Pandas 模块-操纵数据(4)-数据排序- .sort_index()
目录
4. 使用 .sort_index() 查看按照轴排序的数据
4.1 .sort_index() 语法
4.2 .sort_index() 范例
4.2.1 axis 用法
4.2.2 ascending 用法
4.2.3 inplace 用法
4.2.4 kind 用法
4.2.5 na_position 的用法
4.2.6 ignore_index 用法
4.2.6 key 用法
4.2.7 key 用法拓展----问题代码1)和解决方案
4.2.8 key 用法拓展----问题代码2)和未知解决方案
4. 使用 .sort_index() 查看按照轴排序的数据
df. sort_index() 可以完成和 df. sort_values() 完全相同的功能,但python更推荐用只用df. sort_index()对“根据行标签”和“根据列标签”排序,其他排序方式推荐用df.sort_values()。
4.1 .sort_index() 语法
语法:下面是最新的,
DataFrame.sort_index(axis=0, level=None, ascending=True, inplace=False, kind='quicksort', na_position='last', sort_remaining=True, ignore_index=False, key=None)
大家可能在很多版本上看到下面的语法结构,尤其是 by,已经被删掉了。
sort_index(axis=0, level=None, ascending=True, inplace=False, kind='quicksort', na_position='last', sort_remaining=True, by=None)
参数说明:
axis:axis 默认为 0,即指按照行的索引进行排序;axis 设置为 1,即指按照列的索引进行排序
level:默认None,否则按照给定的 level 顺序排列。
ascending:ascending 默认为 True,即升序,设置为 False 时候为降序。
inplace:默认False,否则排序之后的数据直接替换原来的数据框
kind:排序方法,{‘quicksort’, ‘mergesort’, ‘heapsort’}, default ‘quicksort’。用户可以自己选用
na_position:缺失值默认排在最后{"first","last"},参数“ first”将NaN放在开头,“ last”将NaN放在结尾。by:按照某一列或几列数据进行排序,但是by参数貌似不建议使用,已经被删除
ignore_index:布尔量,默认为 False,如果为 True, 那么 axis 则是 label 0,1,2;这是新加的
key:这是一个可调用的函数,即在排序之前先对 index 的值执行 key 函数。这有点类似于内置函数 sorted() 函数里面的 key 函数
Help on method sort_index in module pandas.core.frame:
sort_index(axis=0, level=None, ascending: 'Union[Union[bool, int], Sequence[Union[bool, int]]]' = True, inplace: 'bool' = False, kind: 'str' = 'quicksort', na_position: 'str' = 'last', sort_remaining: 'bool' = True, ignore_index: 'bool' = False, key: 'IndexKeyFunc' = None) method of pandas.core.frame.DataFrame instance
Sort object by labels (along an axis).
Returns a new DataFrame sorted by label if `inplace` argument is
``False``, otherwise updates the original DataFrame and returns None.
Parameters
----------
axis : {0 or 'index', 1 or 'columns'}, default 0
The axis along which to sort. The value 0 identifies the rows,
and 1 identifies the columns.
level : int or level name or list of ints or list of level names
If not None, sort on values in specified index level(s).
ascending : bool or list-like of bools, default True
Sort ascending vs. descending. When the index is a MultiIndex the
sort direction can be controlled for each level individually.
inplace : bool, default False
If True, perform operation in-place.
kind : {'quicksort', 'mergesort', 'heapsort'}, default 'quicksort'
Choice of sorting algorithm. See also ndarray.np.sort for more
information. `mergesort` is the only stable algorithm. For
DataFrames, this option is only applied when sorting on a single
column or label.
na_position : {'first', 'last'}, default 'last'
Puts NaNs at the beginning if `first`; `last` puts NaNs at the end.
Not implemented for MultiIndex.
sort_remaining : bool, default True
If True and sorting by level and index is multilevel, sort by other
levels too (in order) after sorting by specified level.
ignore_index : bool, default False
If True, the resulting axis will be labeled 0, 1, …, n - 1.
.. versionadded:: 1.0.0
key : callable, optional
If not None, apply the key function to the index values
before sorting. This is similar to the `key` argument in the
builtin :meth:`sorted` function, with the notable difference that
this `key` function should be *vectorized*. It should expect an
``Index`` and return an ``Index`` of the same shape. For MultiIndex
inputs, the key is applied *per level*.
.. versionadded:: 1.1.0
Returns
-------
DataFrame or None
The original DataFrame sorted by the labels or None if ``inplace=True``.
See Also
--------
Series.sort_index : Sort Series by the index.
DataFrame.sort_values : Sort DataFrame by the value.
Series.sort_values : Sort Series by the value.
Examples
--------
>>> df = pd.DataFrame([1, 2, 3, 4, 5], index=[100, 29, 234, 1, 150],
... columns=['A'])
>>> df.sort_index()
A
1 4
29 2
100 1
150 5
234 3
By default, it sorts in ascending order, to sort in descending order,
use ``ascending=False``
>>> df.sort_index(ascending=False)
A
234 3
150 5
100 1
29 2
1 4
A key function can be specified which is applied to the index before
sorting. For a ``MultiIndex`` this is applied to each level separately.
