一键智能视频语音转文本——基于PaddlePaddle语音识别与Python轻松提取视频语音并生成文案
前言
如今进行入自媒体行业的人越来越多,短视频也逐渐成为了主流,但好多时候是想如何把视频里面的语音转成文字,比如,录制会议视频后,做会议纪要;比如,网课教程视频,想要做笔记;比如,需要提取视频中文案使用;比如,需要给视频加个字幕;这时候,只要把视频转文字就好。
对于不是视频编辑专业人员,处理起来还是比较麻烦的,但网上也有好多可以用的小工具,这些工具大多数都标榜有自己技术和模型,但都是在线模型或者使用过一段时间之后就无法再使用了,这些工具实际上都是基于一些大公司提供的接口衍生出来的AI工具,使用效果也不错。但在处理的过程中,处理的文件要上传到大公司的服务器进行处理,这里可能会涉及到一些数据的安全问题。这些数据很大一部分有可能会涉及到数据泄露与安全的问题。
这个项目的核心算法是基于PaddlePaddle的语音识别加Python实现,使用的模型可以有自己训练,支持本地部署,支持GPU与CPU推理两种文案,可以处理短语音识别、长语音识别、实现输入的语音识别。
一、视频语音提取
想要把视频里面的语音进行识别,首先要对视频里面的语音进行提取,提取视频里的语音有很多用办法,可以借助视频编辑软件(如Adobe Premiere Pro、Final Cut Pro)中提取音频轨道,然后将其导出为音频文件。 也可以借助工具如FFmpeg或者moviepy,通过命令行将视频中的音频提取出来。
这里使用moviepy对视频里面的语音进行提取,MoviePy是一个功能丰富的Python模块,专为视频编辑而设计。使用MoviePy,可以轻松执行各种基本视频操作,如视频剪辑、视频拼接、标题插入等。此外,它还支持视频合成和高级视频处理,甚至可以添加自定义高级特效。这个模块可以读写绝大多数常见的视频格式,包括GIF。无论使用的是Mac、Windows还是Linux系统,MoviePy都能无缝运行,可以在不同平台上使用它。
MoviePy与FFmpeg环境安装:
pip install moviepy
pip install ffmpeg
因为使用moviepy提取出视频里面的音轨的比特率不是16000,不能直接输入到语音识别模型里面,这里还要借助FFmpeg的命来把音频采样率转成16000
提取音轨:
def video_to_audio(video_path,audio_path):
video = VideoFileClip(video_path)
audio = video.audio
audio_temp = "temp.wav"
if os.path.exists(audio_path):
os.remove(audio_temp)
audio.write_audiofile(audio_temp)
audio.close()
if os.path.exists(audio_path):
os.remove(audio_path)
cmd = "ffmpeg -i " + audio_temp + " -ac 1 -ar 16000 " + audio_path
subprocess.run(cmd,shell=True)
二、语音识别
1.PaddleSpeech语音识别
PaddleSpeech是一款由飞浆开源全能的语音算法工具箱,其中包含多种领先国际水平的语音算法与预训练模型。它提供了多种语音处理工具和预训练模型供用户选择,支持语音识别、语音合成、声音分类、声纹识别、标点恢复、语音翻译等多种功能。在这里可以找到基于PaddleSpeech精品项目与训练教程:https://aistudio.baidu.com/projectdetail/4692119?contributionType=1
语音识别(Automatic Speech Recognition, ASR) 是一项从一段音频中提取出语言文字内容的任务。
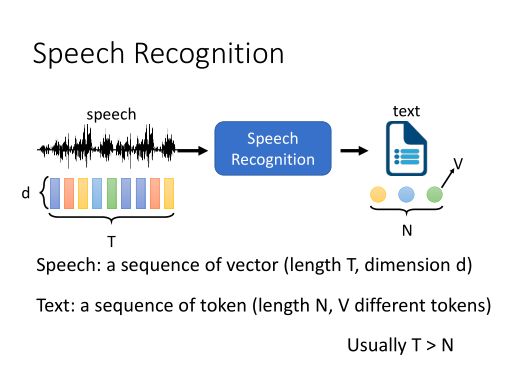
目前 Transformer 和 Conformer 是语音识别领域的主流模型,关于这方面的教程可以看飞浆官方发的课程:飞桨PaddleSpeech语音技术课程
2.环境依赖安装
我当前的环境是win10,GPU是N卡3060,使用cuda 11.8,cudnn 8.5,为了之后方便封装,使用conda来安装环境,如果没有GPU,也可以装cpu版本:
conda create -n video_to_txt python=3.8
python -m pip install paddlepaddle-gpu==2.5.1 -i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple
3. 模型下载
可以从官方git上下载到合适自己的模型:https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleSpeech/blob/develop/README_cn.md
转换模型:
import argparse
import functools
from ppasr.trainer import PPASRTrainer
from ppasr.utils.utils import add_arguments, print_arguments
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description=__doc__)
add_arg = functools.partial(add_arguments, argparser=parser)
add_arg('configs', str, 'models/csfw/configs/conformer.yml', '配置文件')
add_arg("use_gpu", bool, True, '是否使用GPU评估模型')
add_arg("save_quant", bool, False, '是否保存量化模型')
add_arg('save_model', str, 'models', '模型保存的路径')
