Visual Representation of SQL Joins
本文来源:http://www.codeproject.com/KB/database/Visual_SQL_Joins.aspx
Using the code
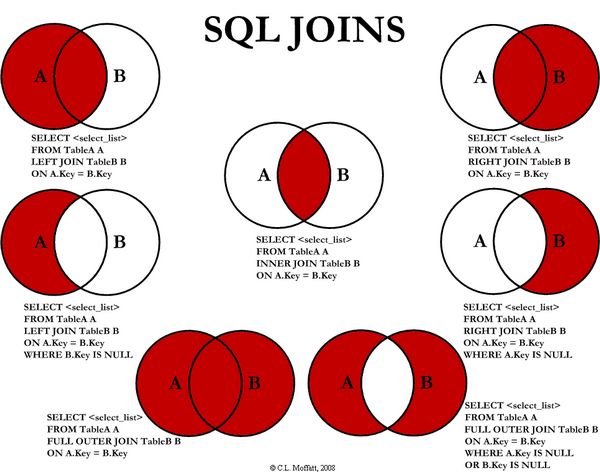
I am going to discuss seven different ways you can return data from two relational tables. I will be excluding cross Joins and self referencing Joins. The seven Joins I will discuss are shown below:
INNER JOINLEFT JOINRIGHT JOINOUTER JOINLEFT JOIN EXCLUDING INNER JOINRIGHT JOIN EXCLUDING INNER JOINOUTER JOIN EXCLUDING INNER JOIN
For the sake of this article, I'll refer to 5, 6, and 7 as LEFT EXCLUDING JOIN, RIGHT EXCLUDING JOIN, and OUTER EXCLUDING JOIN, respectively. Some may argue that 5, 6, and 7 are not really joining the two tables, but for simplicity, I will still refer to these as Joins because you use a SQL Join in each of these queries (but exclude some records with a WHERE clause).
Inner JOIN
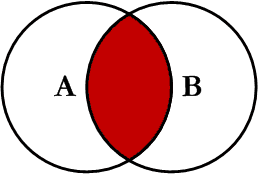
This is the simplest, most understood Join and is the most common. This query will return all of the records in the left table (table A) that have a matching record in the right table (table B). This Join is written as follows:
SELECT <select_list>
FROM Table_A A
INNER JOIN Table_B B
ON A.Key = B.Key
Left JOIN
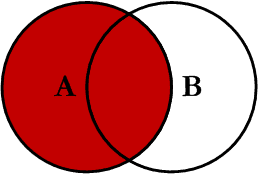
This query will return all of the records in the left table (table A) regardless if any of those records have a match in the right table (table B). It will also return any matching records from the right table. This Join is written as follows:
SELECT <select_list>
FROM Table_A A
LEFT JOIN Table_B B
ON A.Key = B.Key
Right JOIN
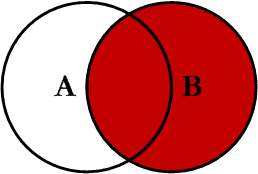
This query will return all of the records in the right table (table B) regardless if any of those records have a match in the left table (table A). It will also return any matching records from the left table. This Join is written as follows:
SELECT <select_list>
FROM Table_A A
RIGHT JOIN Table_B B
ON A.Key = B.Key
Outer JOIN

This Join can also be referred to as a FULL OUTER JOIN or a FULL JOIN. This query will return all of the records from both tables, joining records from the left table (table A) that match records from the right table (table B). This Join is written as follows:
SELECT <select_list>
FROM Table_A A
FULL OUTER JOIN Table_B B
ON A.Key = B.Key
Left Excluding JOIN
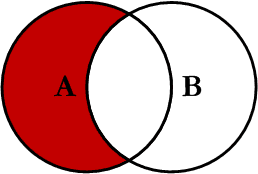
This query will return all of the records in the left table (table A) that do not match any records in the right table (table B). This Join is written as follows:
SELECT <select_list>
FROM Table_A A
LEFT JOIN Table_B B
ON A.Key = B.Key
WHERE B.Key IS NULL
Right Excluding JOIN
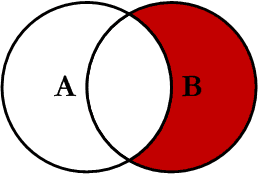
This query will return all of the records in the right table (table B) that do not match any records in the left table (table A). This Join is written as follows:
SELECT <select_list>
FROM Table_A A
RIGHT JOIN Table_B B
ON A.Key = B.Key
WHERE A.Key IS NULL
Outer Excluding JOIN
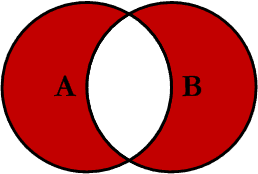
This query will return all of the records in the left table (table A) and all of the records in the right table (table B) that do not match. I have yet to have a need for using this type of Join, but all of the others, I use quite frequently. This Join is written as follows:
SELECT <select_list>
FROM Table_A A
FULL OUTER JOIN Table_B B
ON A.Key = B.Key
WHERE A.Key IS NULL OR B.Key IS NULL
另附:http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sql_join