一文详解如何用GPU来运行Python代码/基于Python自制一个文件解压缩小工具
前几天捣鼓了一下Ubuntu,正是想用一下我旧电脑上的N卡,可以用GPU来跑代码,体验一下多核的快乐,感兴趣的小伙伴快跟随小编一起了解一下吧
简介
前几天捣鼓了一下Ubuntu,正是想用一下我旧电脑上的N卡,可以用GPU来跑代码,体验一下多核的快乐。
还好我这破电脑也是支持Cuda的:
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 |
|
安装相关工具
首先安装一下Cuda的开发工具,命令如下:
| 1 |
|
查看一下相关信息:
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 |
|
通过Conda安装相关的依赖包:
| 1 |
|
通过pip安装也可以,一样的。
测试与驱动安装
简单测试了一下,发觉报错了:
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 |
|
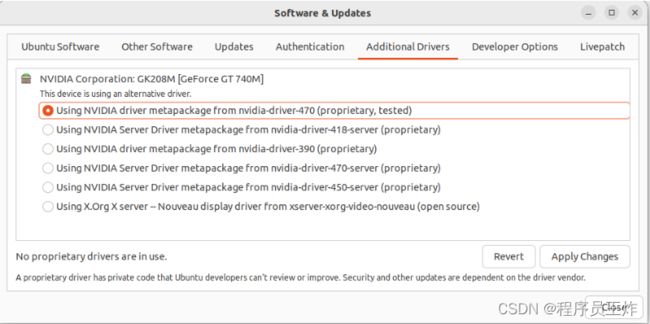
网上搜了一下,发现是驱动问题。通过Ubuntu自带的工具安装显卡驱动:
还是失败:
| 1 2 |
|
最后,通过命令行安装驱动,成功解决这个问题:
| 1 |
|
检查后发现正常了:
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 |
|
测试代码也可以跑了。
测试Python代码
打印ID
准备以下代码:
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 |
|
这个代码主要有两个函数,一个是用CPU执行,一个是用GPU执行,执行打印操作。关键在于@cuda.jit这个注解,让代码在GPU上执行。运行结果如下:
$ /home/larry/anaconda3/bin/python /home/larry/code/pkslow-samples/python/src/main/python/cuda/print_test.py
gpu print 0 3 4 12
gpu print 1 3 4 13
gpu print 2 3 4 14
gpu print 3 3 4 15
gpu print 0 2 4 8