add_arg('resume_model', str, 'models/csfw/models', '准备导出的模型路径')
args = parser.parse_args()
print_arguments(args=args)
# 获取训练器
trainer = PPASRTrainer(configs=args.configs, use_gpu=args.use_gpu)
# 导出预测模型
trainer.export(save_model_path=args.save_model,
resume_model=args.resume_model,
save_quant=args.save_quant)
4.语音识别
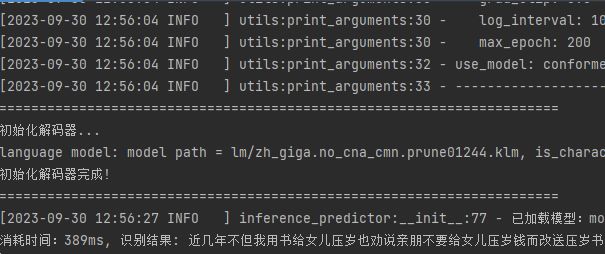
使用模型进行短语音识别:
def predict(self,
audio_data,
use_pun=False,
is_itn=False,
sample_rate=16000):
# 加载音频文件,并进行预处理
audio_segment = self._load_audio(audio_data=audio_data, sample_rate=sample_rate)
audio_feature = self._audio_featurizer.featurize(audio_segment)
input_data = np.array(audio_feature).astype(np.float32)[np.newaxis, :]
audio_len = np.array([input_data.shape[1]]).astype(np.int64)
# 运行predictor
output_data = self.predictor.predict(input_data, audio_len)[0]
# 解码
score, text = self.decode(output_data=output_data, use_pun=use_pun, is_itn=is_itn)
result = {'text': text, 'score': score}
return result
5.断句与标点符号
可以基于飞浆的ERNIE训练标点行号模型:
添加标点符号代码:
import json
import os
import re
import numpy as np
import paddle.inference as paddle_infer
from paddlenlp.transformers import ErnieTokenizer
from ppasr.utils.logger import setup_logger
logger = setup_logger(__name__)
__all__ = ['PunctuationPredictor']
class PunctuationPredictor:
def __init__(self, model_dir, use_gpu=True, gpu_mem=500, num_threads=4):
# 创建 config
model_path = os.path.join(model_dir, 'model.pdmodel')
params_path = os.path.join(model_dir, 'model.pdiparams')
if not os.path.exists(model_path) or not os.path.exists(params_path):
raise Exception("标点符号模型文件不存在,请检查{}和{}是否存在!".format(model_path, params_path))
self.config = paddle_infer.Config(model_path, params_path)
# 获取预训练模型类型
pretrained_token = 'ernie-1.0'
if os.path.exists(os.path.join(model_dir, 'info.json')):
with open(os.path.join(model_dir, 'info.json'), 'r', encoding='utf-8') as f:
data = json.load(f)
pretrained_token = data['pretrained_token']
if use_gpu:
self.config.enable_use_gpu(gpu_mem, 0)
else:
self.config.disable_gpu()
self.config.set_cpu_math_library_num_threads(num_threads)
# enable memory optim
self.config.enable_memory_optim()
self.config.disable_glog_info()
# 根据 config 创建 predictor
self.predictor = paddle_infer.create_predictor(self.config)
# 获取输入层
self.input_ids_handle = self.predictor.get_input_handle('input_ids')
self.token_type_ids_handle = self.predictor.get_input_handle('token_type_ids')
# 获取输出的名称
self.output_names = self.predictor.get_output_names()
self._punc_list = []
if not os.path.join(model_dir, 'vocab.txt'):
raise Exception("字典文件不存在,请检查{}是否存在!".format(os.path.join(model_dir, 'vocab.txt')))
with open(os.path.join(model_dir, 'vocab.txt'), 'r', encoding='utf-8') as f:
for line in f:
self._punc_list.append(line.strip())
self.tokenizer = ErnieTokenizer.from_pretrained(pretrained_token)
# 预热
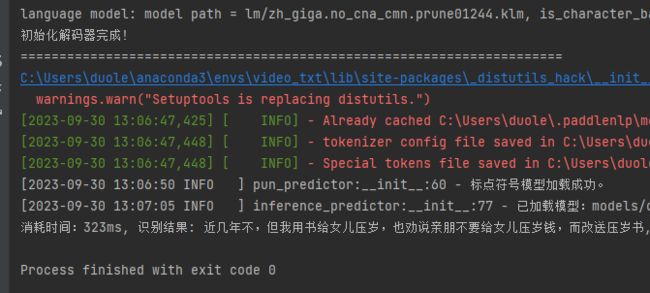
self('近几年不但我用书给女儿儿压岁也劝说亲朋不要给女儿压岁钱而改送压岁书')
logger.info('标点符号模型加载成功。')
def _clean_text(self, text):
text = text.lower()
text = re.sub('[^A-Za-z0-9\u4e00-\u9fa5]', '', text)
text = re.sub(f'[{"".join([p for p in self._punc_list][1:])}]', '', text)
return text
# 预处理文本
def preprocess(self, text: str):
clean_text = self._clean_text(text)
if len(clean_text) == 0: return None
tokenized_input = self.tokenizer(list(clean_text), return_length=True, is_split_into_words=True)
input_ids = tokenized_input['input_ids']
seg_ids = tokenized_input['token_type_ids']
seq_len = tokenized_input['seq_len']
return input_ids, seg_ids, seq_len
def infer(self, input_ids: list, seg_ids: list):
# 设置输入
self.input_ids_handle.reshape([1, len(input_ids)])
self.token_type_ids_handle.reshape([1, len(seg_ids)])
self.input_ids_handle.copy_from_cpu(np.array([input_ids]).astype('int64'))
self.token_type_ids_handle.copy_from_cpu(np.array([seg_ids]).astype('int64'))
# 运行predictor
self.predictor.run()
# 获取输出
output_handle = self.predictor.get_output_handle(self.output_names[0])
output_data = output_handle.copy_to_cpu()
return output_data
# 后处理识别结果
def postprocess(self, input_ids, seq_len, preds):
tokens = self.tokenizer.convert_ids_to_tokens(input_ids[1:seq_len - 1])
labels = preds[1:seq_len - 1].tolist()
assert len(tokens) == len(labels)
text = ''
for t, l in zip(tokens, labels):
text += t
if l != 0:
text += self._punc_list[l]
return text
def __call__(self, text: str) -> str:
# 数据batch处理
try:
input_ids, seg_ids, seq_len = self.preprocess(text)
preds = self.infer(input_ids=input_ids, seg_ids=seg_ids)
if len(preds.shape) == 2:
preds = preds[0]
text = self.postprocess(input_ids, seq_len, preds)
except Exception as e:
logger.error(e)
return text
6.长音频识别
长音频识别要通过VAD分割音频,再对短音频进行识别,拼接结果,最终得到长语音识别结果。 VAD也就是语音端点检测技术,是Voice Activity Detection的缩写。它的主要任务是从带有噪声的语音中准确的定位出语音的开始和结束点。
def get_speech_timestamps(self, audio, sampling_rate):
self.reset_states()
min_speech_samples = sampling_rate * self.min_speech_duration_ms / 1000
min_silence_samples = sampling_rate * self.min_silence_duration_ms / 1000
speech_pad_samples = sampling_rate * self.speech_pad_ms / 1000
audio_length_samples = len(audio)
speech_probs = []
for current_start_sample in range(0, audio_length_samples, self.window_size_samples):
chunk = audio[current_start_sample: current_start_sample + self.window_size_samples]
if len(chunk) < self.window_size_samples:
chunk = np.pad(chunk, (0, int(self.window_size_samples - len(chunk))))
speech_prob = self(chunk, sampling_rate).item()
