Flink1.11 intervalJoin watermark生成,状态清理机制源码理解&Demo分析
参考博客 https://cloud.tencent.com/developer/article/1738836
数据类型为左流 FlinkClick(userid=gk01, click=Pay, ctime=2020-12-14 09:55:00.000) ; 右流为 FlinkPay(userid=gk01, payway=alipy, ptime=2020-12-14 09:58:00.000)
join的这段代码如下
clickOut.keyBy(t->t.getUserid())
.intervalJoin(payOunt.keyBy(t->t.getUserid()))
.between(Time.minutes(1),Time.minutes(5))
.lowerBoundExclusive() //默认是闭区间,这样就变成了开区间
.upperBoundExclusive()
.process(new ProcessJoinFunction() {
@Override
public void processElement(FlinkClick left, FlinkPay right, Context ctx, Collector out) throws Exception {
out.collect(StringUtils.join(Arrays.asList(
left.getUserid(),
left.getClick(),
right.getPayway()
),'\t'));
}
}).print().setParallelism(1);
一:watermark生成规则:
watermark的计算为 min(ctime,ptime)-watermark (watermark为左右流定义的乱序时间,我这里设置的0),贴出其中一个流的demo,注意watermark
env
.addSource(payConsumer).map(new MapFunction() {
@Override
public FlinkPay map(String pv) throws Exception {
JSONObject clickObject = JSONObject.parseObject(pv);
String userid = clickObject.getString("userid");
String payway = clickObject.getString("payway");
String ptime = clickObject.getString("ptime");
FlinkPay payO = new FlinkPay(userid, payway, ptime);
return payO;
}
}).assignTimestampsAndWatermarks(
WatermarkStrategy.forBoundedOutOfOrderness(Duration.ZERO) //watermark时间
.withTimestampAssigner(new SerializableTimestampAssigner() {
@Override
public long extractTimestamp(FlinkPay element, long recordTimestamp) {
Date dateP = new Date();
try {
System.out.println(element);
dateP = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.SSS").parse(element.getPtime());
} catch (ParseException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
// System.out.println(dateP.getTime());
return dateP.getTime();
}
}
)); 二:状态清理机制
贴上几段源码,均在 IntervalJoinOperator 类中
private transient MapState>> leftBuffer;
private transient MapState>> rightBuffer;
@Override
public void initializeState(StateInitializationContext context) throws Exception {
super.initializeState(context);
this.leftBuffer = context.getKeyedStateStore().getMapState(new MapStateDescriptor<>(
LEFT_BUFFER,
LongSerializer.INSTANCE,
new ListSerializer<>(new BufferEntrySerializer<>(leftTypeSerializer))
));
this.rightBuffer = context.getKeyedStateStore().getMapState(new MapStateDescriptor<>(
RIGHT_BUFFER,
LongSerializer.INSTANCE,
new ListSerializer<>(new BufferEntrySerializer<>(rightTypeSerializer))
));
} 在IntervalJoinOperator中,会利用两个MapState分别缓存左流和右流的数据。其中,Long表示时间时间戳,List
@Override
public void processElement1(StreamRecord record) throws Exception {
processElement(record, leftBuffer, rightBuffer, lowerBound, upperBound, true);
}
@Override
public void processElement2(StreamRecord record) throws Exception {
processElement(record, rightBuffer, leftBuffer, -upperBound, -lowerBound, false);
}
private void processElement(
final StreamRecord record,
final MapState>> ourBuffer,
final MapState>> otherBuffer,
final long relativeLowerBound,
final long relativeUpperBound,
final boolean isLeft) throws Exception {
final THIS ourValue = record.getValue();
final long ourTimestamp = record.getTimestamp();
