数据结构上机测试题超全合集【C语言描述算法】(完整可编译代码,含运行结果截图)
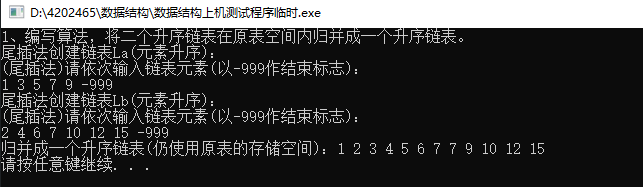
1、 编写算法,将二个升序链表在原表空间内归并成一个升序链表。
/* 1、 编写算法,将二个升序链表在原表空间内归并成一个升序链表。*/
#include 2、 编写算法,将二个升序链表在原表空间内归并成一个降序链表。
/* 2、 编写算法,将二个升序链表在原表空间内归并成一个降序链表。*/
#include 3、 编写算法,用顺序存储结构实现二个升序集合的A=A-B运算。
/*3、 编写算法,用顺序存储结构实现二个升序集合的A=A-B运算。*/
#include4、 编写算法,用单链表实现二个升序集合A和B的差集存放在集合C,即C=A-B运算,要求C中元素递增有序。
/*4、 编写算法,用单链表实现二个升序集合A和B的差集存放在集合C,即C=A-B运算,要求C中元素递增有序。*/
#include 5、 编写算法,用单链表实现二个升序集合A和B的差集存放在集合C,即C=A-B运算,要求C中元素递减有序。
/*5、 编写算法,用单链表实现二个升序集合A和B的差集存放在集合C,即C=A-B运算,要求C中元素递减有序。*/
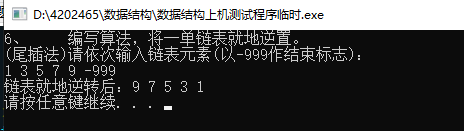
#include 6、 编写算法,将一单链表就地逆置。
/*6、 编写算法,将一单链表就地逆置。*/
#include 7、 编写算法,在一个双链表的第i个元素前插入一个元素。
/*7、 编写算法,在一个双链表的第i个元素前插入一个元素。*/
#include 8、 编写算法,删除一个双链表的第i个元素。
/*8、 编写算法,删除一个双链表的第i个元素。*/
#include 9、 编写算法,删除一升序单链表中所有值相同的多余元素,释放被删结点空间。
/*9、 编写算法,删除一升序单链表中所有值相同的多余元素,释放被删结点空间。*/
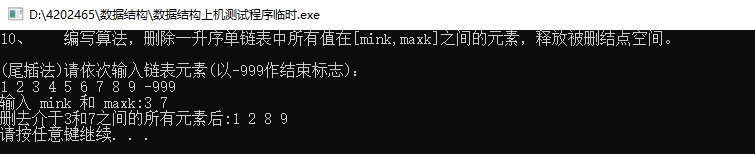
#include 10、 编写算法,删除一升序单链表中所有值在[mink,maxk]之间的元素,释放被删结点空间。
/*10、 编写算法,删除一升序单链表中所有值在[mink,maxk]之间的元素,释放被删结点空间。*/
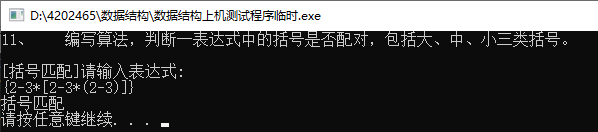
#include 11、 编写算法,判断一表达式中的括号是否配对,包括大、中、小三类括号。
/*11、 编写算法,判断一表达式中的括号是否配对,包括大、中、小三类括号。*/
#include 12、 编写算法,实现hanoi塔问题。
/*12、 编写算法,实现hanoi塔问题。*/
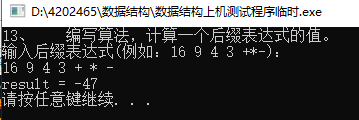
#include 13、 编写算法,计算一个后缀表达式的值。
/*13、 编写算法,计算一个后缀表达式的值。*/
#include 14、 编写算法,求子串t在主串s中的位置。
