而非protobuf-java-2.4.1.jar。
注:对于LITE_MESSAGE选项而言,其生成的代码均将继承自MessageLite,而非Message。
3)pb_callback_t结构
pb_callback_t 是一个结构体,有两个成员变量,一个是回调函数指针,这个回调函数是一个union,在编码的时候,需要赋值encode函数,解码的时候赋值decode,如果不赋值,则该属性值会忽略.
另外一个变量是arg,这是一个指针,会在回调函数中作为最后一个参数传递给回调函数.
typedef struct pb_callback_s pb_callback_t;
struct pb_callback_s {
#ifdef PB_OLD_CALLBACK_STYLE
/* Deprecated since nanopb-0.2.1 */
union {
bool (*decode)(pb_istream_t *stream, const pb_field_t *field, void *arg);
bool (*encode)(pb_ostream_t *stream, const pb_field_t *field, const void *arg);
} funcs;
#else
/* New function signature, which allows modifying arg contents in callback. */
union {
bool (*decode)(pb_istream_t *stream, const pb_field_t *field, void **arg);
bool (*encode)(pb_ostream_t *stream, const pb_field_t *field, void * const *arg);
} funcs;
#endif
/* Free arg for use by callback */
void *arg;
};struct _pb_ostream_t
{
bool (*callback)(pb_ostream_t *stream, const uint8_t *buf, size_t count);
void *state;
size_t max_size;
size_t bytes_written;
};struct _pb_istream_t
{
bool (*callback)(pb_istream_t *stream, uint8_t *buf, size_t count);
void *state;
size_t bytes_left;
};
调用举例:
项目结构:
main.c
#include "metric.pb.h"
#include "nanopb_tools.h"
#define DATA_BUFFER_SIZE 1024
bool write_string_list(pb_ostream_t *stream, const pb_field_t *field, void * const *arg)
{
char *str = *arg;
if (!pb_encode_tag_for_field(stream, field))
return false;
printf("write_string_list %s\n", str);
return pb_encode_string(stream, (uint8_t*)str, strlen(str));
}
//打包
static int pack_data(uint8_t *buffer)
{
com_union_fun_Metric metric = com_union_fun_Metric_init_zero;
memset(buffer, 0, DATA_BUFFER_SIZE);
char name[41];
pb_callback_t type;
float value;
pb_size_t tags_count;
char tags[5][40];
int32_t id;
pb_callback_t remarks;
com_union_fun_MetricStatus status;
pb_callback_t version;
strcpy(metric.name, "liudehua");
metric.type.funcs.encode = write_string;
metric.type.arg = &"welcome to using nanopb";
metric.value = 99.01;
metric.tags_count = 5;
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
sprintf(metric.tags[i], "%d ok", i);
}
metric.id = 110;
//metric.remarks.funcs.encode = &write_string_list;
//metric.remarks.arg = &"hello hello hello hello hello";
metric.status = com_union_fun_MetricStatus_BUSY;
metric.version.funcs.encode = &nanopb_encode_map_bytes;
char strVersion[128] = {0};
strcpy(strVersion, "V1.0.0.1");
struct pb_bytes_array byteData;
byteData.size = strlen(strVersion);
byteData.bytes = (uint8_t*)strVersion;
metric.version.arg = &byteData;
pb_ostream_t enc_stream;
enc_stream = pb_ostream_from_buffer(buffer, DATA_BUFFER_SIZE);
if (!pb_encode(&enc_stream, com_union_fun_Metric_fields, &metric))
{
printf("pb_encode error in %s [%s]\n", __func__, PB_GET_ERROR(&enc_stream));
return -1;
}
return enc_stream.bytes_written;
}
//解包
static int unpack_data(const uint8_t *buffer, size_t len)
{
com_union_fun_Metric metric;
metric.type.funcs.decode = read_ints;
char tmp[128] = {0};
metric.type.arg = &tmp;
metric.version.funcs.decode = nanopb_decode_map_bytes;
metric.version.arg = NULL;
pb_istream_t dec_stream;
dec_stream = pb_istream_from_buffer(buffer, len);
if (!pb_decode(&dec_stream, com_union_fun_Metric_fields, &metric))
{
printf("pb_decodeerror in %s [%s]\n", __func__, PB_GET_ERROR(&dec_stream));
return -1;
}
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
printf("unpack_data: %d %s %s %f %s %d %s\n",
metric.id, metric.name, tmp, metric.value, metric.tags[i], metric.status, (char*)metric.version.arg);
}
nanopb_release_map_bytes(&metric.version);
return 0;
}
int main(int argc,char *argv[])
{
uint8_t buffer[DATA_BUFFER_SIZE];
int lenght = pack_data(buffer);
if(lenght < 0) {
printf("pack_data fail \n");
return -1;
}
printf("pack_data len: %d\n", lenght);
unpack_data(buffer, lenght);
return 0;
}metric.pb.h
/* Automatically generated nanopb header */
/* Generated by nanopb-0.3.9.4 at Mon Mar 13 20:12:37 2023. */
#ifndef PB_COM_UNION_FUN_METRIC_PB_H_INCLUDED
#define PB_COM_UNION_FUN_METRIC_PB_H_INCLUDED
#include
/* @@protoc_insertion_point(includes) */
#if PB_PROTO_HEADER_VERSION != 30
#error Regenerate this file with the current version of nanopb generator.
