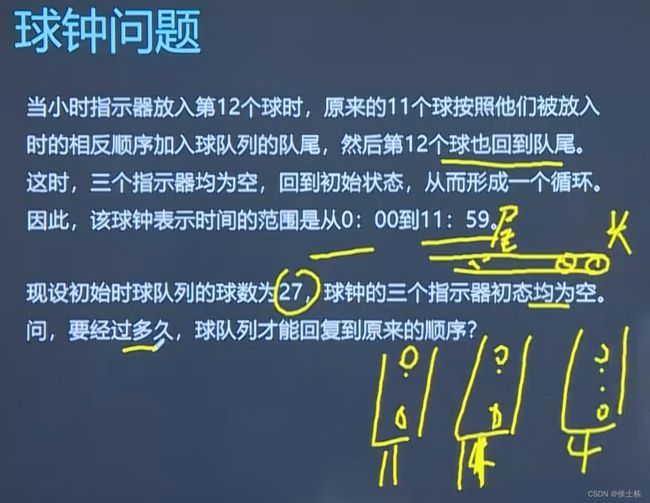
嵌入式数据结构(栈和队列的应用)
嵌入式自学第十天
#include sqstak.c
#include sqstak.h
typedef int data_t;
typedef struct {
data_t *data;
int maxlen;
int top;
}sqstack;
sqstack * stack_create(int len);
int stack_push(sqstack * s, data_t value);
int stack_empty(sqstack *s);
int stack_full(sqstack *s);
data_t stack_pop(sqstack *s);
data_t stack_top(sqstack *s);
int stack_clear(sqstack *s);
int stack_free(sqstack *s);
linkqueue.c
#include linkqueue.h
typedef int datatype;
typedef struct node {
datatype data;
struct node *next;
}listnode , *linklist;
typedef struct {
linklist front;
linklist rear;
}linkqueue;
linkqueue * queue_create();
int enqueue(linkqueue *lq, datatype x);
datatype dequeue(linkqueue *lq);
int queue_empty(linkqueue *lq);
int queue_clear(linkqueue *lq);
linkqueue * queue_free(linkqueue *lq);