【从入门到起飞】IO高级流(1)(缓冲流,转换流,序列化流,反序列化流)
专栏【JavaSE】
喜欢的诗句:天行健,君子以自强不息。
音乐分享【如愿】
欢迎并且感谢大家指出小吉的问题
文章目录
- 缓冲流
-
- 字节缓冲流
-
- 一次读取一个字节
- 一次读取多个字节
- 字符缓冲流
- 转换流
-
- 利用转换流按照指定的字符编码读取数据
- 利用转换流按照指定的字符编码写入数据
- 读写结合,使用转换流读取数据并且写入数据,并且转换编码方式
-
- 乱码的解决方法
- 序列化流(对象操作输出流)
-
- 写出一个对象
-
- 创建类Student.java
- 创建类Demo1.java
- 反序列化流(对象操作输入流)
-
- 小练习——读写多个对象
-
- 创建类Student.java
- 创建类Write.Java
- 创建类Read.Java
-
- 结果
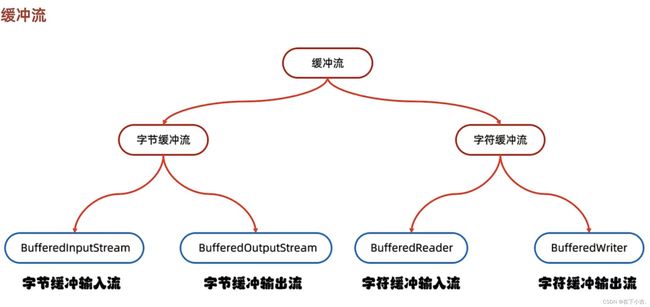
缓冲流
在代码中使用缓冲流(Buffered Streams)有许多好处,特别是在处理I/O操作时,它们可以显著提高性能和效率。缓冲流是一种在内存中创建缓冲区的I/O流,可以将数据暂时存储在缓冲区中,然后一次性地进行批量读取或写入,而不是每次操作都直接与底层数据源(如文件、网络套接字等)交互。
字节缓冲流
原理:底层自带了长度为8192的缓冲区来提高性能
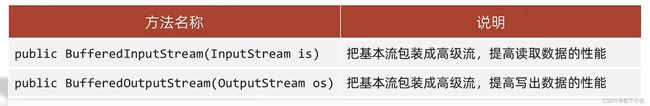
在创建对象的时候还是使用原来的基本流,但是在缓冲流的加持下,提高了基本流读写的效率
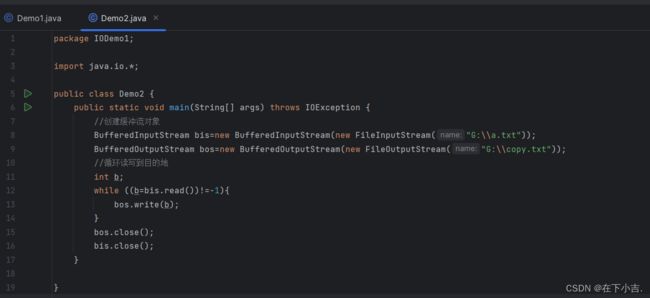
一次读取一个字节
package IODemo1;
import java.io.*;
public class Demo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//创建缓冲流对象
BufferedInputStream bis=new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream("G:\\a.txt"));
BufferedOutputStream bos=new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("G:\\copy.txt"));
//循环读写到目的地
int b;
while ((b=bis.read())!=-1){
bos.write(b);
}
bos.close();
bis.close();
}
}
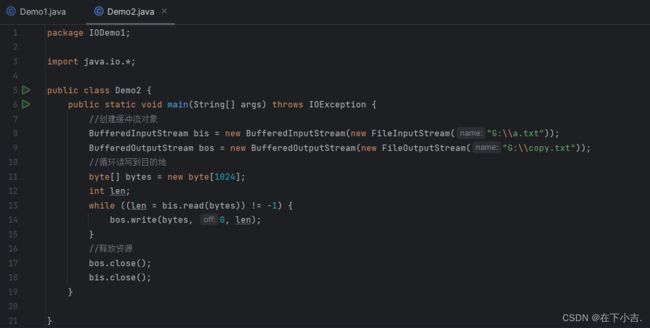
一次读取多个字节
package IODemo1;
import java.io.*;
public class Demo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//创建缓冲流对象
BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream("G:\\a.txt"));
BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("G:\\copy.txt"));
//循环读写到目的地
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];
int len;
