集成Swagger终极版(狂神说SpringBoot14)
一、学习
1、目标:
-
了解Swagger的概念及作用
-
掌握在项目中集成Swagger自动生成API文档
2、Swagger简介
前后端分离:
-
前端 -> 前端控制层、视图层
-
后端 -> 后端控制层、服务层、数据访问层
-
前后端通过API进行交互
-
前后端相对独立且松耦合
产生的问题:
-
前后端集成,前端或者后端无法做到“及时协商,尽早解决”,最终导致问题集中爆发
解决方案:
-
首先定义schema [ 计划的提纲 ],并实时跟踪最新的API,降低集成风险
Swagger:
-
号称世界上最流行的API框架
-
Restful Api 文档在线自动生成器 => API 文档 与API 定义同步更新
-
直接运行,在线测试API
-
支持多种语言 (如:Java,PHP等)
-
官网:https://swagger.io/
3、SpringBoot集成Swagger
SpringBoot集成Swagger => springfox,两个jar包
-
Springfox-swagger2
-
swagger-springmvc
使用Swagger
要求:jdk 1.8 + 否则swagger2无法运行
步骤:
1、新建一个SpringBoot-web项目
2、添加Maven依赖
io.springfox springfox-swagger2 2.9.2 io.springfox springfox-swagger-ui 2.9.2
3、编写HelloController,测试确保运行成功!
4、要使用Swagger,我们需要编写一个配置类-SwaggerConfig来配置 Swagger
@Configuration //配置类
@EnableSwagger2// 开启Swagger2的自动配置
public class SwaggerConfig {
}
5、访问测试 :http://localhost:8080/swagger-ui.html ,可以看到swagger的界面;
4、配置Swagger
1、Swagger实例Bean是Docket,所以通过配置Docket实例来配置Swaggger。
@Bean //配置docket以配置Swagger具体参数
public Docket docket() {
return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2);
}
2、可以通过apiInfo()属性配置文档信息
//配置文档信息
private ApiInfo apiInfo() {
Contact contact = new Contact("联系人名字", "http://xxx.xxx.com/联系人访问链接", "联系人邮箱");
return new ApiInfo(
"Swagger学习", // 标题
"学习演示如何配置Swagger", // 描述
"v1.0", // 版本
"http://terms.service.url/组织链接", // 组织链接
contact, // 联系人信息
"Apach 2.0 许可", // 许可
"许可链接", // 许可连接
new ArrayList<>()// 扩展
);
}
3、Docket 实例关联上 apiInfo()
@Bean
public Docket docket() {
return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2).apiInfo(apiInfo());
}
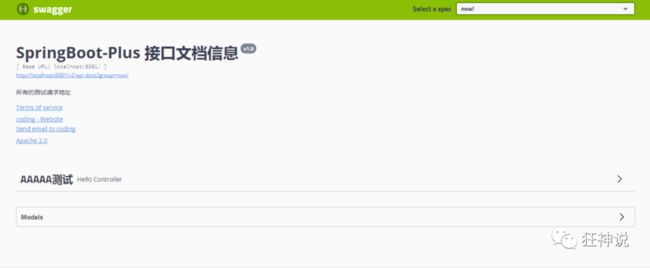
4、重启项目,访问测试 http://localhost:8080/swagger-ui.html 看下效果;
5、配置扫描接口
1、构建Docket时通过select()方法配置怎么扫描接口。
@Bean
public Docket docket() {
return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2)
.apiInfo(apiInfo())
.select()// 通过.select()方法,去配置扫描接口,RequestHandlerSelectors配置如何扫描接口
.apis(RequestHandlerSelectors.basePackage("com.kuang.swagger.controller"))
.build();
}
2、重启项目测试,由于我们配置根据包的路径扫描接口,所以我们只能看到一个类
3、除了通过包路径配置扫描接口外,还可以通过配置其他方式扫描接口,这里注释一下所有的配置方式:
any() // 扫描所有,项目中的所有接口都会被扫描到 none() // 不扫描接口 // 通过方法上的注解扫描,如withMethodAnnotation(GetMapping.class)只扫描get请求 withMethodAnnotation(final Class annotation) // 通过类上的注解扫描,如.withClassAnnotation(Controller.class)只扫描有controller注解的类中的接口 withClassAnnotation(final Class annotation) basePackage(final String basePackage) // 根据包路径扫描接口
4、除此之外,我们还可以配置接口扫描过滤:
@Bean
public Docket docket() {
return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2)
.apiInfo(apiInfo())
.select()//通过.select()方法,去配置扫描接口,RequestHandlerSelectors配置如何扫描接口
.apis(RequestHandlerSelectors.basePackage("com.kuang.swagger.controller"))
// 配置如何通过path过滤,即这里只扫描请求以/kuang开头的接口
.paths(PathSelectors.ant("/kuang/**"))
.build();
}
5、这里的可选值还有
any() // 任何请求都扫描 none() // 任何请求都不扫描 regex(final String pathRegex) // 通过正则表达式控制 ant(final String antPattern) // 通过ant()控制
6、配置Swagger开关
1、通过enable()方法配置是否启用swagger,如果是false,swagger将不能在浏览器中访问了
@Bean
public Docket docket() {
return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2)
.apiInfo(apiInfo())
.enable(false) //配置是否启用Swagger,如果是false,在浏览器将无法访问
.select()//通过.select()方法,去配置扫描接口,RequestHandlerSelectors配置如何扫描接口
.apis(RequestHandlerSelectors.basePackage("com.kuang.swagger.controller"))
// 配置如何通过path过滤,即这里只扫描请求以/kuang开头的接口
.paths(PathSelectors.ant("/kuang/**"))
.build();
}
2、如何动态配置当项目处于test、dev环境时显示swagger,处于prod时不显示?
@Bean
public Docket docket(Environment environment) {
// 设置要显示swagger的环境
Profiles of = Profiles.of("dev", "test");
// 判断当前是否处于该环境
// 通过 enable() 接收此参数判断是否要显示
boolean b = environment.acceptsProfiles(of);
return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2)
.apiInfo(apiInfo())
.enable(b) //配置是否启用Swagger,如果是false,在浏览器将无法访问
.select()//通过.select()方法,去配置扫描接口,RequestHandlerSelectors配置如何扫描接口
.apis(RequestHandlerSelectors.basePackage("com.kuang.swagger.controller"))
// 配置如何通过path过滤,即这里只扫描请求以/kuang开头的接口
.paths(PathSelectors.ant("/kuang/**"))
.build();
}
3、可以在项目中增加一个dev的配置文件查看效果!
7、配置API分组
1、如果没有配置分组,默认是default。通过groupName()方法即可配置分组:
@Bean
public Docket docket(Environment environment) {
return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2).apiInfo(apiInfo())
.groupName("hello") // 配置分组
// 省略配置....
}
2、重启项目查看分组
3、如何配置多个分组?配置多个分组只需要配置多个docket即可:
@Bean
public Docket docket1(){
return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2).groupName("group1");
}
@Bean
public Docket docket2(){
return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2).groupName("group2");
}
@Bean
public Docket docket3(){
return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2).groupName("group3");
}
4、重启项目查看即可
8、实体配置
1、新建一个实体类
@ApiModel("用户实体")
public class User {
@ApiModelProperty("用户名")
public String username;
@ApiModelProperty("密码")
public String password;
}
2、只要这个实体在请求接口的返回值上(即使是泛型),都能映射到实体项中:
@RequestMapping("/getUser")
public User getUser(){
return new User();
}
3、重启查看测试
注:并不是因为@ApiModel这个注解让实体显示在这里了,而是只要出现在接口方法的返回值上的实体都会显示在这里,而@ApiModel和@ApiModelProperty这两个注解只是为实体添加注释的。
@ApiModel为类添加注释
@ApiModelProperty为类属性添加注释
9、常用注解
Swagger的所有注解定义在io.swagger.annotations包下
下面列一些经常用到的,未列举出来的可以另行查阅说明:
| Swagger注解 | 简单说明 |
|---|---|
| @Api(tags = "xxx模块说明") | 作用在模块类上 |
| @ApiOperation("xxx接口说明") | 作用在接口方法上 |
| @ApiModel("xxxPOJO说明") | 作用在模型类上:如VO、BO |
| @ApiModelProperty(value = "xxx属性说明",hidden = true) | 作用在类方法和属性上,hidden设置为true可以隐藏该属性 |
| @ApiParam("xxx参数说明") | 作用在参数、方法和字段上,类似@ApiModelProperty |
我们也可以给请求的接口配置一些注释
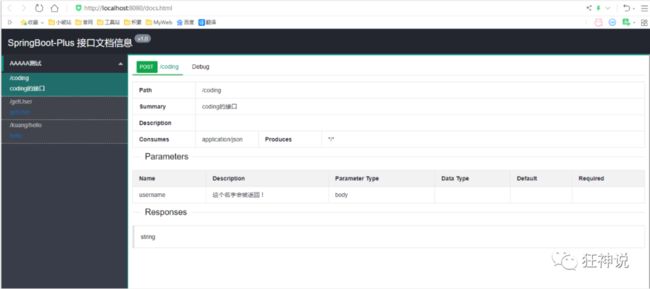
@ApiOperation("狂神的接口")
@PostMapping("/kuang")
@ResponseBody
public String kuang(@ApiParam("这个名字会被返回")String username){
return username;
}
这样的话,可以给一些比较难理解的属性或者接口,增加一些配置信息,让人更容易阅读!
相较于传统的Postman或Curl方式测试接口,使用swagger简直就是傻瓜式操作,不需要额外说明文档(写得好本身就是文档)而且更不容易出错,只需要录入数据然后点击Execute,如果再配合自动化框架,可以说基本就不需要人为操作了。
Swagger是个优秀的工具,现在国内已经有很多的中小型互联网公司都在使用它,相较于传统的要先出Word接口文档再测试的方式,显然这样也更符合现在的快速迭代开发行情。当然了,提醒下大家在正式环境要记得关闭Swagger,一来出于安全考虑二来也可以节省运行时内存。
10、拓展:其他皮肤
我们可以导入不同的包实现不同的皮肤定义:
1、默认的 访问 http://localhost:8080/swagger-ui.html
io.springfox springfox-swagger-ui 2.9.2
2、bootstrap-ui 访问 http://localhost:8080/doc.html
com.github.xiaoymin swagger-bootstrap-ui 1.9.1
3、Layui-ui 访问 http://localhost:8080/docs.html
com.github.caspar-chen swagger-ui-layer 1.1.3
4、mg-ui 访问 http://localhost:8080/document.html
com.zyplayer swagger-mg-ui 1.0.6
狂神讲解的配套视频地址:https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1Y441197Lw
原文出处:狂神说SpringBoot14:集成Swagger终极版 (qq.com)
二、案例
1、第一步:引入三个依赖,其中第三个是为了优化页面用;
io.springfox
springfox-swagger2
2.4.0
io.springfox
springfox-swagger-ui
2.4.0
com.github.xiaoymin
swagger-bootstrap-ui
1.6
2、第二步:编写配置类;
package com.imooc.config;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import springfox.documentation.builders.ApiInfoBuilder;
import springfox.documentation.builders.PathSelectors;
import springfox.documentation.builders.RequestHandlerSelectors;
import springfox.documentation.service.ApiInfo;
import springfox.documentation.service.Contact;
import springfox.documentation.spi.DocumentationType;
import springfox.documentation.spring.web.plugins.Docket;
import springfox.documentation.swagger2.annotations.EnableSwagger2;
/**
* @author Created by wcg
* @Date 2019/11/7 21:39
*/
@Configuration
@EnableSwagger2
public class Swagger2 {
//http://localhost:8088/swagger-ui.html 原路径
//http://localhost:8088/doc.html bootstarp路径
//配置swagger2核心配置 docket,主要是添加要扫描controller的路径
@Bean
public Docket createResApi(){
return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2)
.apiInfo(apiInfo())
.select().apis(RequestHandlerSelectors
.basePackage("com.imooc.controller"))
.paths(PathSelectors.any())
.build();
}
private ApiInfo apiInfo(){
return new ApiInfoBuilder()
.title("天天吃货,电商平台接口api").
