JAXB(Java Architecture for XML Binding)下载、使用
简介
JAXB(Java Architecture for XML Binding)就是XML数据绑定的java架构。JAXB可以根据XML Schema生成java类,也能根据java类生成XML Schema,XML数据绑定指定了XML请求和XML响应如何映射成java对象。
JAXB提供了API和工具,可以自动在XML文档和java对象之间映射。
JAXB框架可以使开发者进行如下操作:
- 将XML内容解包为java表示。
- 访问和更新java表示。
- 将java表示的XML内容打包回XML内容。
JAXB为开发者提供了一个高效、标准的方式来映射XML和java代码。java开发者的效率可以更高,因为他们可以写更少的代码,而且不必是XML专家。JAXB使开发者结合XML和Web服务技术更加容易扩展他们的应用。
各版本参考资源
JAXB 2.0版本参考资源
https://jcp.org/en/jsr/detail?id=222

JAXB 2.3版本详情页:
https://jcp.org/aboutJava/communityprocess/mrel/jsr222/index3.html

从该页面可以下载规范文档、和javadoc文档:
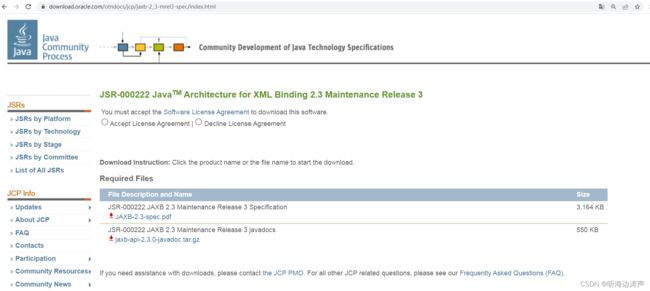
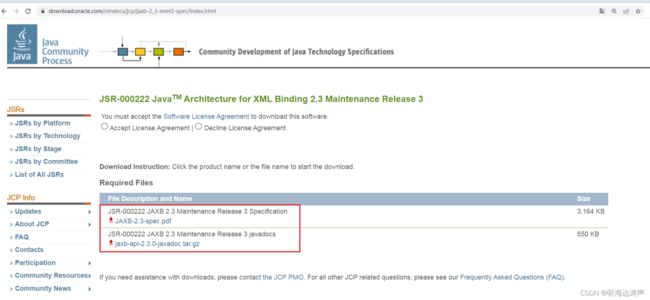
JAXB 2.3版本规范:
https://download.oracle.com/otn-pub/jcp/jaxb-2_3-mrel3-eval-spec/JAXB-2.3-spec.pdf

JAXB 3.0版本参考资源
https://jakarta.ee/specifications/xml-binding/3.0/
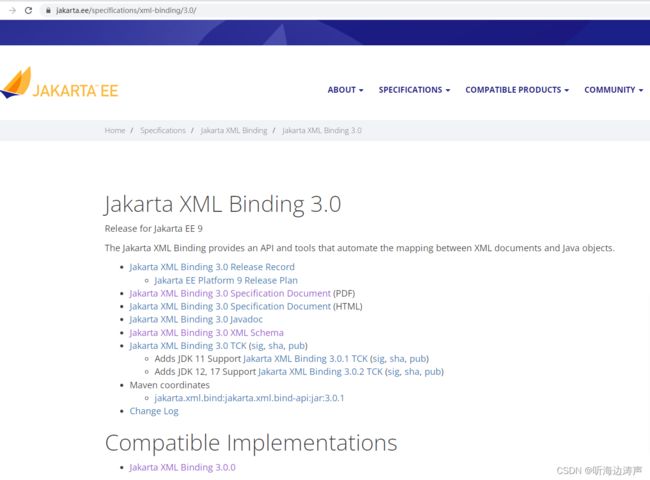
JAXB 4.0版本参考资源
https://jakarta.ee/specifications/xml-binding/4.0/
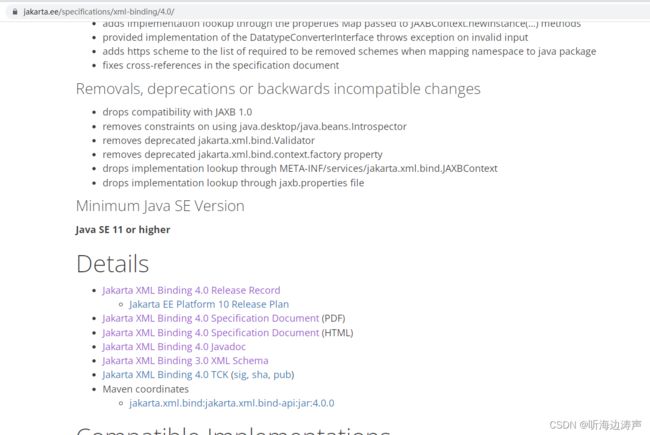
JAXB参考实现
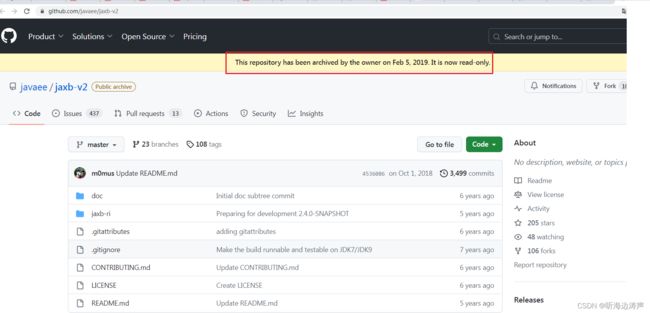
旧版本(已经归档,只读)
https://github.com/javaee/jaxb-v2
这个项目库2019年2月份已经归档了,现在只读。新的项目这已经转移到https://github.com/eclipse-ee4j/jaxb-ri
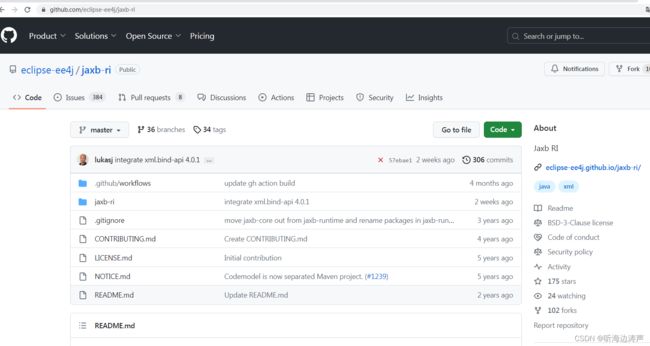
新版本
代码库:https://github.com/eclipse-ee4j/jaxb-ri
主页:https://eclipse-ee4j.github.io/jaxb-ri/

