SpringBoot中使用Easyexcel实现Excel导入导出功能(一)
目录
前言
1.常规导入
2.读取到指定的列
3.读取全部的sheet页
4.日期、数字及其他自定义格式的转换
5.表头有多行的表格读取
6.表头数据的读取
7.单元格内的备注内容读取
前言
excel表格的导入与导出,可以说是业务系统里比较常见的功能了,早些时候相信很多人都是使用POI实现excel的导入与导出功能,后来出现了easyexcel,从我自己的使用感受来说,我更喜欢使用easyexcel,除了封装的比较好外,最重要的是对超级大excel导入有了更好的方案,与POI相比,速度更快,占用内存更少。
1.常规导入
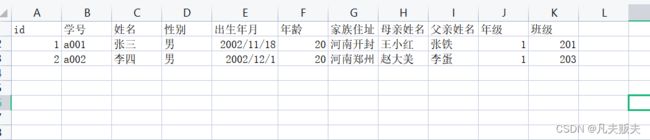
有一个学生的信息如下图,后台解析excel并把数据封装好。
1.根据excel表格的内容封装好实体类Student.java;
2.实现读取监听器ReadListenerr接口,(在上一篇文章中刚分享过事件监听机制,这里就用到了),主要原理就是easyexcel在解析excel的时候,会把每一行数据封装成一个事件,每一个事件被触发的时候监听器的回调方法invoke()就会被调用;
3.ReadListenerr接口的实现类里定义一个成员变量,用来接受解析出来的数据;(监听器的实现方式比poi的实现要灵活的多,这里可以根据实际业务场景来定义解析出来多少行数据再执行入库的操作,easyexcle本身提供了这样一种实现PageReadListener,可以自行参考);
4.使用easyexcel的工厂类EasyExcel可执行读取的相关操作;
@Data
public class Student implements Serializable {
private Integer id;
private String stuCode;
private String stuName;
private String sex;
private String born;
private Integer age;
private String address;
private String motherName;
private String fatherName;
private Integer grade;
private Integer classNum;
}public class StudentReadListener implements ReadListener {
private List students=new ArrayList<>();
public List getStudents() {
return students;
}
@Override
public void invoke(Student data, AnalysisContext context) {
//easyexcel是逐行读取,每读取一行就放到集合里;
//如果导入数据不多,可以读取结束后,再统一入库
students.add(data);
}
@Override
public void doAfterAllAnalysed(AnalysisContext context) {
}
} @Test
public void read(){
String userDir = System.getProperty("user.dir");
String importPath=userDir+File.separator+"import";
File dir = new File(importPath);
if (!dir.exists()) {
dir.mkdirs();
}
String importFile=importPath+File.separator+"学生信息表.xlsx";
StudentReadListener studentReadListener = new StudentReadListener();
EasyExcel.read(importFile, Student.class, studentReadListener).sheet().doRead();
List students = studentReadListener.getStudents();
System.out.println(students.size());
} 2.读取到指定的列
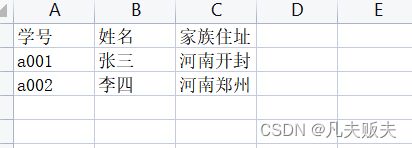
有的时候会有这样的需求,导入数据时打算导入3列(学号、姓名、地址),但是Student类里会有很多属性(id、学号、姓名、性别、年龄、地址、出生年月),直接导入会有异常抛出;像这样读取到指定列的需求很简单,保持其他不变,只需要在Student类的指定列加上@ExcelProperty(index=xx)就好了。
@Data
public class Student implements Serializable {
private Integer id;
@ExcelProperty(index =0)
private String stuCode;
@ExcelProperty(index =1)
private String stuName;
private String sex;
private String born;
private Integer age;
@ExcelProperty(index = 2)
private String address;
private String motherName;
private String fatherName;
private Integer grade;
private Integer classNum;
}@Test
public void readCustomColumn(){
String userDir = System.getProperty("user.dir");
String importPath = userDir + File.separator + "import";
File dir = new File(importPath);
if (!dir.exists()) {
dir.mkdirs();
}
String importFile = importPath + File.separator + "学生信息表.xlsx";
StudentReadListener studentReadListener = new StudentReadListener();