>>> df = pd.DataFrame({"a": [1, 2, 3, 4]}, index=['A', 'b', 'C', 'd'])
>>> df.sort_index(key=lambda x: x.str.lower())
a
A 1
b 2
C 3
d 4
4.2 .sort_index() 范例
先准备数据
在使用各种api之前,先创建测试使用数据:
代码:
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
dict_data={"a":list("abcdef"),"b":list("defghi"),"c":list("ghijkl")}
df=pd.DataFrame.from_dict(dict_data)
df运行结果:
Out[1]:
| a | b | c | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | a | d | g |
| 1 | b | e | h |
| 2 | c | f | i |
| 3 | d | g | j |
| 4 | e | h | k |
| 5 | f | i | l |
4.2.1 axis 用法
axis =0,按照行排序;axis = 1,按照列排序;
In [27]: df.sort_index(axis=0,ascending=False)
Out[27]:
a b c 5 f i l 4 e h k 3 d g j 2 c f i 1 b e h 0 a d g In [28]: df.sort_index(axis=1,ascending=False)
Out[28]:
c b a 0 g d a 1 h e b 2 i f c 3 j g d 4 k h e 5 l i f
4.2.2 ascending 用法
In [25]: df.sort_index(ascending=False)
Out[25]:
a b c 5 f i l 4 e h k 3 d g j 2 c f i 1 b e h 0 a d g In [26]: df.sort_index(ascending=True)
Out[26]:
a b c 0 a d g 1 b e h 2 c f i 3 d g j 4 e h k 5 f i l
4.2.3 inplace 用法
inplace 默认为 False,也就是不改变原来的 DataFrame;使用 inplace 参数为 True 时候,则改变原来的 DataFrame。代码如下
df.sort_index(axis=1,ascending=False,inplace=True)
print(df)运行结果如下,可以看到 df 已经被改变了
c b a 0 g d a 1 h e b 2 i f c 3 j g d 4 k h e 5 l i f
4.2.4 kind 用法
kind:排序方法,{‘quicksort’, ‘mergesort’, ‘heapsort’}, default ‘quicksort’。用户可以自己选用
这个其实在大量数据进行排序时候才有意义,也和数据的特点有关系,具体选择哪个排序方法,需要使用者知道一定的数据排序知识,在此不赘述。
4.2.5 na_position 的用法
na_position:{'first','last'},默认为'last'
如果 na_position 为 “first”,则将NaNs置于开头, na_position 为`last' 将 NaNs 置于末尾。
不是为多索引实现的。
4.2.6 ignore_index 用法
ignore_index:布尔量,默认为 False,如果为 True, 那么 axis 则是 label 0,1,2;
直接看代码
dict_data={"a":list("abcdef"),"b":list("defghi"),"c":list("ghijkl")}
df=pd.DataFrame.from_dict(dict_data)
print(("*"*20+" 初始的 DataFrame 数据"+"*"*20).ljust(80))
print(df)
print(("*"*20+" 修改 index 后的 DataFrame 数据"+"*"*20).ljust(80))
df.index=["01","002","03","004","005","006"]
print(df)
print(("*"*20+" 再修改 columns 后的 DataFrame 数据"+"*"*20).ljust(80))
df.columns=["X","Y","Z"]
print(df)
print(("*"*20+" sort_index 排序 axis =0 ignore_index=True "+"*"*20).ljust(80))
print(df.sort_index(ignore_index=True,axis=0))
print(("*"*20+" sort_index 排序 axis =1 ignore_index=True "+"*"*20).ljust(80))
print(df.sort_index(ignore_index=True,axis=1)) # 这时候 axis 不起作用
print(("*"*20+" 当前的 DataFrame 数据"+"*"*20).ljust(80))
print(df)运行结果
******************** 初始的 DataFrame 数据********************
a b c
0 a d g
1 b e h
2 c f i
3 d g j
4 e h k
5 f i l
******************** 修改 index 后的 DataFrame 数据********************
a b c
01 a d g
002 b e h
03 c f i
004 d g j
005 e h k
006 f i l
******************** 再修改 columns 后的 DataFrame 数据********************
X Y Z
01 a d g
002 b e h
03 c f i
004 d g j
005 e h k
006 f i l
******************** sort_index 排序 axis =0 ignore_index=True ********************
X Y Z
0 b e h
1 d g j
2 e h k
3 f i l
4 a d g
5 c f i
******************** sort_index 排序 axis =1 ignore_index=True ********************
X Y Z
01 a d g
002 b e h
03 c f i
004 d g j
005 e h k
006 f i l
******************** 当前的 DataFrame 数据********************
X Y Z
01 a d g
002 b e h
03 c f i
004 d g j
005 e h k
006 f i l
4.2.6 key 用法
key 的用法据说和 sorted 内置函数里面的key 类似,让我们看看是不是这样。
看起来很简单,key 这个地方用一个函数,可以是自己写的,也可以是内置的。
当真如此简单吗?
4.2.7 key 用法拓展----问题代码1)和解决方案
一开始我写了这样一段代码,但是结果很出乎意料,index 明明是 str 类型,但是经过一系列拷贝之后,却变成了 int 类型,导致报错。
print(("*"*20+" 初始的 DataFrame 数据"+"*"*20).ljust(80))
df.index=["01","002","03","004","005","006"]
print(df)
# 打印出每个index 的 长度、类型
print(("*"*20+" 打印每个index 的长度 、类型"+"*"*20).ljust(80))
for tmp in df.index:
print(tmp,len(tmp),type(tmp))
print(("*"*20+" sort_index 排序 key=len,ascending=False "+"*"*20).ljust(80))
print(df.sort_index(key=len,ascending=False))
print(("*"*20+" sort_index 排序 key=len,ascending=True "+"*"*20).ljust(80))
print(df.sort_index(key=len,ascending=True))
# 这里升序降序好像有点问题,好像反了运行结果
******************** 初始的 DataFrame 数据******************** X Y Z 01 a d g 002 b e h 03 c f i 004 d g j 005 e h k 006 f i l ******************** 打印每个index 的长度 、类型******************** 01 2002 3 03 2 004 3 005 3 006 3 ******************** sort_index 排序 key=len,ascending=False ******************** --------------------------------------------------------------------------- TypeError Traceback (most recent call last)in 9 10 print(("*"*20+" sort_index 排序 key=len,ascending=False "+"*"*20).ljust(80)) ---> 11 print(df.sort_index(key=len,ascending=False)) 12 13 print(("*"*20+" sort_index 排序 key=len,ascending=True "+"*"*20).ljust(80)) ~\Anaconda3\lib\site-packages\pandas\core\frame.py in sort_index(self, axis, level, ascending, inplace, kind, na_position, sort_remaining, ignore_index, key) 5580 d 4 5581 """ -> 5582 return super().sort_index( 5583 axis, 5584 level, ~\Anaconda3\lib\site-packages\pandas\core\generic.py