/*14、 编写算法,求子串t在主串s中的位置。*/
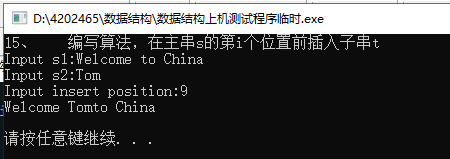
#include 15.编写算法,在主串s的第i个位置前插入子串t
/*15.编写算法,在主串s的第i个位置前插入子串t*/
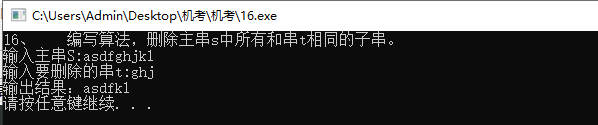
#include 16、 编写算法,删除主串s中所有和串t相同的子串。
//16、 编写算法,删除主串s中所有和串t相同的子串。
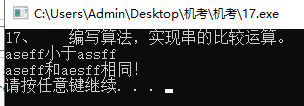
#include17、 编写算法,实现串的比较运算。
//17、 编写算法,实现串的比较运算。
#include18、 编写算法,实现串的连接运算。
//18、 编写算法,实现串的连接运算。
#include19、 编写算法,实现串的置换操作,即将串s中所有的子串t用子串v替换。
/*19、 编写算法,实现串的置换操作,即将串s中所有的子串t用子串v替换。*/
#include 20、 编写算法,实现先序遍历二叉树。
//20、 编写算法,实现先序遍历二叉树。
#include 21、 编写算法,实现中序遍历二叉树。
//21、 编写算法,实现中序遍历二叉树。
#include 22、 编写算法,实现后序遍历二叉树。
//22、 编写算法,实现后序遍历二叉树。
#include 23、 编写算法,实现层序遍历二叉树。
//23、 编写算法,实现层序遍历二叉树。
#include 24、 编写算法,计算一棵二叉树的高度。
//24、 编写算法,计算一棵二叉树的高度。
#include 25、 编写算法,计算一棵二叉树的叶子结点个数。
//25、 编写算法,计算一棵二叉树的叶子结点个数。
#include 26、 编写算法,计算一棵二叉树的非叶子结点个数。
//26、 编写算法,计算一棵二叉树的非叶子结点个数。
#include 27、 编写算法,交换一棵二叉树的左右子树。
//27、 编写算法,交换一棵二叉树的左右子树。
#include 28、 编写算法,判断二棵二叉树是否相等。
//28、 编写算法,判断二棵二叉树是否相等。
#include 29、 编写算法,完成将一棵二叉树进行复制。
//29、 编写算法,完成将一棵二叉树进行复制。
#include 30、 编写算法,判断二棵二叉树是否形态相似。
//30、 编写算法,判断二棵二叉树是否形态相似。
#include 31、 为二叉链表的节点增加Descnum域,编写一个算法,求二叉树的每个节点的子孙数目并存入Descnum域。
//31、 为二叉链表的节点增加Descnum域,编写一个算法,求二叉树的每个节点的子孙数目并存入Descnum域。
#include 32、 编写算法,计算一棵以孩子兄弟表示法存储的树的高度。
//32、 编写算法,计算一棵以孩子兄弟表示法存储的树的高度。
#include 33、 给出哈夫曼树的构造算法。
//33、 给出哈夫曼树的构造算法。
#include 34、 假定以二叉链表存放一颗哈夫曼树,编写算法计算其WPL值。