#endif
#ifdef __cplusplus
extern "C" {
#endif
/* Enum definitions */
typedef enum _com_union_fun_MetricStatus {
com_union_fun_MetricStatus_UNKNOWN = 0,
com_union_fun_MetricStatus_IDLE = 1,
com_union_fun_MetricStatus_BUSY = 2
} com_union_fun_MetricStatus;
#define _com_union_fun_MetricStatus_MIN com_union_fun_MetricStatus_UNKNOWN
#define _com_union_fun_MetricStatus_MAX com_union_fun_MetricStatus_BUSY
#define _com_union_fun_MetricStatus_ARRAYSIZE ((com_union_fun_MetricStatus)(com_union_fun_MetricStatus_BUSY+1))
/* Struct definitions */
typedef struct _com_union_fun_Metric {
char name[41];
pb_callback_t type;
float value;
pb_size_t tags_count;
char tags[5][40];
int32_t id;
pb_callback_t remarks;
com_union_fun_MetricStatus status;
pb_callback_t version;
/* @@protoc_insertion_point(struct:com_union_fun_Metric) */
} com_union_fun_Metric;
/* Default values for struct fields */
/* Initializer values for message structs */
#define com_union_fun_Metric_init_default {"", {{NULL}, NULL}, 0, 0, {"", "", "", "", ""}, 0, {{NULL}, NULL}, _com_union_fun_MetricStatus_MIN, {{NULL}, NULL}}
#define com_union_fun_Metric_init_zero {"", {{NULL}, NULL}, 0, 0, {"", "", "", "", ""}, 0, {{NULL}, NULL}, _com_union_fun_MetricStatus_MIN, {{NULL}, NULL}}
/* Field tags (for use in manual encoding/decoding) */
#define com_union_fun_Metric_name_tag 1
#define com_union_fun_Metric_type_tag 2
#define com_union_fun_Metric_value_tag 3
#define com_union_fun_Metric_tags_tag 4
#define com_union_fun_Metric_id_tag 5
#define com_union_fun_Metric_remarks_tag 6
#define com_union_fun_Metric_status_tag 7
#define com_union_fun_Metric_version_tag 8
/* Struct field encoding specification for nanopb */
extern const pb_field_t com_union_fun_Metric_fields[9];
/* Maximum encoded size of messages (where known) */
/* com_union_fun_Metric_size depends on runtime parameters */
/* Message IDs (where set with "msgid" option) */
#ifdef PB_MSGID
#define METRIC_MESSAGES \
#endif
#ifdef __cplusplus
} /* extern "C" */
#endif
/* @@protoc_insertion_point(eof) */
#endif
metric.pb.c
/* Automatically generated nanopb constant definitions */
/* Generated by nanopb-0.3.9.4 at Mon Mar 13 20:12:37 2023. */
#include "metric.pb.h"
/* @@protoc_insertion_point(includes) */
#if PB_PROTO_HEADER_VERSION != 30
#error Regenerate this file with the current version of nanopb generator.
