《数据结构、算法与应用C++语言描述》-栈的应用-迷宫老鼠问题
迷宫老鼠
问题描述
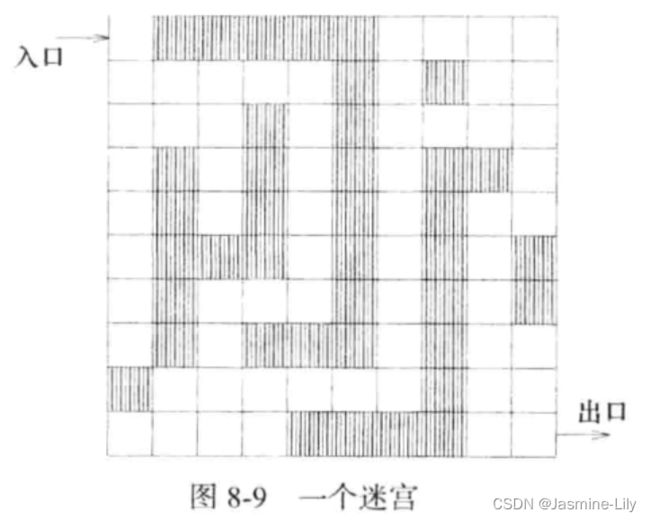
迷宫(如图 8-9 所示)是一个矩形区域,有一个入口和一个出口。迷宫内部包含不能穿越的墙壁或障碍物。这些障碍物沿着行和列放置,与迷宫的边界平行。迷宫的入口在左上角,出口在右下角。
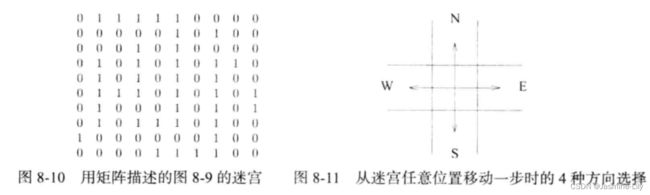
假定用 nxm 的矩阵来描述迷宫,矩阵的位置(1,1)表示入口,(n,m)表示出口,n 和m分别代表迷宫的行数和列数。迷宫的每个位置都可用其行号和列号表示。在矩阵中,当且仅当在位置(i,j)处有一个障碍时,其值为 1,否则其值为 0。图 8-10 给出了图8-9 中的迷宫所对应的矩阵表示。迷宫老鼠(rat in a maze)问题是要寻找一条从入口到出口的路径。路径是一个由位置组成的序列,每一个位置都没有障碍,而且除入口之外,路径上的每个位置都是前一个位置在东、南、西或北方向上相邻的一个位置(如图8-11 所示)。
我们要编写程序来解决迷宫老鼠问题。假设迷宫是一个方阵(即m=n)且足够小,能够整个存储在目标计算机的内存中。程序应是独立的,一个用户可以输入自己选择的迷宫来直接寻找迷宫路径。
求解策略
逻辑:首先把迷宫的入口作为当前位置。如果当前位置是迷宫出口,那么已经找到了一条路径,寻找工作结束。如果当前位置不是迷宫出口,则在当前位置上放置障碍物,以阻止寻找过程又绕回到这个位置。然后检查相邻位置是否有空闲(即没有障碍物),如果有,就移动到一个空闲的相邻位置上,然后从这个位置开始寻找通往出口的路径。如果不成功,就选择另一个空闲的相邻位置,并从它开始寻找通往出口的路径。为了方便移动,在进入新的相邻位置之前,把当前位置保存在一个栈中。如果所有空闲的相邻位置都已经被探索过,但还未能找到路径,则表明迷宫不存在从入口到出口的路径。
路径的表示:注意,在栈中始终有一条从入口到当前位置的路径。如果最终到达了出口,那么栈中的路径就是从入口到出口的路径。
padding:为了避免在处理内部位置和边界位置时存在差别,可以在迷宫的周围增加一圈障碍物。对于一个mxm的数组maze,这一圈障碍物将占据数组maze的第0行、第m+1行、第0列和第m+1列。
最长路径:一个没有障碍物的 m× m 迷宫,最长的路径可包含 m 2 m^2 m2个位置。
因为路径包含的位置没均不相同,而且迷宫仅有 m 2 m^2 m2 个位置,所以一条路径所包含的位置最多不超过 m 2 m^2 m2。又因为路径的最后一个位置不必存储到栈中,所以在栈中存储的位置最多是 m 2 − 1 m^2 - 1 m2−1。注意,在一个没有障碍物的迷宫中,在入口和出口之间,总有一条最多包含 2m 个位置的路径。
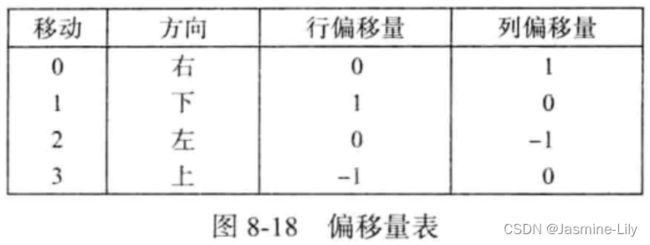
偏移量表:例如,如果当前位置是(3,4),则其右边相邻位置的行坐标为3+offset[0].row=3,列坐标为 4+offset[0].col=5。
防止走回去:为了不重蹈已经走过的位置,我们在每一个走过的位置maze[i] [j]上设置障碍物。
代码
#include 运行结果
C:\Users\15495\Documents\Jasmine\Work\coding\cmake-build-debug\coding.exe
RAT IN A MAZE********************
******Welcome To RAT IN A MAZE******
************Jasmine,2022************
Please enter the size of Maze-Matrix:3
Please enter maze[1,1]:0
Please enter maze[1,2]:0
Please enter maze[1,3]:0
Please enter maze[2,1]:1
Please enter maze[2,2]:1
Please enter maze[2,3]:0
Please enter maze[3,1]:1
Please enter maze[3,2]:1
Please enter maze[3,3]:0
The maze =
1 1 1 1 1
1 0 0 0 1
1 1 1 0 1
1 1 1 0 1
1 1 1 1 1
The path = (3,3)->(2,3)->(1,3)->(1,2)->(1,1)->(1,1)->(1,2)->(1,3)->(2,3)->(3,3)
Process finished with exit code 0