gpu print 1 2 4 9
gpu print 2 2 4 10
gpu print 3 2 4 11
gpu print 0 1 4 4
gpu print 1 1 4 5
gpu print 2 1 4 6
gpu print 3 1 4 7
gpu print 0 0 4 0
gpu print 1 0 4 1
gpu print 2 0 4 2
gpu print 3 0 4 3
cpu print
可以看到GPU总共打印了16次,使用了不同的Thread来执行。这次每次打印的结果都可能不同,因为提交GPU是异步执行的,无法确保哪个单元先执行。同时也需要调用同步函数cuda.synchronize(),确保GPU执行完再继续往下跑。
查看时间
我们通过这个函数来看GPU并行的力量:
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 |
|
结果如下:
$ /home/larry/anaconda3/bin/python /home/larry/code/pkslow-samples/python/src/main/python/cuda/time_test.py
without GPU: 3.7136273959999926
with GPU: 0.4040513340000871
可以看到使用CPU需要3.7秒,而GPU则只要0.4秒,还是能快不少的。当然这里不是说GPU一定比CPU快,具体要看任务的类型。
以上就是一文详解如何用GPU来运行Python代码的详细内容。
基于Python自制一个文件解压缩小工具
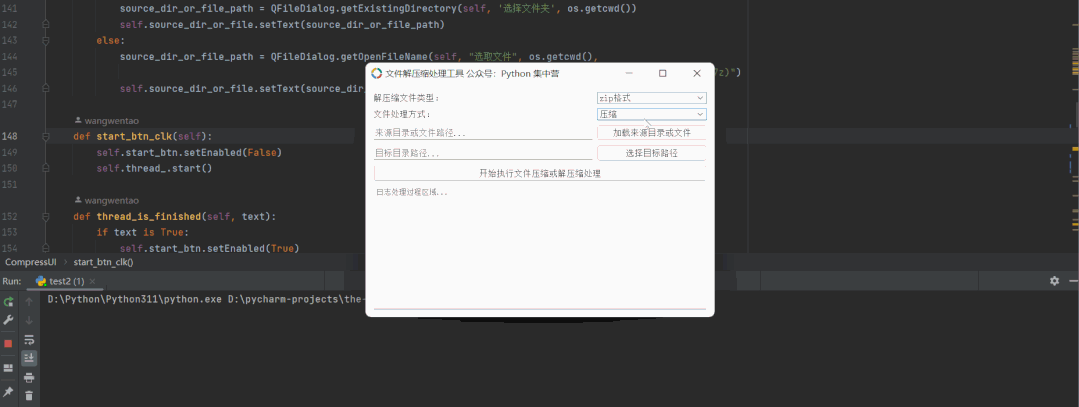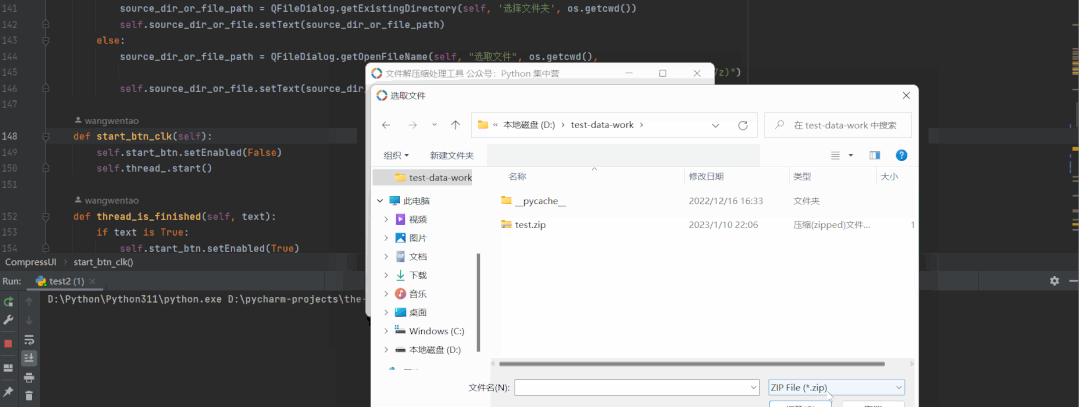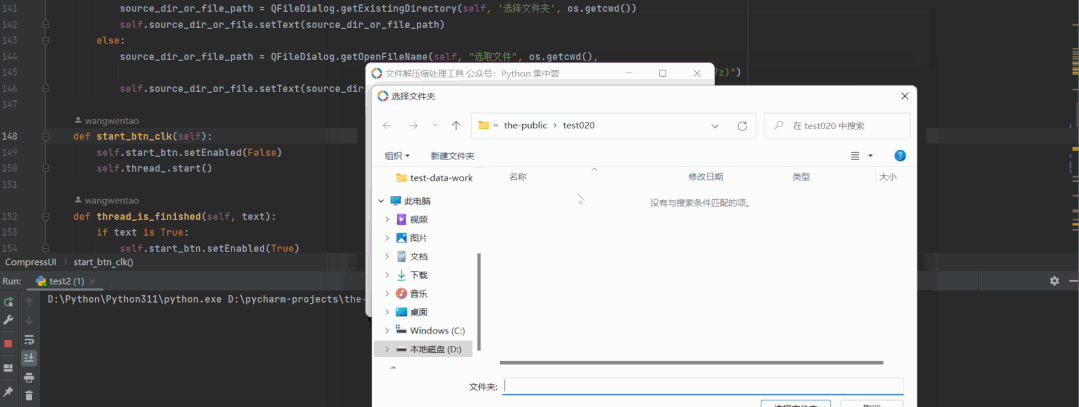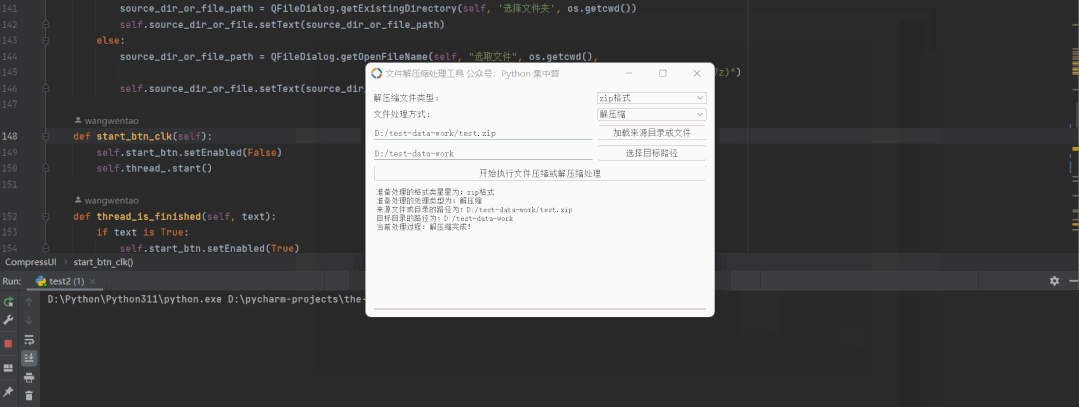
经常在办公的过程中会遇到各种各样的压缩文件处理,但是呢每个压缩软件支持的格式又是不同的。本文就来用Python自制一个文件解压缩小工具,可以支持7z/zip/rar三种格式,希望对大家有所帮助
经常在办公的过程中会遇到各种各样的压缩文件处理,但是呢每个压缩软件支持的格式又是不同的。