EasyExcel.read(importFile, Student.class, studentReadListener).sheet("Sheet2").doRead();
List students = studentReadListener.getStudents();
for (Student student : students) {
System.out.println(student.getStuName());
}
} 3.读取全部的sheet页
这里需要注意两个地方:1、读取shee页的数据结构是一样的;2、excel的列与接收数据类的属性是一一对应的,如果不对应,可参考读取到指定列部分,使用@ExcelProperty(index=xx)显性的指定对应关系;
@Data
public class Student implements Serializable {
private Integer id;
private String stuCode;
private String stuName;
private String sex;
private String born;
private Integer age;
private String address;
private String motherName;
private String fatherName;
private Integer grade;
private Integer classNum;
}@Test
public void readAllSheet(){
String userDir = System.getProperty("user.dir");
String importPath = userDir + File.separator + "import";
File dir = new File(importPath);
if (!dir.exists()) {
dir.mkdirs();
}
String importFile = importPath + File.separator + "学生信息表.xlsx";
StudentReadListener studentReadListener = new StudentReadListener();
EasyExcel.read(importFile, Student.class, studentReadListener).doReadAll();
List students = studentReadListener.getStudents();
for (Student student : students) {
System.out.println(student.getStuName());
}
} 4.日期、数字及其他自定义格式的转换
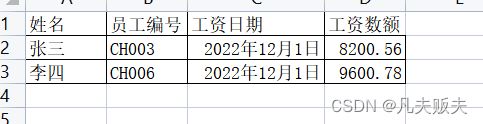
在导入或者导出excel的时候,如果想对某一列的数据格式作调整转换,可以自定义一个转换器(com.alibaba.excel.converters.Converter),然后这个个转换器通过@ExcelProperty(converter=xxxxx.class)标记在接收参数的类型的属性上;
这种转换数据格式的需求,有时候是主动的,有时候是被动的。什么是主动的的呢?假如前数据为库存储的日期格式是yyyyMMdd,导出的时候想要的是xxxx年xx月xx日,然后你就可以实现一个类型转换器(Converter)主动完成这个事。下面举个被动的例子,excel中关于日期的一个坑,绕不过的坑,所以是“被动”滴。
excel中单元格式格式是日期时,easyexcel解析后是一个数字,这不是解析错误了,而是excel中对于日期存储的格式就是数字,这个数字代表的是1900年1月1日,到单元格式内日期的天数,所以解析结果中是一个数字并不难理解,但是这不是我我们想要的结果呀。更恶心的是,java中的Date的时间起点1970年1月1日,所以被动的需求就产生了,需要把一个以1900-1-1为起天的天数代表的日期,转换为以1970-1-1为起点的java.util.Date。标准的不统一,产生的结果就是这么恶心。
public class SalaryDateConverter implements Converter {
@Override
public Class supportJavaTypeKey() {
return String.class;
}
@Override
public CellDataTypeEnum supportExcelTypeKey() {
return CellDataTypeEnum.STRING;
}
//导入的时候会走这个方法,导入的转换逻辑可以在这个方法里实现
@Override
public String convertToJavaData(ReadCellData cellData, ExcelContentProperty contentProperty, GlobalConfiguration globalConfiguration) throws Exception {
BigDecimal numberValue = cellData.getNumberValue();
//平时不要动不动就搞个util工具类,我曾经目睹一个新同事,用上用不上的也不管,上来在工程里导入了几十个工具类,搞得maven依赖冲突
// org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.DateUtil是POI的工具类,
// DateUtil.getJavaDate()的功能就是把以1900-1-1为起点的日期天数转换成java.util.Date,直接拿来用就好了,基本不用担心里面有bug
Date javaDate = DateUtil.getJavaDate(numberValue.doubleValue());
//com.alibaba.excel.util.DateUtils是easyexcel封装的日期转换工具类,能用就用上呗,基本也不用担心有bug
String format = DateUtils.format(javaDate, DateUtils.DATE_FORMAT_10);
return format;
}
//导出的时候会走这个方法,导出的转换逻辑可以在这个方法里实现
@Override
public WriteCellData convertToExcelData(String value, ExcelContentProperty contentProperty, GlobalConfiguration globalConfiguration) throws Exception {
