Spring常用扩展点
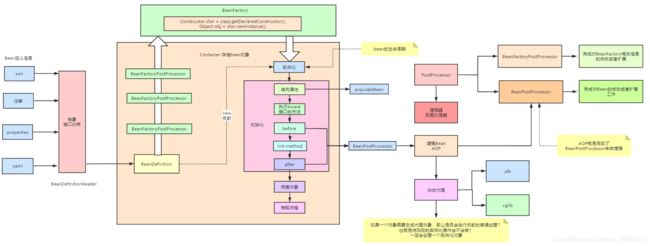
一、SpringBean的生命周期
Spring Bean的生命周期
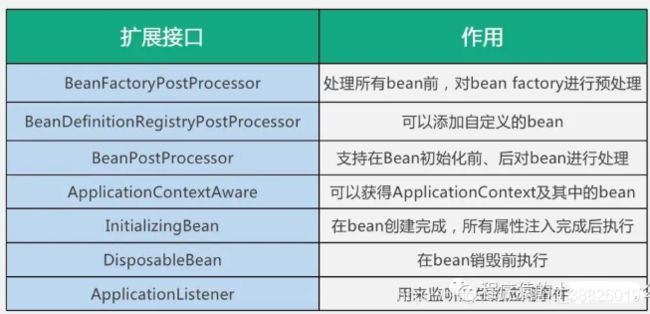
二、后置处理器postProcessor
一个是针对BeanDefinition的容器级别的后处理器 - BeanFactoryPostProcessor
- 一个是针对getBean操作获得的对象的后处理器 - BeanPostProcessor
两者的不同:
触发时机不同,前者BeanFactoryPostProcessor是在容器refresh方法中调用,而后者实际调用时机是在getBean方法获取对象时调用;
因触发时机不同导致二者处理的对象不同。BeanFactoryPostProcessor处理的是解析完配置文件后注册在容器中的BeanDefinition,而BeanPostProcessor处理的是通过反射生成的实例Bean;
接口样式不同,BeanFactoryPostProcessor只有一个后处理方法,而BeanPostProcessor有一个前置处理方法一个后置处理方法。
三、BeanPostProcessor
Spring主要提供了两类扩展点BeanPostProcessor和BeanFactoryPostProcessor。前者是操作bean的实例,后者使对bean的元数据定义进行扩展。
BeanPostProcessor提供对bean实例的操作扩展,在spring容器对bean实例化和设置依赖之后,其回调开始执行。BeanPostProcessor接口定义的两个方法,分别在bean的初始化方法(InitializingBean接口,或者init-method定义)执行的前后执行:
如果你想在Spring容器完成实例化,配置和初始化bean之后实现一些自定义逻辑,则可以插入一个或多个自定义BeanPostProcessor实现。这些实现成为后置处理器。
BeanPostProcessor接口包含两个回调方法。
当实现此接口类通过容器注册为后处理器时,由Spring容器实例的Bean,Spring容器会在bean 的init方法执行前回调postProcessBeforeInitialization方法,
然后会在bean初始化之后回调postProcessAfterInitialization方法。
后置处理器可以对这些Bean做任何自定义操作。一些Spring Aop 的基础实现类就是通过实现BeanPostProcessor从而提供代理包装逻辑 。
Spring容器能够自动检测任何实现了BeanPostProcessor接口的Bean。容器会自动将这些bean注册成后置处理器以便后续调用。
另外我们可以定义多个BeanPostProcessor,他们执行的顺序可以通过实现PriorityOrdered、Ordered接口来控制。
我们定义一个类实现了BeanPostProcessor,默认会对整个Spring容器中所有的bean进行处理
方法的参数:
- 每个Bean的实例
- 每个Bean的name 或者 id属性
实现 PriorityOrdered、Ordered,可以定义顺序
下面的示例演示如何在ApplicationContext中编写,注册和使用BeanPostProcessor实例(Spring AOP的实现方式就是如下。
@Component
public interface Person {
void sayHello();
}
@Component("student")
public class StudentImpl implements Person {
private String name;
@Override
public void sayHello() {
System.out.println("Hello World, " + this.name);
}
@PostConstruct
public void init() {
this.name = "student";
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "HelloWorldImpl{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
'}';
}
}@Component("teacher")
public class TeacherImpl implements Person {
private String name;
@Override
public void sayHello() {
System.out.println("Hello World, "+this.name);
}
@PostConstruct
public void init(){
this.name="teacher";
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "TeacherImpl{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
'}';
}
}@Configuration
@ComponentScan(value = "com.best")
public class AppConfig {
}
/**
* 自定义HelloWorldBeanPostProcessor实现BeanPostProcessor接口
*/
@Component
public class HelloWorldBeanPostProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor {
@Autowired
private ApplicationContext applicationContext;
// 直接返回实例化的bean,在bean初始化之前执行
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("postProcessBeforeInitialization: " + bean + ", " + beanName + ", " + applicationContext.getApplicationName());
return bean;
}
// 直接返回实例化的bean,在bean初始化之后执行
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("postProcessAfterInitialization: " + bean + ", " + beanName + ", " + applicationContext.getApplicationName());
return Proxy.newProxyInstance(bean.getClass().getClassLoader(), bean.getClass().getInterfaces(), new InvocationHandler() {
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("BeanPostProcessor织入,Spring AOP实现原理");
return method.invoke(bean, args);
}
});
}
}执行入口:
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AppConfig.class);
Person student = (Person) applicationContext.getBean("student");
System.out.println(student.getClass().getName());
student.sayHello();
Person teacher = (Person) applicationContext.getBean("teacher");
System.out.println(teacher.getClass().getName());
teacher.sayHello();
}
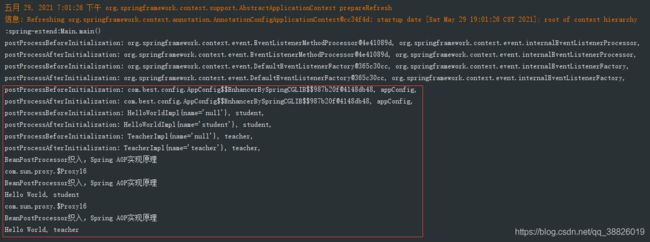
}上面程序执行的结果如下:
四、BeanFactoryPostProcessor
BeanFactory级别的处理,是针对整个Bean的工厂进行处理。
这是Spring容器的另外一个扩展点,和BeanPostProcessor不同的地方在于,它是对beanDefiniton进行操作。
实现该接口,可以在spring的bean创建之前,修改bean的定义属性。
当调用BeanFactoryPostProcess 方法时,这时候bean还没有实例化,此时Bean刚被解析成 BeanDefinition对象。
也就是说,Spring允许BeanFactoryPostProcessor在容器实例化任何其它bean之前读取配置元数据,并可以根据需要进行修改,
例如可以把bean的scope从singleton改为prototype,也可以把property的值给修改掉。可以同时配置多个BeanFactoryPostProcessor,并通过设置'order'属性或实现ordered接口来控制各个BeanFactoryPostProcessor的执行次序,
这些和BeanPostProcessor很类似,并且其启用方式和容器相关性也与之一致。
注意:BeanFactoryPostProcessor是在spring容器加载了bean的定义文件之后,在bean实例化之前执行的。接口方法的入参是ConfigurrableListableBeanFactory,使用该参数,可以获取到相关bean的定义信息:
BeanDefinition obj = arg0.getBeanDefinition("sumBean");
Spring内置实现了很多的BeanFactoryPostProcessor实现,例如:
org.springframework.beans.factory.config.PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer
org.springframework.beans.factory.config.PropertyOverrideConfigurer
org.springframework.beans.factory.config.CustomEditorConfigurer:用来注册自定义的属性编辑器。
public class TestBeanFactoryPostProcessor implements BeanFactoryPostProcessor {
@Override
public void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException {
System.out.println(" IOC 容器调用了 YjBeanFactoryPostProcessor 的 postProcessBeanFactory方法");
for(String name:beanFactory.getBeanDefinitionNames()) {
if("yjLog".equals(name)) {
BeanDefinition beanDefinition = beanFactory.getBeanDefinition(name);
//beanDefinition.setLazyInit(true);
}
}
}
}下面示例,如何通过BeanFactoryPostProcessor动态注册Bean进去。
@Component
public class User {
private Integer id;
private String name;
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User{" +
"id=" + id +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
@Configuration
@ComponentScan(value = "com.best")
public class AppConfig {
}
@Component
public class HelloWorldBeanFactoryPostProcessor implements BeanFactoryPostProcessor {
// 实现BeanFactoryPostProcessor,在spring的bean创建之前,对beanDefinition进行操作,修改bean的定义属性
@Override
public void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory configurableListableBeanFactory) throws BeansException {
DefaultListableBeanFactory defaultListableBeanFactory = (DefaultListableBeanFactory) configurableListableBeanFactory;
BeanDefinitionBuilder beanDefinitionBuilder = BeanDefinitionBuilder.genericBeanDefinition(User.class);
beanDefinitionBuilder.addPropertyValue("id", 1);
beanDefinitionBuilder.addPropertyValue("name", "jak");
defaultListableBeanFactory.registerBeanDefinition("user", beanDefinitionBuilder.getBeanDefinition());