speech_probs.append(speech_prob)
triggered = False
speeches: List[dict] = []
current_speech = {}
neg_threshold = self.threshold - 0.15
temp_end = 0
for i, speech_prob in enumerate(speech_probs):
if (speech_prob >= self.threshold) and temp_end:
temp_end = 0
if (speech_prob >= self.threshold) and not triggered:
triggered = True
current_speech['start'] = self.window_size_samples * i
continue
if (speech_prob < neg_threshold) and triggered:
if not temp_end:
temp_end = self.window_size_samples * i
if (self.window_size_samples * i) - temp_end < min_silence_samples:
continue
else:
current_speech['end'] = temp_end
if (current_speech['end'] - current_speech['start']) > min_speech_samples:
speeches.append(current_speech)
temp_end = 0
current_speech = {}
triggered = False
continue
if current_speech and (audio_length_samples - current_speech['start']) > min_speech_samples:
current_speech['end'] = audio_length_samples
speeches.append(current_speech)
for i, speech in enumerate(speeches):
if i == 0:
speech['start'] = int(max(0, speech['start'] - speech_pad_samples))
if i != len(speeches) - 1:
silence_duration = speeches[i + 1]['start'] - speech['end']
if silence_duration < 2 * speech_pad_samples:
speech['end'] += int(silence_duration // 2)
speeches[i + 1]['start'] = int(max(0, speeches[i + 1]['start'] - silence_duration // 2))
else:
speech['end'] = int(min(audio_length_samples, speech['end'] + speech_pad_samples))
speeches[i + 1]['start'] = int(max(0, speeches[i + 1]['start'] - speech_pad_samples))
else:
speech['end'] = int(min(audio_length_samples, speech['end'] + speech_pad_samples))
return speeches
进行长语音识别:
def predict_long(self,
audio_data,
use_pun=False,
is_itn=False,
sample_rate=16000):
self.init_vad()
# 加载音频文件,并进行预处理
audio_segment = self._load_audio(audio_data=audio_data, sample_rate=sample_rate)
# 重采样,方便进行语音活动检测
if audio_segment.sample_rate != self.configs.preprocess_conf.sample_rate:
audio_segment.resample(self.configs.preprocess_conf.sample_rate)
# 获取语音活动区域
speech_timestamps = self.vad_predictor.get_speech_timestamps(audio_segment.samples, audio_segment.sample_rate)
texts, scores = '', []
for t in speech_timestamps:
audio_ndarray = audio_segment.samples[t['start']: t['end']]
# 执行识别
result = self.predict(audio_data=audio_ndarray, use_pun=False, is_itn=is_itn)
score, text = result['score'], result['text']
if text != '':
texts = texts + text if use_pun else texts + ',' + text
scores.append(score)
logger.info(f'长语音识别片段结果:{text}')
if texts[0] == ',': texts = texts[1:]
# 加标点符号
if use_pun and len(texts) > 0:
if self.pun_predictor is not None:
texts = self.pun_predictor(texts)
else:
logger.warning('标点符号模型没有初始化!')