in sort_index(self, axis, level, ascending, inplace, kind, na_position, sort_remaining, ignore_index, key) 4535 target = self._get_axis(axis) 4536 -> 4537 indexer = get_indexer_indexer( 4538 target, level, ascending, kind, na_position, sort_remaining, key 4539 ) ~\Anaconda3\lib\site-packages\pandas\core\sorting.py in get_indexer_indexer(target, level, ascending, kind, na_position, sort_remaining, key) 67 """ 68 ---> 69 target = ensure_key_mapped(target, key, levels=level) 70 target = target._sort_levels_monotonic() 71 ~\Anaconda3\lib\site-packages\pandas\core\sorting.py in ensure_key_mapped(values, key, levels) 492 493 result = key(values.copy()) --> 494 if len(result) != len(values): 495 raise ValueError( 496 "User-provided `key` function must not change the shape of the array." TypeError: object of type 'int' has no len()
我一开始怀疑 sorting.py 有些地方有问题,使用数值时候没有问题。
代码如下
print(("*"*20+" 初始的 DataFrame 数据"+"*"*20).ljust(80))
print(df)
print(("*"*20+" sort_index 排序 key=abs,ascending=False "+"*"*20).ljust(80))
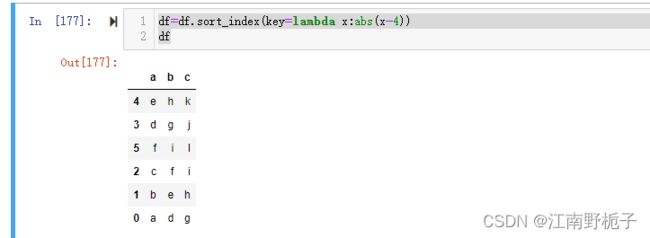
print(df.sort_index(key=abs,ascending=False))
print(("*"*20+" sort_index 排序 key=abs,ascending=True "+"*"*20).ljust(80))
print(df.sort_index(key=abs,ascending=True))
# 这里升序降序没问题 运行结果
******************** 初始的 DataFrame 数据********************
X Y Z
-3 a d g
2 b e h
-5 c f i
1 d g j
-7 e h k
0 f i l
******************** sort_index 排序 key=abs,ascending=False ********************
X Y Z
-7 e h k
-5 c f i
-3 a d g
2 b e h
1 d g j
0 f i l
******************** sort_index 排序 key=abs,ascending=True ********************
X Y Z
0 f i l
1 d g j
2 b e h
-3 a d g
-5 c f i
-7 e h k
好吧,遇到问题其实是一件好事,那么先解决问题吧。
首先针对问题代码 1),我想根据 index的长度来进行排序,经过对 pandas 的源代码进行分析,发现了问题所在。大家注意到这行代码没有 result = key(values.copy())
result = key(values.copy())
if len(result) != len(values):
raise ValueError(
"User-provided `key` function must not change the shape of the array."
)所在脚本:
如果 key 是一般的函数,例如 f=lambda x:x.str.count("0") ,那么返回的还是 index 类型的,如果是 len,它是把整个index当成一个整体,而不是单独对 index 里面的数据进行处理。
所以,这样就会导致上一行代码中 result 已经变成 int 类型了,导致报错。 我个人觉得,这个可能是 pandas sort_index 函数不太完美的地方。
好了,我试了另外一种写法,目前能得到理想的结果。
代码如下:
import pandas as pd
import pdb
#pdb.set_trace()
dict_data={"a":list("abcdef"),"b":list("defghi"),"c":list("ghijkl")}
df=pd.DataFrame.from_dict(dict_data)
print(("*"*20+" 初始的 DataFrame 数据"+"*"*20).ljust(80))
df.index=["01","002","03","004","005","006"]
df.columns=["X","Y","Z"]
print(df)
# 打印出每个index 的 长度、类型
print(("*"*20+" 打印每个index 的长度 、类型"+"*"*20).ljust(80))
for tmp in df.index:
print(tmp,len(tmp),type(tmp))
print(("*"*20+" sort_index 排序 key=len,ascending=False "+"*"*20).ljust(80))
print(df.sort_index(key=lambda x:x.str.len(),ascending=False))
print(("*"*20+" sort_index 排序 key=len,ascending=True "+"*"*20).ljust(80))
print(df.sort_index(key=lambda x:x.str.len(),ascending=True))
运行结果:
******************** 初始的 DataFrame 数据********************
X Y Z
01 a d g
002 b e h
03 c f i
004 d g j
005 e h k
006 f i l
******************** 打印每个index 的长度 、类型********************
01 2
002 3
03 2
004 3
005 3
006 3
******************** sort_index 排序 key=len,ascending=False ********************
X Y Z
002 b e h
004 d g j
005 e h k
006 f i l
01 a d g
03 c f i
******************** sort_index 排序 key=len,ascending=True ********************
X Y Z
01 a d g
03 c f i
002 b e h
004 d g j
005 e h k
006 f i l
4.2.8 key 用法拓展----问题代码2)和未知解决方案
在我检查问题代码 1)时候,我还试过其他写法,将 index 先用 str 函数转换一下再使用 len 函数进行长度检查,代码如下,但是又有新的问题产生,感觉 ascending 的含义反了。
import pandas as pd
dict_data={"a":list("abcdef"),"b":list("defghi"),"c":list("ghijkl")}
df=pd.DataFrame.from_dict(dict_data)
print(("*"*20+" 初始的 DataFrame 数据"+"*"*20).ljust(80))
df.index=["01","002","03","004","005","006"]
df.columns=["X","Y","Z"]
print(df)
# 打印出每个index 的 长度、类型
print(("*"*20+" 打印每个index 的长度 、类型"+"*"*20).ljust(80))
for tmp in df.index:
print(tmp,len(tmp),type(tmp))
print(("*"*20+" sort_index 排序 key=len(str()),ascending=False "+"*"*20).ljust(80))
print(df.sort_index(key=len(str()),ascending=False))
print(("*"*20+" sort_index 排序 key=len(str()),ascending=True "+"*"*20).ljust(80))
print(df.sort_index(key=len(str()),ascending=True))运行结果
******************** 初始的 DataFrame 数据********************
X Y Z
01 a d g
002 b e h
03 c f i
004 d g j
005 e h k
006 f i l
******************** 打印每个index 的长度 、类型********************
01 2
002 3
03 2
004 3
005 3
006 3
******************** sort_index 排序 key=len(str()),ascending=False ********************
X Y Z
03 c f i
01 a d g
006 f i l
005 e h k
004 d g j
002 b e h
******************** sort_index 排序 key=len(str()),ascending=True ********************
X Y Z
002 b e h
004 d g j
005 e h k
006 f i l
01 a d g
03 c f i
现在来针对问题代码 2) 进行分析:
首先,ascending 确实起作用了,只是看起来作用反了
其次,key=len(str()) 这种写法符合语法要求,因为没报错(我真机智!)