下载zip独立发行包版本
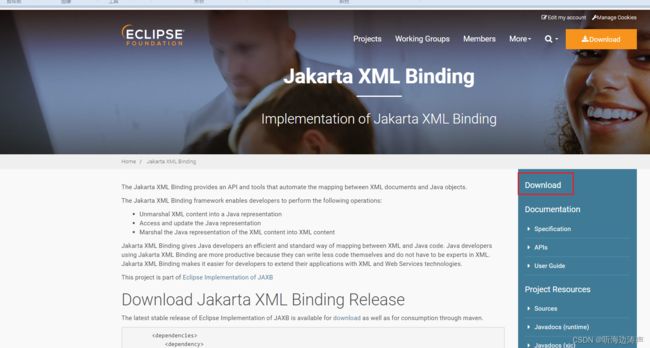
打开主页:https://eclipse-ee4j.github.io/jaxb-ri/
点击右边的Download,可以下载最新的版本,例如jaxb-ri-4.0.3.zip:
对JDK版本的要求
参考实现4.0.3版本需要Java SE 11及以上。
利用运行时绑定框架
https://eclipse-ee4j.github.io/jaxb-ri/4.0.3/docs/release-documentation.html#section-3589085759105448
Schema到Java:开发应用的基本步骤
Schema转Java是将1个或多个schema文件编译为生成java类的过程。用这种方式开发一个应用的基本步骤如下:
- 开发或者定位到schema
- 如果需要的话,用绑定定制化注解schema,或者将它们放在一个外部的绑定文件
- 用xjc绑定编译器编译schema,生成java内容类

- 用上面生成的java内容类和jakarta.xml.bind运行时框架来开发JAXB应用
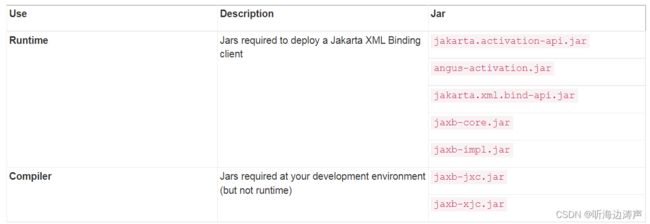
- 设置CLASSPATH变量,将下面的jar文件包含到路径中
https://eclipse-ee4j.github.io/jaxb-ri/4.0.3/docs/ch02.html#jars
- 用javac编译所有的java源文件
- 运行程序
Java到Schema:开发应用的基本步骤
Java到Schema是利用jakarta.xml.bind.annotation包中的注解来增强已经存在的java类的过程,由此JAXB运行时绑定框架可以进行解包/打包的操作。用这种方式开发一个应用的基本步骤如下:
- 设置CLASSPATH变量,将下面的jar文件包含到路径中
https://eclipse-ee4j.github.io/jaxb-ri/4.0.3/docs/ch02.html#jars