result = {'text': texts, 'score': round(sum(scores) / len(scores), 2)}
return result
有些大宝贝,我是真的不知道你们是咋想的?我给一对单身男女叫我对象,男女都是同岁的二十八岁女方是幼儿园老师,这个南方是工程师,上个月初两人是第一次见面,互相印象都不错呀,于是又安排见了三四次,就这么断断续续地认识了一个多月,昨天晚上两人又见了面啊,吃了饭之后呢…
三、UI与保存
1. UI界面
为了方便应用,这里使用Gradio这个库,Gradio是一个开源的Python库,用于快速构建机器学习和数据科学演示的应用。它可以帮助你快速创建一个简单漂亮的用户界面,以便向客户、合作者、用户或学生展示你的机器学习模型。此外,还可以通过自动共享链接快速部署模型,并获得对模型性能的反馈。在开发过程中,你可以使用内置的操作和解释工具来交互式地调试模型。Gradio适用于多种情况,包括为客户/合作者/用户/学生演示机器学习模型、快速部署模型并获得性能反馈、以及在开发过程中使用内置的操作和解释工具交互式地调试模型。
pip install gradio
#可以使用清华镜像源来更快的安装
pip install -i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple gradio
import os
from moviepy.editor import *
import subprocess
import gradio as gr
from ppasr.predict import PPASRPredictor
from ppasr.utils.utils import add_arguments, print_arguments
configs = "models/csfw/configs/conformer.yml"
pun_model_dir = "models/pun_models/"
model_path = "models/csfw/models"
predictor = PPASRPredictor(configs=configs,
model_path=model_path,
use_gpu=True,
use_pun=True,
pun_model_dir=pun_model_dir)
def video_to_audio(video_path):
file_name, ext = os.path.splitext(os.path.basename(video_path))
video = VideoFileClip(video_path)
audio = video.audio
audio_temp = "temp.wav"
audio_name = file_name + ".wav"
if os.path.exists(audio_temp):
os.remove(audio_temp)
audio.write_audiofile(audio_temp)
audio.close()
if os.path.exists(audio_name):
os.remove(audio_name)
cmd = "ffmpeg -i " + audio_temp + " -ac 1 -ar 16000 " + audio_name
subprocess.run(cmd,shell=True)
return audio_name
def predict_long_audio(wav_path):
result = predictor.predict_long(wav_path, True, False)
score, text = result['score'], result['text']
return text
# 短语音识别
def predict_audio(wav_path):
result = predictor.predict(wav_path, True, False)
score, text = result['score'], result['text']
return text
def video_to_text(video,operation):
audio_name = video_to_audio(video)
if operation == "短音频":
text = predict_audio(audio_name)
elif operation == "长音频":
text = predict_long_audio(audio_name)
else:
text = ""
print("视频语音提取识别完成!")
return text
ch = gr.Radio(["短音频","长音频"],label="选择识别音频方式:")
demo = gr.Interface(fn=video_to_text,inputs=[gr.Video(), ch],outputs="text")
demo.launch()
执行结果:
视频语音提取并转文字
四、优化与升级
1.优化
该项目目前能识别的语音的词错率为0.083327,对一些语音相近的词语并不能联系上下文进行修改,比如这句
“这个南方是工程师”
这里通过上下文联想,正确的应该是:
“这个男方是工程师”
这样的识别错误并不是很多,还有一些断句没有断好的,如果要优化可以加LLM(大语言模型)来进行一次错误的筛选,这个接入LLM的代码在训练和测试阶段。
2.升级
项目可升级:
- 当前项目只针对中文语音,之后会加多语言支持。
- 视频没有字幕可以给视频添加字幕生成模块。
- 视频有字幕,读取视频画面的字幕并使用OCR识别与语音识别相互验证。
- 添加支持web版本。
- 可选段对视频语音进行提取识别。
- 对多人对话的场景的视频,可以加入声纹识别后格式化识别。
- 把生成的文字输出到word并进行排版。
3. 项目源码
源码:https://download.csdn.net/download/matt45m/88386353
模型:
源码配置:
conda create -n video_to_txt python=3.8
python -m pip install paddlepaddle-gpu==2.5.1 -i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple
cd VideoToTxt
pip install -r requirements.txt
python video_txt.py
然后用浏览器打开:http://127.0.0.1:7860/ ,就可以使用了。
4.备注
如果对该项目感兴趣或者在安装的过程中遇到什么错误的的可以加我的企鹅群:487350510,大家一起探讨。