while ((len = bis.read(bytes)) != -1) {
bos.write(bytes, 0, len);
}
//释放资源
bos.close();
bis.close();
}
}
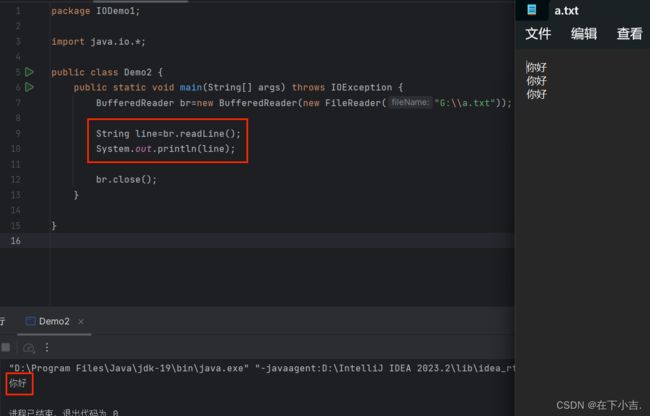
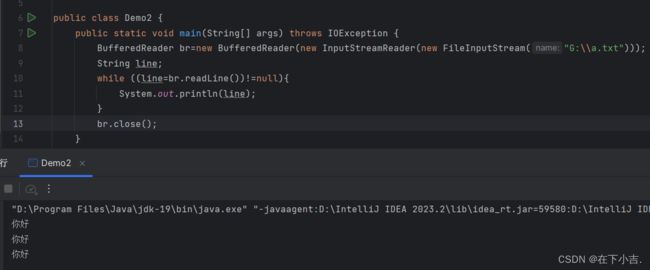
字符缓冲流
为什么文件有三行数据,但是读出的只有一行呢
因为readline在读取的时候,一次只读一整行,读到回车换行符结束
如何把文件全部都读出来
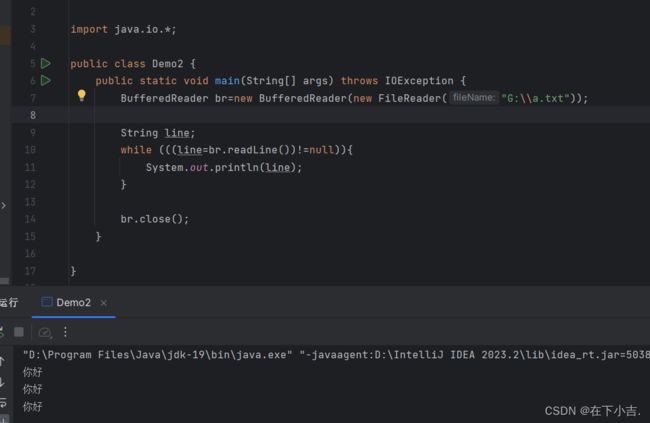
package IODemo1;
import java.io.*;
public class Demo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br=new BufferedReader(new FileReader("G:\\a.txt"));
String line;
while (((line=br.readLine())!=null)){
System.out.println(line);
}
br.close();
}
}
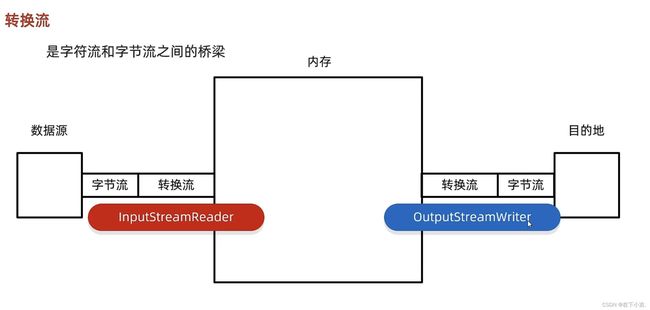
转换流
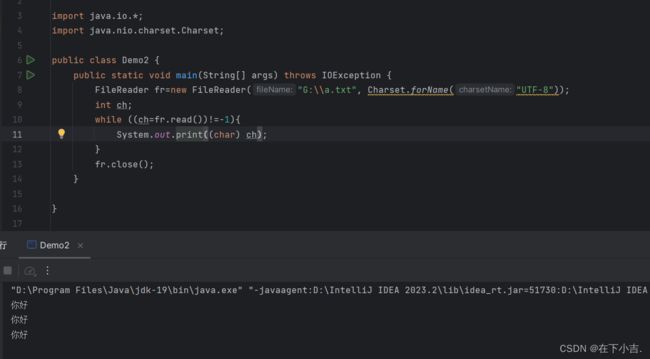
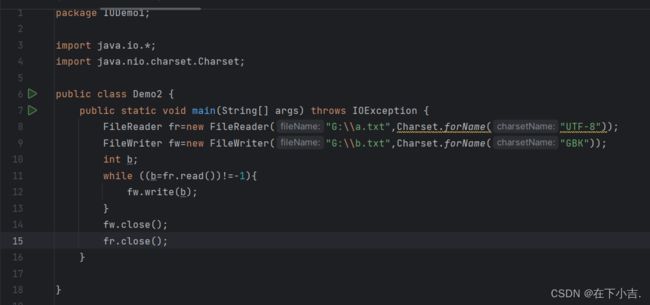
利用转换流按照指定的字符编码读取数据
读取数据
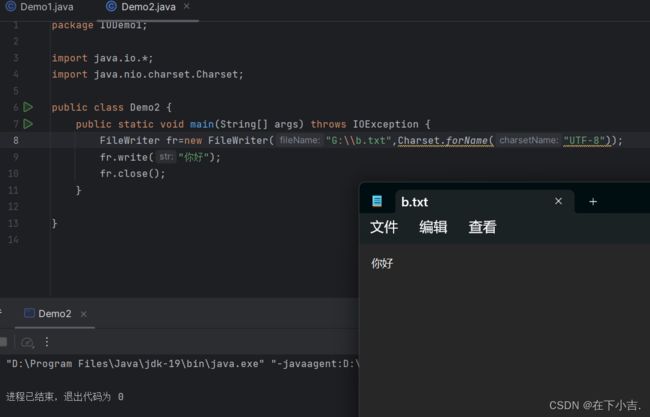
利用转换流按照指定的字符编码写入数据
写入数据
读写结合,使用转换流读取数据并且写入数据,并且转换编码方式
读写结合
乱码的解决方法
序列化流(对象操作输出流)
写出一个对象
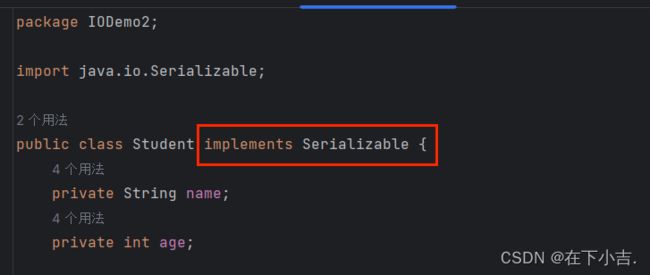
创建类Student.java
package IODemo2;
import java.io.Serializable;
public class Student implements Serializable {
private String name;
private int age;
public Student() {
}
public Student(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
}
创建类Demo1.java
package IODemo2;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;
public class Demo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//创建对象
Student stu=new Student("zhangsan",23);
//创建序列化流的对象
ObjectOutputStream oos=new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("G:\\a.txt"));
//写出数据
oos.writeObject(stu);
//释放资源
oos.close();
}
}
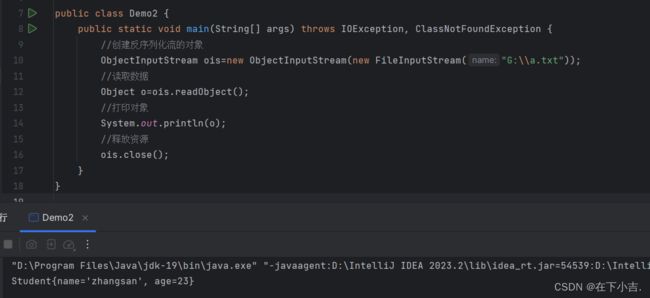
反序列化流(对象操作输入流)
