C# 类型、变量与对象
变量一共7种:
静态变量(静态字段)、实例变量(成员变量、字段)、数组元素、值参数、引用参数、输出形参、局部变量
狭义的变量就是局部变量
内存的最小单位是比特(byte),8个比特为1个字节
内存为每个字节准备一个编号。
内存地址就是一个字节在计算机科学当中的编号。
byte类型数据的内存大小:8byte,即1个字节,范围:0-255(无符号数)
sbyte,所占内存大小与byte相同,但是有符号数。范围:-128-127
当存入正数时首位为0,其余转二进制;若存入负数,则先将其正数转二进制,然后按位取反再加1
ushort, 占16byte,2个字节。取值范围:0-65535
short,有符号数,占16byte,取值范围:-32768-32767
引用类型变量里存储的是引用类型的实例在堆内存上的内存地址
通过地址访问实例
局部变量在栈上分配内存
方法永远都是类(或结构体)的成员,是类(或结构体)最基本的成员之一。
类最基本的成员只有两个:字段和方法(成员变量和成员函数),本质还是数据+算法
耦合是指不同类之间方法的依赖性,方法在一个类中只会增加内聚而不会耦合。
parameter: 形参
argument:实参
快捷生成:ctor+2下Tab自动生成构造器
int? 表示此int值可以是空值
方法的重载:
方法签名唯一,由方法的名称、类型形参的个数和它的每一个形参(从左到右顺序)的类型和种类(值、引用或输出)组成。方法签名不包含返回类型。
逐语句:Step Into F11
逐过程:Step Over F10
跳出: Step Out shift + F11
带有赋值的操作符从右向左运算。
为匿名类型创建对象,并用隐式类型变量引用这个实例:
var person = new {Name="Mr.Okay", Age=34};new作为操作符使用: Form myForm = new Form();
重写方法是override,隐藏方法是new
C++匿名函数例子:
auto add = [](int x, int y) -> int { return x + y; }; // 定义一个匿名函数,用于两个整数相加
cout << add(3, 4) << endl; // 调用匿名函数,输出7使用sizeof关键字,只能得到struct类型的内存大小,string和object都不可以。
在获取自定义struct类型的内存大小时,需要将sizeof()代码放在unsafe下。
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
unsafe
{
int l = sizeof(Student);
}
}
}
struct Student
{
int ID;
long Score;
}C#的指针只能用来操作struct类型。
不安全的上下文:sizeof、->、&x、*x
原码取反加1得相反数。
checked关键字使用例子
namespace checkedExample
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
uint x = uint.MaxValue;
Console.WriteLine(x);
string binStr = Convert.ToString(x, 2);
Console.WriteLine(binStr);
//try
//{
// uint y = checked(x + 1); //检查是否溢出
// //uint y = unchecked(x + 1);
// Console.WriteLine(y);
//}
//catch (OverflowException ex)
//{
// Console.WriteLine("This is overflow!");
//}
//写法2
checked
{
try
{
uint y = x + 1;
Console.WriteLine(y);
}
catch (OverflowException ex)
{
Console.WriteLine("This is overflow!");
}
}
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
判断字符串是否为空,若为空抛出异常。
namespace checkedExample
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Student s = new Student(null);
Console.WriteLine(s.Name);
}
}
class Student
{
public Student(string initName)
{
//判断字符是否为空
if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(initName))
{
this.Name = initName;
}
else
{
throw new ArgumentException("initName cannot be null or empty!");
}
}
public string Name;
}
}块语句:block
迭代器
foreach
最佳使用场景:对集合遍历
属性
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace AttributeExample
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
try
{
Student stu1 = new Student();
stu1.Age = 20;
Student stu2 = new Student();
stu2.Age = 30;
Student stu3 = new Student();
stu3.Age = 490;
int avgAge = (stu1.Age + stu2.Age + stu3.Age) / 3;
Console.WriteLine(avgAge);
}
catch (Exception e)
{
Console.WriteLine(e.Message);
}
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
class Student
{
private int age;
public int Age
{
get
{
return this.age;
}
set
{
if(value>0 && value<=120)
{
this.age = value;
}
else
{