return null;
}
} @Data
public class EmpSalary {
@ExcelProperty("姓名")
private String realName;
@ExcelProperty("员工编号")
private String empNo;
@ExcelProperty(value = "工资日期",converter = SalaryDateConverter.class)
private String salaryDate;
@ExcelProperty("工资数额")
private Float amount;
}@Test
public void readByConvert(){
String userDir = System.getProperty("user.dir");
String importPath = userDir + File.separator + "import";
File dir = new File(importPath);
if (!dir.exists()) {
dir.mkdirs();
}
String importFile = importPath + File.separator + "员工工资表.xlsx";
EmpSalaryReadListener empSalaryReadListener = new EmpSalaryReadListener();
EasyExcel.read(importFile, EmpSalary.class, empSalaryReadListener).sheet().doRead();
List empSalaries = empSalaryReadListener.getEmpSalaries();
System.out.println(empSalaries.size());
} 5.表头有多行的表格读取
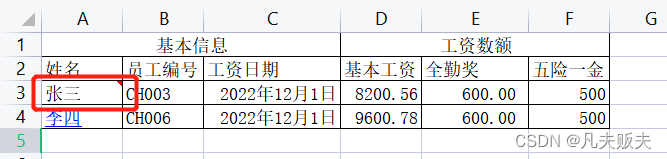
easyexcel在读取表格内容的时候,默认是从第二行开始读的,因为第一行通常是表头,所以上面没有指定从第几行开始读也没有问题。但是遇到下图样式的复合表头的时候,表头是占了两行,数据是从第三行开始的,那么在读取的时候读取监听器、接收数据的类没有变化,而是在读取的时候要显性指定从第几行开始读,实际指定的时候是索引,从0开始,第三行的索引就是2;
@Test
public void readManyRow(){
String userDir = System.getProperty("user.dir");
String importPath = userDir + File.separator + "import";
File dir = new File(importPath);
if (!dir.exists()) {
dir.mkdirs();
}
String importFile = importPath + File.separator + "员工工资表 - 副本.xlsx";
EmpSalaryReadListener empSalaryReadListener = new EmpSalaryReadListener();
//数据从第三行开始,索引是2
EasyExcel.read(importFile, EmpSalary.class, empSalaryReadListener).sheet().headRowNumber(2).doRead();
List empSalaries = empSalaryReadListener.getEmpSalaries();
System.out.println(empSalaries.size());
} @Data
public class EmpSalary {
private String realName;
private String empNo;
@ExcelProperty(value = "工资日期",converter = SalaryDateConverter.class)
private String salaryDate;
private Float baseAmount;
private Float fullAttendAmount;
private Float insurance;
}6.表头数据的读取
有时候也会有这样的需求,就是除了读取表格的数据外,表头的数据也要读取出来,easyexcel的读取监听器里的实现类里重写invokeHead()方法即可,下面以读取多行表头,写一个示例:
public class EmpSalaryReadListener implements ReadListener {
private List empSalaries=new ArrayList<>();
public List getEmpSalaries() {
return empSalaries;
}
@Override
public void invoke(EmpSalary data, AnalysisContext context) {
empSalaries.add(data);
}
@Override
public void doAfterAllAnalysed(AnalysisContext context) {
}
@Override
public void invokeHead(Map> headMap, AnalysisContext context) {
for (Integer key : headMap.keySet()) {
System.out.println("key:"+key+","+headMap.get(key).getStringValue());
}
System.out.println("---------");
}
}
表头信息也是逐行读取的,即每读取一行就会回调一下监听器的表头读取回调方法(invokeHead()),表头信息结果是存储在一个map中,map的key为excel表格列上的索引,value是表头信息。对于多行合并单元格后,合并单元格后的内容在第一个格里,其他单元格也会占一个位置但是是空的;
7.单元格内的备注内容读取
业务上需求有时候是千变万化的,比如读取了excel表格内容,还要求读取某些单元格上的备注内容,并记录好是第几行第几列,easyexcel的读取监听器实际也有这样的回调方法(extra()),需要在读取监听器的实现类里重写这个方法;