}
}
程序入口,获取User并输出。
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AppConfig.class);
User user = (User) applicationContext.getBean("user");
System.out.println(user.toString());
}
}
程序输出结果,如下。
五、BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor
这个接口继承了
BeanFactoryPostProcessor. 从名字上来看, 这个接口是BeanDefinitionRegistry的后处理器,我们先介绍下
BeanDefinitionRegistry.
BeanDefinitionRegistry是用来注册BeanDefinition的.
BeanDefinition就是Bean的配置元数据或Bean的描述信息, 比如Bean的属性值, 构造方法的参数值等. 上面的BeanFactory的BeanDefinition也是由它注册的.
BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor是BeanFactoryPostProcessor的扩展, 允许在BeanFactoryPostProcessor被调用之前对BeanDefinition做一些操作, 尤其是它可以注册BeanFactoryPostProcessor的BeanDefinition.它提供了一个方法
postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(), 这个方法被调用的时候, 所有的BeanDefinition已经被加载了, 但是所有的Bean还没被创建.注意:
- 所有的
Bean生成都有个顺序:定义 --> 创建 --> 初始化.BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor的postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry方法在Bean被定义但还没被创建的时候执行.BeanFactoryPostProcessor的postProcessBeanFactory方法在Bean被创建但还没被初始化的时候执行
@Component
public class BestBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor implements BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor {
//该方法用来注册更多的bean到spring容器中
@Override
public void postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("BestBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor的postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry方法");
//框架自己的 BeanDefiniton Count
System.out.println("bean定义的数据量:" + registry.getBeanDefinitionCount());
RootBeanDefinition rootBeanDefinition = new RootBeanDefinition(BestBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class);
registry.registerBeanDefinition("bestBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor", rootBeanDefinition);
}
// 继承自BeanFactoryPostProcessor的方法 主要用来对bean定义做一些改变
@Override
public void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("BestBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor的postProcessBeanFactory方法");
System.out.println("bean定义的数据量:" + beanFactory.getBeanDefinitionCount());
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AppConfig.class);
BestBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor bestBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor = (BestBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor) applicationContext.getBean("bestBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor");
System.out.println(bestBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.getClass().getCanonicalName());
}
}
运行结果:
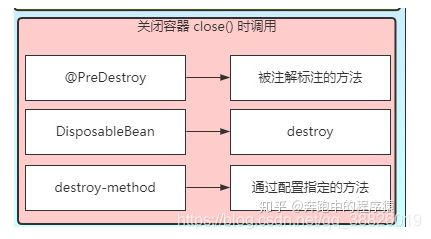
六、InitializingBean和DisposableBean
Spring 中定义了 3 种自定义初始化和销毁方法。
- 通过@Bean指定init-method和destroy-method属性
- Bean实现InitializingBean(定义初始化逻辑),DisposableBean(定义销毁逻辑);
- @PostConstruct:在bean创建完成并且属性赋值完成;来执行初始化方法
Spring bean 通过实现 InitializingBean ,DisposableBean 接口实现初始化方法和销毁前操作
这个接口有一个方法:afterPropertiesSet, 该方法在所有的属性都被赋值后调用. 属性被赋值是在初始化的时候做的, 与
BeanPostProcessor结合来看,
afterPropertiesSet方法将在postProcessBeforeInitialization和postProcessAfterInitialization之间被调用.