- 用java开发数据模型
- 利用jakarta.xml.bind.annotation包中的注解来控制绑定过程
- 用数据模型开发应用;编写代码,用JAXB运行时框架的打包/解包操作持久化数据模型
- 编译、运行应用
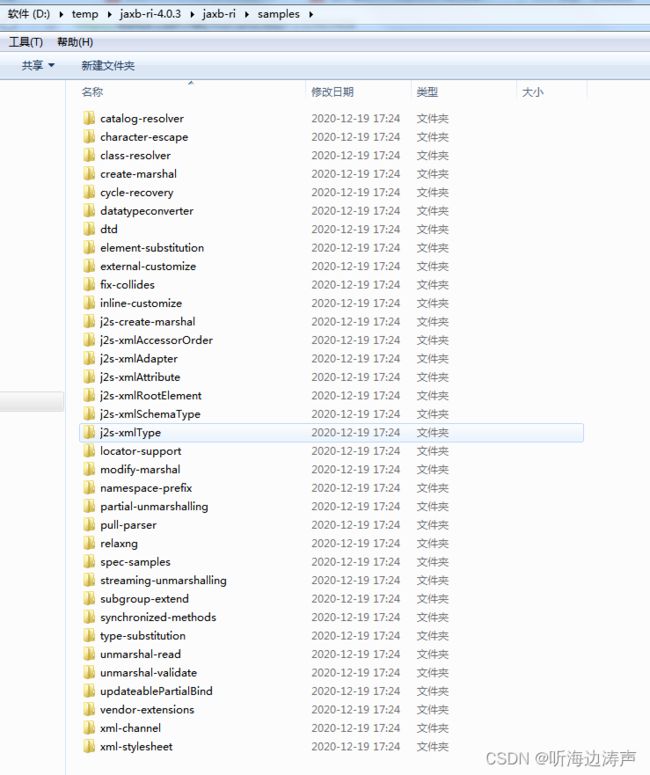
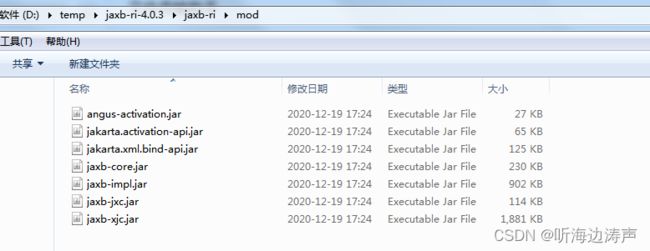
xjc(根据xml schema生成java代码)
备注:xjc命令行脚本只存在于JAXB的zip独立发行包版本中。
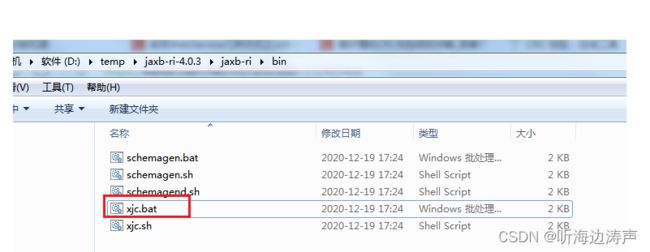
拉起xjc的方式
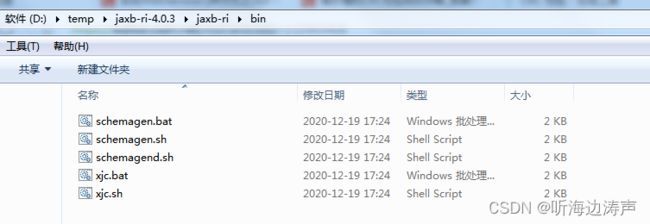
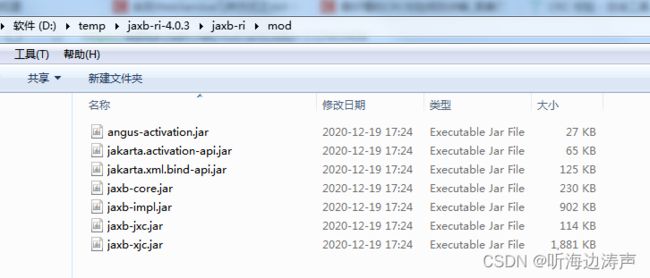
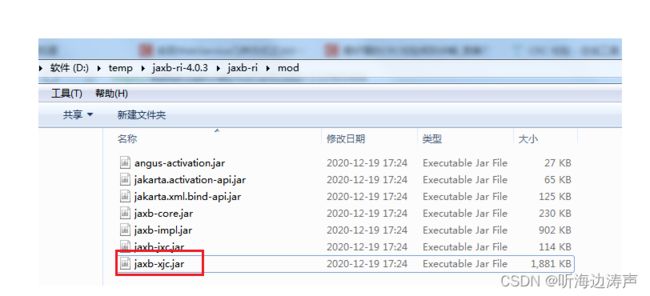
以在Windows下使用为例,可以运行bin目录下的批处理文件xjc.bat、或者mod目录下的jaxb-xjc.jar文件来拉起xjc。
xjc.bat文件在解压包的bin子目录下:
jaxb-xjc.jar文件在解压包的mod子目录下:
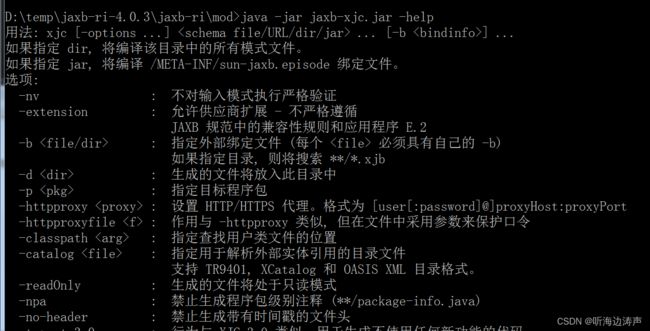
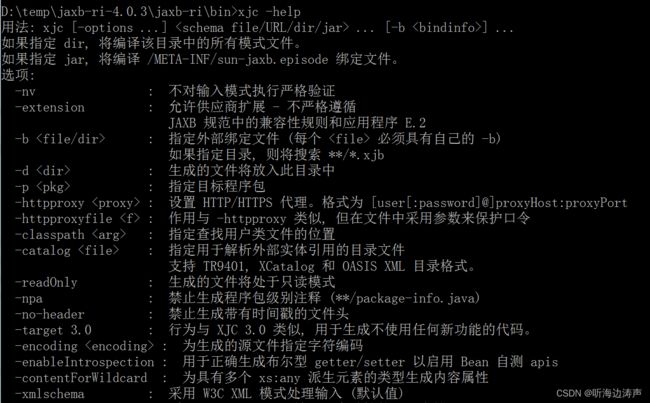
xjc语法
可以通过运行xjc.bat文件、或者jaxb-xjc.jar文件,后面加上-help参数,来查看具体的用法,有哪些选项。
也可以查询官网来了解具体用法:
https://eclipse-ee4j.github.io/jaxb-ri/4.0.3/docs/ch04.html#tools-xjc
xjc [OPTION]... [-b ...]
举例
根据一个schema文件生成java文件
例如,在cmd窗口下执行如下命令:
xjc D:\temp\xmlschema\test.xsd -d D:\temp\outcode
其中:
D:\temp\xmlschema\test.xsd指定schema文件
-d D:\temp\outcode指定生成的java文件存放目录。注意,输出目录必须已经存在,xjc编译器不会创建。

