提高边缘分割精度-边缘区域Dice损失函数
文章目录
- 1. 前言
- 2. 损失函数
-
- 2.1 介绍
- 2.2 代码实现
- 2.3 用法
1. 前言
提高边缘分割的准确率对于图像分割具有重要意义,而准确的边缘可以很好表现结构特征和细节特征。下面我实现了论文相关的损失函数代码。
论文:CTS-Net: A Segmentation Network for Glaucoma Optical Coherence Tomography Retinal Layer Images
2. 损失函数
2.1 介绍
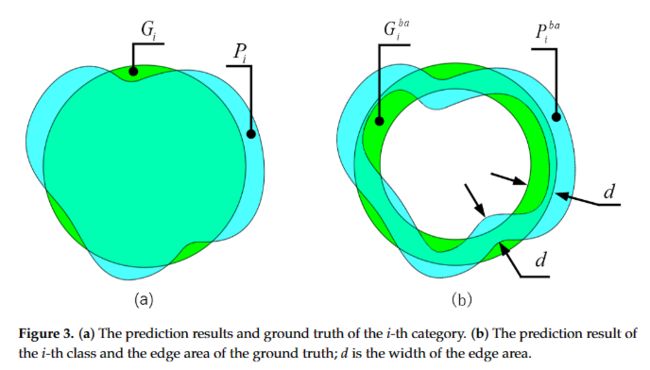
如下图所示,绿色表示真实标签,蓝色表示预测结果,将这两块区域边缘同样大小的区域提取出来单独计算Dice损失函数,就是论文所说的边缘区域Dice损失函数。
2.2 代码实现
class BoundaryAreaDiceLoss(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, n_classes, boundary_area_width=1):
super(BoundaryAreaDiceLoss, self).__init__()
self.n_classes = n_classes
if boundary_area_width != 1:
self.boundary_area_width = boundary_area_width
else:
self.boundary_area_width = [1 for i in range(self.n_classes)]
def _one_hot_encoder(self, input_tensor):
tensor_list = []
for i in range(self.n_classes):
temp_prob = input_tensor == i # * torch.ones_like(input_tensor)
tensor_list.append(temp_prob.unsqueeze(1))
output_tensor = torch.cat(tensor_list, dim=1)
return output_tensor.float()
def _mask(self, img_org, boundary_area):
img_org = img_org.unsqueeze(0)
_, H, W = img_org.shape
pad_up = nn.ZeroPad2d((0, 0, boundary_area, 0))
pad_down = nn.ZeroPad2d((0, 0, 0, boundary_area))
pad_left = nn.ZeroPad2d((boundary_area, 0, 0, 0))
pad_right = nn.ZeroPad2d((0, boundary_area, 0, 0))
img_pad_up = pad_up(img_org.float()).squeeze(0)
img_pad_up = img_pad_up[:img_pad_up.shape[0] - boundary_area, :]
img_pad_down = pad_down(img_org.float()).squeeze(0)
img_pad_down = img_pad_down[boundary_area:, :]
img_pad_left = pad_left(img_org.float()).squeeze(0)
img_pad_left = img_pad_left[:, :img_pad_left.shape[1] - boundary_area]
img_pad_right = pad_right(img_org.float()).squeeze(0)
img_pad_right = img_pad_right[:, boundary_area:]
intersect = img_pad_up * img_pad_down * img_pad_left * img_pad_right
mask_mid1_others0 = intersect.squeeze(0).int()
mask_mid0_others1 = torch.where((mask_mid1_others0 == 0) | (mask_mid1_others0 == 1), mask_mid1_others0 ^ 1,
mask_mid1_others0) ##取反
return mask_mid0_others1, mask_mid1_others0
def _dice_loss(self, score, target, boundary_area_width): ##score, target: (B, 56, 56)
target = target.float()
final_target = []
for i in range(target.shape[0]):
mask_mid0_others1, mask_mid1_others0 = self._mask(target[i], boundary_area_width)
mask_score = mask_mid1_others0 * score[i].float()
mask_target = mask_mid0_others1 * target[i].float()
target_ = mask_score + mask_target
final_target.append(target_)
target = torch.stack(final_target) ##(B, H, W)
smooth = 1e-5
intersect = torch.sum(score * target) #是一个值
y_sum = torch.sum(target * target)
z_sum = torch.sum(score * score)
loss = (2 * intersect + smooth) / (z_sum + y_sum + smooth)
loss = 1 - loss
return loss
def forward(self, inputs, target, weight=None, softmax=False): ##inputs:(B, 4, 56, 56) target: (B, 56, 56)
if softmax:
inputs = torch.softmax(inputs, dim=1)
target = self._one_hot_encoder(target) ##target: (B, 4, 56, 56)
if weight is None:
weight = [1] * self.n_classes
assert inputs.size() == target.size(), 'predict {} & target {} shape do not match'.format(inputs.size(), target.size())
class_wise_dice = []
loss = 0.0
for i in range(0, self.n_classes):
dice = self._dice_loss(inputs[:, i], target[:, i], self.boundary_area_width[i])
class_wise_dice.append(1.0 - dice.item())
loss += dice * weight[i]
return loss / self.n_classes
2.3 用法
用法和Dice损失函数类似,只是需要增加一个参数boundary_area_width。
定义
baDiceLoss = BoundaryAreaDiceLoss(n_classes=3, boundary_area_width=10) # 每个类别指定相同边缘大小
# 或者
baDiceLoss = BoundaryAreaDiceLoss(n_classes=3, boundary_area_width=[3, 6, 7]) # 为每个类别指定不同边缘大小
使用
lossBaDice = baDiceLoss (pred, label, weight=weights, softmax=True) # weight的意义和Dice损失函数一样