@Component
public class Student implements InitializingBean, DisposableBean {
@Override
public void destroy() throws Exception {
System.out.println("DisposableBean destroy");
}
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
System.out.println("InitializingBean afterPropertiesSet");
}
}
@Configuration
@ComponentScan(value = "com.best")
public class AppConfig {
}
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/**
* 1.把类扫描出来--扫描以后干了什么事情
* 2.把bean实例化
*/
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AppConfig.class);
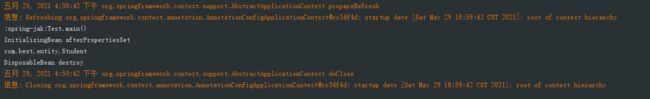
Student student = applicationContext.getBean(Student.class);
System.out.println(student.getClass().getName());
applicationContext.close();
}
}运行结果:
七、 Aware接口
Spring中提供了各种Aware接口,如果检测到一个bean实现了Aware接口,则能在bean中获取相应的Spring资源;
如果某个对象实现了某个Aware接口,比如需要依赖Spring的上下文容器(ApplicationContext),则可以实现ApplicationContextAware接口。
Spring在Bean进行初始化(注意与实例化的区别)之前,会将依赖的ApplicationContext对象通过调用ApplicationContextAware#setApplicationContext注入。
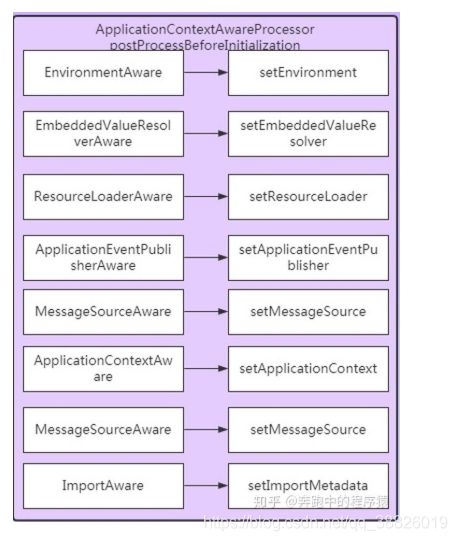
Spring 提供的Aware接口如下:
那么这些Aware接口在源码中是什么时候调用的呢?