schema文件的内容:
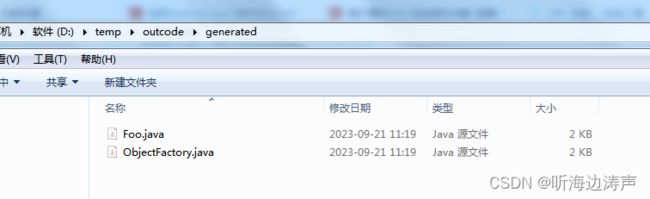
到输出目录下查看生成的内容:
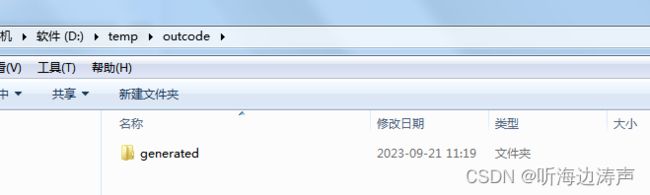
其中generated是默认生成的包名。
生成的Foo.java文件的内容:
//
// 此文件是由 Eclipse Implementation of JAXB v4.0.3 生成的
// 请访问 https://eclipse-ee4j.github.io/jaxb-ri
// 在重新编译源模式时, 对此文件的所有修改都将丢失。
//
package generated;
import jakarta.xml.bind.annotation.XmlAccessType;
import jakarta.xml.bind.annotation.XmlAccessorType;
import jakarta.xml.bind.annotation.XmlType;
/**
* foo complex type的 Java 类。
*
*
以下模式片段指定包含在此类中的预期内容。
*
*
{@code
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
* }
*
*
*/
@XmlAccessorType(XmlAccessType.FIELD)
@XmlType(name = "foo", propOrder = {
"age"
})
public class Foo {
protected int age;
/**
* 获取age属性的值。
*
*/
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
/**
* 设置age属性的值。
*
*/
public void setAge(int value) {
this.age = value;
}
}
生成的ObjectFactory.java文件的内容:
//
// 此文件是由 Eclipse Implementation of JAXB v4.0.3 生成的
// 请访问 https://eclipse-ee4j.github.io/jaxb-ri
// 在重新编译源模式时, 对此文件的所有修改都将丢失。
//
package generated;
import javax.xml.namespace.QName;
import jakarta.xml.bind.JAXBElement;
import jakarta.xml.bind.annotation.XmlElementDecl;
import jakarta.xml.bind.annotation.XmlRegistry;
/**
* This object contains factory methods for each
* Java content interface and Java element interface
* generated in the generated package.
* An ObjectFactory allows you to programmatically
* construct new instances of the Java representation
* for XML content. The Java representation of XML
* content can consist of schema derived interfaces
* and classes representing the binding of schema
* type definitions, element declarations and model
* groups. Factory methods for each of these are
* provided in this class.
*
*/
@XmlRegistry
public class ObjectFactory {
private static final QName _Root_QNAME = new QName("", "root");
/**
* Create a new ObjectFactory that can be used to create new instances of schema derived classes for package: generated
*
*/
public ObjectFactory() {
}
/**
* Create an instance of {@link Foo }
*
* @return
* the new instance of {@link Foo }
*/
public Foo createFoo() {
return new Foo();
}
/**
* Create an instance of {@link JAXBElement }{@code <}{@link Foo }{@code >}
*
* @param value
* Java instance representing xml element's value.
* @return
* the new instance of {@link JAXBElement }{@code <}{@link Foo }{@code >}
*/
@XmlElementDecl(namespace = "", name = "root")
public JAXBElement createRoot(Foo value) {
return new JAXBElement<>(_Root_QNAME, Foo.class, null, value);
}
}
schemagen(根据java文件生成schema)
备注:schemagen命令行脚本只存在于JAXB的zip独立发行包版本中。
介绍
schemagen可以处理java源文件、或者class文件。
拉起schemagen的方式
以windows为例,可以运行bin目录下的schemagen.bat文件来拉起schemagen。
如果java源文件或者类文件引用了其它的类,那么被引用的类必须通过系统环境变量CLASSPATH可以访问到,否则就必须在工具命令中通过-classpath/ -cp可选参数来指定。
例如:

schemagen语法
介绍
schemagen [-options ...]
可以通过官网查看命令参数详细介绍:
https://eclipse-ee4j.github.io/jaxb-ri/4.0.3/docs/ch04.html#tools-schemagen
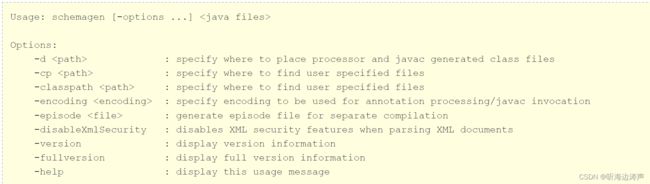
查看帮助信息
执行命令:
schemagen -help
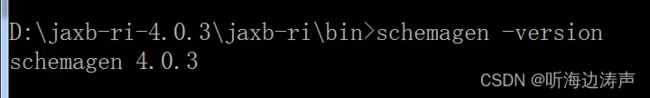
查看版本信息
执行命令:
schemagen -version
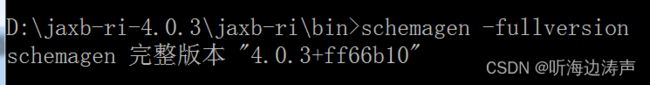
查看完整版本信息
执行命令:
schemagen -fullversion
举例
根据java源文件生成schema文件
java源文件的内容如下。其中属性name用了JavaBeans样式(get和set),属性age用了JAXB的注释:
package com.thb;
import jakarta.xml.bind.annotation.XmlElement;
public class Demo {
private String name;
@XmlElement
private int age;
public String getName() {
return this.name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
执行命令及输出:
schemagen D:\temp\eclipse-workspace\java_work\java_test2\src\com\thb\Demo.java -d D:\temp\outschema
其中 -d D:\temp\outschema指定了生成的schema文件、class文件的存放路径。

到outschema目录下查看生成的内容:

可以看到,生成了schema文件schema1.xsd,另外,也将java源文件编译成了class文件。
打开生成的schema1.xsd文件,内容如下:
通过maven下载JAXB的Eclipse实现
在maven工程的pom.xml文件中依赖部分增加如下片段:
jakarta.xml.bind
jakarta.xml.bind-api
4.0.0
com.sun.xml.bind
jaxb-impl
4.0.3
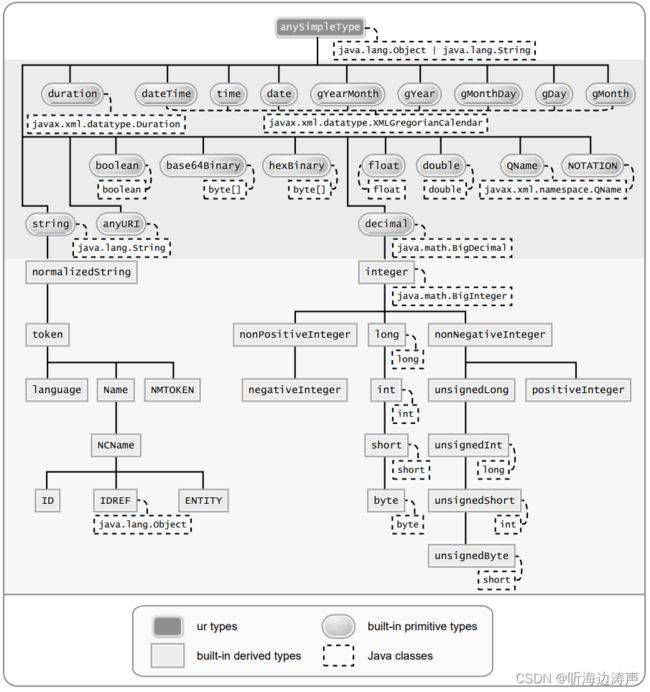
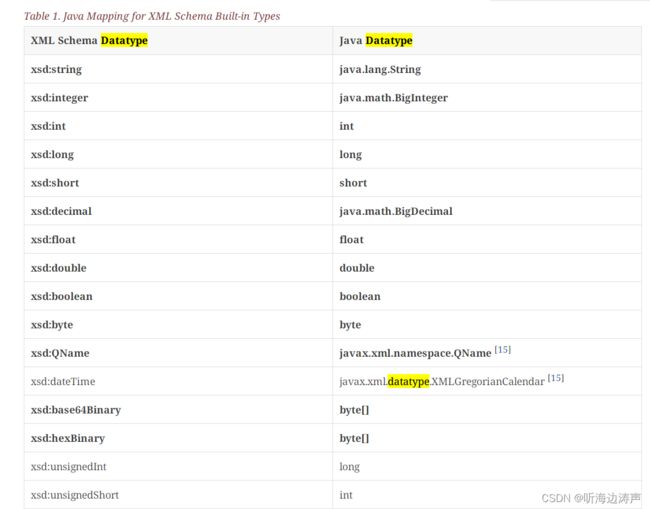
xml简单数据类型到java类型的映射
xml中用简单类型定义的schema部件(component)通常绑定一个java属性。
xml原子类型到java类型的映射
https://jakarta.ee/specifications/xml-binding/4.0/jakarta-xml-binding-spec-4.0#atomic-datatype
所谓原子类型,就是XML规范认为值不可再分的数据类型。

XmlElement注解
介绍
https://jakarta.ee/specifications/xml-binding/4.0/apidocs/jakarta.xml.bind/jakarta/xml/bind/annotation/xmlelement
jakarta.xml.bind.annotation.XmlElement注解的作用是将一个JavaBean 属性映射到一个XML 元素,元素的名字取自属性的名字。
举例:将一个 XmlElement注解的java类的属性映射为一个XML的元素,元素的名字默认就是java类的名字
java类的源码:
package com.thb;
import jakarta.xml.bind.annotation.XmlElement;
public class Request {
@XmlElement
private String reqType;
}
用schemagen命令生成schema:

schema文件的内容:
从上面内容可以看出,java中的属性reqType映射到了 xml中的元素reqType,元素的名字默认就是java中属性的名字。
举例:java类的属性没有使用JAXB注解,也没有采用JavaBean样式(即没有get 和 set),不会转化为xml的元素
java类的内容,其中age没有使用JAXB注解,也没有采用JavaBean样式(即没有get 和 set):
package com.thb;
import jakarta.xml.bind.annotation.XmlElement;
public class Request {
@XmlElement
private String reqType;
private int age;
}
用schemagen命令生成schema:

schema文件的内容:
可以看到,java的属性age没有被转换为XML的属性。
举例:java类的属性没有使用JAXB注解,但采用JavaBean样式(即有get 和 set),会转化为xml的元素
java类的源码,其中age没有使用JAXB注解,但有getter和setter:
package com.thb;
import jakarta.xml.bind.annotation.XmlElement;
public class Request {
@XmlElement
private String reqtype;
private int age;
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public int getAge() {
return this.age;
}
}
用schemagen命令生成schema:

schema文件的内容:
可以看到,java类的JavaBean属性age转换到了XML的元素age。
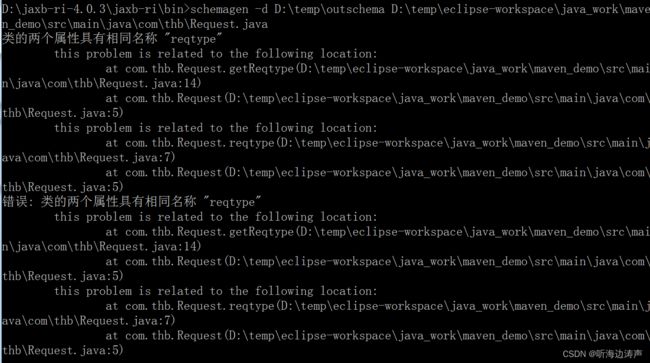
举例:java类的属性使用JAXB注解,并且采用JavaBean样式(即有get 和 set),转换的时候会报错
java代码:
package com.thb;
import jakarta.xml.bind.annotation.XmlElement;
public class Request {
@XmlElement
private String reqtype;
public void setReqtype(String reqtype) {
this.reqtype = reqtype;
}
public String getReqtype() {
return this.reqtype;
}
}
举例:用XmlElement注解的name属性指定XML中元素的名字
java代码如下,其中reqType采用驼峰写法,用XmlElement注解的name属性指定XML中元素的名字是reqtype(不是驼峰写法):
package com.thb;
import jakarta.xml.bind.annotation.XmlElement;
public class Request {
@XmlElement(name = "reqtype")
private String reqType;
}
用schemagen命令生成schema:

schema文件的内容:
举例:用XmlElement注解的name属性指定XML中元素的名字采用java属性的名字
java代码如下,其中XmlElement注解的name属性的值等于"##default",表示XML中元素的名字就采用java属性的名字:
package com.thb;
import jakarta.xml.bind.annotation.XmlElement;
public class Request {
@XmlElement(name = "##default")
private String reqType;
}
用schemagen命令生成schema:

schema文件的内容:
举例:XmlElement注解的required属性值等于true
java代码如下,其中XmlElement注解的required 属性的值等于true。在此情况下,如果java属性是单值数据,那么该XML元素的minOccurs=“1”,maxOccurs=“1”;如果java属性是多值数据,那么XML元素的minOccurs=“1”,maxOccurs=“unbounded”:
package com.thb;
import jakarta.xml.bind.annotation.XmlElement;
public class Request {
@XmlElement(name = "reqtype", required = true)
private String reqType;
@XmlElement(required = true)
private String[] events;
}
schema文件的内容:
举例:XmlElement注解的required属性值为false
java代码如下,其中XmlElement注解的required 属性的值等于false。在此情况下,如果java属性是单值数据,那么该XML元素的minOccurs=“0”,maxOccurs=“1”;如果java属性是多值数据,那么XML元素的minOccurs=“0”,maxOccurs=“unbounded”:
package com.thb;
import jakarta.xml.bind.annotation.XmlElement;
public class Request {
@XmlElement(name = "reqtype", required = false)
private String reqType;
@XmlElement(required = false)
private String[] events;
}
用schemagen命令生成schema:

schema文件的内容:
XmlRootElement注解
介绍
jakarta.xml.bind.annotation.XmlRootElement注解的作用是将一个java类、或者枚举类型映射为XML元素(element)。
XmlRootElement注解可以用在顶层类、或者枚举。
XmlRootElement注解的类必须有一个公共、或者保护、或者包类型的不带参数的构造器。
举例:XmlRootElement注解的类没有不带参数的构造器,生成schema时出错
java代码:
package com.thb;
import jakarta.xml.bind.annotation.XmlElement;
import jakarta.xml.bind.annotation.XmlRootElement;
@XmlRootElement
public class Point {
@XmlElement
private int x;
@XmlElement
private int y;
//public Point() {}
public Point(int x, int y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
}
举例:XmlRootElement注解的类有不带参数的构造器,正常生成schema
java代码:
package com.thb;
import jakarta.xml.bind.annotation.XmlElement;
import jakarta.xml.bind.annotation.XmlRootElement;
@XmlRootElement
public class Point {
@XmlElement
private int x;
@XmlElement
private int y;
public Point() {}
public Point(int x, int y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
}
执行生成schema的命令:
![]()
生成的schema文件的内容:
JAXBContext、Marshaller、Unmarshaller
JAXBContext介绍
jakarta.xml.bind.JAXBContext类提供了到Jakarta XML 绑定API的入口点,它提供了管理XML/Java绑定信息的抽象,这些绑定信息对于实现Jakarta XML绑定框架操作是需要的。涉及到的操作有:打包(marshal )、解包(unmarshal)、验证(validate)。
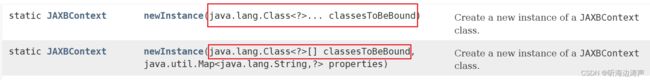
newInstance方法的参数可以是需要被JAXBContext识别的类
JAXBContext context = JAXBContext.newInstance(Point.class);
newInstance方法的参数也可以是需要被JAXBContext识别的类的上下文路径
上下文路径就是包名的列表,包内包含schema导出的类、和(或者)java到schema映射的类(即(Jakarta XML Binding-annotated),多个包名之间用冒号(:)分割。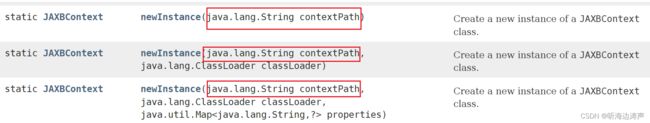
例如:
JAXBContext.newInstance( "com.acme.foo:com.acme.bar" )
如果newInstance方法传入的是上下文路径,其中包含的每个包必须满足下面条件中的一个、或者两个,否则就会抛出JAXBException :
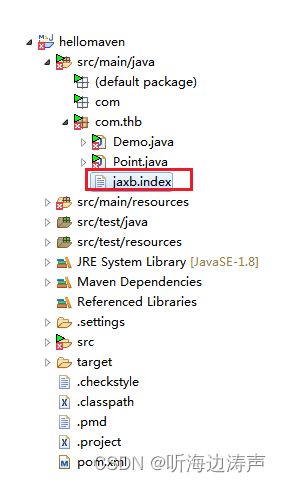
- 包含ObjectFactory.class
- 包含jaxb.index文件
其中jaxb.index文件是一个资源文件,罗列出了被JAXB注解的XML 绑定映射的类。
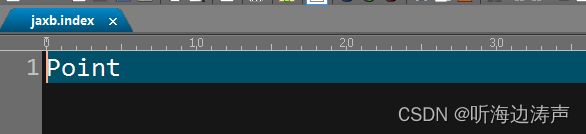
jaxb.index文件的格式:
- 文件中包含了被新行分割的lei类名列表
- 空格、tab、空行被忽略
- 注释符号用’#’ (0x23)
- 在每一行,紧跟注释符的字符被忽略
- 文件必须采用 UTF-8编码
jaxb.index文件中类名的限制:
- 不能以.class结尾
- 类名必须相对包含*jaxb.index文件的包来解析。只有直接包含在该包中的类名才允许放在该文件中。
- 完全限定的类名不允许。相对当前包的限定类名只有声明一个嵌套类或者一个内部类的时候才允许。
Marshaller介绍
- jakarta.xml.bind.Marshaller控制将java内容树序列化到XML数据的过程。