没有可以一种可以同时多种格式的并且免费的文件解压缩工具,于是我使用python的PyQt5开发出这个文件解压缩的小工具。
接下来,我们将开发过程中需要的python非标准库以及代码块做一个简单的介绍,有兴趣的小伙伴可以停下脚步一起来看看。
一般在windows的操作系统下文件解压缩的格式就是7z/zip/rar这三种,首先我们需要安装一下PyQt5以及需要文件解压缩处理的模块。
这里我们直接使用的是pip的安装方式进行安装,我的pip默认配置的是全局的清华大学镜像站。
| 1 2 3 |
|
然后,在开始之前我们将需要的python标准或非标准模块全部导入代码块中准备进入下面的开发环节。
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 |
|
至此,我们开发需要使用到的python模块就全部导入进来了,这里说明一下我们使用到的英文注释是通过pycharm的AI插件直接生成的。
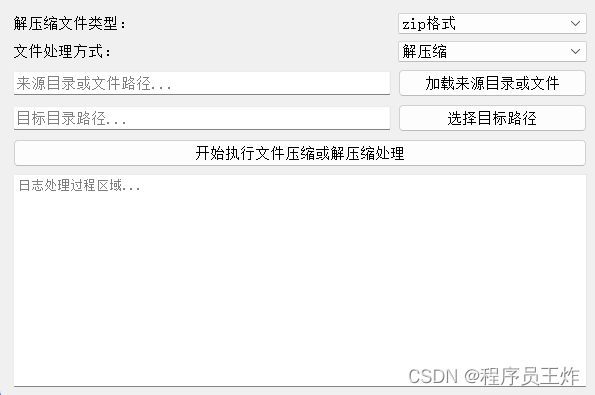
首先,创建一个名称为CompressUI的python类,将所有的UI页面组件及布局全部放在这个类中进行开发。
以及包括UI页面组件关联的槽函数也放在这个类中,也就是在CompressUI类中我们只处理页面操作相关的部分不做具体逻辑的实现。
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 |
|
以上就是整个UI页面组件/布局以及组件对应的槽函数的的开发过程了,有需要的小伙伴可以仔细研究一下。
接下来进入具体业务的开发环节,我们创建一个名称为WorkThread的python类,该类继承自QThread的子线程。
并且在子线程中可以接收主线程的变量参数,以及向主线程中传递信息的操作。将子线程执行的过程信息实时传递到主线程的文本浏览器中。
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 |
|
最后,使用python模块的主函数main,将整个应用加入到主体循环过程中就可以启动整个桌面应用了。
| 1 2 3 4 5 |
|
完成上述的开发工作之后,我们可以选择使用常用的pyinstaller打包模块对整个应用进行打包操作,打包细节可以参考我的历史文章中的说明!
点击拿去
50G+学习视频教程
100+Python初阶、中阶、高阶电子书籍