//34、 假定以二叉链表存放一颗哈夫曼树,编写算法计算其WPL值。
#include35、 编写算法,实现在一个单链表中查找关键字为K的元素,若查找成功,返回TRUE,并将查找到的结点调整到表头,否则返回FALSE。
//35、 编写算法,实现在一个单链表中查找关键字为K的元素,若查找成功,返回TRUE,并将查找到的结点调整到表头,否则返回FALSE。
#include36、 给出折半查找的非递归算法。
37、 给出折半查找的递归算法。
//36、 给出折半查找的非递归算法。
//37、 给出折半查找的递归算法。
#include38、 给出索引顺序表的分块查找算法。
//38、 给出索引顺序表的分块查找算法。
#include39、 给出二叉排序树的插入算法。
40、 给出二叉排序树的删除算法。
具体见https://blog.csdn.net/lei20172017/article/details/117487372?spm=1001.2014.3001.5501
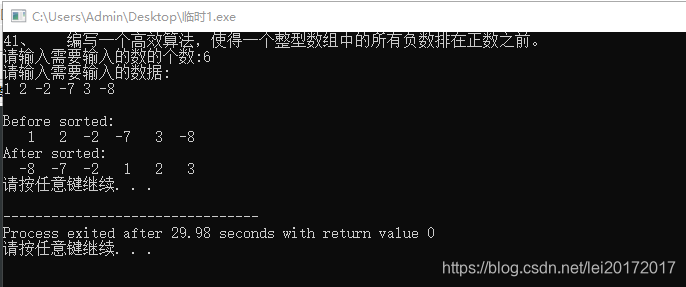
41、 编写一个高效算法,使得一个整型数组中的所有负数排在正数之前。
/*41、 编写一个高效算法,使得一个整型数组中的所有负数排在正数之前。*/
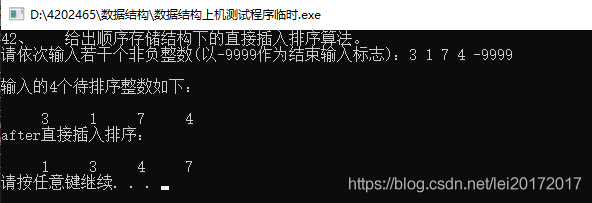
#include 42、 给出顺序存储结构下的直接插入排序算法。
/*42、 给出顺序存储结构下的直接插入排序算法。*/
#include 43、 给出以单链表为存储结构的直接插入排序算法。
/*43、 给出以单链表为存储结构的直接插入排序算法。*/
//单链表上实现直接插入排序
//输入任意N个数,按“回车”结束输入。递增排序后输出(若要实现递减,修改"l1->datadata"为“l1->data>l2->data”)。
#include 44、 给出折半插入排序算法。
/*44、 给出折半插入排序算法。*/
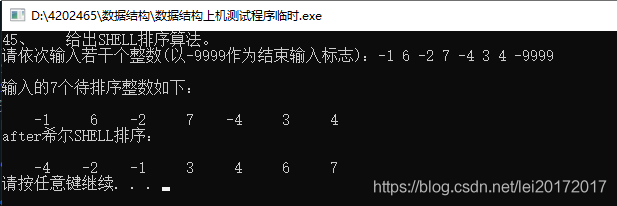
#include 45、 给出SHELL排序算法。
//45、 给出SHELL排序算法。
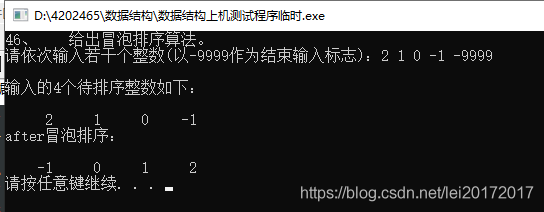
#include 46、 给出冒泡排序算法。
//46、 给出冒泡排序算法。
#include 47、 给出双向冒泡排序算法。
//47、 给出双向冒泡排序算法。
#include48、 给出快速排序算法。
//48、 给出快速排序算法。
#include 49、 给出顺序存储结构下的简单选择排序算法。
//49、 给出顺序存储结构下的简单选择排序算法。
#include 50、 给出以单链表为存储结构的简单选择排序算法。
//50、 给出以单链表为存储结构的简单选择排序算法。
#include 51、 给出堆排序算法。
//51、 给出堆排序算法。
#include 52、 给出归并排序算法。
//52、 给出归并排序算法。
#include