throw new Exception("Age was has error!");
}
}
}
}
}
属性的完整声明:
快捷键:propfull+俩下tab键
属性的简略声明:
快捷键:prop+俩下tab键
public string Name{get; set;}ctrl+R+E定义get set中的内容
静态只读字段VS常量
常量不能定义类类型或结构体类型;
可以用static resdonly来代替。
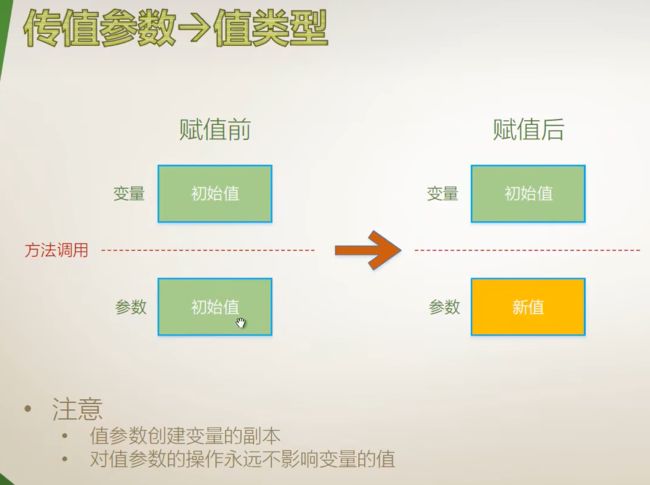
传值参数
当无法靠属性值来判断两个对象是否一致,可使用GetHashCode(),每个对象的hashCode都不一样。
在方法中创建新对象时,原对象和方法中的对象不一样
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Student stu = new Student(){Name="Tim");
SomeMethod(stu);
Console.WriteLine("{0}, {1}", stu.GetHashCode(), stu.Name);
}
static void SomeMethod(Student stu)
{
stu = new Student(){Name="Tim");
Console.WriteLine("{0}, {1}", stu.GetHashCode(), stu.Name);
}
class Student
{
public string Name{get; set;}
}方法中没有创建新对象时,原对象和方法中的对象一样
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Student stu = new Student(){Name="Tim");
SomeMethod(stu);
Console.WriteLine("{0}, {1}", stu.GetHashCode(), stu.Name);
}
static void SomeMethod(Student stu)
{
stu.Name="Tom"; //副作用,side-effect
Console.WriteLine("{0}, {1}", stu.GetHashCode(), stu.Name);
}
class Student
{
public string Name{get; set;}
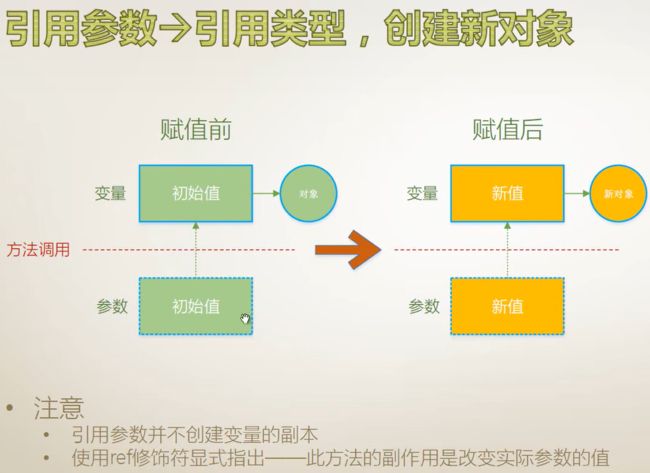
}引用参数
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int y = 1;
IWantSideEffect(ref y);
Console.WriteLine(y);
}
static void IWantSideEffect(ref int x)
{
x += 100;
}static void Main(string[] args)
{
Student outterStu = new Student(){Name="Tim"};
Console.WriteLine("{0}, {1}", stu.GetHashCode(), stu.Name);
Console.WriteLine("----------------------------------");
IWantSideEffect(ref outterStu);
Console.WriteLine("{0}, {1}", stu.GetHashCode(), stu.Name);
}
static void IWantSideEffect(ref Student stu)
{
stu = new Student(){Name="Tom");
Console.WriteLine("{0}, {1}", stu.GetHashCode(), stu.Name);
}
class Student
{
public string Name{get; set;}
}static void Main(string[] args)
{
Student outterStu = new Student(){Name="Tim"};
Console.WriteLine("{0}, {1}", stu.GetHashCode(), stu.Name);
Console.WriteLine("----------------------------------");
IWantSideEffect(ref outterStu);
Console.WriteLine("{0}, {1}", stu.GetHashCode(), stu.Name);
}
static void IWantSideEffect(ref Student stu)
{
stu.Name="Tom";
Console.WriteLine("{0}, {1}", stu.GetHashCode(), stu.Name);
}
class Student
{
public string Name{get; set;}
}此种对象操作引用参数和传值参数得到的结果一样,
但是传值参数在内存当中创建了实际参数的副本,即outterStu和stu两个变量所指向的内存地址不一样,但是两个不同的内存地址中却存储着一个相同的地址,即实例在堆内存中的地址。
对于引用参数来说,outterStu和stu两个变量所指向的内存地址是同一个内存地址
输出参数
使用输出参数实例:
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine("Please input first number:");
string arg1 = Console.ReadLine();
double x = 0;
bool b1 = double.TryParse(arg1, out x);
if(b1==false)
{
Console.WriteLine("Input error!");
return;
}
Console.WriteLine("Please input second number:");
string arg2 = Console.ReadLine();
double y = 0;
bool b2 = double.TryParse(arg2, out y);
if(b2==false)
{
Console.WriteLine("Input error");
return;
}
Console.WriteLine("{0}+{1}={2}", x, y, x+y);
}
}实现TryParse内容:
class DoubleParser
{
