8.情态动词
1.什么是情态动词
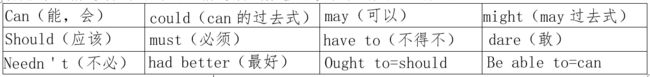
情态动词是一类特殊的动词,在英语中用来表达说话人的意图、态度、能力、推测等情态或情感。情态动词常常和其他动词一起使用,来构成各种各样的句子。情态动词数量不多,只有下面的几个:
2.情态动词在句中的位置
情态动词加上动词原型构成复合谓语。可以用在主谓宾或主系表的句子里面。
-
主语+情态动词+实义动词原型/动词短语原型+宾语
- 主语+情态动词+be+表语
3.含有情态动词句子的时态变化
一般情况下,含有情态动词的句子基本没有时态结构的变化,比如,Must可以直接表达过去,将来,现在。要表达不同的时间必须做某事,直接加上时间状语就可以了。请看下面例子:
I must go now 我现在必须走了
I must go home tomorrow 我明天必须回家
I must teach English every day 我每天必须教英语
I must sleep early yesterday 我昨天必须很早睡觉
但是,有些情态动词有格式变化,比如“can”的过去式“could”、“have to”的过去式“had to”、“may”的过去式是“might”。这些情态动词可以有时态结构变化,但是只能变“情态动词本身”,情态动词后面依然必须得用“动词原型”。
4.含有情态动词句子的否定句、疑问句
否定句
含有情态动词的句子变成否定句的时候,就在情态动词后面加“not”当然,也有特殊的情况。比如下面的“have to”,变否定句就是特殊的。情态动词的否定句也可以使用缩写格式,情态动词否定式的缩写分别是:
疑问句
含有情态动词的句子变成一般疑问句的时候,通常把情态动词移到句首。
5.情态动词的用法
5.1 can
can 可以表示现在或者将来的情况,也就是本身就含有一般现在时态和将来时态的功能。表示“现在能做什么事情”或“将来能做什么事情”,都是直接用“can+动词原型”,“can”不需要发生变化,表示将来直接加“一个时间状语”就可以了。比如:
I can buy a house in the future 我以后可以买一套房
I can buy a house now 我现在可以买一套房
can 是一个多义词,不同情况,不同语境下,有不同的意思。
1.表示能力
can 可以表示“有做某事的能力”的意思,即:能做某事。
1)He can eat five bowls of rice every day 他每天能吃五碗饭。
2)He can move the big stone 他能搬动这块大石头
3) He can earn one million yuan a year 他一年可以赚一百万。
4)Can you write a composition in English?你可以用英语写一篇作文吗?
5)He can run very fast 他能跑得很快。
6)Who can answer this question?谁能回答这个问题?
2.表示可能性
can 可以表示猜测和做某事的可能性
1)Can you help me?你可以帮我吗?
2)We can eat in a restaurant 我们可以在餐馆吃饭。
3)I can call you tomorrow 我明天可以打电话给你。
4)I am afraid I can't go with you 很抱歉恐怕我不能和你去。
5)Can he still be alive after all these years?这些年后,他还可能活着吗?
6)Can he receive my email?他能收到我的电子邮件吗?
1) That can't be Mary,she is in hospital 那不可能是玛丽,她住院了
3.表示允许做某事
主语被人允许去做某事。
1)You can park here 你可以在这里停车。
2)You can take the book home 你可以把这本书带回家。
3) You can call me 你可以打电话给我。
4)She can pick my mangoes 她可以摘我的芒果。
5) You can catch my fishes 你们可以抓我的鱼
6) Every one can watch my videos 每个人都可以看我的视频
5.2 could
1.作为 can 的过去式,
表示过去的情况。也就是把含有can的句子变成一般过去时态,然后把can改成过去式could
1) I can eat three bowls ofrice 我可以吃三碗饭(一般现在时态)
2) I could eat three bowls of rice ten years ago.十年前我可以吃三碗饭(一般过去时)
3) You could go fishing ten years ago 十年前,你可以钓鱼
4) I could buy a book yesterday 昨天我可以买一本书
5) I could write a composition ten years ago 十年前,我可以写一篇作文。
6)She couldn't answer the teacher's question yesterday 她昨天不能回答老师的问题。
2.could 可以用在婉转地、礼貌地提出请求、想法、建议等情况里
和 can 的表示可能性用法的问句相似,只是提出的请求、想法、建议更婉转、礼貌,注意,这个时候,跟一般过去时态没有关系,在这里,“could”不属于“can”的过去式。
1)Could you show me the way?你可以给我带路吗?
2)Could you tell me how to get to the station 你可以告诉我怎么去车站吗?
3)I could get you a copy 我可以帮你弄一份。
5.3 may
may 跟 can 一样,也可以表示现在或者将来的情况,也就是本身就含有一般现在时态和将来时态的功能,may主要有下面几种用法:
1.征求别人的许可
一般翻译为:可以...吗?。基本上只能用在一般疑问句里面,而且主语基本上就是 I,也就是“May I”。注意,一般不能说“may you”,因为习惯上,用“Can you”来问对方“可以不可以”。
1)May I use your phone?我可以用你的电话吗?
2)May I be your partner?
3)May I come in?我可以进来吗?
4)May I come around in the afternoon?我可以在下午的时候过来吗?
5)May I stay here?我可以待在这里吗?
6)May I call you tomorrow?明天我可以打电话给你吗?
2.用于陈述句,表示允许主语做某事,
跟上面“can”的第三种用法是一样的。区别在于,may更礼貌一点,所以口语多用“can”。
1)You may park here= You can park here 你可以在这里停车
2)You may only keep books for two weeks 书你只能借两个星期。
3)You may come if you wish 如果你愿意,你可以来。
4)You may not take photos in the museum.你不可以在博物馆里面照相。
5) You may use my computer=You can use my computer 你可以用我的电脑。
6)You may not use my computer=you can't use my computer 你不可以用我的电脑
3.表示可能,表示猜测
一般翻译成“也许”
1) Anna may know Tom's address.安娜可能知道汤姆的地址。
2) Jack may know lily's secret 杰克也许知道莉莉的秘密。
这个用法跟上面“can”第三种用法很接近。有时候差不多意思,但是“may”可以跟“have+过去分词”,表示对过去的猜测,这是“can”没有用的用法,比如:
He may have gone abroad. 他可能已经出国了。
上面这句话强调,可能早就出国了,在过去某个时间出国了。
“may + be+现在分词”,表示可能正在做某事。比如:
They may be waiting at the station 他们可能正在车站等。
当然,这句话跟“They may wait at the station”差不多。
4.表示祝愿
“may”可以表示对某人的祝福或祝愿,有两种情况:
第一:May+主语+be+表语!
1)May you be happy!祝你幸福!
2)May God be with you!愿上帝与你同在!
3)May you be rich!祝你发财!
4)May you be safe!祝你安全,顺利!
第二:May+主语+动词原型+(宾语)
1)May you succeed!祝你成功!
2)May you have a good time!祝你玩得开心!
3)May she rest in peace.愿她安息。
5.4 might
1.作 may 的过去式。
也就是把含有“may”的句子变成一般过去时,需要把“may”变成过去式“might”.比如:
1)Jack may know Tom's address 杰克也许知道汤姆的地址
Jack might know tom's address yesterday 昨天杰克也许知道汤姆的地址
2) You may keep the book for three days 书你可以借三天。
You might keep the book for one day ten years ago 十年前你可以借这书一天。
另外,在含有宾语从句的复合句里面,如果主句用了一般过去时,从句含有“may”,那么也要变成过去式“might”。这个属于中级的内容,可以先不管。
1)He asked if he might use the phone 他问是否可以用一下电话。
2) I thought you might stay with us 我想你可以和我们一起留下来。
3)He said he might be late 他说他可能迟到了
4)I guessed she might come next day 我猜她可能明天来。
2.征求别人的许可,
但此处 might 不是 may 的过去式,而是用来代替may,谈现在的情况,口气比may更婉转,一般翻译为可以...吗?
1)May I go with you?我可以和你一起去吗?
2)Might I go with you?我可以和你一起去吗?(比用“may I”更婉转)
3)Might I use your cellphone?我可以用你的手机吗?
4)Might I say something?我可以说点什么吗?
5.5 must
1.在肯定句里面表示“必须、一定要”的意思,
没有时态变化,可以表示过去,现在,将来的情况。
1)You must cut down on smoking你必须少抽些烟
2)You must learn English 你必须学英语
3)I must earn money 我必须赚钱
4)I must go now 现在我必须走了
5)I must remember to go to the bank today 今天我必须记得去银行。
注意,must变成一般疑问句的时候,否定回答不能用mustn't,变否定句的时候,也不能用mustn't,要用 have to 的否定格式。为什么呢?因为“must”的否定格式 mustn't 表达的意思不一样。下面就要专门学习 mustn't 的用法。
肯定句:You must learn English
否定句:You don't have to learn English
疑问句:Must we finish the homework today? 我们必须今天完成作业吗?
Yes,you must 是的,你们必须
No,you don't have to 不,你们不必。
2.must 的否定格式 mustn't 表示“禁止主语做某事,不准主语做某事”
1)You mustn't take pictures here,it is forbidden 你不得在这里照相,这是禁止的。
2)Cars must not park in front of the supermarket 车不得停在超市门口。
3)You mustn't drive without a license.你不得无证驾车。
4)You mustn't steal apples 你不得偷苹果。
3.主语+must be+表语中的 must 表推想
可翻译为 一定、准是、肯定是,但是主要用在“主系表句型”
1)You must be hungry.have something to eat 你肯定饿了,吃点东西吧?
2)They must be twins 她们肯定是双胞胎。
must 在主谓宾肯定句里面,一般不能表示推想。但是,特殊情况可以,比如:
普通的主谓宾结构:主语 + must + 谓语 + 宾语。但到底是表一定还是表推测要根据上下文来确定。
You must hate me 你一定恨我吧
如果句型是:Must+have+过去分词+(宾语)。这个特殊结构是强调对过去的事情非常肯定的推想、猜测。比如:
1)I can't find my English book.I must have left it at home 我找不到我的英语书了,肯定是放在家里了吧。
2)She must have been to America 她肯定去过美国吧。
3)She must have eaten dinner 她肯定吃过饭了吧。
5.6 have to
have to 的意思接近 must,但是 must 强调说话人的意愿,而 have to 表示客观上的必要性,常可译为“不得不”,否定形式表示“不必”:
1)I have to go to work on time 我不得不按时上班。
2)We have to be careful in such matters 处理这类事情,我们必须得小心。
3)He has to do a lot of reading 他得看很多书。
have to 是一个比较特殊的情态动词,初学者很容易跟实义动词 have 混淆,所以切记,必须把have to 当一个情态动词,不能当两个单词。另外 have to 要根据不同的时态,需要发生不同的结构变化。为了方便造句和理解 have to 的时态结构变化,下面根据句型和时态分成不同的小句型讲解。
1.一般现在时态
句型1:主语非小三 +have to+动词原型+(宾语)
1)We have to help him 我们不得不帮他
2)You have to sleep 你必须得睡觉
句型2:主语非小三 +have to+be+表语
3)My students have to be careful 我的学生必须得小心
句型3:主语小三+has to+动词原型+(宾语)
4)She has to take pills 她必须得吃药
5)The doctor has to help him 这个医生不得不帮他
句型4:主语小三+has to+be+表语
6)The girl has to be careful 这女孩必须得小心
Note:情态动词的形式不受主语名词的单复数影响。无论是单数还是复数名词作为主语,"have to" 的形式都保持不变
2.一般过去时
一般过去时态的句子中,情态动词 hava to 变为 had to
句型1:主语 + had to+动词原型+(宾语)
1)They had to jump into the river last night 昨晚他们不得不跳河里。
2)I missed the bus and had to walk home 我错过了公车,不得不走路回家。
句型2:主语 + had to+be+表语
4)You had to be careful yesterday 昨天你不得不小心。
3.一般将来时态
一般现在时态的句子中,情态动词 hava to 变为 will have to
句型1:主语+will have to+动词原型+(宾语)
1)We will have to take the bus tomorrow 我们明天必须得坐公交车
2)We will not have to take the bus tomorrow 我们明天不必坐公交车
3)We will have to help him as much as we can我们将不得不尽量帮他。
句型2:主语 will have to+be+表语
4)You will have to be careful in the future 以后你必须得小心
一般将来时态,也可以用 be going to+have to 构成,比如:
2)I am going to have to take the bus tomorrow.我明天不得不坐公交车。
3) She is going to have to go home tomorrow. 她明天必须得回家
Note:“Have to”一般没有现在进行时态和现在完成时态。
4.含有 have to 的疑问句和否定句
-
一般现在时的否定句加助动词 don't、doesn't,疑问句句首加 do、does,如果是 has to,需要把 has to 变回原型 have to
-
一般过去时的否定句在 had to 前面加 didn't,疑问句句首加 did。
-
一般将来时态的否定句在 will 后面加 not,可缩写为won't。疑问句是把 will 移到句首。
1)Do you have to leave soon?你一定要马上离开吗?
2)Does she have to go with you?她一定要跟你去吗?
3)You don't have to say sorry 你不必说对不起。
4)She doesn't have to take the bus 她不必坐公交车
5)They didn't had to jump into the river last night 昨晚他们不必跳河里。
6)We won't hava to take the bus tomorrow
7)We will have to take the bus tomorrow?
5.7 ought to
通常 ought to 没有一般疑问句,只有肯定句和否定句,否定句要在 ought 和 to 中间加 not。一般翻译为"应该"。
1)We ought to get up early. 我们应该早起
2)We ought to be careful 我们应该小心
3)We ought not to eat too much sugar 我们不应该吃太多糖
4)I ought to go home today 我今天应该回家。
5)You ought to read this book,it is very interesting.你应该读一读这本书,很有趣的
5.8 should
should 可以作助动词,也可以作情态动词,作情态动词的时候,就是“应该”的意思,跟 ought to 差不多。should的否定句直接在should后面加not,疑问句将should移到句首。
1)we should get up early=we ought to get up early.我们应该早起
2)we should help the poor people 我们应该帮助这些穷人
3) we shouldn't sit in the office all day long 我们不应该一整天坐在办公室里面。
should 有一般疑问句, oughtto 则没有,比如:
4)should we stay here?我们应该留在这里吗?
5)Should we help the old man?我们应该帮助这个老人吗?
5.9 dare
dare 是一个特别的词语,可以作实义动词,也可以作情态动词。在肯定句里面作实义动词,在疑问句,否定句,条件句里面作情态动词。作情态动词时,“dare”没有人称形式的变化,也就是不管主语是什么人称,都用“dare”。dare 有一个过去式“dared”,可能是因为“dare”本身也是实义动词,所以“dare”作情态动词用在否定句的时候比较麻烦,有两种表达方式。比如:
I dare not look at her = I don't dare look at her 我不敢看她
这里,dare not = don't dare,喜欢用哪个都可以
She dare not look at me=She doesn't dare look at me 她不敢看我
这里,dare not=doesn't dare
I dared not drink beer last night=I didn't dare drink beer last night 昨晚我不敢喝啤酒
这里,dared not=didn't dare
1.否定句
dare not 或者加助动词:doesn't dare,don't dare,didn't dare。当“dare”出现在否定句的时候,“dare”就是一个情态动词,后面直接跟动词原型。但是,“dare”另一种否定结构。比如:
1)I dare not ask her to marry me 我不敢向她求婚。(一般现在时态)
这句话也可以说:I don't dare ask her to marry me.
2)They dared not move 他们不敢动。(一般过去时态)
这话也可以说:they didn't dare move.
3)He doesn't dare say anything 他什么也不敢说。(一般现在时态)
这句话也可以说:he dare not say anything.
4)They didn't dare disobey 他不敢不服从
“dare”在带有否定意思的句子中也可以作情态动词,直接跟动词原型,而且本身有否定意思了,“dare”不需要变否定格式。比如:
1)No one dared speak ofit 没有人敢谈及此事。
2)He never dared stay long 他从来不敢待久。
3)I hardly dared look at her eyes 我几乎不敢看她的眼睛。
2.疑问句及条件从句
当“dare”出现在疑问句或条件句的时候也属于情态动词,后面跟动词原型。变成一般疑问句的时候,只要把 dare 移到主语前面就可以了,当然也可以用助动词 do,比如:
1) Dare she look at me?= Does she dare look at me? 她敢看我吗?
2)Dare I look at her?=Do I dare look at her? 我敢看她吗?
3) Did you dare drink beer last night?=dared you drink beer last night?昨晚你敢喝啤酒吗?
4)Dare you interrupt him?=do you dare interrupt him?你敢打扰他吗?
5) How dare you speak to me like that? 你怎么敢这样跟我说话?
6) Do you dare tell him the truth?=dare you tell him the truth?你敢告诉她真相吗?
7) I wonder if she dared come home 我想知道她是否敢回家。(条件句)
Note:dare在肯定句里面,是一个典型的及物动词,后面不能跟“动词原型”,需要跟“动词不定式短语”作宾语,比如这个句子“I dare go home alone”就是错的,要改成“I dare to gohome alone”
5.10 be able to
一般翻译为"能、可以",用法和意思跟 can 差不多,大多数时候可以互用。除现在完成时态外,be able to 变否定句时在be动词后面加not,变疑问句时将be动词移到句首。
I am not able to answer your question. 我不能回答你的问题。
Are you able to type? 你会打字吗?