package IODemo2;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.ObjectInputStream;
public class Demo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
//创建反序列化流的对象
ObjectInputStream ois=new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("G:\\a.txt"));
//读取数据
Object o=ois.readObject();
//打印对象
System.out.println(o);
//释放资源
ois.close();
}
}
小练习——读写多个对象
注意是
多个对象
创建类Student.java
package IODemo2;
import java.io.Serializable;
public class Student implements Serializable {
private String name;
private int age;
public Student() {
}
public Student(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
}
创建类Write.Java
package IODemo2;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class Write {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Student s1 = new Student("zhangsan", 23);
Student s2 = new Student("lisi", 24);
Student s3 = new Student("wangwu", 25);
ArrayList<Student> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add(s1);
list.add(s2);
list.add(s3);
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("G:\\a.txt"));
oos.writeObject(list);
}
}
创建类Read.Java
package IODemo2;
import java.io.*;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class Read {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
ObjectInputStream ois=new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("G:\\a.txt"));
ArrayList<Student>list=(ArrayList<Student>) ois.readObject();//强转
for (Student student:list){
System.out.println(student);
}
ois.close();
}
}
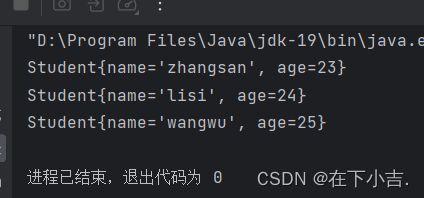
结果
一定要
先写再读
先执行Write.java
再执行Read.java
如果大家对于这篇文章有问题,欢迎在评论区进行讨论