Springboot全局异常处理
一、springboot异常处理源码分析
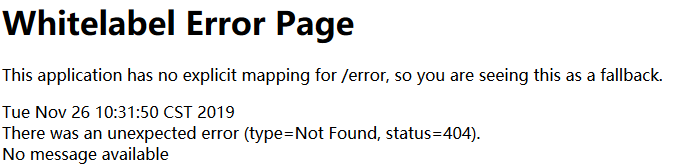
当发生4xx错误时候,如果是pc端,springboot默认响应的是页面,页面内容如下
如果是移动端(手机端),默认响应的是jsob格式的数据,json格式的数据如下
为什么我们请求错误的路径,springboot会给我们返回错误页面或者json格式数据呢?
Springboot项目启动带有@SpringBootApplication注解的main方法,通@EnableAutoConfiguration加载springbootAutoConfiguration.jar包下的META-INF/spring.factories中的所有配置类(这些配置类加载之后,会将每个配置类里面的组件注入容器使用),其中的ErrorMvcAutoConfiguration配置类,位置如下:
通过代码可以看到用到了以下四个组件
DefaultErrorAttributes、BasicErrorController、errorPageCustomizer、DefaultErrorViewResolver
@Configuration(
proxyBeanMethods = false
)
@ConditionalOnWebApplication(
type = Type.SERVLET
)
@ConditionalOnClass({Servlet.class, DispatcherServlet.class})
@AutoConfigureBefore({WebMvcAutoConfiguration.class})
@EnableConfigurationProperties({ServerProperties.class, WebMvcProperties.class})
public class ErrorMvcAutoConfiguration {
private final ServerProperties serverProperties;
public ErrorMvcAutoConfiguration(ServerProperties serverProperties) {
this.serverProperties = serverProperties;
}
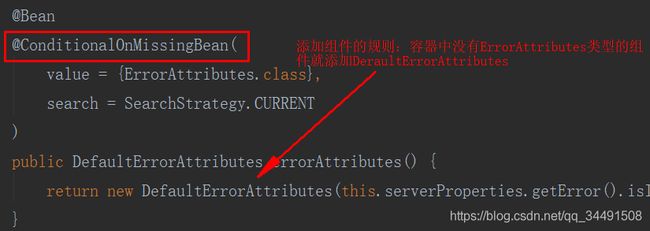
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(
value = {ErrorAttributes.class},
search = SearchStrategy.CURRENT
)
public DefaultErrorAttributes errorAttributes() {
return new DefaultErrorAttributes();
}
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(
value = {ErrorController.class},
search = SearchStrategy.CURRENT
)
public BasicErrorController basicErrorController(ErrorAttributes errorAttributes, ObjectProvider errorViewResolvers) {
return new BasicErrorController(errorAttributes, this.serverProperties.getError(), (List)errorViewResolvers.orderedStream().collect(Collectors.toList()));
}
@Bean
public ErrorMvcAutoConfiguration.ErrorPageCustomizer errorPageCustomizer(DispatcherServletPath dispatcherServletPath) {
return new ErrorMvcAutoConfiguration.ErrorPageCustomizer(this.serverProperties, dispatcherServletPath);
}
@Bean
public static ErrorMvcAutoConfiguration.PreserveErrorControllerTargetClassPostProcessor preserveErrorControllerTargetClassPostProcessor() {
return new ErrorMvcAutoConfiguration.PreserveErrorControllerTargetClassPostProcessor();
}
static class PreserveErrorControllerTargetClassPostProcessor implements BeanFactoryPostProcessor {
PreserveErrorControllerTargetClassPostProcessor() {
}
public void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException {
String[] errorControllerBeans = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(ErrorController.class, false, false);
String[] var3 = errorControllerBeans;
int var4 = errorControllerBeans.length;
for(int var5 = 0; var5 < var4; ++var5) {
String errorControllerBean = var3[var5];
try {
beanFactory.getBeanDefinition(errorControllerBean).setAttribute(AutoProxyUtils.PRESERVE_TARGET_CLASS_ATTRIBUTE, Boolean.TRUE);
} catch (Throwable var8) {
}
}
}
}
static class ErrorPageCustomizer implements ErrorPageRegistrar, Ordered {
private final ServerProperties properties;
private final DispatcherServletPath dispatcherServletPath;
protected ErrorPageCustomizer(ServerProperties properties, DispatcherServletPath dispatcherServletPath) {
this.properties = properties;
this.dispatcherServletPath = dispatcherServletPath;
}
public void registerErrorPages(ErrorPageRegistry errorPageRegistry) {
ErrorPage errorPage = new ErrorPage(this.dispatcherServletPath.getRelativePath(this.properties.getError().getPath()));
errorPageRegistry.addErrorPages(new ErrorPage[]{errorPage});
}
public int getOrder() {
return 0;
}
}
private static class StaticView implements View {
private static final MediaType TEXT_HTML_UTF8;
private static final Log logger;
private StaticView() {
}
public void render(Map model, HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
if (response.isCommitted()) {
String message = this.getMessage(model);
logger.error(message);
} else {
response.setContentType(TEXT_HTML_UTF8.toString());
StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder();
Object timestamp = model.get("timestamp");
Object message = model.get("message");
Object trace = model.get("trace");
if (response.getContentType() == null) {
response.setContentType(this.getContentType());
}
builder.append("Whitelabel Error Page
").append("This application has no explicit mapping for /error, so you are seeing this as a fallback.
").append("").append(timestamp).append("").append("There was an unexpected error (type=").append(this.htmlEscape(model.get("error"))).append(", status=").append(this.htmlEscape(model.get("status"))).append(").");
if (message != null) {
builder.append("").append(this.htmlEscape(message)).append("");
}
if (trace != null) {
builder.append("").append(this.htmlEscape(trace)).append("");
}
builder.append("");
response.getWriter().append(builder.toString());
}
}
private String htmlEscape(Object input) {
return input != null ? HtmlUtils.htmlEscape(input.toString()) : null;
}
private String getMessage(Map model) {
Object path = model.get("path");
String message = "Cannot render error page for request [" + path + "]";
if (model.get("message") != null) {
message = message + " and exception [" + model.get("message") + "]";
}
message = message + " as the response has already been committed.";
message = message + " As a result, the response may have the wrong status code.";
return message;
}
public String getContentType() {
return "text/html";
}
static {
TEXT_HTML_UTF8 = new MediaType("text", "html", StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
logger = LogFactory.getLog(ErrorMvcAutoConfiguration.StaticView.class);
}
}
private static class ErrorTemplateMissingCondition extends SpringBootCondition {
private ErrorTemplateMissingCondition() {
}
public ConditionOutcome getMatchOutcome(ConditionContext context, AnnotatedTypeMetadata metadata) {
Builder message = ConditionMessage.forCondition("ErrorTemplate Missing", new Object[0]);
TemplateAvailabilityProviders providers = new TemplateAvailabilityProviders(context.getClassLoader());
TemplateAvailabilityProvider provider = providers.getProvider("error", context.getEnvironment(), context.getClassLoader(), context.getResourceLoader());
return provider != null ? ConditionOutcome.noMatch(message.foundExactly("template from " + provider)) : ConditionOutcome.match(message.didNotFind("error template view").atAll());
}
}
@Configuration(
proxyBeanMethods = false
)
@ConditionalOnProperty(
prefix = "server.error.whitelabel",
name = {"enabled"},
matchIfMissing = true
)
@Conditional({ErrorMvcAutoConfiguration.ErrorTemplateMissingCondition.class})
protected static class WhitelabelErrorViewConfiguration {
private final ErrorMvcAutoConfiguration.StaticView defaultErrorView = new ErrorMvcAutoConfiguration.StaticView();
protected WhitelabelErrorViewConfiguration() {
}
@Bean(
name = {"error"}
)
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(
name = {"error"}
)
public View defaultErrorView() {
return this.defaultErrorView;
}
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
public BeanNameViewResolver beanNameViewResolver() {
BeanNameViewResolver resolver = new BeanNameViewResolver();
resolver.setOrder(2147483637);
return resolver;
}
}
@Configuration(
proxyBeanMethods = false
)
@EnableConfigurationProperties({ResourceProperties.class, WebProperties.class, WebMvcProperties.class})
static class DefaultErrorViewResolverConfiguration {
private final ApplicationContext applicationContext;
private final Resources resources;
DefaultErrorViewResolverConfiguration(ApplicationContext applicationContext, ResourceProperties resourceProperties, WebProperties webProperties) {
this.applicationContext = applicationContext;
this.resources = (Resources)(webProperties.getResources().hasBeenCustomized() ? webProperties.getResources() : resourceProperties);
}
@Bean
@ConditionalOnBean({DispatcherServlet.class})
@ConditionalOnMissingBean({ErrorViewResolver.class})
DefaultErrorViewResolver conventionErrorViewResolver() {
return new DefaultErrorViewResolver(this.applicationContext, this.resources);
}
}
} 以DefaultErrorAttributes为例(其他三个组件类似)
当出现4xx或者5xx等错误时,errorPageCustomizer就会生效, this.properties.getError().getPath())并来到/error请求,核心代码
//errorPageCustomizer
@Value("${error.path:/error}")
private String path = "/error";
而这个/error请求再由BasicErrorController处理,BasicErrorController是一个Controller,其中里面有两种处理方法,一种是HTML形式,一种是JSON格式。关键代码
@RequestMapping(produces = "text/html") //HTML
public ModelAndView errorHtml(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response) {
HttpStatus status = getStatus(request);
Map model = Collections.unmodifiableMap(getErrorAttributes(
request, isIncludeStackTrace(request, MediaType.TEXT_HTML)));
response.setStatus(status.value());
ModelAndView modelAndView = resolveErrorView(request, response, status, model);
return (modelAndView == null ? new ModelAndView("error", model) : modelAndView);
}
@RequestMapping
@ResponseBody //JSON
public ResponseEntity> error(HttpServletRequest request) {
Map body = getErrorAttributes(request,
isIncludeStackTrace(request, MediaType.ALL));
HttpStatus status = getStatus(request);
return new ResponseEntity<>(body, status);
}
其中访问者的信息可以从getErrorAttributes从获取。DefaultErrorAttributes是ErrorAttributes的实现类。
当前JSON模式时,直接返回一个ResponseEntity类
当为HTML模式时,就会构建一个resolveErrorView类,而resolverErrorView继续调用ErrorViewResolver。关键代码
protected ModelAndView resolveErrorView(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response, HttpStatus status, Map model) {
for (ErrorViewResolver resolver : this.errorViewResolvers) {
ModelAndView modelAndView = resolver.resolveErrorView(request, status, model);
if (modelAndView != null) {
return modelAndView;
}
}
return null;
}
在我们没有做自定义配置时,ErrorViewResolver就会指向DefaultErrorViewResolver。
static {
//可以用4xx,5xx文件名来统一匹配错误,但是会以精确优先的原则
Map views = new EnumMap<>(Series.class);
views.put(Series.CLIENT_ERROR, "4xx");
views.put(Series.SERVER_ERROR, "5xx");
SERIES_VIEWS = Collections.unmodifiableMap(views);
}
@Override
public ModelAndView resolveErrorView(HttpServletRequest request, HttpStatus status,
Map model) {
ModelAndView modelAndView = resolve(String.valueOf(status), model);
if (modelAndView == null && SERIES_VIEWS.containsKey(status.series())) {
modelAndView = resolve(SERIES_VIEWS.get(status.series()), model);
}
return modelAndView;
}
private ModelAndView resolve(String viewName, Map model) {
//将错误代码拼接到error后
String errorViewName = "error/" + viewName;
TemplateAvailabilityProvider provider = this.templateAvailabilityProviders
.getProvider(errorViewName, this.applicationContext);
//如果模版引擎可用就让模版引擎进行解析如:Template/error/404
if (provider != null) {
return new ModelAndView(errorViewName, model);
}
//如果模版引擎不可用,就在静态资源文件夹下找资源文件,error/404
return resolveResource(errorViewName, model);
}
二、异常处理
熟悉了springboot异常处理原理,我们就可以自定义控制异常响应
方式1、自定义错误页面方式
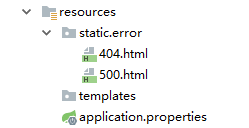
如果项目中有模板引擎(jsp,thmeleaf,freemarker)的情况下,可以将错误页面命名为状态码.html放在模板引擎文件夹下的error文件夹下,发生异常,不管是前端请求还是后端程序错误会来到对应的错误页面。可以将错误页面命名为4xx和5xx匹配所有的错误,但是优先返回精确状态码.html页面;并且在模板引擎页面可以获取如下相关信息
这里模版引擎使用thmeleaf
4xx代码
5xx代码
500
我们请求一个错误的地址路径
请求一个存在异常的路径
上面是有模版引擎的情况下处理错误以及异常的方式,
如果项目中没有模板引擎,(模板引擎找不到这个错误页面),静态资源文件夹static下找对应的4xx或者5xx或者更精确的错误页面。但是如果不用模板引擎,页面不能获取上面说的页面信息;
以上有模板和没有模板引起时,pc端会返回页面,手机端返回boot默认的json数据
方式2、自定义异常信息
上面第一种可以轻松的的处理异常,只需在指定的路径下放静态页面(无模版引擎的情况)或者携带相关信息的页面(有模版引擎),缺点就是不能在页面携带我们想要展示的数据,比如当我们程序某处放生异常,我们要返回我们自己提示的错误信息而不是默认的异常信息。这种异常如果处理呢?
Spring Boot 默认异常信息就是方式1所展示出来的 5条数据,这些数据定义在 org.springframework.boot.web.reactive.error.DefaultErrorAttributes 类中,具体定义在 getErrorAttributes 方法中 :核心代码如下
@Override
public Map getErrorAttributes(ServerRequest request,
boolean includeStackTrace) {
Map errorAttributes = new LinkedHashMap<>();
errorAttributes.put("timestamp", new Date());
errorAttributes.put("path", request.path());
Throwable error = getError(request);
HttpStatus errorStatus = determineHttpStatus(error);
errorAttributes.put("status", errorStatus.value());
errorAttributes.put("error", errorStatus.getReasonPhrase());
errorAttributes.put("message", determineMessage(error));
handleException(errorAttributes, determineException(error), includeStackTrace);
return errorAttributes;
} DefaultErrorAttributes 类本身则是在 org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.error.ErrorMvcAutoConfiguration 异常自动配置类中定义的,如果开发者没有自己提供一个 ErrorAttributes 的实例的话,那么 Spring Boot 将自动提供一个 ErrorAttributes 的实例,也就是 DefaultErrorAttributes 。
基于此 ,开发者自定义 ErrorAttributes 有两种方式 实现自定义数据:
1.直接实现 ErrorAttributes 接口
2.继承 DefaultErrorAttributes(推荐),因为 DefaultErrorAttributes 中对异常数据的处理已经完成,开发者可以直接使用。
package com.javayihao.top.config;
import org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.error.DefaultErrorAttributes;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import org.springframework.web.context.request.WebRequest;
import java.util.Map;
@Component
public class MyErrorAttributes extends DefaultErrorAttributes {
@Override
public Map getErrorAttributes(WebRequest webRequest, boolean includeStackTrace) {
Map map = super.getErrorAttributes(webRequest, includeStackTrace);
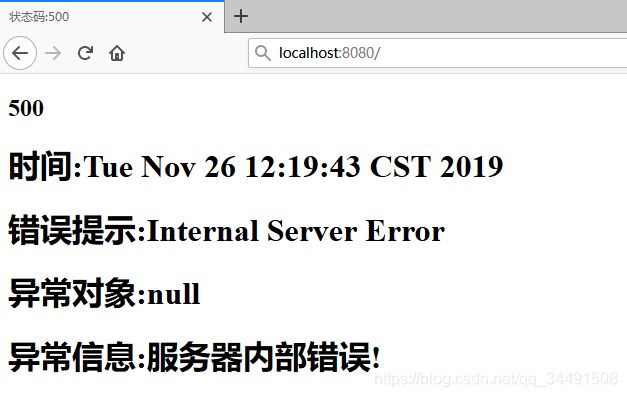
if ((Integer)map.get("status") == 500) {
//这里根据自己需求设置
map.put("message", "服务器内部错误!");
}
if ((Integer)map.get("status") == 404) {
map.put("message", "路径不存在!");
}
return map;
}
} pc端访问一个不存在的路径
移动端访问一个不存在的路径返回
访问存在异常的路径
客户端响应
方式3、自定义ErrorAttributes结合全局异常处理
使用方式二介绍的我们首先自定义一个ErrorAttributes
@Component
public class MyErrorAttributes extends DefaultErrorAttributes {
//返回的map就是页面或者json能获取的所有字段
@Override
public Map getErrorAttributes(WebRequest webRequest, boolean includeStackTrace) {
Map map = super.getErrorAttributes(webRequest, includeStackTrace);
//可以额外添加内容
map.put("company", "javayihao");
//取出异常处理器中的携带的数据
Map ext = (Map) webRequest.getAttribute("ext", 0);//传入0代表从request中获取
map.put("ext", ext);
return map;
}
}
再自定义一个异常,可以在程序任意位置抛出这个异常
使用全局异常处理器处理异常
@ControllerAdvice
public class MyExceptionHandler {
@ExceptionHandler(MyException.class)
public String jsonErrorHandler(HttpServletRequest request, Exception e) {
Map map = new HashMap<>();
request.setAttribute("java.servlet.error.status_code", 500);
map.put("code", -1);
map.put("msg", e.getMessage());
request.setAttribute("ext", map);
//统一返回error下的500页面
return "error/500";
}
}
方式4、使用全局异常处理器处理统一返回json
使用 @ControllerAdvice 结合@ExceptionHandler 注解可以实现统一的异常处理,@ExceptionHandler注解的类会自动应用在每一个被 @RequestMapping 注解的方法。当程序中出现异常时会层层上抛
@ControllerAdvice
public class ExceptionHandle {
@ResponseBody
@ExceptionHandler(Exception.class)
public MyResult handleException(Exception e) {
return MyResult.error(ResponseEnum.UNKNOW_ERROR);
}
}
{
"code": "-1",
"data": [],
"message": "未知错误"
}
我们还可以自定义一个异常,在程序中用于抛出
定义一个返回结果对象(也可以不用定义,直接使用map)存储异常信息
/*ControllerAdvice用来配置需要进行异常处理的包和注解类型,
比如@ControllerAdvice(annotations = RestController.class)
只有类标有rescontrolle才会被拦截
*/
@ControllerAdvice
public class MyExceptionHandler {
//自己创建的异常按照自己编写的信息返回即可
@ExceptionHandler(value = MyException.class)
@ResponseBody
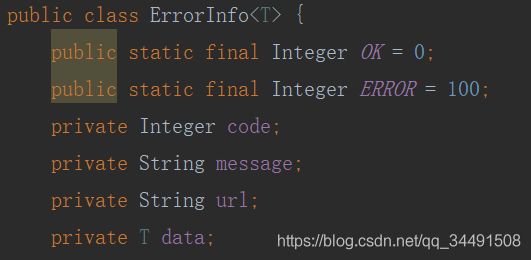
public ErrorInfo errorInfo(HttpServletRequest req, MyException e) {
ErrorInfo r = new ErrorInfo<>();
r.setCode(ErrorInfo.ERROR);
r.setMessage(e.getMessage());
r.setData("测试数据");
r.setUrl(req.getRequestURL().toString());
return r;
}
//系统异常时返回的异常编号为 -1 ,返回的异常信息为 “系统正在维护”;不能将原始的异常信息返回
@ExceptionHandler(value = Exception.class)
@ResponseBody
public ErrorInfo errorInfo(HttpServletRequest req, Exception e) {
ErrorInfo r = new ErrorInfo<>();
r.setCode(ErrorInfo.ERROR);
r.setMessage("系统维护中");
return r;
}
}
方式5、重写ErrorController
重写ErrorController,手动抛出自定义ErrorPageException异常,方便404、403等被统一处理。
@Controller
public class ErrorPageController extends BasicErrorController {
public ErrorPageConfig(){
super(new DefaultErrorAttributes(),new ErrorProperties());
}
@Override
@RequestMapping(
produces = {"text/html"}
)
public ModelAndView errorHtml(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) {
doError(request);
return null;
}
@Override
@RequestMapping
public ResponseEntity> error(HttpServletRequest request) {
doError(request);
return null;
}
private void doError(HttpServletRequest request) {
Map model = this.getErrorAttributes(request, this.isIncludeStackTrace(request, MediaType.ALL));
//抛出ErrorPageException异常,方便被ExceptionHandlerConfig处理
String path = model.get("path").toString();
String status = model.get("status").toString();
//静态资源文件发生404,无需抛出异常 其他抛出自定义的errorpageexcepiton
if(!path.contains("/common/") && !path.contains(".")){
throw new ErrorPageException(status, path);
}
}
} 全局异常处理器增加ErrorPageException拦截方法
/**
* 错误页面异常 统一处理
可以根据异常code自定义异常信息
*/
@ExceptionHandler(value = ErrorPageException.class)
@ResponseBody
public Object exceptionHandler(ErrorPageException e){
String errorMsg;
switch (Integer.parseInt(e.getCode())) {
case 404:
errorMsg= "资源找不到";
break;
case 403:
errorMsg= "没有权限访问";
break;
case 401:
errorEnum = "登录凭证过期";
break;
case 400:
errorEnum = "请求的数据格式不符";
break;
default:
errorEnum = "未知异常";
break;
}
return returnResult(e,Result.error(errorEnum));
}三、ControllerAdvice 注解的三种使用场景