contact(new Contact("imooc","https://www.imooc.com","[email protected]"))
.description("专门为天天吃货提供的api文档")
.version("1.0.1")
.termsOfServiceUrl("https://www.imooc.com")
.build();
}
}
上边代码中的类主要描述了文档的基本信息,以及访问路径:
//http://localhost:8088/swagger-ui.html (这是原路径是swagger本身的路径配置好,直接就可以进行访问;)
//http://localhost:8088/doc.html ( bootstarp路径是优化后的页面的路径);
3、第三步:增加注释,用于中文进行直观的页面展示,主要有以下几个:
(1)@ApiIgnore:就是将配置中扫描的包下的controller进行排除,这样文档页面就不会进行展示对应的controller了;
(2)@Api(value = “注册登陆”,tags = “注册登陆的相关接口”):这个注释添加到要展示的controller类上,以及相关中文注释;
(3)@ApiOperation(value = “用户名是否存在”,notes = “用户名是否存在”,httpMethod = “GET”): 主要放置在方法前边,用于展示对应接口的信息,以及请求方式;
(4)@ApiModel(value = “用户对象BO”, description = “从客户端,由用户传入的数据封装在此entity中”) :这个主要是放在BO类上(BO类在这个项目就是为了接收参数的封装类),
(5)@ApiModelProperty(value = “用户名”,name = “usernmae”,example = “imooc”,required = true): 这个主要是放在BO类中的属性前边,用于描述具体参数信息
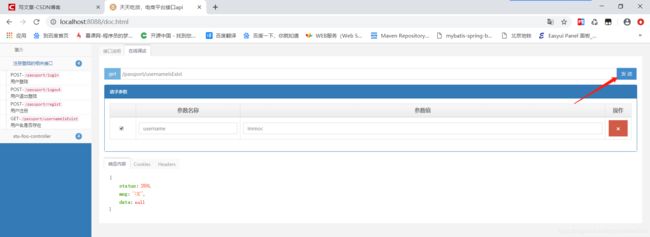
4、第四步:好了主要是就是这几个最主要的注释,那么让我们来看一下最终的成果页面吧:
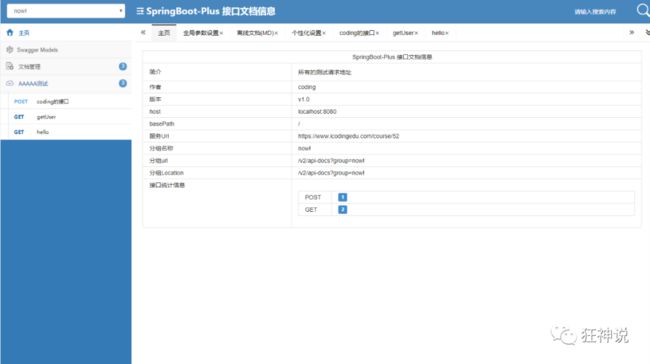
1、输入http://localhost:8088/doc.html进入首页,会看到咱们在配置类中定制的基本信息:
好了,就这么些了,完全够你在大部分的项目进行实用了!
三、参考
狂神说SpringBoot14:集成Swagger终极版
【狂神说Java】一小时掌握Swagger技术_哔哩哔哩_bilibili
Swagger2最完整的文档_修心光的博客-CSDN博客_swagger中文文档
(176条消息) 【Swagger】1_Spring Boot 中搭建 Swagger_Code_27的博客-CSDN博客
swagger教程、Swagger视频教程_飞飞不 会飞的博客-CSDN博客_swagger教程