#endif
const pb_field_t com_union_fun_Metric_fields[9] = {
PB_FIELD( 1, STRING , SINGULAR, STATIC , FIRST, com_union_fun_Metric, name, name, 0),
PB_FIELD( 2, STRING , SINGULAR, CALLBACK, OTHER, com_union_fun_Metric, type, name, 0),
PB_FIELD( 3, FLOAT , SINGULAR, STATIC , OTHER, com_union_fun_Metric, value, type, 0),
PB_FIELD( 4, STRING , REPEATED, STATIC , OTHER, com_union_fun_Metric, tags, value, 0),
PB_FIELD( 5, INT32 , SINGULAR, STATIC , OTHER, com_union_fun_Metric, id, tags, 0),
PB_FIELD( 6, STRING , REPEATED, CALLBACK, OTHER, com_union_fun_Metric, remarks, id, 0),
PB_FIELD( 7, UENUM , SINGULAR, STATIC , OTHER, com_union_fun_Metric, status, remarks, 0),
PB_FIELD( 8, BYTES , SINGULAR, CALLBACK, OTHER, com_union_fun_Metric, version, status, 0),
PB_LAST_FIELD
};
/* @@protoc_insertion_point(eof) */
nanopb_tools.h
#ifndef _NANOPB_TOOL_H_
#define _NANOPB_TOOL_H_
#include "pb.h"
#include "pb_encode.h"
#include "pb_decode.h"
#include
#include
#include
struct pb_bytes_array {
int size;
uint8_t* bytes;
};
bool write_string(pb_ostream_t *stream, const pb_field_t *field, void * const *arg);
bool read_ints(pb_istream_t *stream, const pb_field_t *field, void **arg);
/**
* nanopb库解析bytes类型
*
* @param [in] stream nanop:b输入数据流
* @param [in] field proto对象属性域数组
* @param [in] arg callback回调的参数(外部传入NULL即可,内存动态申请内存)
*
* @return 是否解析成功
* @note: nanopb在解析不定长对象时需要指定解析的回调函数,为了方便,解析string类型,封装该方法
*
*/
bool nanopb_decode_map_bytes(pb_istream_t *stream, const pb_field_t *field, void **arg);
//
bool nanopb_decode_map_string(pb_istream_t *stream, const pb_field_t *field, void **arg);
/**
* nanopb库构造string 类型buffer
*
* @param [in] stream nanop:b输入数据流
* @param [in] field proto对象属性域数组
* @param [in] arg callback回调的参数(外部传入)
*
* @return 是否解析成功
* @note: nanopb在解析不定长对象时需要指定解析的回调函数,为了方便,解析string类型,封装该方法
*
*/
bool nanopb_encode_map_string(pb_ostream_t *stream, const pb_field_t *field, void * const *arg);
bool nanopb_encode_map_bytes(pb_ostream_t *stream, const pb_field_t *field, void * const *arg);
/**
* nanopb库释放callback申请的heap内存
*
* @param [in] pCallBack 指向callback申请内存的指针
*
* @return N/A
* @note:
*
*/
void nanopb_release_map_string(pb_callback_t* pCallBack);
/**
* nanopb库释放callback申请的heap内存
*
* @param [in] pCallBack 指向callback申请内存的指针
*
* @return N/A
* @note:
*
*/
void nanopb_release_map_bytes(pb_callback_t* pCallBack);
/**
* nanopb库设置string类型
*
* @param [in] pCallBack string的callback
* @param [in] pSrcChar 源字符串
* @return N/A
* @note: nanopb的字符串类型赋值封装接口,内部会申请内存
*
*/
void nanopb_map_set_string(pb_callback_t* pCallBack, const char* pSrcChar);
#endif nanopb_tools.c
#include "nanopb_tools.h"
bool write_string(pb_ostream_t *stream, const pb_field_t *field, void * const *arg)
{
char *str = *arg;
if (!pb_encode_tag_for_field(stream, field))
return false;
// printf("11111111111111111\n");
return pb_encode_string(stream, (uint8_t*)str, strlen(str));
}
bool read_ints(pb_istream_t *stream, const pb_field_t *field, void **arg)
{
int i=0;
char* tmp = *arg;