if (ourTimestamp == Long.MIN_VALUE) {
throw new FlinkException("Long.MIN_VALUE timestamp: Elements used in " +
"interval stream joins need to have timestamps meaningful timestamps.");
}
if (isLate(ourTimestamp)) {
return;
}
addToBuffer(ourBuffer, ourValue, ourTimestamp);
for (Map.Entry>> bucket: otherBuffer.entries()) {
final long timestamp = bucket.getKey();
if (timestamp < ourTimestamp + relativeLowerBound ||
timestamp > ourTimestamp + relativeUpperBound) {
continue;
}
for (BufferEntry entry: bucket.getValue()) {
if (isLeft) {
collect((T1) ourValue, (T2) entry.element, ourTimestamp, timestamp);
} else {
collect((T1) entry.element, (T2) ourValue, timestamp, ourTimestamp);
}
}
}
long cleanupTime = (relativeUpperBound > 0L) ? ourTimestamp + relativeUpperBound : ourTimestamp;
if (isLeft) {
internalTimerService.registerEventTimeTimer(CLEANUP_NAMESPACE_LEFT, cleanupTime);
} else {
internalTimerService.registerEventTimeTimer(CLEANUP_NAMESPACE_RIGHT, cleanupTime);
}
} 代码最后调用TimerService.registerEventTimeTimer(),注册时间戳为timestamp+relativeUpperBound的定时器,该定时器负责在水印超过区间的上界时执行状态的清理逻辑,防止数据堆积。注意左右流的定时器所属的namespace是不同的,具体逻辑位于onEventTime()方法中
@Override
public void onEventTime(InternalTimer timer) throws Exception {
long timerTimestamp = timer.getTimestamp();
String namespace = timer.getNamespace();
logger.trace("onEventTime @ {}", timerTimestamp);
switch (namespace) {
case CLEANUP_NAMESPACE_LEFT: {
long timestamp = (upperBound <= 0L) ? timerTimestamp : timerTimestamp - upperBound;
logger.trace("Removing from left buffer @ {}", timestamp);
leftBuffer.remove(timestamp);
break;
}
case CLEANUP_NAMESPACE_RIGHT: {
long timestamp = (lowerBound <= 0L) ? timerTimestamp + lowerBound : timerTimestamp;
logger.trace("Removing from right buffer @ {}", timestamp);
rightBuffer.remove(timestamp);
break;
}
default:
throw new RuntimeException("Invalid namespace " + namespace);
}
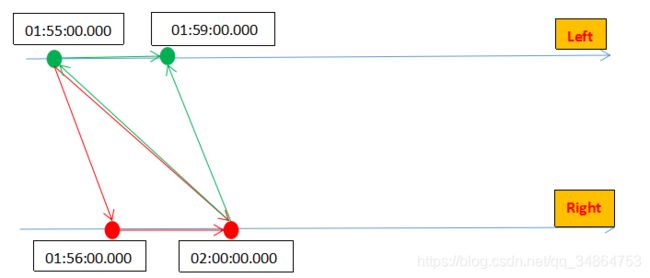
} 先把测试数据及结果贴在这里
| id | 左流数据时间戳(ctime) | 右流数据时间戳(ptime) | 左流清理时间 | 右侧清理时间 |
| 1 | 2020-12-14 01:55:00.000 | 无 | 2020-12-14 02:00:00.000 | |
| 2 | 无 | 2020-12-14 01:55:00.000 | 2020-12-14 01:55:00.000 |
对这个结果说明一下:
我们在自己的代码里设置了:.between(Time.minutes(1),Time.minutes(5))
上述源码中有这一行
long cleanupTime = (relativeUpperBound > 0L) ? ourTimestamp + relativeUpperBound : ourTimestamp;从这里我们就可以计算左右流的清理时间了:
当左流数据进来时,(lowerBound, upperBound) 为 (1 ,5) ,当右流数据进来时,(lowerBound, upperBound) 为 (-5 ,-1),其实就是 left+1min < right 2020-12-14 01:55:00.000 的左侧数据进来,upperBound大于0,cleanupTime = 时间戳+5min 即等于2020-12-14 02:00:00.000;这是因为,当右侧流在2020-12-14 02:00:00.000需要查找左侧流的数据时间为 [2020-12-14 01:55:00.000,2020-12-14 01:59:00.000],所以watermark> 2020-12-14 02:00:00.000 时可以清除2020-12-14 01:55:00.000的数据 2020-12-14 01:55:00.000的右侧数据进来,upperBound小于0,clearnupTime = 时间戳,即等于 2020-12-14 01:55:00.000;这是因为,左侧数据流在 2020-12-14 01:55:00.000时,需要查找的右侧流时间戳范围 [2020-12-14 01:56:00.000, 2020-12-14 02:00:00.000],所以当watermark达到2020-12-14 01:55:00.000时 可以清除 2020-12-14 01:55:00.000 的数据 在 https://cloud.tencent.com/developer/article/1417447 这篇博客中,博主说watermark讲到 WaterMark是根据实际最小值减去UpperBound生成,即:Min(左,右)-upperBound,个人觉得不太对,如果有小伙伴对我这篇博客有疑问,欢迎留言,会积极改正!!