@ControllerAdvice是一个@Component,用于定义@ExceptionHandler(最主要用途),@InitBinder和@ModelAttribute方法,适用于所有使用@RequestMapping方法(拦截)。除了上面的全局异常处理,@ControllerAdvice其他两种使用场景
1、全局数据绑定
全局数据绑定功能可以用来做一些初始化的数据操作,我们可以将一些公共的数据定义在添加了 @ControllerAdvice 注解的类中,这样,在每一个 Controller 的接口中,就都能够访问导致这些数据。
使用步骤,首先定义全局数据,如下:
使用 @ModelAttribute 注解标记该方法的返回数据是一个全局数据,默认情况下,这个全局数据的 key 就是返回的变量名,value 就是方法返回值,当然开发者可以通过 @ModelAttribute 注解的 name 属性去重新指定 key。
@ControllerAdvice
public class ControllerAdviceTest {
/**
* 把值绑定到Model中,使全局@RequestMapping可以获取到该值
* @param model
*/
@ModelAttribute
public void addAttributes(Model model) {
System.out.println("添加全局变量");
model.addAttribute("userName", "Jack");
}
}
@RestController
public class ExceptionController {
/**
* 使用注入的ModelMap来取变量
* @param modelMap
* @return
*/
@RequestMapping("modelMapTest1")
public Object modelMapTest1(ModelMap modelMap){
Object globalVal = modelMap.get("userName");
System.out.println("全局变量为:"+globalVal);
return globalVal;
}
}
2、全局数据预处理
考虑我有两个实体类,Book 和 Author,分别定义如下:
public class Book {
private String name;
private Long price;
//getter/setter
}
public class Author {
private String name;
private Integer age;
//getter/setter
}
此时,如果我定义一个数据添加接口,如下:
@PostMapping("/book")
public void addBook(Book book, Author author) {
System.out.println(book);
System.out.println(author);
}
这个时候,添加操作就会有问题,因为两个实体类都有一个 name 属性,从前端传递时 ,无法区分。此时,通过 @ControllerAdvice 的全局数据预处理可以解决这个问题
解决步骤如下:
1.给接口中的变量取别名
@PostMapping("/book")
public void addBook(@ModelAttribute("b") Book book, @ModelAttribute("a") Author author) {
System.out.println(book);
System.out.println(author);
}
2.进行请求数据预处理
在 @ControllerAdvice 标记的类中添加如下代码:
@InitBinder("b")
public void b(WebDataBinder binder) {
binder.setFieldDefaultPrefix("b.");
}
@InitBinder("a")
public void a(WebDataBinder binder) {
binder.setFieldDefaultPrefix("a.");
}
@InitBinder(“b”) 注解表示该方法用来处理和Book和相关的参数,在方法中,给参数添加一个 b 前缀,即请求参数要有b前缀.
3.发送请求
请求发送时,通过给不同对象的参数添加不同的前缀,可以实现参数的区分.
再如:转换日期格式
@ControllerAdvice
public class ControllerAdviceTest {
/**
* 应用到所有@RequestMapping注解方法,在其执行之前初始化数据绑定器
* WebDataBinder是用来绑定请求参数到指定的属性编辑器
* @param binder
*/
@InitBinder
public void initBinder(WebDataBinder binder) {
System.out.println("initBinder执行");
SimpleDateFormat dateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd");
dateFormat.setLenient(false); //日期格式是否宽容(只能判断是否需要跳到下个月去)
/*
* spring mvc在绑定表单之前,都会先注册这些编辑器,
* Spring自己提供了大量的实现类,诸如CustomDateEditor,CustomBooleanEditor,CustomNumberEditor等
* 使用时候调用WebDataBinder的registerCustomEditor方法注册
*/
binder.registerCustomEditor(Date.class, new CustomDateEditor(dateFormat,false));
}
}
@RestController
public class ExceptionController {
@RequestMapping("/date")
public Date index(Date date){
System.out.println("date="+date);
return date;
}
}
浏览器访问:localhost:8080/date?date=2019-3-20
控制台输出:initBinder执行 date=2019-3-20
浏览器显示:"2019-3-20"