while (stream->bytes_left)
{
uint64_t value;
if (!pb_decode_varint(stream, &value))
return false;
*(tmp+i)=value;
i++;
// printf("222222222222222222\n");
}
return true;
}
/**
* nanopb库解析bytes类型
*
* @param [in] stream nanop:b输入数据流
* @param [in] field proto对象属性域数组
* @param [in] arg callback回调的参数(外部传入NULL即可,内存动态申请内存)
*
* @return 是否解析成功
* @note: nanopb在解析不定长对象时需要指定解析的回调函数,为了方便,解析string类型,封装该方法
*
*/
bool nanopb_decode_map_bytes(pb_istream_t *stream, const pb_field_t *field, void **arg)
{
#if 1
if (*arg != NULL)
{
free(*arg);
*arg = NULL;
}
#else
if (*arg != NULL)
{
pb_bytes_array* pBytes = (pb_bytes_array*)*arg;
if (pBytes->bytes)
{
free(pBytes->bytes);
pBytes->bytes = NULL;
}
pBytes->size = 0;
delete[] pBytes;
*arg = NULL;
}
#endif
#if 1
size_t alloc_size = 0;
bool status = false;
size_t size = stream->bytes_left;
/* Space for null terminator */
alloc_size = size + 1;
if (alloc_size < size) {
PB_RETURN_ERROR(stream, "size too large");
}
char* pData = (char*)malloc(alloc_size);
if (!pData) {
return false;
}
memset(pData, 0, alloc_size);
status = pb_read(stream, (uint8_t*)pData, size);
*((uint8_t*)pData + size) = 0;
*arg = pData;
#else
pb_bytes_array* pDest = new pb_bytes_array;
if (!pDest)
return V_FALSE;
bool status;
size_t alloc_size = stream->bytes_left;
pDest->bytes = (uint8_t*)malloc(alloc_size);
if (!pDest->bytes)
{
delete pDest;
return V_TRUE;
}
pDest->size = alloc_size;
memset(pDest->bytes, 0, alloc_size);
status = pb_read(stream, (uint8_t*)pDest->bytes, pDest->size);
*arg = pDest;
#endif
return status;
}
//
bool nanopb_decode_map_string(pb_istream_t *stream, const pb_field_t *field, void **arg)
{
if ( *arg != NULL )
{
free(*arg);
*arg = NULL;
}
size_t alloc_size;
bool status;
//if (!pb_decode_varint32(stream, &size))
// return false;
size_t size = stream->bytes_left;
/* Space for null terminator */
alloc_size = size + 1;
if (alloc_size < size)
PB_RETURN_ERROR(stream, "size too large");
char* pData = (char*)malloc( alloc_size );
if ( !pData )
return false;
memset(pData, 0, alloc_size);
status = pb_read(stream, (uint8_t*)pData, size);
*((uint8_t*)pData + size) = 0;
*arg = pData;
return status;
}
/**
* nanopb库构造string 类型buffer
*
* @param [in] stream nanop:b输入数据流
* @param [in] field proto对象属性域数组
* @param [in] arg callback回调的参数(外部传入)
*
* @return 是否解析成功
* @note: nanopb在解析不定长对象时需要指定解析的回调函数,为了方便,解析string类型,封装该方法
*
*/
bool nanopb_encode_map_string(pb_ostream_t *stream, const pb_field_t *field, void * const *arg)
{
if ( !stream || !field )
return false;
int nLen = 0;
if ( *arg )
{
nLen = strlen((const char *)*arg);
}
return pb_encode_tag_for_field(stream, field) &&
pb_encode_string(stream, (const uint8_t *)*arg, nLen);
}
bool nanopb_encode_map_bytes(pb_ostream_t *stream, const pb_field_t *field, void * const *arg)
{
if (!stream || !field)
return false;
const struct pb_bytes_array *bytes = (const struct pb_bytes_array*)*arg;
if (bytes == NULL)
{
printf("nanopb_encode_map_bytes 1\n");
/* Threat null pointer as an empty bytes field */