- 客户端可以marshall java内容树到java.io.OutputStream、或者java.io.Writer。
Unmarshaller
jakarta.xml.bind.Unmarshaller用来控制将XML数据反序列到新创建的java内容树的过程。可选地,可以在反序列化过程中,校验XML数据的正确性。
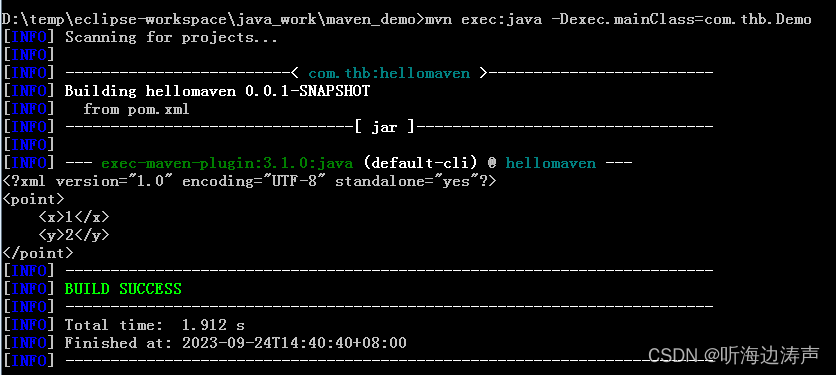
举例:newInstance函数的参数是需要JAXBContext识别的java类、将java内容树marshall到了System.out
调用JAXBContext.newInstance(Point.class)函数,传递了需要JAXBContext识别的java类Point.class,将java内容树marshall到System.out,设置Marshaller的JAXB_FORMATTED_OUTPUT属性为true(表示对生成的xml数据用换行、缩进格式化):
package com.thb;
import jakarta.xml.bind.JAXBContext;
import jakarta.xml.bind.JAXBException;
import jakarta.xml.bind.Marshaller;
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws JAXBException {
JAXBContext context = JAXBContext.newInstance(Point.class);
Marshaller marshaller = context.createMarshaller();
marshaller.setProperty(Marshaller.JAXB_FORMATTED_OUTPUT, true);
marshaller.marshal(new Point(1, 2), System.out);
}
}
package com.thb;
import jakarta.xml.bind.annotation.XmlElement;
import jakarta.xml.bind.annotation.XmlRootElement;
@XmlRootElement
public class Point {
@XmlElement
private int x;
@XmlElement
private int y;
public Point() {}
public Point(int x, int y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
}
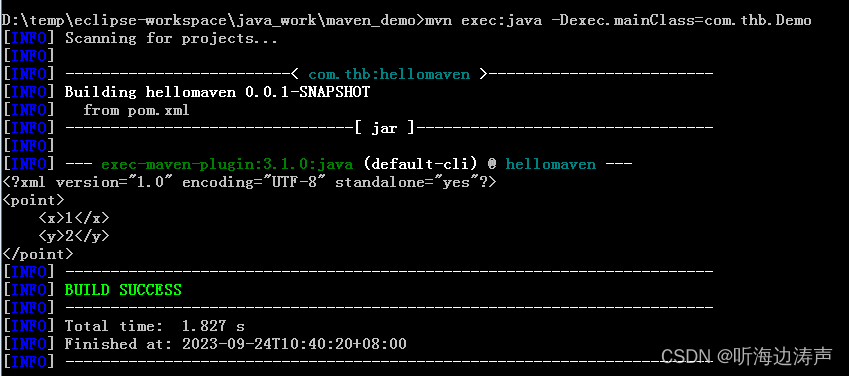
用maven的mvn命令运行程序:
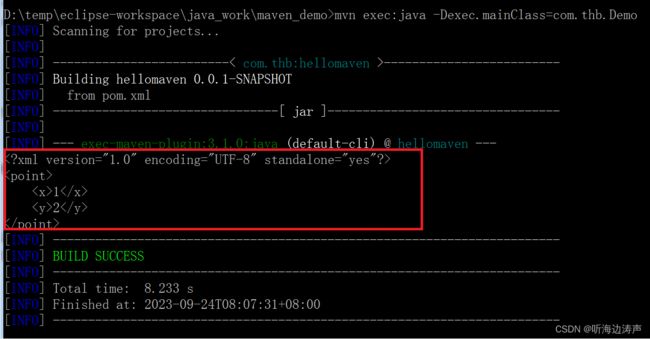
将生成的xml数据打印到了System.out。
举例:不设置 Marshaller的JAXB_FORMATTED_OUTPUT属性
不设置Marshaller的JAXB_FORMATTED_OUTPUT属性(表示对生成的xml数据不用换行、缩进格式化):
package com.thb;
import jakarta.xml.bind.JAXBContext;
import jakarta.xml.bind.JAXBException;
import jakarta.xml.bind.Marshaller;
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws JAXBException {
JAXBContext context = JAXBContext.newInstance(Point.class);
Marshaller marshaller = context.createMarshaller();
marshaller.marshal(new Point(1, 2), System.out);
}
}
package com.thb;
import jakarta.xml.bind.annotation.XmlElement;
import jakarta.xml.bind.annotation.XmlRootElement;
@XmlRootElement
public class Point {
@XmlElement
private int x;
@XmlElement
private int y;
public Point() {}
public Point(int x, int y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
}
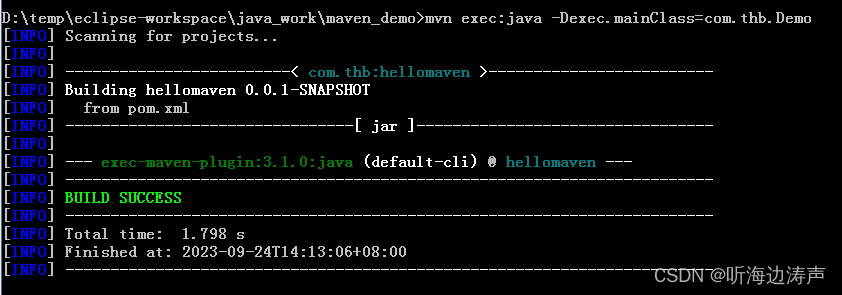
用maven的mvn命令运行程序:

可以看出,生成的xml结果没有格式化。
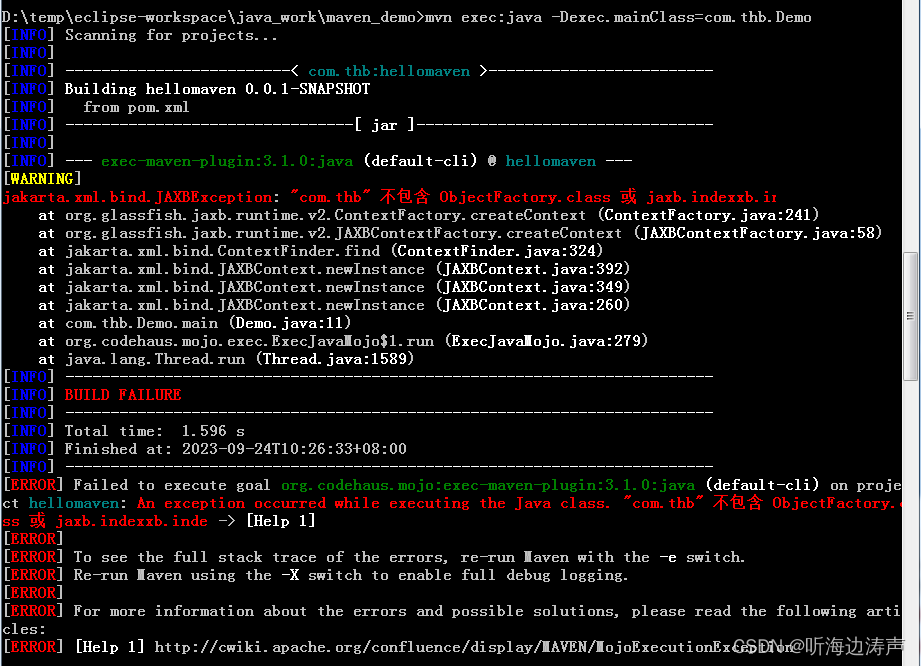
举例:newInstance传入上下文路径,但包路径下没有ObjectFactory.class文件,也没有jaxb.index文件,运行抛出异常
java代码:
package com.thb;
import jakarta.xml.bind.JAXBContext;
import jakarta.xml.bind.JAXBException;
import jakarta.xml.bind.Marshaller;
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws JAXBException {
JAXBContext context = JAXBContext.newInstance("com.thb");
Marshaller marshaller = context.createMarshaller();
marshaller.setProperty(Marshaller.JAXB_FORMATTED_OUTPUT, true);
marshaller.marshal(new Point(1, 2), System.out);
}
}
package com.thb;
import jakarta.xml.bind.annotation.XmlElement;
import jakarta.xml.bind.annotation.XmlRootElement;
@XmlRootElement
public class Point {
@XmlElement
private int x;
@XmlElement
private int y;
public Point() {}
public Point(int x, int y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
}
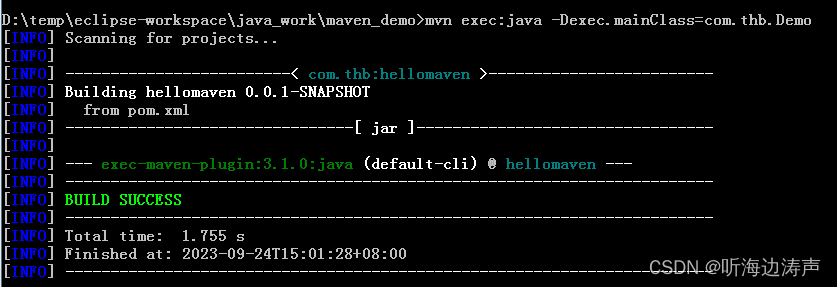
举例:newInstance传入上下文路径,包路径下有jaxb.index文件,运行正常
java代码:
package com.thb;
import jakarta.xml.bind.JAXBContext;
import jakarta.xml.bind.JAXBException;
import jakarta.xml.bind.Marshaller;
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws JAXBException {
JAXBContext context = JAXBContext.newInstance("com.thb");
Marshaller marshaller = context.createMarshaller();
marshaller.setProperty(Marshaller.JAXB_FORMATTED_OUTPUT, true);
marshaller.marshal(new Point(1, 2), System.out);
}
}
package com.thb;
import jakarta.xml.bind.annotation.XmlElement;
import jakarta.xml.bind.annotation.XmlRootElement;
@XmlRootElement
public class Point {
@XmlElement
private int x;
@XmlElement
private int y;
public Point() {}
public Point(int x, int y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
}
marshall到文件
java代码:
package com.thb;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import jakarta.xml.bind.JAXBContext;
import jakarta.xml.bind.JAXBException;
import jakarta.xml.bind.Marshaller;
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws JAXBException, FileNotFoundException {
JAXBContext context = JAXBContext.newInstance(Point.class);
Marshaller marshaller = context.createMarshaller();
marshaller.setProperty(Marshaller.JAXB_FORMATTED_OUTPUT, true);
marshaller.marshal(new Point(1, 2), new FileOutputStream("D:/temp/outputdata/point.xml"));
}
}
package com.thb;
import jakarta.xml.bind.annotation.XmlElement;
import jakarta.xml.bind.annotation.XmlRootElement;
@XmlRootElement
public class Point {
@XmlElement
private int x;
@XmlElement
private int y;
public Point() {}
public Point(int x, int y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
}
1
2
设置marshall的编码格式
java代码:
package com.thb;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import jakarta.xml.bind.JAXBContext;
import jakarta.xml.bind.JAXBException;
import jakarta.xml.bind.Marshaller;
import jakarta.xml.bind.Unmarshaller;
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws JAXBException, FileNotFoundException {
final File file = new File("D:/temp/outputdata/point.xml");
JAXBContext context = JAXBContext.newInstance(Point.class);
Marshaller marshaller = context.createMarshaller();
marshaller.setProperty(Marshaller.JAXB_FORMATTED_OUTPUT, true);
marshaller.setProperty(Marshaller.JAXB_ENCODING, "UTF-8");
marshaller.marshal(new Point(1, 2), new FileOutputStream(file));
}
}
package com.thb;
import jakarta.xml.bind.annotation.XmlElement;
import jakarta.xml.bind.annotation.XmlRootElement;
@XmlRootElement
public class Point {
@XmlElement
private int x;
@XmlElement
private int y;
public Point() {}
public Point(int x, int y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
}
1
2
将xml数据反序列化到java内容树
java代码:
package com.thb;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import jakarta.xml.bind.JAXBContext;
import jakarta.xml.bind.JAXBException;
import jakarta.xml.bind.Marshaller;
import jakarta.xml.bind.Unmarshaller;
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws JAXBException, FileNotFoundException {
final File file = new File("D:/temp/outputdata/point.xml");
JAXBContext context = JAXBContext.newInstance(Point.class);
Marshaller marshaller = context.createMarshaller();
marshaller.setProperty(Marshaller.JAXB_FORMATTED_OUTPUT, true);
marshaller.marshal(new Point(1, 2), new FileOutputStream(file));
Unmarshaller unMarshaller = context.createUnmarshaller();
Object point = unMarshaller.unmarshal(file);
marshaller.marshal(point, System.out);
}
}
package com.thb;
import jakarta.xml.bind.annotation.XmlElement;
import jakarta.xml.bind.annotation.XmlRootElement;
@XmlRootElement
public class Point {
@XmlElement
private int x;
@XmlElement
private int y;
public Point() {}
public Point(int x, int y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
}