public class EmpSalaryReadListener implements ReadListener {
private List empSalaries = new ArrayList<>();
public List getEmpSalaries() {
return empSalaries;
}
@Override
public void invoke(EmpSalary data, AnalysisContext context) {
empSalaries.add(data);
}
@Override
public void doAfterAllAnalysed(AnalysisContext context) {
}
@Override
public void extra(CellExtra extra, AnalysisContext context) {
if(extra.getType().equals(CellExtraTypeEnum.COMMENT)){
System.out.println("行:"+(extra.getRowIndex()+1));
System.out.println("列:"+(extra.getColumnIndex()+1));
System.out.println("备注内容:"+extra.getText());
}
}
} @Test
public void readExtra(){
String userDir = System.getProperty("user.dir");
String importPath = userDir + File.separator + "import";
File dir = new File(importPath);
if (!dir.exists()) {
dir.mkdirs();
}
String importFile = importPath + File.separator + "员工工资表 - 副本.xlsx";
EmpSalaryReadListener empSalaryReadListener = new EmpSalaryReadListener();
EasyExcel.read(importFile, EmpSalary.class, empSalaryReadListener)
.extraRead(CellExtraTypeEnum.COMMENT)
.sheet().headRowNumber(2).doRead();
List empSalaries = empSalaryReadListener.getEmpSalaries();
System.out.println(empSalaries.size());
} SpringBoot中使用Easyexcel实现Excel导入导出功能(一)_凡夫贩夫的博客-CSDN博客excel表格的导入与导出,可以说是业务系统里比较常见的功能了,早些时候相信很多人都是使用POI实现excel的导入与导出功能,后来出现了easyexcel,从我自己的使用感受来说,我更喜欢使用easyexcel,除了封装的比较好外,最重要的是对超级大excel导入有了更好的方案,与POI相比,速度更快,占用内存更少。https://blog.csdn.net/fox9916/article/details/128242237?spm=1001.2014.3001.5502
SpringBoot中使用Easyexcel实现Excel导入导出功能(二)_凡夫贩夫的博客-CSDN博客自定义格式转换的后导出可以参考上一篇《Springboot+Easyexcel:导入excl》中的日期、数字及其他自定义格式的转换部分,SalaryDateConverter#convertToExcelData(),导出时候的数据格式转换逻辑可以写在这里面;SalaryDateConverter#convertToJavaData()导入时候的数据格式转换的实现逻辑可以写在这里;SalaryDateConverter实现了com.alibaba.excel.converters.Converter接口;https://blog.csdn.net/fox9916/article/details/128258929?spm=1001.2014.3001.5502
SpringBoot中使用Easyexcel实现Excel导入导出功能(三)_凡夫贩夫的博客-CSDN博客我比较喜欢使用easyexcel的一个很重要的原因就是,easyexcel在poi的基础上,封装的比较友好。就比如,在导出的时候,很多情况下需要自定义表格的样式,easyexcel就提供了多种的实现方式。主要有三种:1、通过注解;2、编程式;3、自定义类型转换器。通过编程式来自定义导出表格的样式中,有一个非常关键类HorizontalCellStyleStrategy。1、通过HorizontalCellStyleStrategy可以配置好表头的样式和数据行的样式;https://blog.csdn.net/fox9916/article/details/128270689?spm=1001.2014.3001.5502
Springboot扩展点系列实现方式、工作原理集合:
Springboot扩展点之ApplicationContextInitializer
Springboot扩展点之BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor
Springboot扩展点之BeanFactoryPostProcessor
Springboot扩展点之BeanPostProcessor
Springboot扩展点之InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor
Springboot扩展点之SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor
Springboot扩展点之ApplicationContextAwareProcessor
Springboot扩展点之@PostConstruct
Springboot扩展点之InitializingBean
Springboot扩展点之DisposableBean
Springboot扩展点之SmartInitializingSingleton
Springboot核心功能工作原理:
Springboot实现调度任务的工作原理
Springboot事件监听机制的工作原理