return pb_encode_string(stream, NULL, 0);
}
printf("nanopb_encode_map_bytes 2\n");
return pb_encode_tag_for_field(stream, field) &&
pb_encode_string(stream, (const uint8_t *)bytes->bytes, bytes->size);
}
/**
* nanopb库释放callback申请的heap内存
*
* @param [in] pCallBack 指向callback申请内存的指针
*
* @return N/A
* @note:
*
*/
void nanopb_release_map_string(pb_callback_t* pCallBack)
{
if ( !pCallBack || !pCallBack->arg )
return;
char* pData = (char*)pCallBack->arg;
if ( pData )
{
free(pData);
pCallBack->arg = NULL;
}
}
/**
* nanopb库释放callback申请的heap内存
*
* @param [in] pCallBack 指向callback申请内存的指针
*
* @return N/A
* @note:
*
*/
void nanopb_release_map_bytes(pb_callback_t* pCallBack)
{
if ( !pCallBack || !pCallBack->arg )
return;
#if 1
char* pData = (char*)pCallBack->arg;
if (pData)
{
free(pData);
pCallBack->arg = NULL;
}
#else
pb_bytes_array* pBytes = (pb_bytes_array*)pCallBack->arg;
if (pBytes->bytes)
{
free(pBytes->bytes);
pBytes->bytes = V_NULL;
}
pBytes->size = 0;
delete pBytes;
pCallBack->arg = V_NULL;
#endif
}
/**
* nanopb库设置string类型
*
* @param [in] pCallBack string的callback
* @param [in] pSrcChar 源字符串
* @return N/A
* @note: nanopb的字符串类型赋值封装接口,内部会申请内存
*
*/
void nanopb_map_set_string(pb_callback_t* pCallBack, const char* pSrcChar)
{
if(!pCallBack || !pSrcChar)
return;
int nLen = strlen(pSrcChar);
pCallBack->arg = malloc(nLen+1);
memset( pCallBack->arg, 0, nLen+1 );
if ( pCallBack->arg )
{
memcpy(pCallBack->arg, pSrcChar, nLen);
}
}编译:
gcc -I . main.c metric.pb.c pb_common.c pb_decode.c pb_encode.c nanopb_tools.c
执行:
./a.out
运行结果:
源码下载
3.3python解析nanopb生成的二进制数据
#include "metric.pb.h"
#include "nanopb_tools.h"
#define DATA_BUFFER_SIZE 1024
bool write_string_list(pb_ostream_t *stream, const pb_field_t *field, void * const *arg)
{
char *str = *arg;
if (!pb_encode_tag_for_field(stream, field))
return false;
printf("write_string_list %s\n", str);
return pb_encode_string(stream, (uint8_t*)str, strlen(str));
}
//打包
static int pack_data(uint8_t *buffer)
{
com_union_fun_Metric metric = com_union_fun_Metric_init_zero;
memset(buffer, 0, DATA_BUFFER_SIZE);
char name[41];
pb_callback_t type;
float value;
pb_size_t tags_count;
char tags[5][40];
int32_t id;
pb_callback_t remarks;
com_union_fun_MetricStatus status;
pb_callback_t version;
strcpy(metric.name, "liudehua");
metric.type.funcs.encode = write_string;
metric.type.arg = &"welcome to using nanopb";
metric.value = 99.01;
metric.tags_count = 5;
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
sprintf(metric.tags[i], "%d ok", i);
}
metric.id = 110;
//metric.remarks.funcs.encode = &write_string_list;
//metric.remarks.arg = &"hello hello hello hello hello";
metric.status = com_union_fun_MetricStatus_BUSY;
metric.version.funcs.encode = &nanopb_encode_map_bytes;
char strVersion[128] = {0};
strcpy(strVersion, "V1.0.0.1");
struct pb_bytes_array byteData;
byteData.size = strlen(strVersion);
byteData.bytes = (uint8_t*)strVersion;
metric.version.arg = &byteData;
pb_ostream_t enc_stream;