再次,看起来确实是按照判断 index 的长度来进行排序的,那么问题到底在哪里呢?
同学们,还记得 Python 是一种解释型语言吗,它不是编译好再运行,而是一边跑一边解释。
我对此进行了详细调试,有兴趣的,可以看调试结果。
好,回到我一开始的分析上来。
首先,ascending 确实起作用了,只是看起来作用反了
解释:好吧,算这个没错。
其次,key=len(str()) 这种写法符合语法要求,因为没报错(我真机智!)
解释:因为 Python 是 一种解释型语言,出于某些不完美的特质,len(str()),被认为是可调用的函数。(当然这种写法肯定不对,我想当然了,先抱头鼠窜下。)
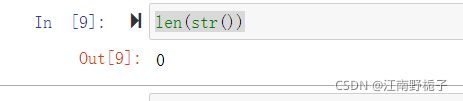
事实上,在 Python 解释 len(str()) 的过程中,它被解释为 0 ,或者 None 或者 是 False !
请看 Key =0
请看 Key = None
再次,看起来确实是按照判断 index 的长度来进行排序的,那么问题到底在哪里呢?
解释:在上面已经说了,在 Python 解释 len(str()) 的过程中,它被解释为 0 ,或者 None 或者 是 False !那么和 ascending 一起用时候,就会变成现在这个样子。
**************************************************************************************************************
备注:当我还是个 C 程序员时候,记得曾经被一个同事气倒,因为他 code review 我的代码,觉得写得太罗嗦,我大概写了 5 行吧,他说他 3 行就可以写完,年轻气盛的我为了证明自己的能力,用 1 行代码把那 5 行代码进行压缩,并且颇为得意。
其实,回过头来想想,真是没有必要。那只是一种炫技的行为,我赞成代码写得优美简洁,但没有必要本末倒置。在不确定的情况下,先保证代码的准确性,然后保证可读性,可兼容性,以及相关性能,然后才看代码是不是浓缩的精华。
**************************************************************************************************************
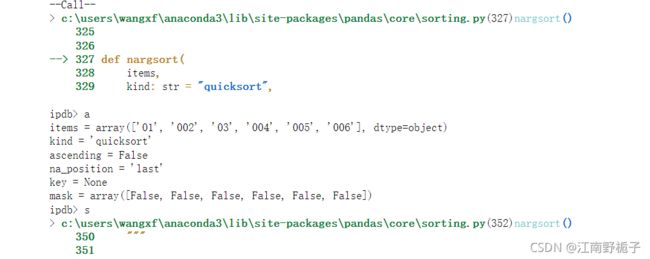
详细的 Debug 过程
--Return-- None >(3) () 1 import pandas as pd 2 import pdb ----> 3 pdb.set_trace() 4 dict_data={"a":list("abcdef"),"b":list("defghi"),"c":list("ghijkl")} 5 df=pd.DataFrame.from_dict(dict_data) ipdb> b 15 Breakpoint 10 at :15 ipdb> continue ******************** 初始的 DataFrame 数据******************** X Y Z 01 a d g 002 b e h 03 c f i 004 d g j 005 e h k 006 f i l ******************** 打印每个index 的长度 、类型******************** 01 2 002 3 03 2 004 3 005 3 006 3 ******************** sort_index 排序 key=len(str()),ascending=False ******************** None > (15) () 11 print(("*"*20+" 打印每个index 的长度 、类型"+"*"*20).ljust(80)) 12 for tmp in df.index: 13 print(tmp,len(tmp),type(tmp)) 14 print(("*"*20+" sort_index 排序 key=len(str()),ascending=False "+"*"*20).ljust(80)) 10-> 15 df.sort_index(key=len(str()),ascending=False) ipdb> s --Call-- > c:\users\wangxf\anaconda3\lib\site-packages\pandas\core\frame.py(5481)sort_index() 5479 return result.__finalize__(self, method="sort_values") 5480 -> 5481 def sort_index( 5482 self, 5483 axis=0, ipdb> s > c:\users\wangxf\anaconda3\lib\site-packages\pandas\core\frame.py(5582)sort_index() 5580 d 4 5581 """ -> 5582 return super().sort_index( 5583 axis, 5584 level, ipdb> a self = X Y Z 01 a d g 002 b e h 03 c f i 004 d g j 005 e h k 006 f i l axis = 0 level = None ascending = False inplace = False kind = 'quicksort' na_position = 'last' sort_remaining = True ignore_index = False key = 0 ipdb> s > c:\users\wangxf\anaconda3\lib\site-packages\pandas\core\frame.py(5583)sort_index() 5581 """ 5582 return super().sort_index( -> 5583 axis, 5584 level, 5585 ascending, ipdb> s > c:\users\wangxf\anaconda3\lib\site-packages\pandas\core\frame.py(5584)sort_index() 5582 return super().sort_index( 5583 axis, -> 5584 level, 5585 ascending, 5586 inplace, ipdb> s > c:\users\wangxf\anaconda3\lib\site-packages\pandas\core\frame.py(5585)sort_index() 5583 axis, 5584 level, -> 5585 ascending, 5586 inplace, 5587 kind, ipdb> s > c:\users\wangxf\anaconda3\lib\site-packages\pandas\core\frame.py(5586)sort_index() 5584 level, 5585 ascending, -> 5586 inplace, 5587 kind, 5588 na_position, ipdb> s > c:\users\wangxf\anaconda3\lib\site-packages\pandas\core\frame.py(5587)sort_index() 5585 ascending, 5586 inplace, -> 5587 kind, 5588 na_position, 5589 sort_remaining, ipdb> s > c:\users\wangxf\anaconda3\lib\site-packages\pandas\core\frame.py(5588)sort_index() 5586 inplace, 5587 kind, -> 5588 na_position, 5589 sort_remaining, 5590 ignore_index, ipdb> s > c:\users\wangxf\anaconda3\lib\site-packages\pandas\core\frame.py(5589)sort_index() 5587 kind, 5588 na_position, -> 5589 sort_remaining, 5590 ignore_index, 5591 key, ipdb> s > c:\users\wangxf\anaconda3\lib\site-packages\pandas\core\frame.py(5590)sort_index() 5588 na_position, 5589 sort_remaining, -> 5590 ignore_index, 5591 key, 5592 ) ipdb> s > c:\users\wangxf\anaconda3\lib\site-packages\pandas\core\frame.py(5591)sort_index() 5589 sort_remaining, 5590 ignore_index, -> 5591 key, 5592 ) 5593 ipdb> s > c:\users\wangxf\anaconda3\lib\site-packages\pandas\core\frame.py(5582)sort_index() 5580 d 4 5581 """ -> 5582 return super().sort_index( 5583 axis, 5584 level, ipdb> s --Call-- > c:\users\wangxf\anaconda3\lib\site-packages\pandas\core\generic.py(4518)sort_index() 4516 raise AbstractMethodError(self) 4517 -> 4518 def sort_index( 4519 self, 4520 axis=0, ipdb> s > c:\users\wangxf\anaconda3\lib\site-packages\pandas\core\generic.py(4531)sort_index() 4529 ): 4530 -> 4531 inplace = validate_bool_kwarg(inplace, "inplace") 4532 axis = self._get_axis_number(axis) 4533 ascending = validate_ascending(ascending) ipdb> n > c:\users\wangxf\anaconda3\lib\site-packages\pandas\core\generic.py(4532)sort_index() 4530 4531 inplace = validate_bool_kwarg(inplace, "inplace") -> 4532 axis = self._get_axis_number(axis) 4533 ascending = validate_ascending(ascending) 4534 ipdb> n > c:\users\wangxf\anaconda3\lib\site-packages\pandas\core\generic.py(4533)sort_index() 4531 inplace = validate_bool_kwarg(inplace, "inplace") 4532 axis = self._get_axis_number(axis) -> 4533 ascending = validate_ascending(ascending) 4534 4535 target = self._get_axis(axis) ipdb> n > c:\users\wangxf\anaconda3\lib\site-packages\pandas\core\generic.py(4535)sort_index() 4533 ascending = validate_ascending(ascending) 4534 -> 4535 target = self._get_axis(axis) 4536 4537 indexer = get_indexer_indexer( ipdb> n > c:\users\wangxf\anaconda3\lib\site-packages\pandas\core\generic.py(4537)sort_index() 4535 target = self._get_axis(axis) 4536 -> 4537 indexer = get_indexer_indexer( 4538 target, level, ascending, kind, na_position, sort_remaining, key 4539 ) ipdb> p target Index(['01', '002', '03', '004', '005', '006'], dtype='object') ipdb> p key 0 ipdb> s > c:\users\wangxf\anaconda3\lib\site-packages\pandas\core\generic.py(4538)sort_index() 4536 4537 indexer = get_indexer_indexer( -> 4538 target, level, ascending, kind, na_position, sort_remaining, key 4539 ) 4540 ipdb> s > c:\users\wangxf\anaconda3\lib\site-packages\pandas\core\generic.py(4537)sort_index() 4535 target = self._get_axis(axis) 4536 -> 4537 indexer = get_indexer_indexer( 4538 target, level, ascending, kind, na_position, sort_remaining, key 4539 ) ipdb> s --Call-- > c:\users\wangxf\anaconda3\lib\site-packages\pandas\core\sorting.py(40)get_indexer_indexer() 38 39 ---> 40 def get_indexer_indexer( 41 target: "Index", 42 level: Union[str, int, List[str], List[int]], ipdb> a target = Index(['01', '002', '03', '004', '005', '006'], dtype='object') level = None ascending = False kind = 'quicksort' na_position = 'last' sort_remaining = True key = 0 ipdb> s > c:\users\wangxf\anaconda3\lib\site-packages\pandas\core\sorting.py(69)get_indexer_indexer() 67 """ 68 ---> 69 target = ensure_key_mapped(target, key, levels=level) 70 target = target._sort_levels_monotonic() 71ipdb> p key 0 ipdb> p target Index(['01', '002', '03', '004', '005', '006'], dtype='object') ipdb> n > c:\users\wangxf\anaconda3\lib\site-packages\pandas\core\sorting.py(70)get_indexer_indexer() 68 69 target = ensure_key_mapped(target, key, levels=level) ---> 70 target = target._sort_levels_monotonic() 71 72 if level is not None: ipdb> p target Index(['01', '002', '03', '004', '005', '006'], dtype='object') ipdb> n > c:\users\wangxf\anaconda3\lib\site-packages\pandas\core\sorting.py(72)get_indexer_indexer() 70 target = target._sort_levels_monotonic() 71 ---> 72 if level is not None: 73 _, indexer = target.sortlevel( 74 level, ascending=ascending, sort_remaining=sort_remaining ipdb> p target Index(['01', '002', '03', '004', '005', '006'], dtype='object') ipdb> s > c:\users\wangxf\anaconda3\lib\site-packages\pandas\core\sorting.py(76)get_indexer_indexer() 74 level, ascending=ascending, sort_remaining=sort_remaining 75 ) ---> 76 elif isinstance(target, ABCMultiIndex): 77 indexer = lexsort_indexer( 78 target._get_codes_for_sorting(), orders=ascending, na_position=na_position ipdb> s --Call-- > c:\users\wangxf\anaconda3\lib\site-packages\pandas\core\dtypes\generic.py(30)_check() 28 # https://github.com/python/mypy/issues/1006 29 # error: 'classmethod' used with a non-method ---> 30 @classmethod # type: ignore[misc] 31 def _check(cls, inst) -> bool: 32 return getattr(inst, attr, "_typ") in comp ipdb> b Num Type Disp Enb Where 1 breakpoint keep yes at:15 breakpoint already hit 1 time 2 breakpoint keep yes at :15 breakpoint already hit 1 time 3 breakpoint keep yes at :15 breakpoint already hit 1 time 4 breakpoint keep yes at :15 breakpoint already hit 1 time 5 breakpoint keep yes at c:\users\wangxf\anaconda3\lib\site-packages\pandas\core\frame.py:368 6 breakpoint keep yes at :15 breakpoint already hit 1 time 7 breakpoint keep yes at c:\users\wangxf\anaconda3\lib\site-packages\pandas\core\sorting.py:368 breakpoint already hit 1 time 8 breakpoint keep yes at :15 breakpoint already hit 1 time 9 breakpoint keep yes at c:\users\wangxf\anaconda3\lib\site-packages\pandas\core\sorting.py:380 breakpoint already hit 1 time 10 breakpoint keep yes at :15 breakpoint already hit 1 time ipdb> n > c:\users\wangxf\anaconda3\lib\site-packages\pandas\core\dtypes\generic.py(32)_check() 30 @classmethod # type: ignore[misc] 31 def _check(cls, inst) -> bool: ---> 32 return getattr(inst, attr, "_typ") in comp 33 34 dct = {"__instancecheck__": _check, "__subclasscheck__": _check} ipdb> n --Return-- False > c:\users\wangxf\anaconda3\lib\site-packages\pandas\core\dtypes\generic.py(32)_check() 30 @classmethod # type: ignore[misc] 31 def _check(cls, inst) -> bool: ---> 32 return getattr(inst, attr, "_typ") in comp 33 34 dct = {"__instancecheck__": _check, "__subclasscheck__": _check} ipdb> n > c:\users\wangxf\anaconda3\lib\site-packages\pandas\core\sorting.py(82)get_indexer_indexer() 80 else: 81 # Check monotonic-ness before sort an index (GH 11080) ---> 82 if (ascending and target.is_monotonic_increasing) or ( 83 not ascending and target.is_monotonic_decreasing 84 ): ipdb> n > c:\users\wangxf\anaconda3\lib\site-packages\pandas\core\sorting.py(83)get_indexer_indexer() 81 # Check monotonic-ness before sort an index (GH 11080) 82 if (ascending and target.is_monotonic_increasing) or ( ---> 83 not ascending and target.is_monotonic_decreasing 84 ): 85 return None ipdb> n > c:\users\wangxf\anaconda3\lib\site-packages\pandas\core\sorting.py(82)get_indexer_indexer() 80 else: 81 # Check monotonic-ness before sort an index (GH 11080) ---> 82 if (ascending and target.is_monotonic_increasing) or ( 83 not ascending and target.is_monotonic_decreasing 84 ): ipdb> n > c:\users\wangxf\anaconda3\lib\site-packages\pandas\core\sorting.py(83)get_indexer_indexer() 81 # Check monotonic-ness before sort an index (GH 11080) 82 if (ascending and target.is_monotonic_increasing) or ( ---> 83 not ascending and target.is_monotonic_decreasing 84 ): 85 return None ipdb> n > c:\users\wangxf\anaconda3\lib\site-packages\pandas\core\sorting.py(82)get_indexer_indexer() 80 else: 81 # Check monotonic-ness before sort an index (GH 11080) ---> 82 if (ascending and target.is_monotonic_increasing) or ( 83 not ascending and target.is_monotonic_decreasing 84 ): ipdb> n > c:\users\wangxf\anaconda3\lib\site-packages\pandas\core\sorting.py(87)get_indexer_indexer() 85 return None 86 ---> 87 indexer = nargsort( 88 target, kind=kind, ascending=ascending, na_position=na_position 89 ) ipdb> b 352 Breakpoint 11 at c:\users\wangxf\anaconda3\lib\site-packages\pandas\core\sorting.py:352 ipdb> b 380 Breakpoint 12 at c:\users\wangxf\anaconda3\lib\site-packages\pandas\core\sorting.py:380 ipdb> b 367 Breakpoint 13 at c:\users\wangxf\anaconda3\lib\site-packages\pandas\core\sorting.py:367 ipdb> a target = Index(['01', '002', '03', '004', '005', '006'], dtype='object') level = None ascending = False kind = 'quicksort' na_position = 'last' sort_remaining = True key = 0 ipdb> n > c:\users\wangxf\anaconda3\lib\site-packages\pandas\core\sorting.py(88)get_indexer_indexer() 86 87 indexer = nargsort( ---> 88 target, kind=kind, ascending=ascending, na_position=na_position 89 ) 90 return indexer ipdb> n > c:\users\wangxf\anaconda3\lib\site-packages\pandas\core\sorting.py(87)get_indexer_indexer() 85 return None 86 ---> 87 indexer = nargsort( 88 target, kind=kind, ascending=ascending, na_position=na_position 89 ) ipdb> n > c:\users\wangxf\anaconda3\lib\site-packages\pandas\core\sorting.py(352)nargsort() 350 """ 351 11> 352 if key is not None: 353 items = ensure_key_mapped(items, key) 354 return nargsort( ipdb> n > c:\users\wangxf\anaconda3\lib\site-packages\pandas\core\sorting.py(363)nargsort() 361 ) 362 --> 363 items = extract_array(items) 364 if mask is None: 365 mask = np.asarray(isna(items)) ipdb> continue > c:\users\wangxf\anaconda3\lib\site-packages\pandas\core\sorting.py(367)nargsort() 365 mask = np.asarray(isna(items)) 366 13> 367 if is_extension_array_dtype(items): 368 return items.argsort(ascending=ascending, kind=kind, na_position=na_position) 369 else: ipdb> p items['01', '002', '03', '004', '005', '006'] Length: 6, dtype: object ipdb> s --Call-- > c:\users\wangxf\anaconda3\lib\site-packages\pandas\core\dtypes\common.py(1470)is_extension_array_dtype() 1468 1469 -> 1470 def is_extension_array_dtype(arr_or_dtype) -> bool: 1471 """ 1472 Check if an object is a pandas extension array type. ipdb> s > c:\users\wangxf\anaconda3\lib\site-packages\pandas\core\dtypes\common.py(1515)is_extension_array_dtype() 1513 False 1514 """ -> 1515 dtype = getattr(arr_or_dtype, "dtype", arr_or_dtype) 1516 return isinstance(dtype, ExtensionDtype) or registry.find(dtype) is not None 1517 ipdb> n > c:\users\wangxf\anaconda3\lib\site-packages\pandas\core\dtypes\common.py(1516)is_extension_array_dtype() 1514 """ 1515 dtype = getattr(arr_or_dtype, "dtype", arr_or_dtype) -> 1516 return isinstance(dtype, ExtensionDtype) or registry.find(dtype) is not None 1517 1518 ipdb> n --Return-- True > c:\users\wangxf\anaconda3\lib\site-packages\pandas\core\dtypes\common.py(1516)is_extension_array_dtype() 1514 """ 1515 dtype = getattr(arr_or_dtype, "dtype", arr_or_dtype) -> 1516 return isinstance(dtype, ExtensionDtype) or registry.find(dtype) is not None 1517 1518 ipdb> n > c:\users\wangxf\anaconda3\lib\site-packages\pandas\core\sorting.py(368)nargsort() 366 13 367 if is_extension_array_dtype(items): --> 368 return items.argsort(ascending=ascending, kind=kind, na_position=na_position) 369 else: 370 items = np.asanyarray(items) ipdb> p items['01', '002', '03', '004', '005', '006'] Length: 6, dtype: object ipdb> s --Call-- > c:\users\wangxf\anaconda3\lib\site-packages\pandas\core\arrays\base.py(548)argsort() 546 return np.array(self) 547 --> 548 def argsort( 549 self, 550 ascending: bool = True, ipdb> s > c:\users\wangxf\anaconda3\lib\site-packages\pandas\core\arrays\base.py(583)argsort() 581 # 1. _values_for_argsort : construct the values passed to np.argsort 582 # 2. argsort : total control over sorting. --> 583 ascending = nv.validate_argsort_with_ascending(ascending, args, kwargs) 584 585 values = self._values_for_argsort() ipdb> n > c:\users\wangxf\anaconda3\lib\site-packages\pandas\core\arrays\base.py(585)argsort() 583 ascending = nv.validate_argsort_with_ascending(ascending, args, kwargs) 584 --> 585 values = self._values_for_argsort() 586 return nargsort( 587 values, ipdb> s --Call-- > c:\users\wangxf\anaconda3\lib\site-packages\pandas\core\arrays\_mixins.py(148)_values_for_argsort() 146 return bool(array_equivalent(self._ndarray, other._ndarray)) 147 --> 148 def _values_for_argsort(self): 149 return self._ndarray 150 ipdb> a self = ['01', '002', '03', '004', '005', '006'] Length: 6, dtype: object ipdb> s > c:\users\wangxf\anaconda3\lib\site-packages\pandas\core\arrays\_mixins.py(149)_values_for_argsort() 147 148 def _values_for_argsort(self): --> 149 return self._ndarray 150 151 def copy(self: NDArrayBackedExtensionArrayT) -> NDArrayBackedExtensionArrayT: ipdb> p self ['01', '002', '03', '004', '005', '006'] Length: 6, dtype: object ipdb> n --Return-- array(['01', ... dtype=object) > c:\users\wangxf\anaconda3\lib\site-packages\pandas\core\arrays\_mixins.py(149)_values_for_argsort() 147 148 def _values_for_argsort(self): --> 149 return self._ndarray 150 151 def copy(self: NDArrayBackedExtensionArrayT) -> NDArrayBackedExtensionArrayT: ipdb> n > c:\users\wangxf\anaconda3\lib\site-packages\pandas\core\arrays\base.py(586)argsort() 584 585 values = self._values_for_argsort() --> 586 return nargsort( 587 values, 588 kind=kind, ipdb> s > c:\users\wangxf\anaconda3\lib\site-packages\pandas\core\arrays\base.py(587)argsort() 585 values = self._values_for_argsort() 586 return nargsort( --> 587 values, 588 kind=kind, 589 ascending=ascending, ipdb> s > c:\users\wangxf\anaconda3\lib\site-packages\pandas\core\arrays\base.py(588)argsort() 586 return nargsort( 587 values, --> 588 kind=kind, 589 ascending=ascending, 590 na_position=na_position, ipdb> s > c:\users\wangxf\anaconda3\lib\site-packages\pandas\core\arrays\base.py(589)argsort() 587 values, 588 kind=kind, --> 589 ascending=ascending, 590 na_position=na_position, 591 mask=np.asarray(self.isna()), ipdb> s > c:\users\wangxf\anaconda3\lib\site-packages\pandas\core\arrays\base.py(590)argsort() 588 kind=kind, 589 ascending=ascending, --> 590 na_position=na_position, 591 mask=np.asarray(self.isna()), 592 ) ipdb> s > c:\users\wangxf\anaconda3\lib\site-packages\pandas\core\arrays\base.py(591)argsort() 589 ascending=ascending, 590 na_position=na_position, --> 591 mask=np.asarray(self.isna()), 592 ) 593 ipdb> n > c:\users\wangxf\anaconda3\lib\site-packages\pandas\core\arrays\base.py(586)argsort() 584 585 values = self._values_for_argsort() --> 586 return nargsort( 587 values, 588 kind=kind, ipdb> p values array(['01', '002', '03', '004', '005', '006'], dtype=object) ipdb> s --Call-- > c:\users\wangxf\anaconda3\lib\site-packages\pandas\core\sorting.py(327)nargsort() 325 326 --> 327 def nargsort( 328 items, 329 kind: str = "quicksort", ipdb> a items = array(['01', '002', '03', '004', '005', '006'], dtype=object) kind = 'quicksort' ascending = False na_position = 'last' key = None mask = array([False, False, False, False, False, False]) ipdb> s > c:\users\wangxf\anaconda3\lib\site-packages\pandas\core\sorting.py(352)nargsort() 350 """ 351 11> 352 if key is not None: 353 items = ensure_key_mapped(items, key) 354 return nargsort( ipdb> n > c:\users\wangxf\anaconda3\lib\site-packages\pandas\core\sorting.py(363)nargsort() 361 ) 362 --> 363 items = extract_array(items) 364 if mask is None: 365 mask = np.asarray(isna(items)) ipdb> p items array(['01', '002', '03', '004', '005', '006'], dtype=object) ipdb> s --Call-- > c:\users\wangxf\anaconda3\lib\site-packages\pandas\core\construction.py(354)extract_array() 352 353 --> 354 def extract_array(obj: object, extract_numpy: bool = False) -> Union[Any, ArrayLike]: 355 """ 356 Extract the ndarray or ExtensionArray from a Series or Index. ipdb> s > c:\users\wangxf\anaconda3\lib\site-packages\pandas\core\construction.py(396)extract_array() 394 array([1, 2, 3]) 395 """ --> 396 if isinstance(obj, (ABCIndexClass, ABCSeries)): 397 obj = obj.array 398 ipdb> n > c:\users\wangxf\anaconda3\lib\site-packages\pandas\core\construction.py(399)extract_array() 397 obj = obj.array 398 --> 399 if extract_numpy and isinstance(obj, ABCPandasArray): 400 obj = obj.to_numpy() 401 ipdb> n > c:\users\wangxf\anaconda3\lib\site-packages\pandas\core\construction.py(402)extract_array() 400 obj = obj.to_numpy() 