java实现动态定时任务(重写 ExecutorService)
场景一: 定时任务,5秒、30秒、60秒、100秒 … 无规律去指定一个指定的任务。
场景二: 假设系统之间相互请求、其中一个系统宕机后,每间隔5秒请求一次。过于频繁、进行优化:5秒请求第一次、10秒请求第二次、30秒请求第四次、1分钟请求第五次、10分钟请求第六次… ,请求成功则取消定时任务。请求失败间隔一段时间继续。
利用 java 8 中现有的类实现,现分享本人实现的思路,若哪里不对或有更好的经验望请留言指出,谢谢!
package com.boot.modules.house.test;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.concurrent.*;
/**
* @author 记得
* @version 1.0
* @desc
* @date 2022/4/12 9:35
*/
public class MyScheduledExecutorService extends AbstractExecutorService implements ScheduledExecutorService {
private final ScheduledExecutorService e;
private TimeUnit unit;
private List<Long> intervalTimes;
private int timeIndex = 0;
private MyScheduledExecutorService(ScheduledExecutorService executor, List<Long> intervalTimes, TimeUnit unit) {
this.intervalTimes = intervalTimes;
this.unit = unit;
e = executor;
}
public void execute(Runnable command) {
e.execute(command);
}
public void shutdown() {
e.shutdown();
}
public List<Runnable> shutdownNow() {
return e.shutdownNow();
}
public boolean isShutdown() {
return e.isShutdown();
}
public boolean isTerminated() {
return e.isTerminated();
}
public boolean awaitTermination(long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
throws InterruptedException {
return e.awaitTermination(timeout, unit);
}
public Future<?> submit(Runnable task) {
return e.submit(task);
}
public <T> Future<T> submit(Callable<T> task) {
return e.submit(task);
}
public <T> Future<T> submit(Runnable task, T result) {
return e.submit(task, result);
}
public <T> List<Future<T>> invokeAll(Collection<? extends Callable<T>> tasks)
throws InterruptedException {
return e.invokeAll(tasks);
}
public <T> List<Future<T>> invokeAll(Collection<? extends Callable<T>> tasks,
long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
throws InterruptedException {
return e.invokeAll(tasks, timeout, unit);
}
public <T> T invokeAny(Collection<? extends Callable<T>> tasks)
throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException {
return e.invokeAny(tasks);
}
public <T> T invokeAny(Collection<? extends Callable<T>> tasks,
long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException, TimeoutException {
return e.invokeAny(tasks, timeout, unit);
}
@Override
public ScheduledFuture<?> schedule(Runnable command, long delay, TimeUnit unit) {
return e.schedule(command, delay, unit);
}
@Override
public <V> ScheduledFuture<V> schedule(Callable<V> callable, long delay, TimeUnit unit) {
return e.schedule(callable, delay, unit);
}
@Override
public ScheduledFuture<?> scheduleAtFixedRate(Runnable command, long initialDelay, long period, TimeUnit unit) {
return e.scheduleAtFixedRate(command, initialDelay, period, unit);
}
@Override
public ScheduledFuture<?> scheduleWithFixedDelay(Runnable command, long initialDelay, long delay, TimeUnit unit) {
return e.scheduleWithFixedDelay(command, initialDelay, delay, unit);
}
public boolean executro(Runnable command) {
ScheduledFuture<?> schedule = e.schedule(command, intervalTimes.get(timeIndex), unit);
timeIndex++;
while (true) {
if (timeIndex >= this.intervalTimes.size()) { //超出计划时间,停止任务
e.shutdown();
return true;
}
//任务完成,递归创建新的任务时间
if (schedule.isDone()) {
executro(command);
}
}
}
public static MyScheduledExecutorService newMyScheduledExecutorService(List<Long> intervalTimes, TimeUnit unit) {
return new MyScheduledExecutorService(new ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(1), intervalTimes, unit);
}
}
//测试 main
package com.boot.modules.house.test;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
/**
* @author 记得
* @version 1.0
* @desc
* @date 2022/4/11 17:21
*/
public class TestDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<Long> intervalTimes = new ArrayList<Long>() {{
this.add(2L);
this.add(4L);
this.add(8L);
this.add(16L);
}};
MyScheduledExecutorService service = MyScheduledExecutorService.newMyScheduledExecutorService(intervalTimes, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
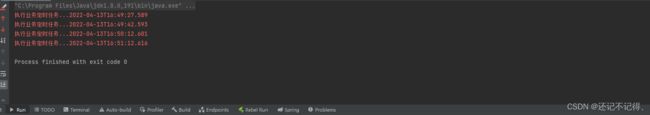
boolean executro = service.executro(() -> {
System.err.println("执行业务定时任务..." + LocalDateTime.now());
});
//若返回 true 则停止任务
if (executro) {
service.shutdown();
}
}
}
说明备注
1、自定义类 MyScheduledExecutorService 继承,实现,AbstractExecutorService、ScheduledExecutorService 方法并重写其方法。
2、自定义 executro 方法,其实也可以直接编写实现 execute 方法。这里本人考虑到的场景比如。请求其它系统,若请求成功,则取消后面所有定时任务不在请求。就自定义 executro 方法,并在方法体中根据自己业务需求,进行处理,若请求成功 则返回 true ,调用者检测为 true 时,调用者停止定时任务、若场景可能是 定时间隔不规则时间执行任务无论结果如何都需要执行,此时重写 execute 方法即可
3、main 方法调用 executro 方法,验证结果。