enc_stream = pb_ostream_from_buffer(buffer, DATA_BUFFER_SIZE);
if (!pb_encode(&enc_stream, com_union_fun_Metric_fields, &metric))
{
printf("pb_encode error in %s [%s]\n", __func__, PB_GET_ERROR(&enc_stream));
return -1;
}
return enc_stream.bytes_written;
}
//解包
static int unpack_data(const uint8_t *buffer, size_t len)
{
com_union_fun_Metric metric;
metric.type.funcs.decode = read_ints;
char tmp[128] = {0};
metric.type.arg = &tmp;
metric.version.funcs.decode = nanopb_decode_map_bytes;
metric.version.arg = NULL;
pb_istream_t dec_stream;
dec_stream = pb_istream_from_buffer(buffer, len);
if (!pb_decode(&dec_stream, com_union_fun_Metric_fields, &metric))
{
printf("pb_decodeerror in %s [%s]\n", __func__, PB_GET_ERROR(&dec_stream));
return -1;
}
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
printf("unpack_data: %d %s %s %f %s %d %s\n",
metric.id, metric.name, tmp, metric.value, metric.tags[i], metric.status, (char*)metric.version.arg);
}
nanopb_release_map_bytes(&metric.version);
return 0;
}
int main(int argc,char *argv[])
{
uint8_t buffer[DATA_BUFFER_SIZE];
int lenght = pack_data(buffer);
if(lenght < 0) {
printf("pack_data fail \n");
return -1;
}
FILE* fp = fopen("metric.bin", "wb");
fwrite(buffer, sizeof(uint8_t), lenght, fp);
fwrite(buffer, sizeof(uint8_t), lenght, fp);
fwrite(buffer, sizeof(uint8_t), lenght, fp);
fclose(fp);
fp = NULL;
printf("pack_data len: %d\n", lenght);
unpack_data(buffer, lenght);
return 0;
}运行结果如下:
从运行结果可以看出每个对象84字节 , 将3个nanopb生成的PB对象存放在metric.bin
利用Python解析读取
/home/tiger/protobuf-3.6.1/protobuf/bin/protoc -I=/home/tiger/nanopb --python_out=/home/tiger/nanopb metric.proto
test_nanopb.py
"""
This is the main module.
"""
#coding=utf-8
import sys
import os
import argparse
import metric_pb2
'''
/home/tiger/protobuf-3.6.1/protobuf/bin/protoc -I=/home/tiger/nanopb --python_out=/home/tiger/nanopb metric.proto
python3 test_nanopb.py -f=metric.bin
'''
def main(pbfile):
print("main start ...", pbfile)
index = 0
with open(pbfile, 'rb') as f:
buf = f.read()
while index < len(buf):
data = buf[index : index+84]
index += 84
#print(data)
read_metric = metric_pb2.Metric()
read_metric.ParseFromString(data)
print(read_metric)
print("================")
if __name__ == "__main__":
#print(sys.argv)
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
parser.add_argument(
'-f', '--file', dest='pbfile', type=str, default="anpVehicleData.log",
help='input pb file'
)
parser.add_argument(
'-s', '--start', dest='startpos', default=123, required=False,
help='input start postion'
)
parser.add_argument(
'-e', '--end', dest='endpos', default=456, required=False,
help='input end postion'
)
args = parser.parse_args()
pbfile = args.pbfile
startpos = args.startpos
endpos = args.endpos
print("pbfile:", pbfile)
print("startpos:", startpos)
print("endpos:", endpos)
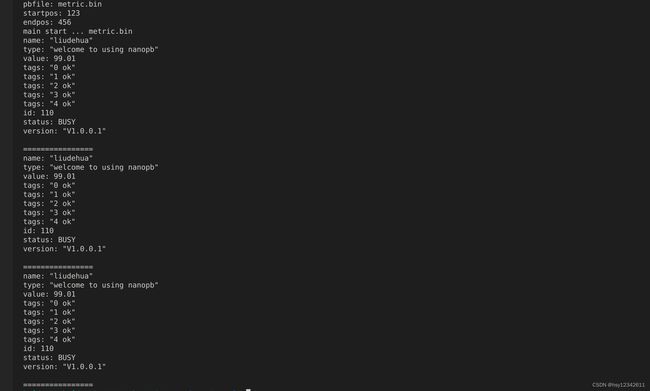
main(pbfile)执行Python脚本:python3 test_nanopb.py -f=metric.bin
可以看到三个PB对象被成功解析出来
说明:另一种支持c语言的框架是protobuf-c,此处不再说明