public static bool TryParse(string input, out double result)
{
try
{
result = double.Parse(input);
return true;
}
catch
{
result = 0;
return false;
}
}
}class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Student stu = null;
bool b = StudentFactory.Create("Tim", 34, out stu);
if(b==true)
{
Console.WriteLine("Student {0}, age is {1}.", stu.Name, stu.Age);
}
}
}
class Student
{
public string Name { get; set; }
public int Age { get; set; }
}
class StudentFactory
{
public static bool Create(string stuName, int stuAge, out Student result)
{
result = null;
if(string.IsNullOrEmpty(stuName))
{
return false;
}
if(stuAge<20 || stuAge>80)
{
return false;
}
result = new Student() { Name = stuName, Age = stuAge };
return true;
}
}数组参数
关键字:params
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//int[] arr = { 1, 2, 3 };
int[] arr = new int{1, 2, 3};
int sum = CalculateSum(arr);
Console.WriteLine(sum);
}
static int CalculateSum(int[] intArray)
{
int sum = 0;
foreach (var item in intArray)
{
sum += item;
}
return sum;
}
}如上面代码,没有params参数时,函数CalculateSum中引用的必须是提前初始化好的数组;
当引用params参数后,可以不提前初始化数组直接填写数组中的内容即可,结果与上面代码相同。如下代码:
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int sum = CalculateSum(1, 2, 3);
Console.WriteLine(sum);
}
static int CalculateSum(params int[] intArray)
{
int sum = 0;
foreach (var item in intArray)
{
sum += item;
}
return sum;
}
}将字符串按指定字符分割
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
string str = "Tim;Tom,Army,Lisa";
string[] result = str.Split(',', ';', '.');
foreach (var item in result)
{
Console.WriteLine(item);
}
}
}具名参数
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
PrintInfo(age: 34, name: "Tim");
}
static void PrintInfo(string name, int age)
{
Console.WriteLine("Hello {0}, you are {1}.", name, age);
}
}可选参数
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
PrintInfo();
}
static void PrintInfo(string name="Tim", int age=34)
{
Console.WriteLine("Hello {0}, you are {1}.", name, age);
}
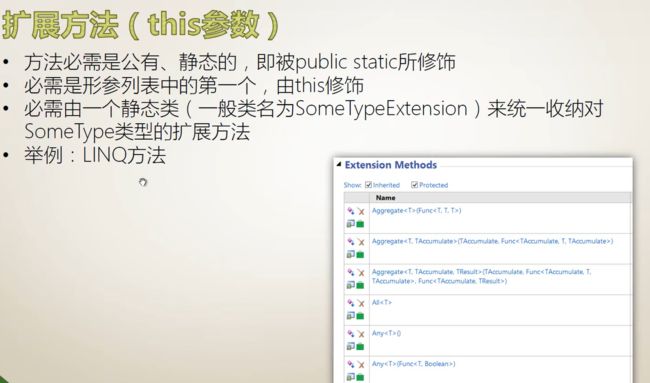
}扩展方法(this 参数)
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
double x = 3.14159;
//double类型不具有Round方法,使用Math.Round实现
double y = Math.Round(x, 4);
Console.WriteLine(y);
//使用扩展类型为double类型自定义Round方法,
//下面x是第一个参数,4是第二个参数
double ny = x.Round(4);
Console.WriteLine(ny);
}
}
static class DoubleExtension
{
public static double Round(this double input, int digits)
{
double result = Math.Round(input, digits);
return result;
}
}注意,定义中有this关键字:public static double Round(this double input, int digits)
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
List arr = new List{ 12, 11, 42 };
//常规判断数组中是否所有数都大于10
bool result = AllGreaterThanTen(arr);
Console.WriteLine(result);
//使用引用 添加命名空间 using System.Linq;
bool result2 = arr.All(i => i > 10);
Console.WriteLine(result2);
}
static bool AllGreaterThanTen(List intList)
{
foreach (var item in intList)
{
if(item<10)
{
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}