Be able to 可以用于更多的时态,can 除了过去式,一般没有其他的变化。Be able to 在不同
的时态里面有不同的结构变化,比如:
1.一般现在时态
Be able to 要根据主语的人称变成相应的:Is able to,am able to,are able to,“be able to”的“be”
跟系动词的“be”用法相同。
1)I am able to repair computers 我会修电脑
2)Are you able to repair computers?你会修电脑吗?
3) She is able to swim 她会游泳
4) Is she able to swim?她会游泳吗?
5)We are able to catch fish 我们可以抓鱼
6) She is not able to cook 她不会做饭
2.一般过去时态
Be able to 要根据主语的人称变成相应的:Was able to,were able to。主语是单数用 was able to,主语复数用 were able to,比如:
I)she was able to drink ten bottles of beer last night 她昨晚能喝十瓶啤酒
2)She wasn't able to find you last night 她昨晚无法找到你。
3)You were able to eat 3 bowls of rice ten years ago.十年前你能吃三碗饭。
3.一般将来时态
Be able to 在一般将来时态里面变成:Will be able to。注意此处 will not 的缩写形式是 won't。
1)I will be able to earn much money 我以后可以赚很多钱
2)I will not be able to come to your wedding 我不能参加你的婚礼了。
4.现在完成时态
有时候 be able to还可以用在现在完成时态,根据主语变成:
Has been able to、Have been able to
否定句是在 has、have 后面加not,疑问句是将 has、have 移到句首
1)He hasn't been able to leave the house since his accident 他出事故以来,一直不能出门。
2)We have been able to earn one million yuan a year 我们已经可以年赚百万了。
5.11 needn't
need 本来是实义动词,也可以作情态动词,但是只有否定格式 needn't 才能作情态动词,才能跟动词原型构成复合谓语。当然,在含有否定意义的句子里或者在少数条件句,疑问句里面也可以作情态动词。needn't 没有人称变化、没有时态变化
1.用于否定结构,表示“不必,没必要”
needn't 作情态动词,不管主语是单数还是复数,一律用 needn't+动词原型 或 needn't+be+表语。比如:
1) I needn't prepare my lessons 我不需要备课。
2)She needn't come here early 她不需要早来这里
3)We needn't be worried 我们不必担心
4)You needn't make two copies.one will be ok 你不必做两份,一份就可以了。
5)They needn't send me a receipt.他们不必寄收条给我
6)You needn't come to the meeting if you are too busy.你不必来开会,如果你忙的话。
2.用在带有否定意思的句子中
“need”在含有否定意义的句子里面也可以作情态动词,直接跟动词原型构成复合谓语。比如:
1)I need hardly tell you the truth 我用不着告诉你真相
2)Nobody need be afraid of catching the disease 谁都不必害怕染上这种病。
3)I don't think you need worry 我认为你不必担心。
Note
need在肯定句中只是一个及物动词,比如这个句子“I need buy a house”是错的,因为这是肯定句,“need”在肯定句里面是一个实义动词,不能跟动词原型“buy”作宾语,需要变成还没有学的“动词不定式短语”才能作宾语,改成“I need to buy a house”。
牛津词典了解。另外,“need”在疑问句或条件句里面也可以作情态动词,这里不做详细解释。
5.12 Had better
had better 表示“最好”的意思,一般缩写成 'd better。Had better 没有疑问句,没有时态结构变化,也不受主语人称影响。不管主语是单数还是复数,都是直接“had better+动词原型+宾语 或 be+表语”。不过,“had better”有否定格式“had better not”,表示“最好不”的意思。比如:
1)You'd better take a nap after lunch 你最好午饭后睡个午觉。
2)We'd better stop arguing 我们最好停止争吵。
3)You had better check your homework carefully 你们最好认真检查作业
4)We had better eat less meat 我们最好少吃肉
5)Girls had better not run at night 女孩子最好不要夜跑
6)She had better learn English grammar first 她最好先学英语语法
Had better 后面也可以跟“助动词原型 be+现在分词”,表示“最好立即做某事”:
1) I think I'd better be going 我想我最好还是走了
2)We'd better be getting our clothes ready 我们最好穿好衣服。