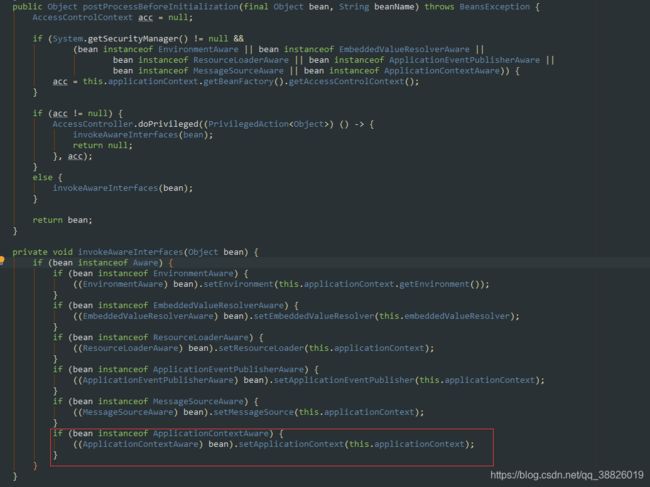
AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory#invokeAwareMethods
其他的Aware接口呢?通过 ApplicationContextAwareProcessor
应用示例
@Component
public class BestApplicationContextAware implements ApplicationContextAware {
ApplicationContext applicationContext;
@Override
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException {
this.applicationContext = applicationContext;
String[] beanDefinitionNames = this.applicationContext.getBeanDefinitionNames();
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(beanDefinitionNames));
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AppConfig.class);
BestApplicationContextAware bestApplicationContextAware = (BestApplicationContextAware) applicationContext.getBean("bestApplicationContextAware");
System.out.println(bestApplicationContextAware.getClass().getCanonicalName());
}
}
运行结果:
八、FactoryBean
一般情况下,Spring通过反射机制利用bean的class属性指定实现类来实例化bean 。
在某些情况下,实例化bean过程比较复杂,如果按照传统的方式,则需要在bean中提供大量的配置信息,配置方式的灵活性是受限的,这时采用编码的方式可能会得到一个简单的方案。
Spring为此提供了一个org.Springframework.bean.factory.FactoryBean的工厂类接口,用户可以通过实现该接口定制实例化bean的逻辑。
(后面Spring又提供了@Configration和@Bean这种方式,一定程度上可以替代FactoryBean)
public interface FactoryBean {
@Nullable
T getObject() throws Exception;
@Nullable
Class getObjectType();
default boolean isSingleton() {
return true;
}
}
FactoryBean和BeanFactory的区别
BeanFactory
FactoryBean
应用场景
@Component
public class BestFactoryBean implements FactoryBean {
private String userInfo;
public User getObject() throws Exception {
User User = new User();
String[] infos = userInfo.split(",");
User.setId(Integer.parseInt(infos[0]));
User.setName(infos[1]);
return User;
}
public Class getObjectType() {
return User.class;
}
public boolean isSingleton() {
return false;
}
public String getUserInfo() {
return this.userInfo;
}
// 接受逗号分割符设置属性信息
public void setUserInfo(String userInfo) {
this.userInfo = userInfo;
}
}
九、ApplicationListener
这跟
Servlet中的监听器一样, 采用了观察者模式. 监听器往往都是监听某些事件源,下面是配合
ApplicationContextAware一起使用的例子.我们定义一个事件, 在实现了
ApplicationContextAware的Bean中触发事件, 在实现了ApplicationListener的类中对事件做出反应.
// 自定义事件
public class RumenEvent extends ApplicationEvent {
public RumenEvent(Object source) {
super(source);
}
}
// 自定义 Bean 实现 ApplicationContextAware 接口
@Component
public class RumenzBean implements ApplicationContextAware {
private ApplicationContext applicationContext;
private String name;
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext context) {
this.applicationContext = context;
}
// 当调用 setName 时, 触发事件
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
applicationContext.publishEvent(new RumenEvent(this)); // 这行代码执行完会立即被监听到
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
}
// 自定义监听器, 监听上面的事件
@Component
public class MyApplicationListener implements ApplicationListener {
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(ApplicationEvent event) {
if (event instanceof RumenEvent) {
System.out.println(((RumenzBean)event.getSource()).getName());
}
}
}参考博客、参考博客、参考博客、参考博客、参考博客、参考博客、参考博客、参考博客、参考博客、视频教程