401 --> 402 return obj 403 404 ipdb> n --Return-- array(['01', ... dtype=object) > c:\users\wangxf\anaconda3\lib\site-packages\pandas\core\construction.py(402)extract_array() 400 obj = obj.to_numpy() 401 --> 402 return obj 403 404 ipdb> n > c:\users\wangxf\anaconda3\lib\site-packages\pandas\core\sorting.py(364)nargsort() 362 363 items = extract_array(items) --> 364 if mask is None: 365 mask = np.asarray(isna(items)) 366 ipdb> p items array(['01', '002', '03', '004', '005', '006'], dtype=object) ipdb> n > c:\users\wangxf\anaconda3\lib\site-packages\pandas\core\sorting.py(367)nargsort() 365 mask = np.asarray(isna(items)) 366 13> 367 if is_extension_array_dtype(items): 368 return items.argsort(ascending=ascending, kind=kind, na_position=na_position) 369 else:ipdb> s --Call-- > c:\users\wangxf\anaconda3\lib\site-packages\pandas\core\dtypes\common.py(1470)is_extension_array_dtype() 1468 1469 -> 1470 def is_extension_array_dtype(arr_or_dtype) -> bool: 1471 """ 1472 Check if an object is a pandas extension array type. ipdb> n > c:\users\wangxf\anaconda3\lib\site-packages\pandas\core\dtypes\common.py(1515)is_extension_array_dtype() 1513 False 1514 """ -> 1515 dtype = getattr(arr_or_dtype, "dtype", arr_or_dtype) 1516 return isinstance(dtype, ExtensionDtype) or registry.find(dtype) is not None 1517 ipdb> n > c:\users\wangxf\anaconda3\lib\site-packages\pandas\core\dtypes\common.py(1516)is_extension_array_dtype() 1514 """ 1515 dtype = getattr(arr_or_dtype, "dtype", arr_or_dtype) -> 1516 return isinstance(dtype, ExtensionDtype) or registry.find(dtype) is not None 1517 1518 ipdb> n --Return-- False > c:\users\wangxf\anaconda3\lib\site-packages\pandas\core\dtypes\common.py(1516)is_extension_array_dtype() 1514 """ 1515 dtype = getattr(arr_or_dtype, "dtype", arr_or_dtype) -> 1516 return isinstance(dtype, ExtensionDtype) or registry.find(dtype) is not None 1517 1518 ipdb> n > c:\users\wangxf\anaconda3\lib\site-packages\pandas\core\sorting.py(370)nargsort() 368 return items.argsort(ascending=ascending, kind=kind, na_position=na_position) 369 else: --> 370 items = np.asanyarray(items) 371 372 idx = np.arange(len(items)) ipdb> p items array(['01', '002', '03', '004', '005', '006'], dtype=object) ipdb> n > c:\users\wangxf\anaconda3\lib\site-packages\pandas\core\sorting.py(372)nargsort() 370 items = np.asanyarray(items) 371 --> 372 idx = np.arange(len(items)) 373 non_nans = items[~mask] 374 non_nan_idx = idx[~mask] ipdb> n > c:\users\wangxf\anaconda3\lib\site-packages\pandas\core\sorting.py(373)nargsort() 371 372 idx = np.arange(len(items)) --> 373 non_nans = items[~mask] 374 non_nan_idx = idx[~mask] 375 ipdb> n > c:\users\wangxf\anaconda3\lib\site-packages\pandas\core\sorting.py(374)nargsort() 372 idx = np.arange(len(items)) 373 non_nans = items[~mask] --> 374 non_nan_idx = idx[~mask] 375 376 nan_idx = np.nonzero(mask)[0] ipdb> n > c:\users\wangxf\anaconda3\lib\site-packages\pandas\core\sorting.py(376)nargsort() 374 non_nan_idx = idx[~mask] 375 --> 376 nan_idx = np.nonzero(mask)[0] 377 if not ascending: 378 non_nans = non_nans[::-1] ipdb> p indexer *** NameError: name 'indexer' is not defined ipdb> p nan_idx *** NameError: name 'nan_idx' is not defined ipdb> p nan_idx *** NameError: name 'nan_idx' is not defined ipdb> n > c:\users\wangxf\anaconda3\lib\site-packages\pandas\core\sorting.py(377)nargsort() 375 376 nan_idx = np.nonzero(mask)[0] --> 377 if not ascending: 378 non_nans = non_nans[::-1] 379 non_nan_idx = non_nan_idx[::-1] ipdb> p nan_idxarray([], dtype=int64) ipdb> p non_nans array(['01', '002', '03', '004', '005', '006'], dtype=object) ipdb> n > c:\users\wangxf\anaconda3\lib\site-packages\pandas\core\sorting.py(378)nargsort() 376 nan_idx = np.nonzero(mask)[0] 377 if not ascending: --> 378 non_nans = non_nans[::-1] 379 non_nan_idx = non_nan_idx[::-1] 12 380 indexer = non_nan_idx[non_nans.argsort(kind=kind)] ipdb> p non_nans array(['01', '002', '03', '004', '005', '006'], dtype=object) ipdb> n > c:\users\wangxf\anaconda3\lib\site-packages\pandas\core\sorting.py(379)nargsort() 377 if not ascending: 378 non_nans = non_nans[::-1] --> 379 non_nan_idx = non_nan_idx[::-1] 12 380 indexer = non_nan_idx[non_nans.argsort(kind=kind)] 381 if not ascending: ipdb> n > c:\users\wangxf\anaconda3\lib\site-packages\pandas\core\sorting.py(380)nargsort() 378 non_nans = non_nans[::-1] 379 non_nan_idx = non_nan_idx[::-1] 12> 380 indexer = non_nan_idx[non_nans.argsort(kind=kind)] 381 if not ascending: 382 indexer = indexer[::-1] ipdb> s > c:\users\wangxf\anaconda3\lib\site-packages\pandas\core\sorting.py(381)nargsort() 379 non_nan_idx = non_nan_idx[::-1] 12 380 indexer = non_nan_idx[non_nans.argsort(kind=kind)] --> 381 if not ascending: 382 indexer = indexer[::-1] 383 # Finally, place the NaNs at the end or the beginning according to ipdb> p indexer array([1, 3, 4, 5, 0, 2]) ipdb> continue