C理解(四):链表
本文主要探讨单链表与双链表相关知识。
linux内核链表(include/linux/list.h)
内核链表中纯链表封装,纯链表的各种操作函数(节点创建、插入、删除、遍历······),纯链表内嵌在驱动结构体中,实现驱动的创建、插入、删除、遍历等
单链表
单链表链表头插入节点,尾插入节点,删除节点,逆序
代码示例:
#include
#include
struct node
{
int data;
struct node *next;
};
//创建节点
struct node * create_node(int data)
{
struct node *p = (struct node *)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
if(p == NULL)
{
printf("malloc error\n");
return NULL;
}
p->data = data;
p->next = NULL;
return p;
}
//头部插入节点
void insert_head(struct node *phead,struct node *new)
{
struct node *p = phead;
if(p == NULL)
exit(0);
new->next = p->next;
p->next = new;
(phead->data)++; //头节点存储节点数量
}
//尾部插入
void insert_tail(struct node *phead,struct node *new)
{
struct node *p = phead;
if(p == NULL)
exit(0);
while(p->next != NULL)
{
p = p->next;
}
p->next = new;
(phead->data)++; //头节点存储节点数量
}
//遍历链表
void printf_link(struct node *phead)
{
if(phead == NULL)
exit(0);
struct node *p = phead;
printf("num of struct : %d \n",p->data);
while(p->next != NULL)
{
p = p->next;
printf("struct data : %d\n",p->data);
}
}
//删除节点
int delete_node(struct node *phead,int data)
{
if(phead == NULL)
exit(-1);
struct node *p = phead;
struct node *prev = NULL;
while(p->next != NULL)
{
prev = p;
p = p->next;
if(p->data == data)
{
if(p->next != NULL)
{
prev->next = p->next; //其他节点
free(p);
}
else
{
prev->next = NULL; //尾节点
free(p);
}
(phead->data)--;
return 0;
}
}
printf("have no data\n");
return -1;
}
//链表逆序
void reserve_link(struct node *phead)
{
if(phead == NULL)
exit(-1);
struct node *p = phead->next;
struct node *back = NULL;
struct node *prev = NULL;
if(p->next == NULL || p == NULL) //只有一个节点,不逆序
return ;
while(p->next != NULL) //两个及两个以上节点
{
back = p->next; //保存链表的下一个节点,由于头插逆序法插入节点与后面节点断开
if(p == phead->next) //第一个节点指向NULL作为逆序首节点
{
p->next = NULL;
}
else
{
p->next = phead->next;
}
phead->next = p;
p = back;
}
insert_head(phead,p); //最后一个节点插入到链表,由于最后一个节点指向NULL,while判断失效
(phead->data)--; //头插最后一个节点时,默认新增一个节点
}
int main()
{
//创建头节点
struct node *head = create_node(0);
//头部插入节点
insert_head(head,create_node(1));
insert_head(head,create_node(2));
insert_head(head,create_node(3));
insert_head(head,create_node(4));
insert_head(head,create_node(5));
//尾部插入节点
insert_tail(head,create_node(1));
insert_tail(head,create_node(2));
insert_tail(head,create_node(3));
insert_tail(head,create_node(4));
insert_tail(head,create_node(5));
//遍历节点
printf_link(head);
//删除节点
delete_node(head,5);
delete_node(head,5);
delete_node(head,4);
//遍历节点
printf_link(head);
//链表逆序
reserve_link(head);
//遍历节点
printf_link(head);
return 0;
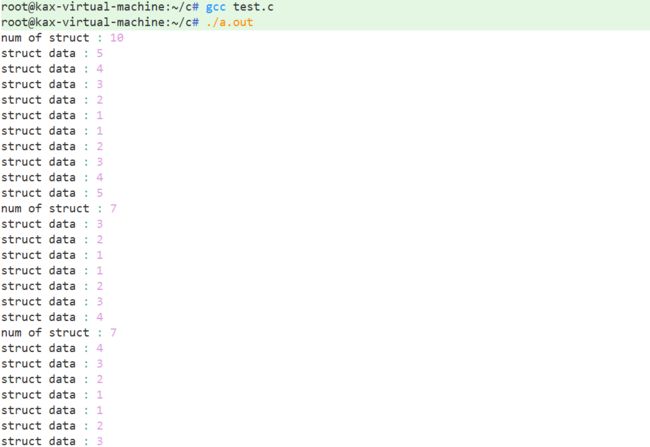
} 结果示例:
双链表
双链表尾插入,头插入,删除节点,前向遍历,后向遍历
代码示例:
#include
#include
struct node
{
int data;
struct node *next;
struct node *prev;
};
//创建节点
struct node * create_node(int data)
{
struct node *p = (struct node *)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
if(p == NULL)
{
printf("malloc error\n");
return NULL;
}
p->data = data;
p->next = NULL;
p->prev = NULL;
return p;
}
//头部插入节点
void insert_head(struct node *phead,struct node *new)
{
struct node *p = phead;
if(p == NULL)
exit(0);
new->next = p->next;
if(p->next != NULL)
p->next->prev = new;
p->next = new;
new->prev = p;
(phead->data)++; //头节点存储节点数量
}
//尾部插入
void insert_tail(struct node *phead,struct node *new)
{
struct node *p = phead;
if(p == NULL)
exit(0);
while(p->next != NULL)
{
p = p->next;
}
p->next = new;
new->prev = p;
new->next = NULL;
(phead->data)++; //头节点存储节点数量
}
//后项遍历链表
void next_printf_link(struct node *phead)
{
if(phead == NULL)
exit(0);
struct node *p = phead;
printf("num of struct : %d \n",p->data);
while(p->next != NULL)
{
p = p->next;
printf("struct data : %d\n",p->data);
}
}
//前项遍历链表
void prev_printf_link(struct node *phead)
{
if(phead == NULL)
exit(0);
struct node *p = phead;
printf("num of struct : %d \n",p->data);
while(p->next != NULL)
{
p = p->next;
}
while(p->prev != NULL)
{
printf("struct data : %d\n",p->data);
p = p->prev;
}
}
//删除节点
int delete_node(struct node *phead,int data)
{
if(phead == NULL)
exit(-1);
struct node *p = phead;
struct node *test = NULL;
while(p->next != NULL)
{
p = p->next;
if(p->data == data)
{
if(p->next == NULL)
{
p->prev->next = NULL; //尾节点
}
else
{
//其他节点
p->prev->next = p->next;
p->next->prev = p->prev;
}
free(p);
(phead->data)--;
return 0;
}
}
printf("have no data\n");
return -1;
}
int main()
{
//创建头节点
struct node *head = create_node(0);
//头部插入节点
insert_head(head,create_node(1));
insert_head(head,create_node(2));
insert_head(head,create_node(3));
insert_head(head,create_node(4));
insert_head(head,create_node(5));
//尾部插入节点
insert_tail(head,create_node(1));
insert_tail(head,create_node(2));
insert_tail(head,create_node(3));
insert_tail(head,create_node(4));
insert_tail(head,create_node(5));
//遍历节点
next_printf_link(head);
//删除节点
delete_node(head,2);
delete_node(head,5);
delete_node(head,4);
//next遍历节点
next_printf_link(head);
//prev遍历节点
prev_printf_link(head);
return 0;
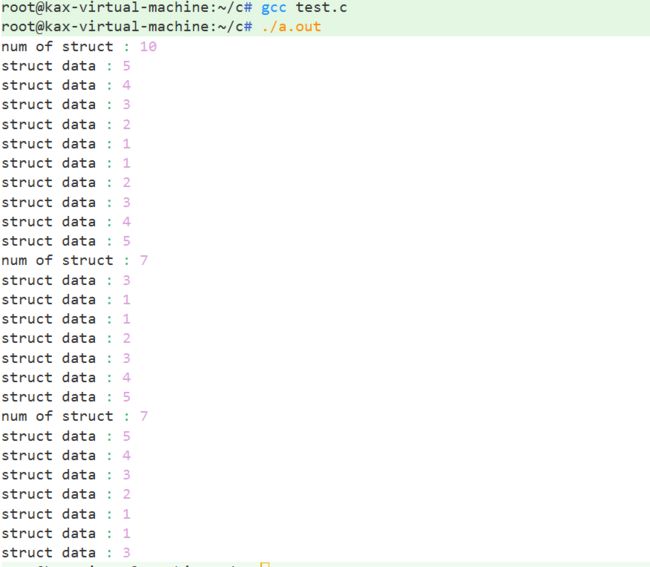
} 结果示例: